Crypto World
Revolutionising Advanced Problem-Solving with AI
by Gonzalo Wangüemert Villalba
•
4 September 2025
Introduction The open-source AI ecosystem reached a turning point in August 2025 when Elon Musk’s company xAI released Grok 2.5 and, almost simultaneously, OpenAI launched two new models under the names GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B. While both announcements signalled a commitment to transparency and broader accessibility, the details of these releases highlight strikingly different approaches to what open AI should mean. This article explores the architecture, accessibility, performance benchmarks, regulatory compliance and wider industry impact of these three models. The aim is to clarify whether xAI’s Grok or OpenAI’s GPT-OSS family currently offers more value for developers, businesses and regulators in Europe and beyond. What Was Released Grok 2.5, described by xAI as a 270 billion parameter model, was made available through the release of its weights and tokenizer. These files amount to roughly half a terabyte and were published on Hugging Face. Yet the release lacks critical elements such as training code, detailed architectural notes or dataset documentation. Most importantly, Grok 2.5 comes with a bespoke licence drafted by xAI that has not yet been clearly scrutinised by legal or open-source communities. Analysts have noted that its terms could be revocable or carry restrictions that prevent the model from being considered genuinely open source. Elon Musk promised on social media that Grok 3 would be published in the same manner within six months, suggesting this is just the beginning of a broader strategy by xAI to join the open-source race. By contrast, OpenAI unveiled GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B on 5 August 2025 with a far more comprehensive package. The models were released under the widely recognised Apache 2.0 licence, which is permissive, business-friendly and in line with requirements of the European Union’s AI Act. OpenAI did not only share the weights but also architectural details, training methodology, evaluation benchmarks, code samples and usage guidelines. This represents one of the most transparent releases ever made by the company, which historically faced criticism for keeping its frontier models proprietary. Architectural Approach The architectural differences between these models reveal much about their intended use. Grok 2.5 is a dense transformer with all 270 billion parameters engaged in computation. Without detailed documentation, it is unclear how efficiently it handles scaling or what kinds of attention mechanisms are employed. Meanwhile, GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B make use of a Mixture-of-Experts design. In practice this means that although the models contain 21 and 117 billion parameters respectively, only a small subset of those parameters are activated for each token. GPT-OSS-20B activates 3.6 billion and GPT-OSS-120B activates just over 5 billion. This architecture leads to far greater efficiency, allowing the smaller of the two to run comfortably on devices with only 16 gigabytes of memory, including Snapdragon laptops and consumer-grade graphics cards. The larger model requires 80 gigabytes of GPU memory, placing it in the range of high-end professional hardware, yet still far more efficient than a dense model of similar size. This is a deliberate choice by OpenAI to ensure that open-weight models are not only theoretically available but practically usable. Documentation and Transparency The difference in documentation further separates the two releases. OpenAI’s GPT-OSS models include explanations of their sparse attention layers, grouped multi-query attention, and support for extended context lengths up to 128,000 tokens. These details allow independent researchers to understand, test and even modify the architecture. By contrast, Grok 2.5 offers little more than its weight files and tokenizer, making it effectively a black box. From a developer’s perspective this is crucial: having access to weights without knowing how the system was trained or structured limits reproducibility and hinders adaptation. Transparency also affects regulatory compliance and community trust, making OpenAI’s approach significantly more robust. Performance and Benchmarks Benchmark performance is another area where GPT-OSS models shine. According to OpenAI’s technical documentation and independent testing, GPT-OSS-120B rivals or exceeds the reasoning ability of the company’s o4-mini model, while GPT-OSS-20B achieves parity with the o3-mini. On benchmarks such as MMLU, Codeforces, HealthBench and the AIME mathematics tests from 2024 and 2025, the models perform strongly, especially considering their efficient architecture. GPT-OSS-20B in particular impressed researchers by outperforming much larger competitors such as Qwen3-32B on certain coding and reasoning tasks, despite using less energy and memory. Academic studies published on arXiv in August 2025 highlighted that the model achieved nearly 32 per cent higher throughput and more than 25 per cent lower energy consumption per 1,000 tokens than rival models. Interestingly, one paper noted that GPT-OSS-20B outperformed its larger sibling GPT-OSS-120B on some human evaluation benchmarks, suggesting that sparse scaling does not always correlate linearly with capability. In terms of safety and robustness, the GPT-OSS models again appear carefully designed. They perform comparably to o4-mini on jailbreak resistance and bias testing, though they display higher hallucination rates in simple factual question-answering tasks. This transparency allows researchers to target weaknesses directly, which is part of the value of an open-weight release. Grok 2.5, however, lacks publicly available benchmarks altogether. Without independent testing, its actual capabilities remain uncertain, leaving the community with only Musk’s promotional statements to go by. Regulatory Compliance Regulatory compliance is a particularly important issue for organisations in Europe under the EU AI Act. The legislation requires general-purpose AI models to be released under genuinely open licences, accompanied by detailed technical documentation, information on training and testing datasets, and usage reporting. For models that exceed systemic risk thresholds, such as those trained with more than 10²⁵ floating point operations, further obligations apply, including risk assessment and registration. Grok 2.5, by virtue of its vague licence and lack of documentation, appears non-compliant on several counts. Unless xAI publishes more details or adapts its licensing, European businesses may find it difficult or legally risky to adopt Grok in their workflows. GPT-OSS-20B and 120B, by contrast, seem carefully aligned with the requirements of the AI Act. Their Apache 2.0 licence is recognised under the Act, their documentation meets transparency demands, and OpenAI has signalled a commitment to provide usage reporting. From a regulatory standpoint, OpenAI’s releases are safer bets for integration within the UK and EU. Community Reception The reception from the AI community reflects these differences. Developers welcomed OpenAI’s move as a long-awaited recognition of the open-source movement, especially after years of criticism that the company had become overly protective of its models. Some users, however, expressed frustration with the mixture-of-experts design, reporting that it can lead to repetitive tool-calling behaviours and less engaging conversational output. Yet most acknowledged that for tasks requiring structured reasoning, coding or mathematical precision, the GPT-OSS family performs exceptionally well. Grok 2.5’s release was greeted with more scepticism. While some praised Musk for at least releasing weights, others argued that without a proper licence or documentation it was little more than a symbolic gesture designed to signal openness while avoiding true transparency. Strategic Implications The strategic motivations behind these releases are also worth considering. For xAI, releasing Grok 2.5 may be less about immediate usability and more about positioning in the competitive AI landscape, particularly against Chinese developers and American rivals. For OpenAI, the move appears to be a balancing act: maintaining leadership in proprietary frontier models like GPT-5 while offering credible open-weight alternatives that address regulatory scrutiny and community pressure. This dual strategy could prove effective, enabling the company to dominate both commercial and open-source markets. Conclusion Ultimately, the comparison between Grok 2.5 and GPT-OSS-20B and 120B is not merely technical but philosophical. xAI’s release demonstrates a willingness to participate in the open-source movement but stops short of true openness. OpenAI, on the other hand, has set a new standard for what open-weight releases should look like in 2025: efficient architectures, extensive documentation, clear licensing, strong benchmark performance and regulatory compliance. For European businesses and policymakers evaluating open-source AI options, GPT-OSS currently represents the more practical, compliant and capable choice. In conclusion, while both xAI and OpenAI contributed to the momentum of open-source AI in August 2025, the details reveal that not all openness is created equal. Grok 2.5 stands as an important symbolic release, but OpenAI’s GPT-OSS family sets the benchmark for practical usability, compliance with the EU AI Act, and genuine transparency.
Crypto World
Zama Token Debuts at $400 Milion Valuation
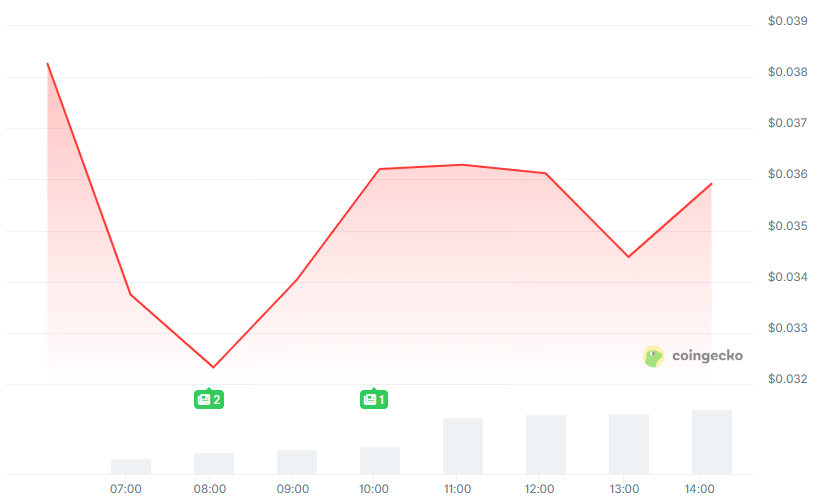
ZAMA is currently trading 30% below its ICO price.
Zama’s highly anticipated $ZAMA token has made headlines as the first production-scale use of Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) on the Ethereum mainnet.
However, the token is currently trading at $0.035, marking a 30% decrease from its initial coin offering (ICO) price).

Zama’s auction format was notable for its confidentiality features. The token sale raised $118.5 million through a sealed-bid Dutch auction, using Zama’s technology to protect the privacy of participants’ bids.
Zama’s focus on FHE is part of a broader strategy to enable confidential smart contracts on Ethereum. This technology enables computation on encrypted data without first decrypting it, enhancing privacy for blockchain applications.
This article was generated with the assistance of AI workflows.
Crypto World
Trump-Linked World Liberty Financial Draws House Scrutiny After $500M UAE Stake Revealed

A US House investigation has turned its focus to World Liberty Financial, a Trump-linked crypto venture.
The move follows a recent Wall Street Journal report of a $500M UAE-linked stake agreed shortly before President Donald Trump’s inauguration.
Rep. Ro Khanna, a Democrat from California and the ranking member of the House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party, on Wednesday sent a letter to World Liberty co-founder Zach Witkoff seeking ownership records, payment details and internal communications tied to the reported deal and related transactions.
Khanna wrote that the Journal reported “lieutenants to an Abu Dhabi royal secretly signed a deal with the Trump Family to purchase a 49% stake in their fledgling cryptocurrency venture [World Liberty Financial] for half a billion dollars” shortly before Trump took office.
He argued the reported investment raises questions about conflicts of interest, national security and whether US technology policy shifted in ways that benefited foreign capital tied to strategic priorities.
Meanwhile, Trump has said he had no knowledge of the deal. Speaking to reporters on Monday, he said he was not aware of the transaction and noted that his sons and other family members manage the business and receive investments from various parties.
Crypto Venture Deal Draws Scurinty Over AI And National Security Policy Intersection
The letter also linked the reported stake to US export controls on advanced AI chips and concerns about diversion to China through third countries.
Khanna said the Journal report suggested the UAE-linked investment “may have resulted in significant changes to U.S. Government policies designed to prevent the diversion of advanced artificial intelligence chips and related computing capabilities to the People’s Republic of China.”
According to the Journal account cited in the letter, the agreement was signed by Eric Trump days before the inauguration.
The investor group was described as linked to Sheikh Tahnoon bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the UAE national security adviser. Two senior figures connected to his network later joined World Liberty’s board.
USD1 Stablecoin Use Raises Questions Over Influence And Profits
Khanna’s letter pointed to another UAE-linked deal involving World Liberty’s USD1 stablecoin, which he said was used to facilitate a $2B investment into Binance by MGX, an entity tied to Sheikh Tahnoon. He wrote that this use “helped catapult USD1 into one of the world’s largest stablecoins”, which could have increased fees and revenues for the project and its shareholders.
The lawmaker also connected the Binance investment to later policy developments, including chip export decisions and a presidential pardon for Binance founder Changpeng Zhao.
He cited a former pardon attorney who said, “The influence that money played in securing this pardon is unprecedented. The self-dealing aspect of the pardon in terms of the benefit that it conferred on President Trump, and his family, and people in his inner circle is also unprecedented.”
Khanna framed the overall picture as more than political optics. “Taken together, these arrangements are not just a scandal, but may even represent a violation of multiple laws and the United States Constitution,” he wrote, citing conflict-of-interest rules and the Constitution’s Foreign Emoluments Clause.
Khanna Warns Of National Security Stakes In WLFI Case
He asked World Liberty to answer detailed questions and produce documents by March 1, 2026, including agreements tied to the reported 49% stake, payment flows, communications with UAE-linked representatives, board appointments, due diligence and records tied to the USD1 stablecoin’s role in the Binance transaction.
Khanna also pressed for details on any discussions around export controls, US policy toward the UAE and strategic competition with China, as well as communications related to President Trump’s decision to pardon Zhao.
The probe lands at a moment when stablecoins sit closer to the center of market structure debates, and when politically connected crypto ventures face sharper questions about ownership, governance and access.
Khanna closed his letter with a warning about the stakes, writing, “Congress will not be supine amid this scandal and its unmistakable implications on our national security.”
The post Trump-Linked World Liberty Financial Draws House Scrutiny After $500M UAE Stake Revealed appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
Feds Crypto Trace Gets Incognito Market Creator 30 Years
The creator of Incognito Market, the online black market that used crypto as its economic heart, has been sentenced to 30 years in prison after some blockchain sleuthing led US authorities straight to the platform’s steward.
The Justice Department said on Wednesday that a Manhattan court gave Rui-Siang Lin three decades behind bars for owning and operating Incognito, which sold $105 million worth of illicit narcotics between its launch in October 2020 and its closure in March 2024.
Lin, who pleaded guilty to his role in December 2024, was sentenced for conspiring to distribute narcotics, money laundering, and conspiring to sell misbranded medication.
Incognito allowed users to buy and sell drugs using Bitcoin (BTC) and Monero (XMR) while taking a 5% cut, and Lin’s undoing ultimately came after the FBI traced the platform’s crypto to an account in Lin’s name at a crypto exchange.
“Today’s sentence puts traffickers on notice: you cannot hide in the shadows of the Internet,” said Manhattan US Attorney Jay Clayton. “Our larger message is simple: the internet, ‘decentralization,’ ‘blockchain’ — any technology — is not a license to operate a narcotics distribution business.”

In addition to prison time, Lin was sentenced to five years of supervised release and ordered to pay more than $105 million in forfeiture.
Crypto tracing led FBI right to Lin
In March 2024, the Justice Department said Lin closed Incognito and stole at least $1 million that its users had deposited in their accounts on the platform.
Lin, known online as “Pharoah,” then attempted to blackmail Incognito’s users, demanding that buyers and vendors pay him or he would publicly share their user history and crypto addresses.

Months later, in May 2024, authorities arrested Lin, a Taiwanese national, at New York’s John F. Kennedy Airport after the FBI tied him to Incognito partly by tracing the platform’s crypto transfers to a crypto exchange account in Lin’s name.
The FBI said a crypto wallet that Lin controlled received funds from a known wallet of Incognito’s, and those funds were then sent to Lin’s exchange account.
Related: AI-enabled scams rose 500% in 2025 as crypto theft goes ‘industrial’
The agency said it traced at least four transfers showing Lin’s crypto wallet sent Bitcoin originally from Incognito to a “swapping service” to exchange it for XMR, which was then deposited to the exchange account.
The exchange gave the FBI a photo of Lin’s Taiwanese driver’s license used to open the account, along with an email address and phone number, and the agency tied the email and number to an account at the web domain registrar Namecheap.
The Namecheap account also used funds from Lin’s crypto wallet and exchange account to buy a domain for a website that promoted Incognito, the FBI said.
The agency added that the size of Lin’s deposits at the exchange grew alongside Incognito, starting from around $63,000 in 2021 to nearly $4.2 million over the course of 2023, while an account at a separate exchange saw $4.5 million deposited between July and November 2023.
Magazine: $3.4B of Bitcoin in a popcorn tin — The Silk Road hacker’s story
Crypto World
Crypto Firms Propose Compromises to Save Stablecoin Yield Bill

Crypto industry insiders say the stalled crypto market-structure bill could hinge on a new set of concessions centered on stablecoins, as Senate negotiations lag and party lines tighten. The House-passed legislation remains stalled in the upper chamber, amid ongoing debates about whether stablecoin issuers should be allowed to offer yields and how such yields would affect traditional banking products. In recent days, anonymous sources cited by Bloomberg described fresh proposals aimed at breaking the impasse, including giving community banks a larger footprint in the stablecoin ecosystem, and pairing that with reserve arrangements and partnerships to issue stablecoins through smaller lenders.
The tension between crypto innovation and traditional banking interests continues to shape the dialogue. Advocates for the sector argue that properly structured stablecoins can enhance payments efficiency and financial inclusion, while banks worry about deposit flight and competition with conventional savings products. The ongoing negotiations reflect a broader question: how to integrate digital-assets rails into a regulated, consumer-protective framework without eroding the stability of the mainstream financial system. The evolving proposals come as negotiations persist over the precise framework for stablecoins and the broader market structure bill.
The freshness of the ideas was underscored by Bloomberg’s reporting that crypto firms are testing compromises aimed at easing passage in the Senate. Among the suggested measures are boosting community banks’ involvement in stablecoin operations, potentially via custody arrangements or governance roles that keep the vaulting and settlement processes within the banking sector. Another strand of the discussions contemplates allowing stablecoin issuers to partner with community banks to issue new tokens, leveraging lenders’ balance-sheet credibility while maintaining regulatory guardrails. The aim is to appease lawmakers who view stablecoins as a potential vector for consumer risk if left unregulated, while giving banks a pathway to participate in the digital-asset economy without surrendering traditional deposit stability.
The ongoing diplomacy faced a critical test in Washington when a White House meeting on Monday between crypto and banking groups concluded without a formal agreement. The discussions, described as constructive but inconclusive, highlighted the difficulty of reconciling industry incentives with the prudential concerns of regulators and the political calculus in a split Senate. In an interview with Fox News, Senate Banking Committee Chairman Tim Scott signaled cautious optimism about permitting crypto firms to pay rewards, but warned against marketing those rewards as if they were a bank deposit. The remarks underscored how the debate remains anchored in fundamental questions about disclosure, consumer protection, and the line between fintech innovation and traditional banking.”””
“The good news is that both sides remain at the table […] we’re going to overcome those hurdles and make sure that America is the crypto capital of the world.”
The policy tug-of-war is not merely procedural. Republicans and Democrats are weighing alternative bill texts that would alter the trajectory of crypto regulation. Earlier in January, the US Senate Agriculture Committee released a Republican-drafted version of the market-structure bill, though it lacked Democratic backing. Lawmakers held a markup session on January 29 that advanced the Agriculture Committee’s version, but full Senate passage would still hinge on cross-party support—specifically, securing at least seven Democratic votes in the chamber. Meanwhile, the Banking Committee has been pursuing a somewhat stricter outline, and party leadership will need to align these tracks before any bill can reach the president’s desk for approval.
The divergence between the committee proposals illustrates the broader political challenge: balancing the pace of innovation with safeguards that reassure retail users and the traditional financial system. As talks continue, observers note that the market remains in a wait-and-see mode. The sector’s attention is fixed on whether negotiated concessions will translate into a single, cohesive framework that satisfies lawmakers’ concerns about consumer protection, systemic risk, and banking competition. The coming weeks are likely to be decisive as negotiators from both chambers attempt to converge on a version that can secure bipartisan support and avoid a protracted stalemate.
Key takeaways
- The market-structure bill, cleared by the House, remains blocked in the Senate as negotiators seek concessions on stablecoins and their yields.
- Proposals under consideration include expanding community banks’ role in stablecoin infrastructure, with reserve and issuance partnerships designed to preserve consumer protections.
- A White House meeting between crypto and banking groups ended without a formal agreement, underscoring the difficulty of reconciling industry and regulatory objectives.
- Senate consideration hinges on cross-party support; the Agriculture Committee’s Republican draft and the Banking Committee’s stricter version both require alignment to advance.
- Public statements by lawmakers reflect a cautious stance on distinguishing crypto incentives from traditional banking products, underscoring the political sensitivity of the issue.
- The dialogue emphasizes the broader aim of defining a clear regulatory pathway for stablecoins, while preserving innovation and financial stability.
Market context: The negotiations unfold against a backdrop of ongoing regulatory scrutiny, evolving stablecoin designs, and a broader push for clearer crypto rules that can attract mainstream financial participation while protecting consumers and market resilience.
Why it matters
For users and builders in the crypto space, the discussions around stablecoins and bank participation signal a potential path to more widely adopted digital-assets rails, provided safeguards are robust and well-communicated. If lawmakers approve a framework that incorporates community banks into the stablecoin lifecycle—custody, reserves, and possible issuing partnerships—there could be increased regulatory clarity and improved consumer protections. At the same time, banks stand to gain access to a new line of business in stablecoins, but only if the rules preserve deposit stability and align with traditional risk-management practices.
From a market perspective, the outcome will shape liquidity dynamics and the pace of stablecoin-driven payments and retail use cases. Regulatory alignment remains a critical driver of investor confidence, and the degree to which the bill accommodates innovation without compromising financial stability will influence how quickly exchanges, wallets, and payment processors integrate stablecoins into routine commerce. The ongoing conversations demonstrate a pragmatic approach: recognize the value of digital assets while insisting on guardrails that address systemic concerns, consumer rights, and market integrity.
What to watch next
- Next week: additional White House and congressional discussions to test whether new concessions can bridge the gap between the House language and Senate preferences.
- Upcoming committee alignments: potential revisions to the Agriculture and Banking Committee texts to facilitate a unified bill.
- Public disclosures or statements from Banking Committee leadership detailing which provisions are most likely to gain bipartisan support.
- Any formal rollout of a joint framework for community banks in stablecoin operations, including proposed reserve arrangements.
Sources & verification
- Bloomberg’s reporting on crypto firms proposing concessions to unlock passage of the market-structure bill, including ideas to expand community banks’ role in stablecoins.
- White House meeting updates between crypto and banking groups regarding stablecoins and market structure legislation.
- Senate Agriculture Committee’s January draft of the market-structure bill and coverage of the January 29 markup session.
- The Banking Committee’s proposals and related discussions on stricter regulatory language for the bill.
- Public remarks by Tim Scott about rewards in crypto and the need to avoid advertising crypto products as bank deposits.
Stablecoin concessions push to unlock stalled market-structure bill
The latest round of talks centers on stabilizing the political and regulatory environment around stablecoins, a class of digital assets designed to maintain a fixed value and enable smoother digital payments. Industry participants argue that the right mix of rules can unlock a path toward broader adoption while preserving the integrity of the financial system. The discussions acknowledge that stablecoins can offer real benefits in terms of speed, cost, and accessibility for everyday transactions, but they also emphasize the need for rigorous reserves, clear disclosures, and appropriate consumer protections.
One of the more concrete proposals circulating in Washington is to enhance the role of community banks in the stablecoin ecosystem. By moving reserve custody and potentially some issuance activities closer to local lenders, policymakers hope to anchor stablecoins in a trusted, regulated banking framework. Proponents say this approach could reduce the risk of large, uncollateralized losses and improve oversight by tying stablecoin reserves to established banking institutions. Critics, however, worry about the concentration of reserve assets and the potential for new forms of bank dependency to emerge in the fast-evolving digital-asset space.
Another facet of the debate concerns whether stablecoin issuers should be allowed to offer yields or rewards on holdings. While supporters argue that regulated yields could attract more users and create competitive pressure for better consumer terms, opponents warn that yield-bearing stablecoins might blur the lines between money-market products and traditional bank deposits. The timing of this debate is critical, as lawmakers seek to avoid a regulatory gap that could be exploited by unscrupulous actors while ensuring that legitimate issuers can operate with clarity and accountability.
Ultimately, the path forward hinges on a carefully calibrated balance between innovation and prudence. The senators’ goal is to craft a framework that does not stifle the growth of legitimate digital-asset services but still provides the safeguards that protect retail users and the broader financial system. The dialogue continues against a backdrop of market volatility, evolving token designs, and a wider push for consistent rules that can support continued growth in the crypto sector while limiting systemic risk. As negotiators test different configurations, the coming weeks will reveal whether a consensus can emerge that satisfies both sides while delivering a credible, enforceable regulatory regime for stablecoins and related digital-assets services.
Crypto World
BTC price news: Bitcoin dumps below $71,000
Bitcoin slid below the $71,000 mark in Asian hours Thursday as a renewed selloff in global technology stocks spilled into crypto markets, undercutting hopes of a sustained rebound after last week’s volatility.
The world’s largest cryptocurrency fell as much as 7.5% over the past 24 hours, touching lows near $70,700 before paring some losses, according to CoinDesk data.
The move followed sharp declines in Asian equities, where mounting concern over artificial intelligence spending, stretched valuations and slowing earnings momentum pushed investors further away from risk assets.
MSCI’s Asia tech index fell for a fifth time in six sessions, led by steep losses in South Korea’s Kospi, which dropped around 4% as heavyweight AI-linked stocks came under pressure.
The weakness followed a slide in the Nasdaq during U.S. trading, where disappointing earnings from firms such as Alphabet, Qualcomm and Arm reinforced fears that AI investment may be peaking faster than expected.
Bitcoin has increasingly traded as a high-beta risk asset during equity-led drawdowns, particularly when liquidity is thin and macro uncertainty rises.
The latest drop comes after bitcoin briefly whipsawed earlier this week, falling toward $73,000 before rebounding above $76,000 — a sign of fragile conviction rather than a clean trend reversal.
Pressure was compounded by sharp moves in commodities. Silver plunged as much as 17% and gold fell over 3%, extending a brutal unwind that has already triggered heavy liquidations in tokenized metals products on crypto venues.
Crypto World
House probe targets World Liberty Financial after report of $500 Million UAE stake


A U.S. House investigation is probing whether World Liberty Financial, a Trump-associated crypto venture, and its dollar-pegged token became entangled with foreign sovereign capital and U.S. technology policy.
The move follows a Wall Street Journal report that an Abu Dhabi-linked entity secretly agreed to buy a 49% stake in World Liberty Financial for $500 Million shortly before President Donald Trump’s inauguration in early 2025.
Rep. Ro Khanna (D-Penn), ranking member of the House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party – a temporary U.S. House panel that investigates and studies how China affects U.S. interests – has sent a formal letter demanding ownership records, payment details and internal communications from the company, framing the inquiry around potential conflicts of interest, national-security risks tied to AI chip export controls and the role of World Liberty’s USD1 stablecoin in a separate $2 Billion Binance investment.
Khanna’s letter asks World Liberty to confirm details of the reported Emirati investment, including whether $187 million flowed to Trump family entities and whether additional payments were made to affiliates of the company’s co-founders.
The House investigation also requested capitalization tables, profit distributions, board appointment records, and due diligence materials tied to Aryam Investment 1, the vehicle identified in press reports.
A significant portion of the inquiry focuses on USD1, World Liberty’s dollar-pegged stablecoin, which was used to settle MGX’s $2 billion investment in the crypto exchange Binance.
Khanna and lawmakers are seeking documentation on how USD1 was selected, the revenue generated by the transaction, and whether company personnel were involved in discussions regarding the later presidential pardon of Binance founder Changpeng Zhao.
The House committee also instructs the company to preserve electronic communications and internal compliance policies related to conflicts of interest, export controls, and dealings with entities tied to the United Arab Emirates or China.
World Liberty has until March 1 to deliver the requested records.
Crypto World
$2.9B Bitcoin ETF Outflow Signals Downside as Bearish Futures Loom
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) traded below $73,000 on Wednesday after briefly retesting the $79,500 level the day prior, as a softer tech backdrop ripples into crypto markets. The move mirrors a broader risk-off tilt that has been evident in the Nasdaq, where a weak sales outlook from chipmaker AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) and softer US payroll data turned investors away from high-beta assets. The price action underscores how crypto is not insulated from macro shifts, even as it trades in a market that remains highly sensitive to liquidity and leverage dynamics.
Key takeaways
- Heavy outflows from Bitcoin spot ETFs persist, with more than $2.9 billion leaving US-listed funds across roughly 12 trading days, signaling renewed pain for leveraged long positions.
- BTC options markets show elevated hedging activity, as professional traders buy downside protection, pushing the 30-day delta skew higher and signaling skepticism about a swift bottom near $72,100.
- Leverage-driven risk outside spot markets remains a pressure point: leveraged long BTC futures liquidations totaled about $3.25 billion during the recent pullback, wiping out substantial margin and forcing rapid deleveraging.
- Industry mechanics remain a focal point: some market observers argue that crypto-exchange liquidation engines are not self-stabilizing in the same way TradFi circuit breakers are, highlighting ongoing fragility even as history suggests eventual recovery.
- Two unfounded rumors continue to circulate: a purported $9 billion Galaxy Digital Bitcoin sale tied to quantum concerns and renewed questions about Binance’s solvency, though on-chain metrics and company statements offer some counterpoints to panic.
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) slid below $73,000 on Wednesday after briefly retesting the $79,500 level on Tuesday, a retreat that aligned with a broader risk-off move in equities led by a downbeat tech sector. The downturn followed a slide in the Nasdaq, reflecting weaker near-term demand signals from major tech companies and the spillover into risk assets beyond stocks. The pressure is not purely cyclical; it is reinforced by flows that have kept outflows from spot Bitcoin ETFs elevated in recent weeks.
The persistent outflows from spot Bitcoin ETFs add a layer of complexity to the price action. The daily rhythm of fund flows has remained negative, with an average net outflow running around $243 million since mid-January. That cadence coincided with Bitcoin’s rejection at the $98,000 level earlier in the month and helped set the stage for a roughly 26% correction over three weeks. In practical terms, the cascading effect of outflows has amplified liquidity stress for leveraged traders, and unless new margin is deposited, the most aggressive 4x or higher positions may have already seen their risk exposure largely eroded.
Another thread driving narrative risk is the potential for continued volatility in the broader crypto ecosystem. The market has faced a mix of volatile events and rumors about the health of counterparties. A longstanding concern is the possibility that outsized losses from a single event could cascade through liquidity-providing venues. One notable episode cited by market observers is the $19 billion liquidation tied to a mid-October 2025 incident that reportedly originated from a performance glitch in Binance’s data feeds, which delayed transfers and fed inaccurate price signals. Binance acknowledged fault and subsequently issued compensation, but the episode left a lasting impression on risk controls across the space.
In conversations with industry participants, Haseeb Qureshi, managing partner at Dragonfly, described the October 2025 event as a case study in how liquidations can hit market-makers and liquidity providers. “Liquidation engines kept firing even when liquidity could not be absorbed, wiping out market makers and forcing a protracted recovery,” he noted. He added that while the crash did not permanently break the market, a return to normal functioning would require time and a repricing of risk for market participants who relied on aggressive leverage. The sentiment among traders is one of cautious realism: the market has recovered from prior shocks, but the path remains bumpy and contingent on liquidity and macro conditions.
Beyond pure price action, the options market provides a lens into how professionals are positioning for further downside. The 30-day delta skew for Bitcoin 25% delta puts against calls rose to about 13% on Wednesday, signaling that demand for downside protection remains elevated and that even seasoned traders are not confident a durable bottom has formed around the $72,100 level. In practice, a skew above several percent is interpreted as a signal that informed participants are bracing for additional weakness, rather than a swift reversal. The data point, sourced from Deribit through Laevitas, underlines a market that is hedging against a continued drawdown rather than embracing a V-shaped recovery—at least in the near term.
The broader macro backdrop has not yet clarified the near-term trajectory for crypto markets. A key question remains whether spot ETF outflows will persist or abate in the weeks ahead, and how that will interplay with liquidity conditions across major crypto venues. Onchain noise and counterparty concerns continue to simmer, but the market has shown time and again that it can adapt to shocks—though not without interim pain for those exposed to highly leveraged bets.
Why it matters
The current sequence of ETF outflows, leveraged liquidations and hedging activity paints a portrait of a market in transition. It highlights how entrenched leverage remains in some segments of the Bitcoin ecosystem and how quickly liquidity can tighten when risk appetite cools. For traders, the combination of elevated downside hedges and growing suspicion about the sustainability of rallies underscores the importance of margin discipline and robust risk controls. For market-makers and liquidity providers, the episode serves as a reminder that crypto markets still rely heavily on automated liquidation mechanisms that can amplify short-term moves during stress, even as the broader market has learned to rebound from past crises.
From a broader perspective, these dynamics unfold within a sector that remains highly sensitive to outside forces—tech stock sentiment, central-bank policy expectations, and regulatory developments all feed into crypto liquidity. The outflows from spot Bitcoin ETFs—paired with a demand for downside protection in options markets—suggest a risk-off impulse that could persist if macro data continues to disappoint or if equity sell-offs intensify. Yet the history of Bitcoin and other digital assets shows resilience: even after sharp declines, recovery tends to follow, driven by new demand fundamentals and tail-risk hedging strategies that gradually re-enter the market.
For users and builders, the current environment emphasizes the need for clarity around risk models, improved liquidity infrastructure, and more robust stress-testing across venues. It also underscores the value of transparent communications from major counterparties and a cautious approach to leverage, given how quickly market dynamics can shift in crypto ecosystems.
What to watch next
- Next 2–4 weeks: track spot Bitcoin ETF inflows/outflows to gauge whether the current risk-off phase persists or eases.
- Watch BTC 30-day delta skew updates for indications of whether professional hedging is cooling or intensifying.
- Monitor Binance withdrawal and on-chain reserve metrics for evidence of liquidity stress or stabilization.
- Follow public statements from Galaxy Digital and other market participants regarding structural risk and counterparty health.
Sources & verification
- CoinGlass data on Bitcoin spot ETF daily net flows and overall ETF outflows.
- Deribit 30-day delta skew (put-call) data via Laevitas, used to gauge professional hedging behavior.
- Dragonfly partner Haseeb Qureshi’s comments on liquidation dynamics and market recovery timelines.
- Galaxy Digital statements denying quantum-risk-driven sales, as reported by company or executives on X.
- On-chain metrics indicating Bitcoin deposits at Binance remained relatively stable amid withdrawal-related concerns.
Market reaction and key details
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) has faced renewed downward pressure as liquidity constraints and risk-off sentiment took hold. The failure to sustain a breakout near the $80,000 level—and the subsequent retreat to the mid-$70,000s—came amid a familiar pattern: outsized ETF outflows, a sharp squeeze on leveraged long positions, and rising skepticism among professional traders about a rapid bottom. The narrative has shifted away from a straightforward macro-driven rally toward a more nuanced story about risk management, liquidity provisioning, and the mechanics of how markets absorb shocks in a highly interconnected, cross-asset ecosystem.
Two notable developments stand out as the market adjusts: first, the swing in option hedging signals shows that seasoned traders are actively protecting against further declines, not simply chasing a rebound. The delta skew, a gauge of put versus call demand, has moved higher, highlighting the demand for downside protection in a climate where tech equities are under stress. Second, while the rumor mill churns with talk of large liquidations and counterparty concerns, on-chain and public disclosures suggest a more nuanced picture of counterparty health and liquidity at major venues. The market remains attentive to any fresh data about exchange resilience and the speed with which risk controls can recalibrate after a sell-off.
As traders weigh the near-term path, the interplay between ETF flows, derivatives positioning, and counterparty risk continues to be the defining feature of Bitcoin’s price action in the current cycle. The consensus remains unsettled: the market has a history of snapping back after downturns, but the path to normalization can be long and episodic, with interim pain for those positioned for a quick recovery. The coming weeks will be closely watched for changes in liquidity conditions, regulatory guidance, and the pace at which market participants adjust their risk tolerances in response to evolving macro signals and internal risk controls.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Drops Sharply Below $93K After Stable Weekend
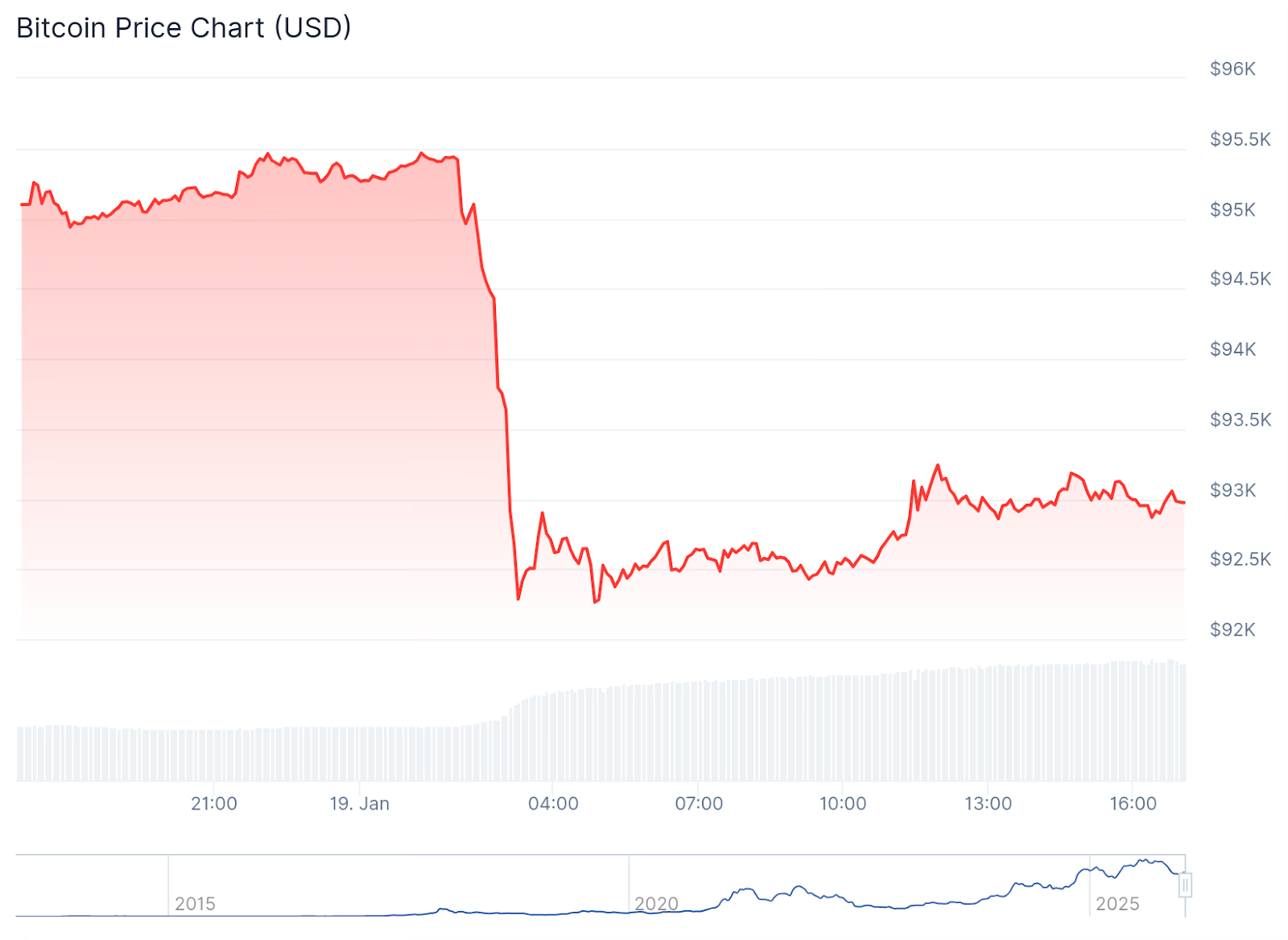
All the top-10 crypto assets by market capitalization are in the red today as markets digest President Trump’s EU tariff threats over Greenland.
Crypto markets are experiencing a correction today after pushing higher last week. The Bitcoin (BTC) price dropped around $4,000 in a few minutes last night and is trading just below $93,000 at press time, down roughly 2.2% over the past 24 hours. The leading cryptocurrency is up over 2% over the past seven days, however, and was trading around $95,000 over the weekend.

All of the top-10 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization 2%-3% in the red today. Ethereum (ETH) fell about 3.2% to $3,215, after trading above $3,300 this weekend. ETH is still up nearly 4% on the weekly timeframe.
Solana (SOL) and Dogecoin (DOGE) showed the biggest losses today among the top-10 assets, both down about 6% on the day.
Total crypto market capitalization slipped to approximately $3.23 trillion, down 2.6% today, reflecting weakness across the board.
Range-Driven Market
Analysts at Matrixport noted in a Monday update on X that despite renewed tariff threats from United States President Donald Trump, this time over Greenland, “implied volatility in both Bitcoin and Ethereum has only marginally edged higher.”

The analysts noted that volatility has fallen sharply since mid-November last year, with a repricing of roughly 18-25 volume points over the past two months, which they described as a “significant compression.” They added:
“This decline signals that traders are neither chasing upside through options nor aggressively hedging downside risk.”
The cryptocurrency market’s Fear & Greed Index has slipped back into the “Fear” zone after briefly touching “Neutral” last week for the first time in several weeks, suggesting that sentiment among investors remains fragile.
Big Movers and Liquidations
Looking at the top-100 assets by market cap, privacy coin Monero (XMR) is today’s strongest performer, rising 8% on the day, followed by Sky (SKY), which posted mild gains of roughly 2.5%.
On the downside, on-chain perpetual futures exchange Aster’s ASTER was the biggest loser today, falling around 13.5% to reach an all-time low. Sui (SUI) lost 12.4% today, making it the second-weakest performer among the top-100 large-caps.
Crypto liquidations built up over the course of last week as volatility picked up, rather than being driven by Sunday’s usually quiet trading. Total crypto liquidations spiked at around $875 million over the past 24 hours, according to Coinglass, with longs making up the majority of liquidated positions at roughly $788 million, versus about $88 million in shorts.
Bitcoin accounted for the largest share at about $234 million, followed by Ethereum with roughly $156 million, while altcoins made up another $133 million.
ETFs and Macro Conditions
Despite net outflows on Friday, crypto exchange-traded flows remained positive on the weekly timeframe. Spot Bitcoin ETFs recorded net inflows of approximately $1.42 billion last week, lifting cumulative inflows to about $57.8 billion, according to data from SoSoValue.
Spot Ethereum ETFs also saw big demand over the past week, seeing a net inflow streak every day last week, closing the week with more modest inflows on Friday. ETH ETFs posted total weekly net inflows of roughly $479 million, while cumulative inflows reached about $12.9 billion.
On the macro side, investors are leaning toward safe havens again as geopolitical tensions return, after President Trump renewed threats to raise tariffs on several European allies, tied to his push to take control of Greenland.
As Reuters reported, Trump unveiled an additional 10% tariff on goods from countries including Denmark, Norway, Sweden, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Finland and the UK, that would take effect on Feb. 1, rising to 25% on June 1 unless progress is made toward a Greenland agreement. European officials are expected to respond later today.
Crypto World
CoolWallet Integrates TRON Energy Rental to Reduce TRX Transaction Costs


CoolWallet, a self-custody hardware wallet provider, has announced the integration of TRON energy rental services, allowing users to reduce transaction costs while securely managing TRX and other TRC-20 assets.
In a press release shared with CryptoNews, the firm said the new feature allows CoolWallet users to access TRON’s blockchain infrastructure while maintaining full control over their private keys and funds through CoolWallet’s hardware wallet paired with its mobile application.
TRON remains one of the most actively used networks among CoolWallet customers, particularly due to its role in stablecoin transfers and low-fee payments.
The update is designed to expand TRON’s accessibility for retail users looking for cost-efficient transactions without sacrificing self-custody protections.
Lower Fees Through Energy Rental
The firm explains that under TRON’s resource model, transactions consume Energy, often requiring users to burn TRX for network fees. CoolWallet’s update introduces an energy rental mechanism that reduces the amount of TRX burned per transaction, helping users retain more of their holdings while maintaining full transaction functionality.
The integration also introduces flexible payment options, allowing users to pay for Energy using either USDT on TRON or TRX, providing greater cost control for frequent transfers and DeFi activity.
By lowering transaction costs, the feature is expected to make token movements and decentralized finance participation more economical for users operating within the TRON ecosystem.
Expanding Secure Self-Custody Access
CoolWallet emphasized that the integration maintains the company’s core focus on security and user sovereignty. Transactions are executed with full self-custody, meaning users retain ownership of their assets at all times without relying on third-party intermediaries.
“TRON plays a critical role in the global stablecoin ecosystem, particularly for users who prioritize cost efficiency and transaction speed,” said Michael Ou, CEO of CoolBitX. “This integration reflects our commitment to supporting the blockchain networks our users depend on most, while ensuring they retain full security and control over their assets.”
Sam Elfarra, Community Spokesperson for the TRON DAO, said the collaboration strengthens access to TRON’s infrastructure through one of the most portable hardware wallet solutions available.
“CoolWallet’s integration represents an important step in making TRON’s infrastructure more accessible to users who prioritize security and self-custody,” Elfarra said. “By bringing TRON support to one of the most portable and user-friendly hardware wallets available, we are expanding access to TRON’s blockchain infrastructure and DeFi applications.”
Strengthening TRON’s Retail and DeFi Ecosystem
The companies said the partnership reflects a shared commitment to reducing barriers to blockchain adoption while maintaining the highest standards of security and user control.
By combining TRON’s scalable infrastructure with CoolWallet’s hardware wallet design, the integration delivers secure, cost-efficient access to blockchain services for everyday users.
The post CoolWallet Integrates TRON Energy Rental to Reduce TRX Transaction Costs appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
Silver’s 17% plunge amid bitcoin drop echoes Michael Burry’s “death spiral” call


Silver sank as much as 17% in the past 24 hours, wiping out a two-day rebound as the metal struggled to find a floor after last week’s historic rout.
The move dragged gold and copper lower as well, extending an unwind that traders say has been magnified by thin liquidity and heavy speculative positioning.
The renewed drop is also showing up on crypto rails. On Hyperliquid, one of the larger liquidation prints tied to tokenized silver was a forced close of roughly $17.75 million in XYZ:SILVER, with about $16.82 million of that coming from long positions, according to trade data shared by market participants.
The lopsided unwind fits the pattern of late, with traders leaning into rebound bets only to get flushed when volatility spikes again.
That spillover is exactly what hedge fund manager Michael Burry flagged earlier this week.
Burry described a “collateral death spiral” dynamic, where leverage builds as metals rise, then falling crypto collateral forces traders to sell tokenized metals to meet margin. He singled out bitcoin losses could force institutions to liquidate profitable metals positions.
In that kind of tape, the liquidation leaderboard can look inverted, with metals products briefly doing more damage than bitcoin itself.
Macro headlines are not helping. Markets are still digesting the policy implications of Kevin Warsh’s nomination as Federal Reserve chair, while President Donald Trump has pushed back on the idea that the Fed could turn more hawkish.
Rate expectations matter for precious metals, but the bigger driver right now is positioning and forced selling, not the clean macro bid that powered last month’s surge.
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoSmart energy pays enters the US market, targeting scalable financial infrastructure
-
Crypto World6 days ago
Software stocks enter bear market on AI disruption fear with ServiceNow plunging 10%
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWhy is the NHS registering babies as ‘theybies’?
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoAdam Back says Liquid BTC is collateralized after dashboard problem
-

 Video2 days ago
Video2 days agoWhen Money Enters #motivation #mindset #selfimprovement
-

 Tech22 hours ago
Tech22 hours agoWikipedia volunteers spent years cataloging AI tells. Now there’s a plugin to avoid them.
-

 Fashion5 days ago
Fashion5 days agoWeekend Open Thread – Corporette.com
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoDonald Trump Criticises Keir Starmer Over China Discussions
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoSky News Presenter Criticises Lord Mandelson As Greedy And Duplicitous
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoU.S. government enters partial shutdown, here’s how it impacts bitcoin and ether
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoSinner battles Australian Open heat to enter last 16, injured Osaka pulls out
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoBitcoin Drops Below $80K, But New Buyers are Entering the Market
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
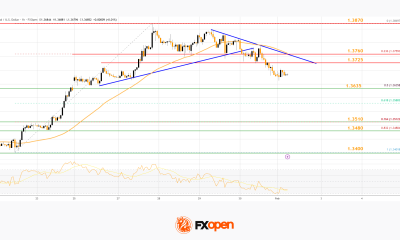
Crypto World3 days agoMarket Analysis: GBP/USD Retreats From Highs As EUR/GBP Enters Holding Pattern
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoKuCoin CEO on MiCA, Europe entering new era of compliance
-
Business5 days ago
Entergy declares quarterly dividend of $0.64 per share
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoShannon Birchard enters Canadian curling history with sixth Scotties title
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoUS-brokered Russia-Ukraine talks are resuming this week
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoGAME to close all standalone stores in the UK after it enters administration
-

 Crypto World1 day ago
Crypto World1 day agoRussia’s Largest Bitcoin Miner BitRiver Enters Bankruptcy Proceedings: Report
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoWhy AI Agents Will Replace DeFi Dashboards






