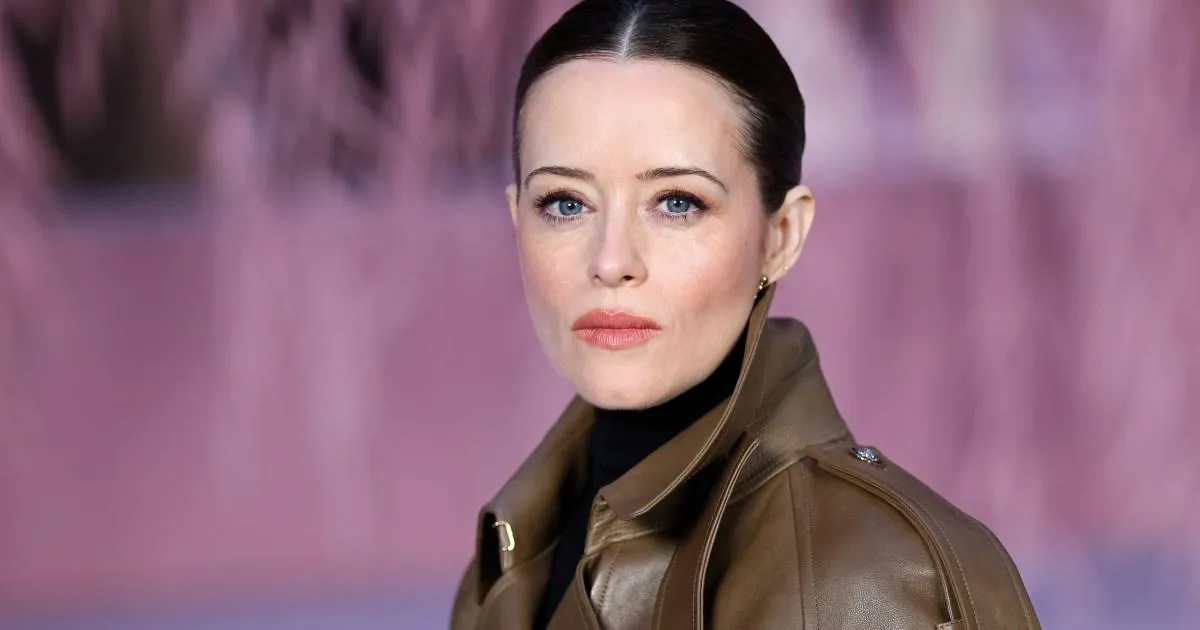
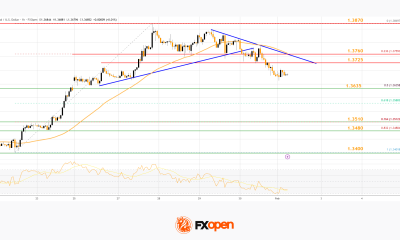
Donny van de Beek has been supported by several of his ex-Manchester United teammates after announcing a huge life update on social media
A number of Manchester United players have shown their support for Donny van de Beek after the former Reds midfielder got engaged to long-term girlfriend Estelle Bergkamp.
Van de Beek, who made 62 appearances during a four-year spell at Old Trafford, started dating Bergkamp, the daughter of Arsenal legend Dennis Bergkamp, back in 2019 when he was playing for Ajax.
The loved-up couple welcomed their first child, a daughter, in April 2022 before their second child, a son, was born in February 2024. Now, Van de Beek and Bergkamp are set to tie the knot after their engagement was announced in a wholesome Instagram post on Monday evening.
In a joint-post – alongside several images of Van de Beek, 28, proposing – Bergkamp, 30, said: “The easiest YES ever [ring emoji and white love heart emoji].”
Dennis Bergkamp commented with two love heart emojis, while ex-Everton midfielder Davy Klassen wrote: “Congratulations [two love heart emojis].”
FOLLOW OUR MAN UNITED FB PAGE! Latest news and analysis via the MEN’s Manchester United Facebook page
Van de Beek’s former United team-mates Bruno Fernandes, Matthijs de Ligt, Christian Eriksen and Willy Kambwala liked the post, while Reds legend Edwin van der Sar also dropped a like.
After leaving United in July 2024, Van de Beek has spent the last 18 months at La Liga side Girona. He played 35 appearances and scored three times in his debut season at the Spanish outfit.
However, he has been restricted to just two appearances this campaign. This is because Van de Beek ruptured his Achilles tendon during a 1-1 draw against Athletic Club in September.
During his time at United, Van de Beek helped the Reds reach the Europa League final in the 2020/21 season before being part of the squad that lifted the Carabao Cup in February 2023.
Upon his departure from the Reds, Van de Beek released an emotional statement on social media. “Dear Manchester United family. Today is a memorable day as my adventure at the club comes to an end,” he said on Instagram.
“I want to thank you all for your support throughout the years. From the moment we arrived at Manchester United, we felt extremely welcome and we are grateful for that.
“Thank you to everyone at the club for making us feel at home. A special thanks to all the fans that made these years unforgettable. Besides the football, the birth of our two children here ensures that Manchester will always have a special place in our hearts.
“Good luck to everybody, we’ll meet again [Japanese Ogre emoji and red love heart emoji].”
Try MEN Premium NOW for just £1
Sky Sports discounted Premier League and EFL package

Sky has slashed the price of its Essential TV and Sky Sports bundle for the 2025/26 season, saving members £336 and offering more than 1,400 live matches across the Premier League, EFL and more.
Sky will show at least 215 live Premier League games this season, an increase of up to 100 more.