Crypto World
Hedera (HBAR) rises 6.7%, leading index higher
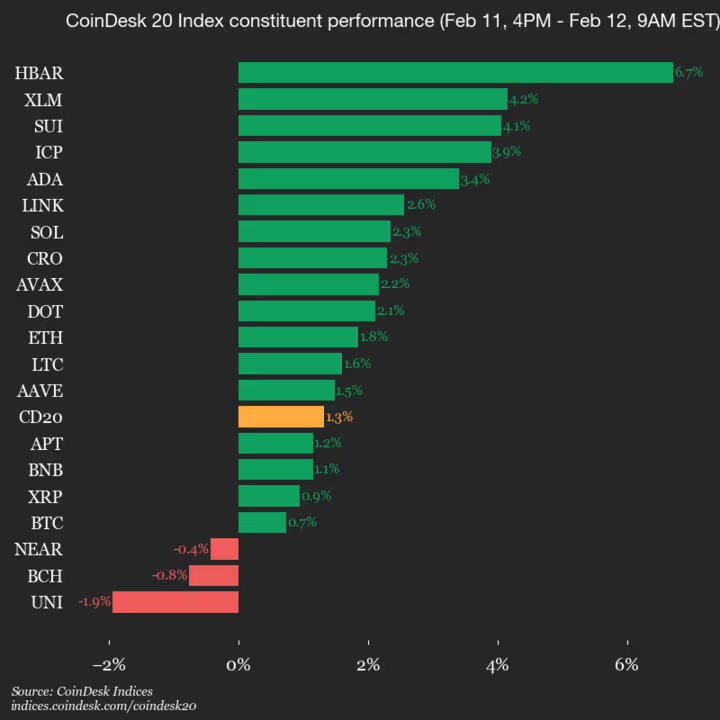
CoinDesk Indices presents its daily market update, highlighting the performance of leaders and laggards in the CoinDesk 20 Index.
The CoinDesk 20 is currently trading at 1943.37, up 1.3% (+25.4) since 4 p.m. ET on Wednesday.
Seventeen of the 20 assets are trading higher.

Leaders: HBAR (+6.7%) and XLM (+4.2%).
Laggards: UNI (-1.9%) and BCH (-0.8%).
The CoinDesk 20 is a broad-based index traded on multiple platforms in several regions globally.
Crypto World
Coinbase posts $670M Q4 loss as it expands beyond trading


Coinbase reported a quarterly loss as it expanded into derivatives, stablecoins, and new markets to reduce reliance on spot crypto trading.
Summary
- Coinbase diversified its business through futures, global expansion, and new financial products.
- Market volatility and lower trading activity weighed on short-term performance.
- Management remains focused on long-term stability and revenue balance.
Coinbase Global, Inc. reported a net loss of $670 million in the fourth quarter of 2025, despite posting record operational metrics for the full year, according to its earnings report released on Feb. 12.
The company said its Q4 results were in line with internal expectations, even as weaker crypto market conditions in late 2025 weighed on transaction revenue and profitability.
Strong growth, weaker bottom line
In its shareholder letter, Coinbase highlighted major gains in trading activity and product adoption throughout 2025. While its crypto market share doubled to 6.4%, the total trading volume reached $5.2 trillion, up 156% year-over-year.
Revenue from subscriptions and services also reached a record $2.8 billion, indicating rising demand for non-trading products such as stablecoins, staking, and custody services. Paid Coinbase One subscribers climbed to nearly one million, tripling over the past three years.
“We drove all-time highs across our products,” said chief executive officer Brian Armstrong. “The Everything Exchange is working, and we’re well-positioned for 2026.”
Chief financial officer Alesia Haas added that the company met or exceeded its revenue and expense targets throughout the year, extending what she described as a multi-year track record of operational discipline.
However, softer market conditions in the final months of 2025 reduced trading activity and lowered asset prices, putting pressure on Coinbase’s core transaction business. According to GAAP accounting standards, these elements played a part in the quarterly net loss.
Expanding beyond spot trading
As part of its “Everything Exchange” strategy, which aims to bring various asset classes onto a single platform, Coinbase continued to grow beyond spot trading in 2025.
The company introduced 24/7 U.S. perpetual-style futures, expanded its global reach by acquiring Deribit, and launched new products like stock trading and prediction markets. At the same time, stablecoin and institutional services were further developed.
These efforts are meant to reduce dependence on traditional crypto trading and make revenue less sensitive to price swings. As a result, average USD Coin (USDC) balances on the platform climbed to $17.8 billion, while customer-held assets tripled over three years. In 2025, more than 12% of the world’s crypto was stored on Coinbase.
After the earnings report was released, Coinbase shares fell about 8% as the wider digital asset market weakened. Analysts pointed to ongoing volatility and uncertain trading volumes as major short-term risks.
Even so, the company ended 2025 with a solid financial position, holding $11.3 billion in cash and equivalents. It also bought back $1.7 billion worth of shares during the year. Early 2026 has shown signs of recovery, with about $420 million in transaction revenue recorded by early February.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Posts $2.3B Loss In Historic Capitulation Event
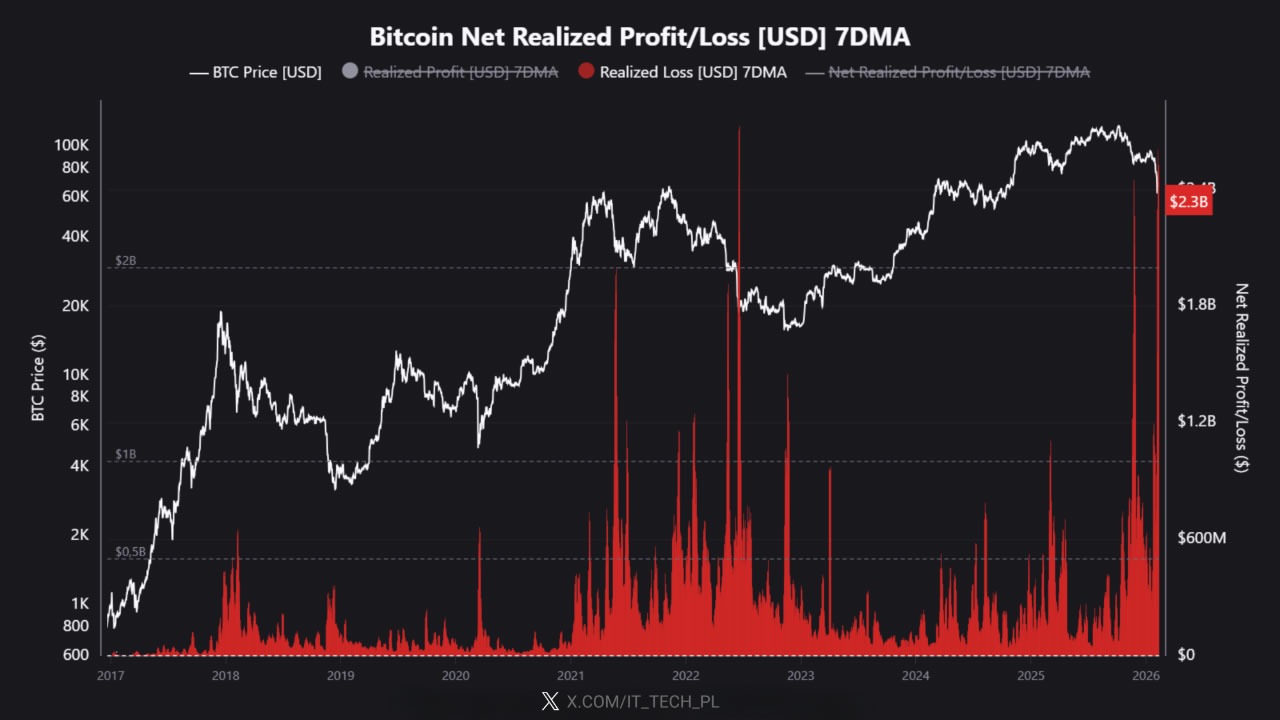
Bitcoin has posted $2.3 billion in realized losses in what an analyst says is one of the largest capitulation events in history, rivaling its crash in 2021.
Bitcoin’s (BTC) seven-day average realized net losses hit $2.3 billion, analyst IT Tech said in a note on CryptoQuant on Thursday, which it called “one of the largest capitulation events in BTC history, rivaling the 2021 crash, 2022 Luna/FTX collapse, and mid-2024 correction.”
“This puts us in the top 3-5 loss events ever recorded,” IT Tech added. “Only a handful of moments in Bitcoin’s history have seen this level of capitulation.”
Bitcoin has dropped nearly 50% from its all-time high of over $126,000 in October to trade around $66,600, having climbed from a low of of $60,000 on Feb. 6.

Deep and slow bleed-out could follow
IT Tech said that previously, “extreme loss spikes like this triggered rebounds,” and noted that Bitcoin had briefly rallied above $70,000 on Tuesday, but added, “this could still be the beginning of a deep and slow bleed-out. Relief rallies happen even in prolonged bear markets.”
Related: Crypto’s ‘age of speculation’ may be ending: Galaxy’s Novogratz
CryptoQuant posted to X on Thursday that $55,000 marks Bitcoin’s realized price, which is “historically tied to bear market bottoms.”
“Past cycles saw BTC trade 24% to 30% below this level before stabilizing,” it stated. “When BTC reaches this area, it usually moves sideways before recovering.”

More time to reach the bottom
Nick Ruck, the director of LVRG Research, told Cointelegraph that the recent capitulation event “reflects intense short-term holder panic and washout amid broader macro pressures and a shift into bear market territory.”
“While this level of oversold conditions historically precedes recovery phases, reaching the full bottom may still require additional time and signals from metrics like sustained institutional buying or miner stabilization,” he added.
Ruck targeted potential support emerging in the $40,000 to $60,000 range, “depending on evolving market dynamics,” a figure in line with predictions from other analysts.
Magazine: Bitcoin difficulty plunges, Buterin sells off Ethereum: Hodler’s Digest
Crypto World
Is The Bull Market Over?
Key takeaways:
-
BTC open interest falls to $34 billion, but stable BTC-denominated volume suggests leverage demand remains unchanged.
-
Weak US jobs data and Bitcoin options skew indicate a bearish shift, even as gold and stocks show relative strength.
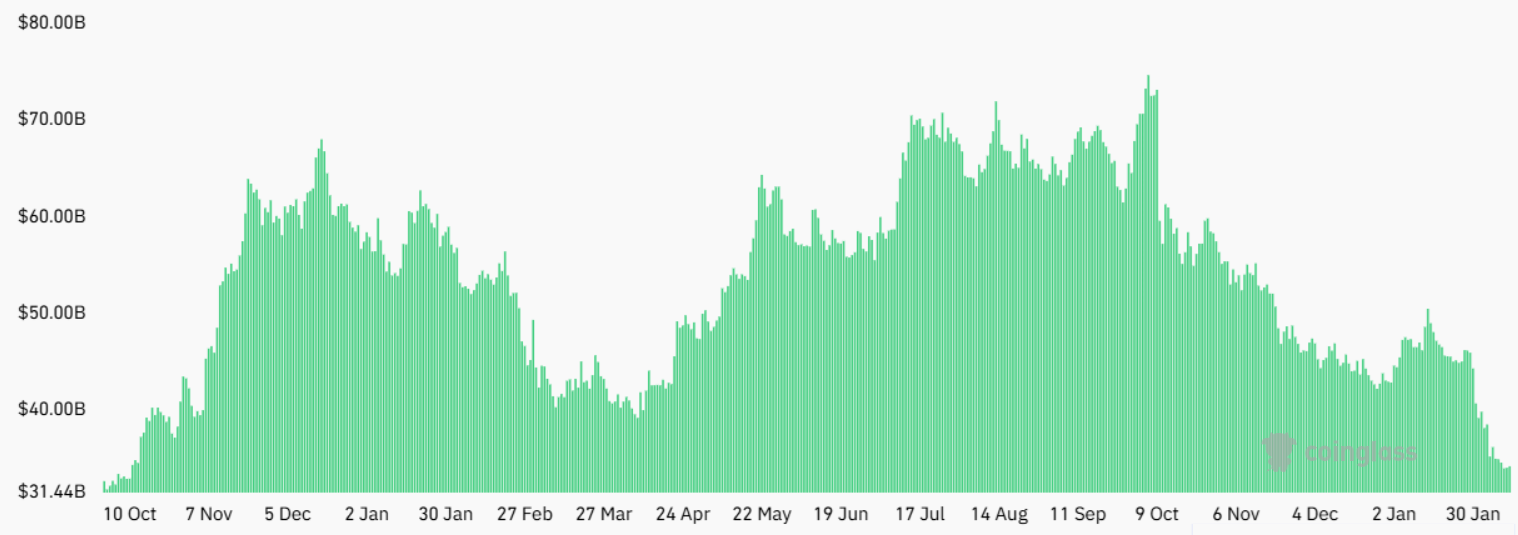
Bitcoin (BTC) price has struggled to sustain levels above $72,000 for the past week, leading investors to question whether institutional demand has evaporated. The aggregate Bitcoin futures open interest plummeted to its lowest level since November 2024, fueling fears of a retest of the $60,000 support as uncertainty grows.

The aggregate BTC futures open interest hit $34 billion on Thursday, a 28% drop from 30 days prior. However, when measured in Bitcoin terms, the metric remains virtually flat at BTC 502,450, suggesting that demand for leverage has not actually decreased. Part of this decline is also attributable to forced liquidations, which totaled $5.2 billion over the past two weeks.
Weak bullish leverage demand confirms BTC’s worrisome market decoupling
Investors are increasingly frustrated by the lack of a clear catalyst for Bitcoin’s 28% decline over the last month, especially as gold reclaimed the $5,000 psychological level and the S&P 500 traded just 1% below its all-time high. Some analysts argue that this risk-aversion stems from emerging signs of weakness in the US labor market.
The US Labor Department revealed on Wednesday that the US economy added only 181,000 jobs in 2025, a figure weaker than previously reported. However, the White House has downplayed these concerns. According to the BBC, officials argue that the slowdown in population growth as a result of its immigration policies has reduced the number of working positions the US needs to create.

Bitcoin’s record 52% crash on March 13, 2020, occurred during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic fears, which anticipated a surge in jobless claims. If economic growth is currently at risk, odds are the US Federal Reserve will cut interest rates sooner than anticipated. This reduces the cost of capital for companies and eases financing conditions for consumers, explaining the stock market strength seen in 2026.
The lack of confidence in Bitcoin is evident through the weak demand for bullish leveraged positions, making the decoupling from traditional markets even more worrisome.

The annualized funding rate on Bitcoin futures held below the neutral 12% threshold for the past four months, signaling fear. Thus, even as the indicator recovered from the negative levels of the prior week, bears continue to have the upper hand. Professional traders remain unwilling to take downside price risk exposure, according to Bitcoin options markets.
Related: Is this crypto winter different? Key observers reevaluate Bitcoin

The BTC options delta skew at Deribit surged to 22% on Thursday as put (sell) instruments traded at a premium. Under normal circumstances, the indicator should range between -6% and +6%, reflecting balanced upside and downside risk aversion. This skew metric last flipped bullish in May 2025 after Bitcoin reclaimed the $93,000 level following a retest of $75,000.
While derivatives metrics reflect weakness, the $5.4 billion average daily trading volume in US-listed Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) contradicts speculation of fading institutional demand. Although it is impossible to predict what will cause buyers to display strength, Bitcoin’s recovery likely depends on improved visibility into the US job market conditions.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision. While we strive to provide accurate and timely information, Cointelegraph does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any information in this article. This article may contain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Cointelegraph will not be liable for any loss or damage arising from your reliance on this information.
Crypto World
HBAR Price Bounces 10%, Already Faces Liquidation Risk?
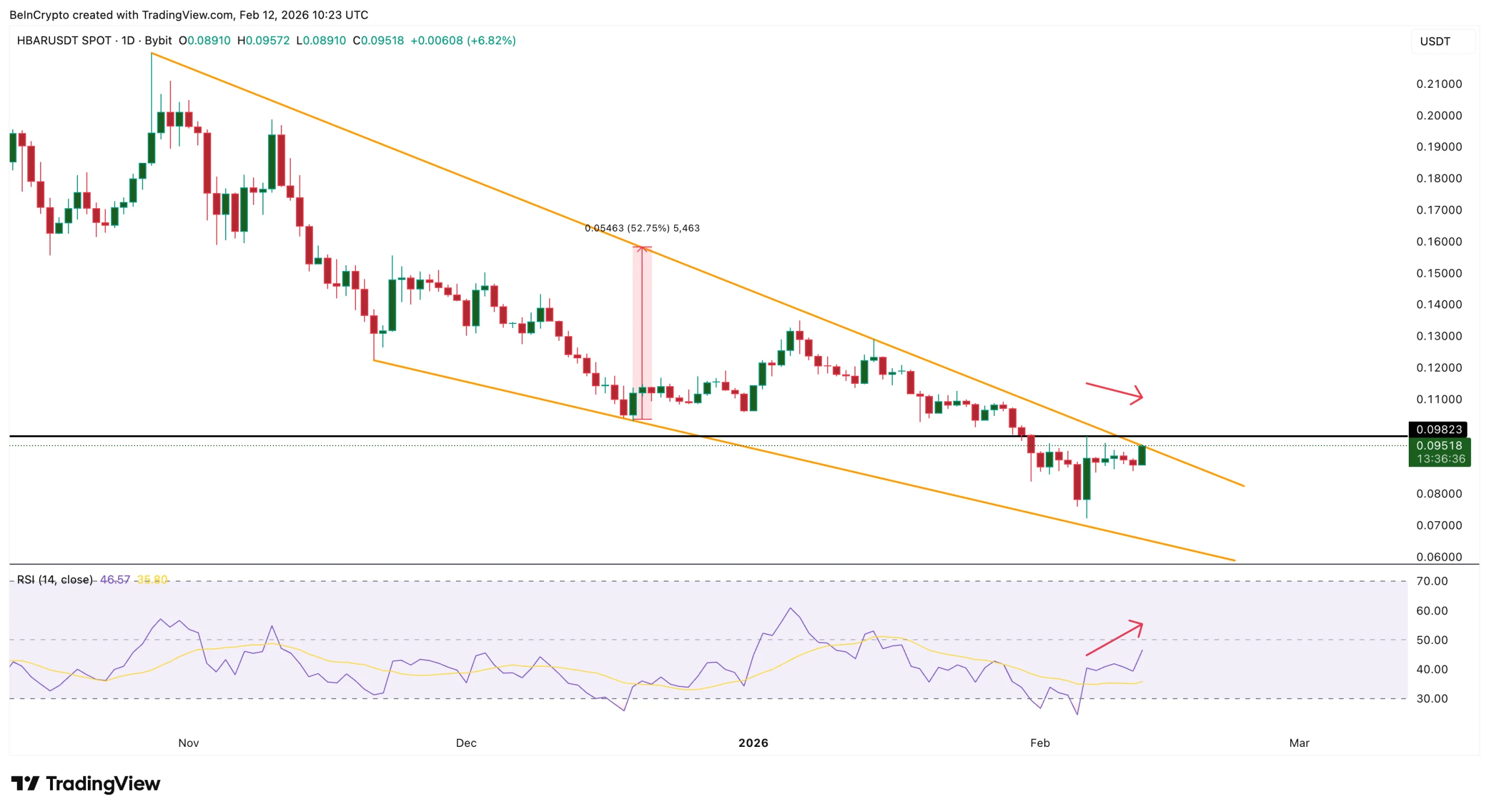
Hedera’s HBAR is outperforming the broader crypto market. While Bitcoin and Ethereum are up around 2% over the past day, HBAR price today has gained nearly 10% over the past week and about 8% in the last 24 hours, trading near $0.096 at press time.
The rally has raised expectations of a breakout. But momentum, volume, and derivatives data suggest risk is rising faster than conviction.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Falling Wedge Breakout Hopes Build, But With A Risk
HBAR has been trading inside a falling wedge pattern since late 2025.
Since early February, HBAR has rebounded from close to the lower boundary of this structure and climbed toward the upper trendline near $0.098. This level has capped the price multiple times and now acts as key resistance.
If HBAR breaks and holds above this zone, the wedge’s measured move points toward an upside of over 50% from current levels. However, momentum is starting to weaken. The Relative Strength Index, or RSI, measures buying and selling strength. When RSI rises, momentum improves. When it weakens, momentum fades.
Between February 6 and February 12, HBAR struggled to move decisively above $0.098 and began forming a potential lower high. At the same time, RSI continued making higher highs.

Want more token insights like this? Sign up for Editor Harsh Notariya’s Daily Crypto Newsletter here.
This creates a hidden bearish divergence. It happens when the price fails to confirm improving momentum. It often signals that buyers are becoming stretched near resistance.
Sponsored
Sponsored
This does not indicate a trend reversal. But it shows that upside efficiency is declining as the price approaches a critical level. The divergence threat passes if the current HBAR price candle touches $0.098, invalidating the lower-high theory.
Money Flow and Derivatives Data Show Rising Risks
Money and leverage indicators reinforce this warning. One key metric is Chaikin Money Flow, or CMF. CMF tracks whether large capital is flowing into or out of an asset by combining price and volume. When CMF stays above zero, strong institutional buying is present. When it remains below zero, major inflows are missing.
Between December 31 and February 11, HBAR’s CMF has trended higher while the price trended lower. This divergence supported the recent rebound. CMF has also broken above its descending trendline. But CMF remains below the zero line.
Sponsored
Sponsored
This means selling pressure has eased, but strong accumulation has not returned. The rally is still driven mainly by short-term traders rather than large wallets. Derivatives data adds further risk. Open interest measures the total value of active futures contracts. When it rises, leverage in the market increases.
Since February 11, HBAR’s open interest has climbed from about $26.96 million to nearly $29.38 million, an increase of roughly 9% in one day. This jump happened as the price approached resistance. At the same time, funding rates turned sharply positive.
Funding shifted from around -0.018 to near +0.05 within 24 hours. This shows that long positions are building rapidly. There is also a divergence between price and leverage.
The HBAR price formed a local peak on February 8 and another on February 12. The second peak is lower, showing weaker price strength. But open interest made a higher high during the same period. More leverage is entering the market even as the price momentum weakens. This combination often precedes pullbacks. When leverage rises near resistance and momentum fades, even small declines can trigger forced liquidations.
In simple terms, risk-taking is rising while conviction remains weak.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Key Levels Will Decide Whether HBAR Price Breaks Out or Pulls Back
With optimism clashing with weak participation, price levels now matter most. The main upside trigger remains $0.098.
This level aligns with wedge resistance and recent swing highs. A clean break and hold above it would invalidate the bearish divergence and reduce liquidation risk. If that happens, HBAR could target $0.107 first, followed by the $0.145 zone, potentially realizing the wedge target.
That would confirm that real demand has returned. Until then, the rally remains vulnerable. On the downside, $0.090 is the first key support. This level has held multiple times during recent consolidation. A breakdown below it would likely trigger long liquidations.

Below $0.090, the next major support sits near $0.076. A move to this zone would erase around 20% from current levels and signal that the breakout attempt has failed.
Crypto World
A Wild Ride for Chip Stocks
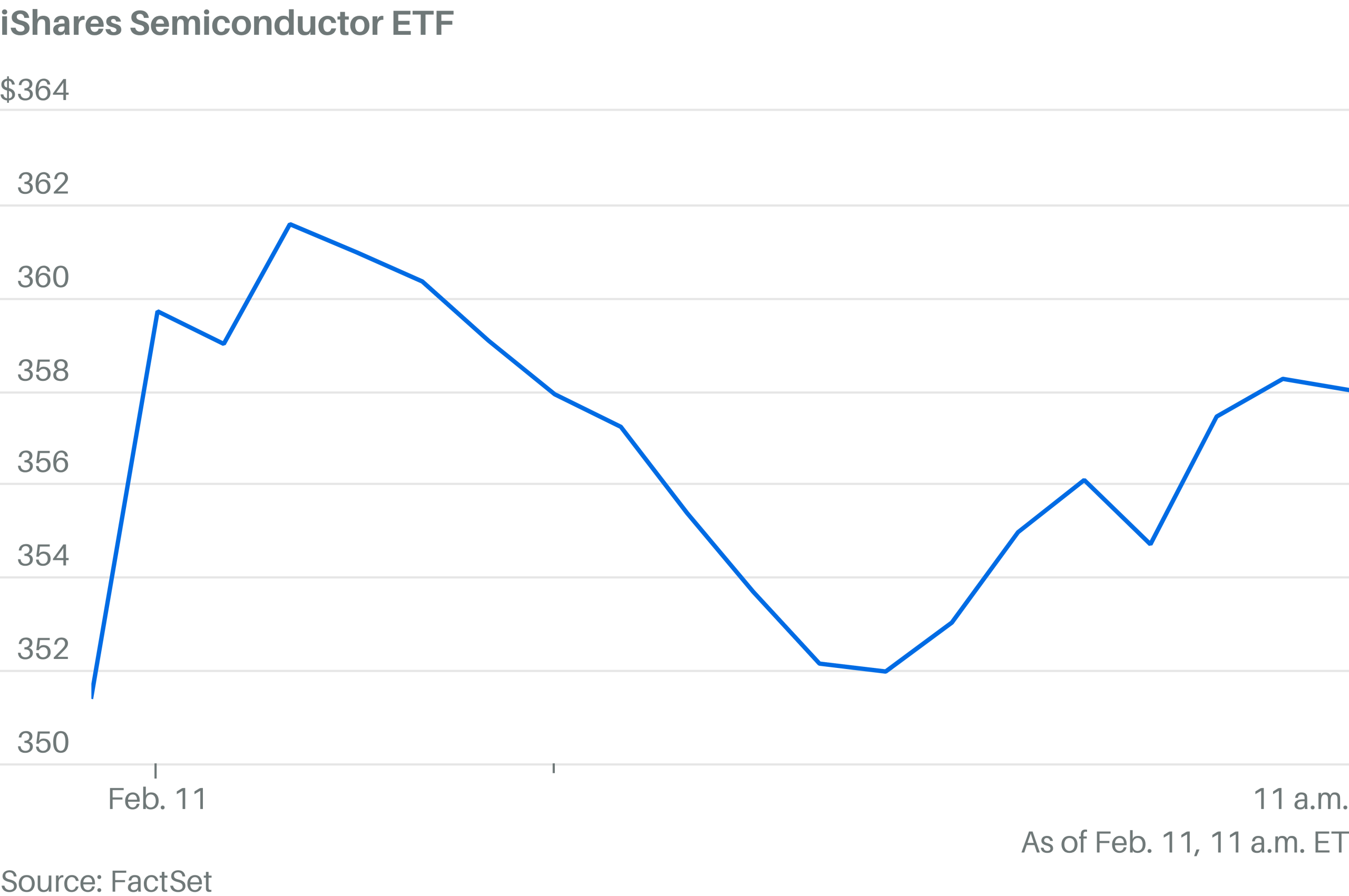
Here come the chip stocks.
The iShares Semiconductor ETF surged 1.9%. The chip stock index rallied at the open, but pulled back sharply. Now it’s making another push higher.
Sandisk, Micron Technology, On Semiconductor, and Western Digital were all among the S&P 500’s top stocks.
Crypto World
Lighter Strikes $920 Million Deal With Circle
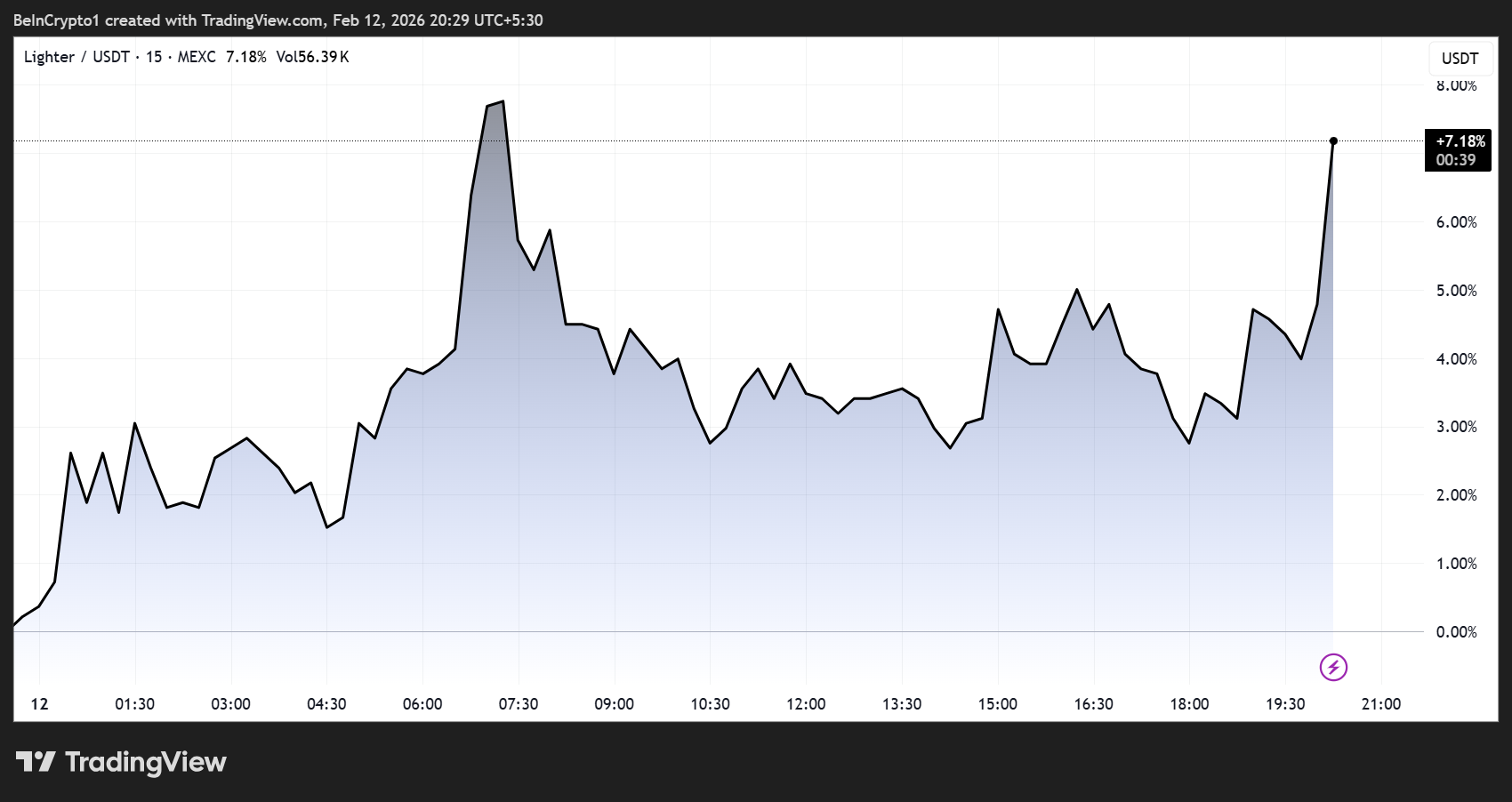
Decentralized perpetuals trading platform Lighter saw its native token LIT surge nearly 10% during the early hours of the US session.
It follows news that it had struck a major revenue-sharing deal with USDC issuer Circle.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Lighter Strikes $920 Million USDC Revenue-Sharing Deal with Circle — A Win for DeFi Traders
LIT, the powering token for the Lighter ecosystem, exploded by nearly 10% on the news, and was trading for $1.46% on the news.
The agreement covers approximately $920 million in USDC deposits on Lighter’s platform, marking a significant milestone for the young DeFi exchange.
Under the partnership, interest income generated from Circle’s USDC reserves will be shared between Circle and Lighter.
This aligns with Circle’s broader revenue-sharing model, which it has previously implemented with leading exchanges such as Coinbase and Bybit.
For Lighter, the deal offers a fast and capital-efficient path to grow its yield engine, fund user incentives, and support platform features such as funding rate rebates and rewards programs.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Unlike some of its competitors, Lighter has opted to lean on USDC rather than launching a proprietary stablecoin.
Hyperliquid, for instance, introduced its native stablecoin USDH in late 2025 after a competitive governance auction. The move diverted billions in deposits and yield away from Circle and other stablecoin issuers.
It allowed Hyperliquid to capture revenue internally and reduce centralization risks, but required significant capital and infrastructure investment.
Lighter Leverages Circle Partnership to Boost Adoption, Liquidity, and LIT Token Sentiment
Lighter’s approach, by contrast, allows the platform to tap directly into Circle’s established reserves while still benefiting from shared yield.
Sponsored
Sponsored
This could accelerate adoption by leveraging Circle’s USDC ecosystem, enabling Lighter to scale more efficiently while delivering value to traders and token holders.
The deal represents a potential win-win scenario:
- Circle benefits by locking in a large volume of USDC on a growing DeFi platform, incentivizing adoption and circulation.
- Lighter gains access to a steady revenue stream, which could enhance platform sustainability, attract more liquidity, and increase user engagement.
Moving forward, interest will be on on-chain USDC flows to Lighter contracts as this could show early signs of the agreement’s impact on liquidity and token sentiment.
Lighter has been gaining traction in the DeFi perpetuals market, with growing trading volumes, loyalty points programs, and community engagement.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Token listings on popular platforms like Robinhood have also contributed to its growing bullish sentiment.
The revenue-sharing announcement is expected to boost confidence, perhaps further than during its LIT token event in December.
Nevertheless, it is impossible to forget past controversies surrounding Lighter, including allegations of secret token sales.
While official details on the exact share split of USDC interest have not yet been disclosed, even a conservative arrangement could provide a meaningful boost to LIT holders.
Crypto investors are advised to monitor announcements from both Lighter and Circle for updates, as revenue-sharing agreements of this scale can change quickly.
Crypto World
Gold and Silver Just Crashed, and It Could be Worse: Here’s Why
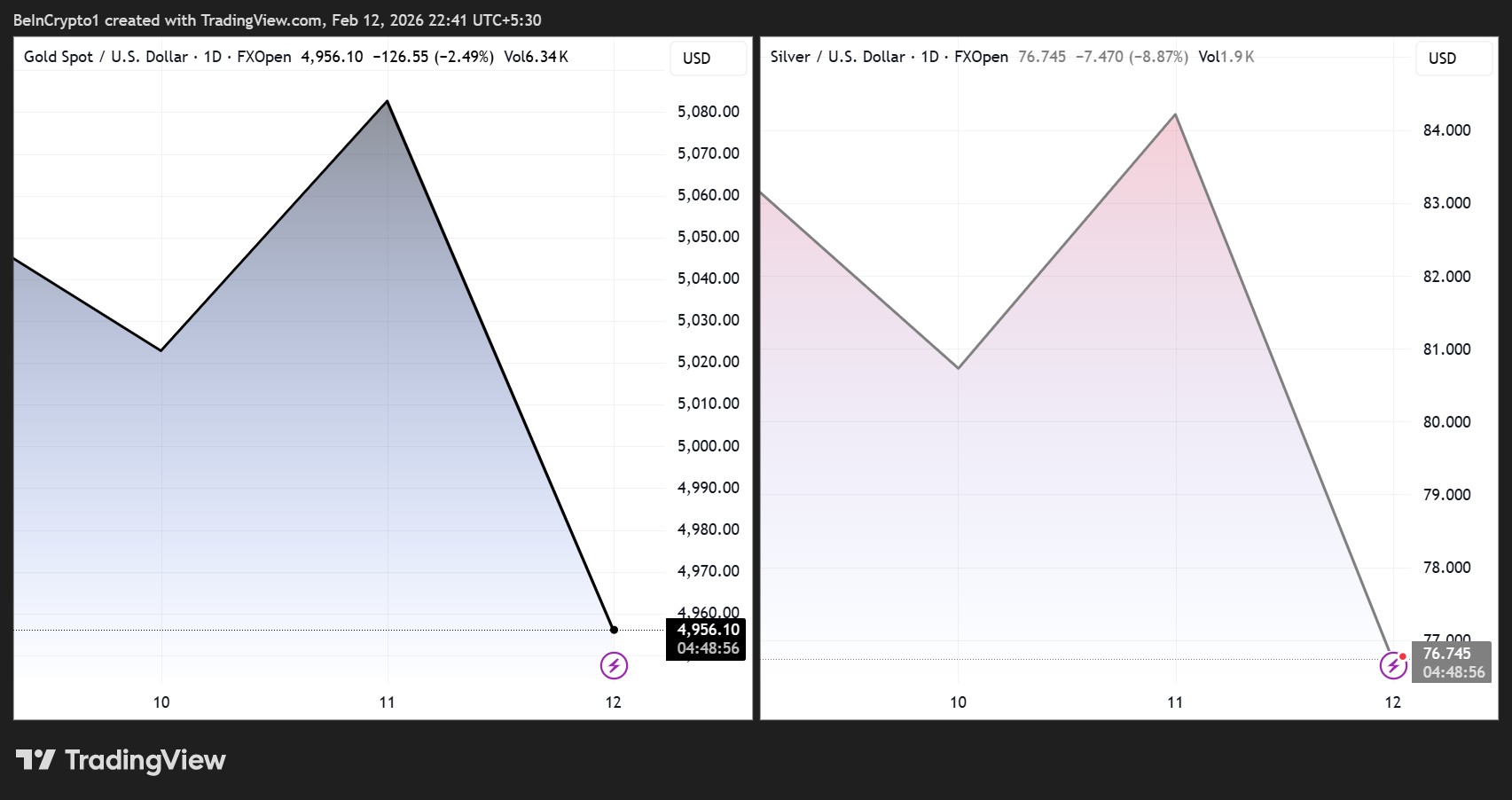
Gold and silver tumbled sharply on Thursday, rattling markets already on edge amid surging US financial stress.
Spot gold dropped by more than 3% while silver plunged by more than 10%, reversing a portion of their recent rally.
Bad News for Gold and Silver Amid Record US Debt and Rising Bankruptcies
As of this writing, gold was trading for $4,956, down 3.97% while silver exchanged hands for $76.74 after losing 10.65% in the last 24 hours.
Sponsored
Sponsored
The sudden sell-off has prompted analysts and investors to question whether a broader repricing of hard assets is unfolding.
The metals’ retreat comes amid intensifying economic stress. Over the past three weeks, 18 US companies with liabilities exceeding $50 million have filed for bankruptcy.
Notably, this is the fastest pace since the pandemic and approaches levels last seen during the 2009 financial crisis.
Meanwhile, the New York Fed said in a press release that household debt has reached a record $18.8 trillion, with mortgages, auto loans, credit card balances, and student loan balances all at historic highs.
Sponsored
Serious credit card delinquencies climbed to 12.7% in Q4 2025, the highest since 2011, with younger households under particular strain.
Such conditions typically emerge late in the economic cycle, often preceding policy interventions like rate cuts or liquidity injections.
Bitcoin has also remained under pressure, falling to the $65,000 range as the pioneer crypto lags both equities and traditional safe-haven assets over the past few months.
While digital assets often present as a hedge against macroeconomic uncertainty, recent trends suggest they are not yet playing that role effectively in this cycle.
Analysts are at a crossroads, offering differing interpretations of the metals’ pullback. Some argue it reflects short-term volatility within a broader trend of hard-asset repricing.
Sponsored
Sponsored
“Gold was repriced to $5,000 by the US, and markets caught up,” wrote macro analyst Marty Party, suggesting that authorities may be positioning precious metals to collateralize sovereign debt alongside digital assets like Bitcoin.
However, others caution that tight liquidity conditions remain dominant, and further weakness could emerge if financial stress continues to mount.
Policy watchers are closely monitoring the Federal Reserve’s potential response. Citi economists project softer job growth in spring and summer after January’s payrolls came in below expectations, which could create room for three rate cuts later in 2026.
Historically, rising corporate bankruptcies and consumer delinquencies precede monetary easing. This suggests that official support could arrive once economic strain becomes more visible in the data.
The confluence of record household debt, accelerating bankruptcies, and declining hard-asset prices suggests a market at a critical inflection point.
Sponsored
Sponsored

“This economic decay, mirroring the indicators of 2008, is not an anomaly. It is the direct consequence of the current administration’s ideologically driven policies, prioritizing inflationary fiscal adventurism and social engineering over foundational economic stability and competitive market principles,” commented Jade Kotonono, a popular user on X.
Is the current precious metals crash a temporary correction or the early stages of a multi-year repricing? Some bullish analysts anticipate that once gold consolidates near $5,000, rotation back into digital assets could accelerate.
Notwithstanding, the current environment presents both opportunities and risks, and investors should conduct their own research.
With markets digesting unprecedented financial stress, gold, silver, and Bitcoin may fall further. Conversely, a stabilizing policy response could catalyze the next leg of the asset repricing cycle.
Crypto World
Bluefin-acquired Nexa Terminal Shuts Down Blaming Sui’s ‘Extremely Low’ Volume
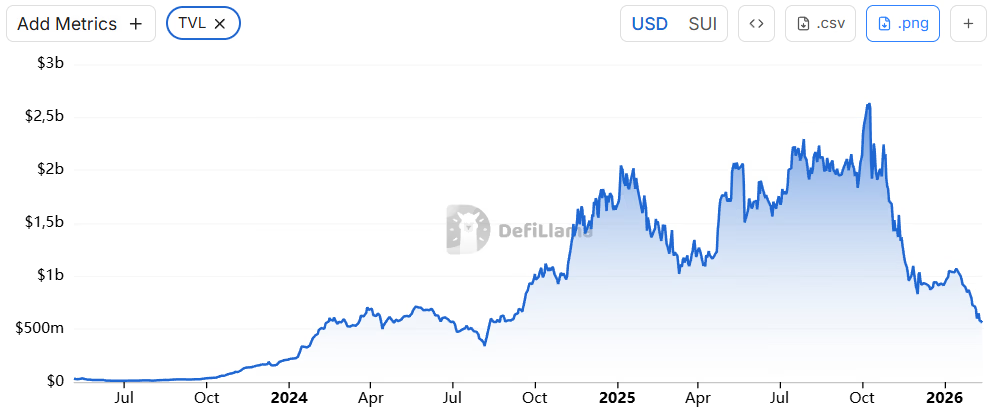
The closure comes as monthly DEX volumes on Sui have dropped 70% from last year’s peak.
Crypto trading terminal Nexa, formerly known as InsiDeX, is shutting down just a year after its acquisition by decentralized exchange Bluefin, citing what it calls “extremely low” trading volumes on the Sui blockchain.
In a Feb. 10 post on X, the team said “only 2-3 coins [are] seeing some decent activity” on Sui, leaving traders with few real opportunities, and added that it was built for fast trades and active markets, conditions that never appeared.
“There’s a real sense of sadness in shutting down Nexa because we succeeded in building a product that was actually the most used trading suite on Sui at one time. Unfortunately, the market it was built for never truly materialized,” the team wrote.
The shutdown follows months of Nexa pushing points-based rewards and other engagement schemes, but that campaign went quiet before the closure.
The move highlights broader weakness across Sui’s DeFi ecosystem. As of Feb. 12, 2026, DefiLlama data shows total value locked (TVL) on Sui at about $561 million, down roughly 78% from a peak of $2.6 billion in October 2025.

DEX volumes have also dropped, falling around 70% from $22.3 billion in October to about $6.8 billion in January. Sui’s native token SUI has also dropped around 50% over the past month to $0.93, per data from CoinGecko.
Moreover, the start of 2026 was rocky for the Sui blockchain as it suffered a six-hour outage that stopped block production. The team later explained that the problem was a bug in the network’s consensus system, which caused validators to disagree on data and temporarily froze transactions.
But Sui isn’t the only network facing challenges amid falling liquidity, as a similar story is unfolding on rival chains like Aptos. As The Defiant reported earlier this month, Merkle Trade — the largest perpetual DEX on Aptos by volume — said it would wind down operations despite processing nearly $30 billion in cumulative trades, as TVL across the network continued to fall too.
Crypto World
Coinbase Misses Q4 Earnings; $667M Loss as Crypto Markets Slump

Investors faced a sobering quarter as Coinbase reported a net loss for Q4 2025, snapping an eight-quarter streak of profitability as the crypto market cooled. The company posted earnings per share of 66 cents, missing consensus of 92 cents, while revenue slipped 21.5% year over year to $1.78 billion. A mixed revenue mix underscored the shift in the business: transaction-related revenue declined sharply, while subscriptions and services advanced, highlighting a bifurcated earnings trajectory in a tighter crypto ecosystem. The quarter arrived against a backdrop of a broader crypto price retreat, with Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) enduring meaningful pressure through the period and into year-end.
Key takeaways
- Q4 2025 net loss of $667 million ends Coinbase’s run of eight straight profitable quarters, reflecting a weaker quarterly mix and softer market conditions.
- Total revenue dropped to $1.78 billion, down 21.5% year over year, underscoring a broader demand slowdown in trading activity.
- Transaction-related revenue tumbled nearly 37% year over year to $982.7 million, while subscription and services revenue rose more than 13% to $727.4 million, signaling a pivot toward non-transactional monetization.
- Bitcoin price action contributed to the macro headwinds, with the leading crypto shedding roughly 30% from its October peak to year-end, illustrating why crypto market cycles continued to weigh on exchange earnings.
- Despite the earnings miss, Coinbase’s stock (EXCHANGE: COIN) recovered in after-hours trading, gaining about 2.9% to $145.18 after a full trading day decline, reflecting a nuanced market reaction to the results and forward guidance.
Tickers mentioned: $BTC, $COIN
Sentiment: Neutral
Price impact: Positive. The stock rose in after-hours trading following the earnings release despite the quarterly miss, signaling a potential reassessment of near-term expectations.
Market context: The results arrive amid a broader macro environment for crypto assets where price volatility and trading volumes have remained central to revenue durability for major exchanges, and where investor focus has shifted toward product diversification and cost discipline.
Why it matters
The quarterly print underscores the ongoing transition for a major crypto exchange from a revenue model heavily reliant on trading activity toward a more diversified mix anchored in subscriptions, services, and value-added offerings. Coinbase, in its Q4 2025 shareholder documentation, highlighted that 2025 was a “strong year” operationally and financially, with full-year revenues reaching $6.88 billion, up 9.4% from 2024. This indicates a strategy aimed at resilience in the face of cyclical downturns, leveraging product expansion and platform reach to sustain long-term profitability even when trading volumes ebb.
From a market structure perspective, the numbers reflect a clear divergence within the crypto economy: trading remains sensitive to price swings and risk sentiment, while an expanding suite of services—including custody, staking, and AI-enabled wallet products—offers revenue visibility beyond quarterly price moves. Coinbase’s leadership has stressed that more than 12% of all crypto globally resided on its platform in 2025, a stark data point that underscores the bankability of scale and network effects in this nascent asset class. The shift toward a steadier subscription and services revenue base could insulate the company from near-term volatility and set the stage for steadier long-run growth.
On the earnings call, CFO Aleshia Haas emphasized operational discipline, noting plans to keep technology, sales, and marketing expenses relatively flat in the near term while evaluating opportunities to deploy resources more efficiently. This stance signals a prioritization of cash-generative activities and careful investment in product development, a balance that may appeal to investors seeking a secular growth story within a still-fragile macro environment.
The quarter’s performance also touches on investor sentiment around cryptoasset risk and institutional flow. The broader market has experienced episodic stress, and the company’s performance appears tightly linked to the health of Bitcoin and other major assets as traders respond to global liquidity shifts, regulatory updates, and evolving market structure debates. In this context, Coinbase’s results offer a lens into how a large crypto exchange navigates a period of cyclical headwinds while pursuing a trajectory that relies less on trading volatility and more on recurring revenue streams and product expansion.
What to watch next
- Q4-25 shareholder letter release and detailed segment breakdown to assess how much the revenue mix shifted beyond transaction revenue.
- Q1 outlook updates, including any revisions to subscription and services revenue guidance and the trajectory of transaction revenue as market conditions evolve.
- Updates on product initiatives, especially any milestones around AI-enabled wallets or other services that broaden asset utility on the platform.
- Bitcoin price trends in early 2026 and corresponding impact on trading volumes and fee-based revenue for Coinbase and similar exchanges.
- Regulatory developments or macro signals that influence risk sentiment in the crypto market, which could affect liquidity and user activity on the platform.
Sources & verification
- Coinbase Q4-25 Shareholder Letter (PDF) – official financial disclosure for the quarter and full-year 2025.
- Q4 2025 earnings data and commentary – as described in the shareholder letter and accompanying materials.
- Bitcoin price movements referenced in market coverage and related context articles linked in the report.
- Post-earnings trading data for Coinbase (COIN) stock, including after-hours move to approximately $145.18 and intraday trade levels.
- Related Coinbase product and strategy articles cited in the earnings narrative, including references to AI wallet initiatives and platform expansion.
Market reaction and key details
Coinbase’s quarterly results foreground a critical moment for the crypto exchange sector: profitability in a market that remains highly sensitive to both crypto price cycles and the intensity of trading activity. In the quarter, Coinbase’s total revenue of $1.78 billion reflected a decline in transactional income, even as the company advanced its services-based revenue. The shift aligns with a broader push in the industry to monetize platform usage beyond buy/sell activity, a move designed to stabilize earnings amid volatile asset prices.
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) endured a meaningful pullback during the quarter, illustrating the bidirectional relationship between asset prices and exchange revenues. The asset’s gradient—from highs near six figures to more subdued levels—has tangible implications for liquidity, trading volumes, and fee accrual on major platforms. While the exact trajectory of crypto price action is inherently uncertain, the quarter’s data points reinforce the importance of a diversified revenue model for exchanges seeking resilience during bear-to-bull transitions in the market.
What it means for users and the market
For users, the emphasis on subscriptions and services could translate into broader access to tools that help manage, secure, and optimize holdings beyond straightforward trading. The potential to link more products to user assets could deepen engagement and wallet utility, potentially driving retention and incremental revenue through non-transactional channels. For builders and investors, Coinbase’s approach underscores the importance of a scalable, multi-pronged business model in the crypto economy, particularly as regulatory clarity evolves and market structure debates continue to unfold.
What to watch next
- Q4-25 investor communications with detailed breakdowns of revenue by services vs. transaction flows.
- Near-term guidance updates, including subscription/services outlook and any changes to capital allocation strategy.
- Progress updates on AI-enabled wallet initiatives and other product launches intended to expand asset use-cases on the platform.
Crypto World
CFTC Adds Crypto Execs to Innovation Advisory Committee
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission has added a slew of crypto executives, including those from Coinbase and Ripple, to its Innovation Advisory Committee, who will shape how the regulator crafts policy.
CFTC chair Mike Selig said on Thursday that the 35 members of the committee will “ensure the CFTC’s decisions reflect market realities” and enable it to “develop clear rules of the road for the Golden Age of American Financial Markets.”
The committee launched in January, and replacing the Technology Advisory Committee, which drew on the advice of tech leaders to dissect how new technologies were impacting the derivatives markets more broadly.
Selig has signalled the CFTC will be more receptive to crypto and has started work with the Securities and Exchange Commission to coordinate on how to regulate the sector.
Crypto executives make up bulk of committee
Of the 35 members making up the committee, 20 are tied to companies involved in crypto, while at least five are involved in prediction markets.
The list includes Gemini CEO Tyler Winklevoss, Polymarket CEO Shayne Coplan, Kalshi CEO Tarek Mansour and Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek, in addition to executives at Nasdaq, Intercontinental Exchange, Cboe Global Markets, CME Group, Kraken and Bullish.
Also on the committee is Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong, Ripple CEO Brad Garlinghouse, a16z Crypto partner Chris Dixon, Solana Labs CEO Anatoly Yakovenko, Uniswap CEO Hayden Adams, Blockchain.com CEO Peter Smith, Robinhood CEO Vladimir Tenev, Grayscale CEO Peter Mintzberg and Anchorage Digital CEO Nathan McCauley.

Related: US fines Paxful $4M for moving funds tied to trafficking, fraud
Executives at Paradigm, DraftKings, and the US Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation were also included.
CFTC to consider input beyond panel
The committee will advise the CFTC on the commercial, economic, and practical considerations of emerging products, platforms and business models in financial markets.
In an announcement in January, the CFTC said that it would also consider the viewpoints of regulatory bodies, academia and public interest groups in forming its policy.
Magazine: A ‘tsunami’ of wealth is headed for crypto: Nansen’s Alex Svanevik
-

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoWhy Israel is blocking foreign journalists from entering
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoJD Vance booed as Team USA enters Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
 Business4 days ago
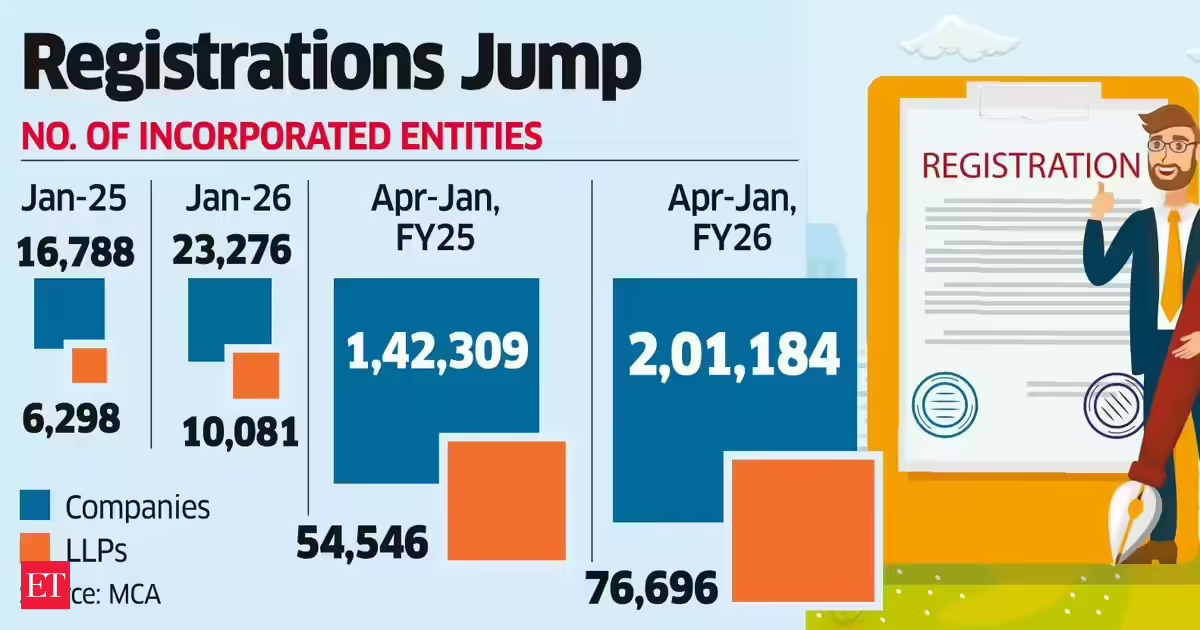
Business4 days agoLLP registrations cross 10,000 mark for first time in Jan
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-
 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoFirst multi-coronavirus vaccine enters human testing, built on UW Medicine technology
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCostco introduces fresh batch of new bakery and frozen foods: report
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Team GB’s Mia Brookes through to snowboard big air final, and curling pair beat Italy
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoBenjamin Karl strips clothes celebrating snowboard gold medal at Olympics
-
Sports6 days ago
Former Viking Enters Hall of Fame
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoThe Health Dangers Of Browning Your Food
-
Sports7 days ago
New and Huge Defender Enter Vikings’ Mock Draft Orbit
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoJulius Baer CEO calls for Swiss public register of rogue bankers to protect reputation
-

 NewsBeat7 days ago
NewsBeat7 days agoSavannah Guthrie’s mother’s blood was found on porch of home, police confirm as search enters sixth day: Live
-
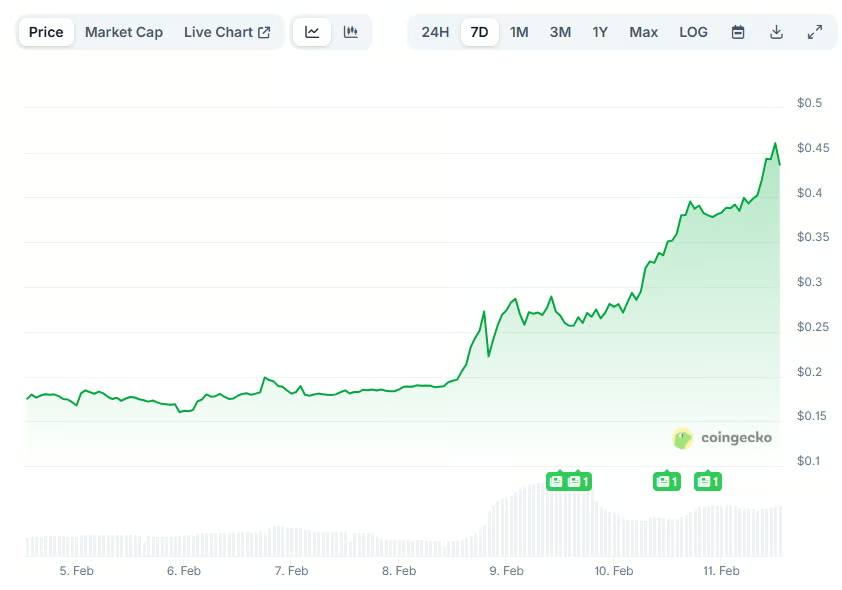
 Crypto World1 day ago
Crypto World1 day agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-

 Video1 day ago
Video1 day agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-

 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoResidents say city high street with ‘boarded up’ shops ‘could be better’
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month














