Science & Environment
Painkiller used in cattle wiped out India’s vultures, and scientists say that led to 500,000 human deaths
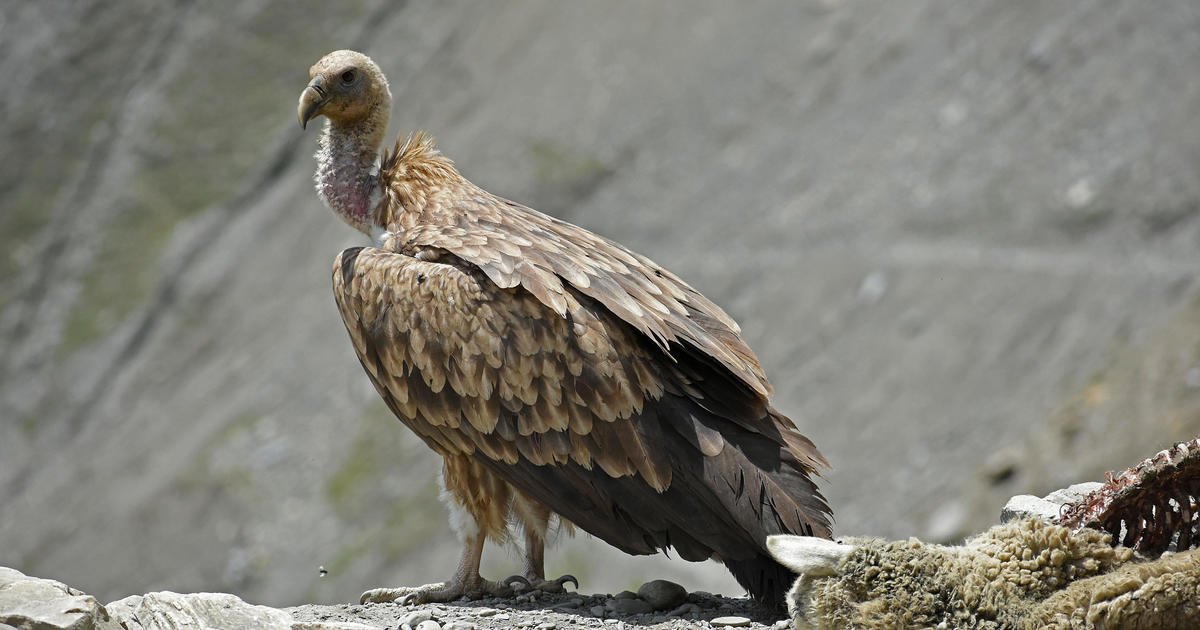

New Delhi — Scientists say Indian farmers’ eager uptake of a painkiller for their cattle in the 1990s has led to the inadvertent deaths of half of a million people and massive economic losses — not from any harm to the cattle, but from the loss of millions of vultures, scavengers that historically devoured animals’ remains before they could rot and become vectors for disease.
In early 1990s, the patent on a painkiller called diclofenac lifted, making it cheap and widely available for India’s massive agricultural sector. Farmers use it to treat a wide array of conditions in cattle. But even a small amount of the drug is fatal to vultures. Since the beginning of its widespread use in India, the domestic vulture population has dropped from a whopping 50 million to just a few thousand — and according to a study published by the American Economic Association, the impact on humans has been monumental, reflecting the vital role the scavengers play.
Vultures have been a crucial part of India’s ecosystems for centuries. According to the authors of the study, entitled “The Social Costs of Keystone Species Collapse: Evidence From The Decline of Vultures in India,” the large, homely birds are a “keystone species” — one that plays an irreplaceable role in an ecosystem.
They’re the only scavengers that feed entirely on carcasses, and they do it extremely efficiently, quickly devouring the remains and leaving little behind to spread disease. The study authors say India’s vultures would typically eat at least 50 million animal carcasses every year, before their population was decimated.
In doing so, they prevented the dead farm animals from rotting, and the deadly bacteria and other pathogens that thrive in carcasses from being transmitted into human populations.
“In a country like India with prohibitions on eating beef, most cattle end up turning into carcasses,” Anant Sudarshan, an associate professor of economics at the University of Warwick in England, who co-authored the study, told CBS News. “Vultures provide an incredible disposal service for free. … A group of vultures takes about 45 minutes to turn a cow carcass into bone.”
The vultures’ keen appetite also helped keep the populations of competing scavengers in check, such as feral dogs and rats, which can transmit rabies and a host of other diseases.
In 1994, farmers began giving diclofenac to their cattle and other livestock. The drug causes kidney failure and death in vultures that feed on the carcasses of animals given the painkiller, and the population of the birds shrank from 50 million to just 20,000 over the course of the ensuing decade alone.
Without the vultures around to do the job, farmers started disposing their dead livestock in local bodies of water, which caused water pollution — and another way for pathogens to reach humans.
Sudarshan and study co-author Eyal Frank, an environmental economist at the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy, examined the impact of the drastically reduced vulture population on human health by mapping vulture habitats with health data from more than 600 districts in India. They said their research shows 100,000 human deaths every year between 2000 and 2005 could be linked with the decreased vulture populations.
It also shows economic losses they estimated at $69 billion per year, largely associated with premature human deaths due to the collapse of the scavenger population.
These deaths were caused, according to their research, by the spread of diseases that a thriving vulture population would have mitigated. Stray dog populations, and with them, the spread of rabies, also increased during the timeframe, as did the amount of bacteria measured in many local water sources.
“India is now the largest center of rabies in the world, as the feral dog population has grown dramatically,” Sudarshan told CBS News.
Without a major vulture rebound, the study authors said the spread of disease and resulting deaths will only continue in the coming years, as will the costs associated with health care.
India did ban diclofenac for veterinary use in 2006, but Sudarshan said the ban needs to be enforced much more effectively. He and Eyal have called for more conservation funding to boost vulture populations, but they’ve warned that even if the Indian government does mount a major effort, it will take at least a decade for the species to bounce back to the extent required because they’re “slow reproducers.”
As an alternative to bringing the vultures back, Sudarshan said India could build a network of incinerators around the country, but the estimated cost of that is about $1 billion per year, and they would use a huge amount of energy and create considerable air pollution, which is already a major problem for India.
“So, it makes more sense to bring back the natural way of dealing with the millions of animal carcasses that India produces each year,” he said.
And he said that work must start urgently, as the “vultures began dying in the 1990s. India has not done anything three decades on.”
The government does spend about $3 million per year to save India’s native tigers. Sudarshan said while vultures may be far less of a tourist attraction, there’s a broader question about “the basis of our conservation policy.”
“Our paper shows that the cost of losing them [vultures] is about $69 billion a year, which is far higher than any benefits the tiger” brings, he said, adding: “We need to think from a cost effectiveness point of view and growth view, how should we pick species to conserve?”
“Understanding the role vultures play in human health underscores the importance of protecting wildlife – and not just the cute and cuddly,” said his co-author, Frank. “They all have a job to do in our ecosystems that impacts our lives.”
Science & Environment
Creature that washed up on New Zealand beach may be world’s rarest whale — a spade-toothed whale
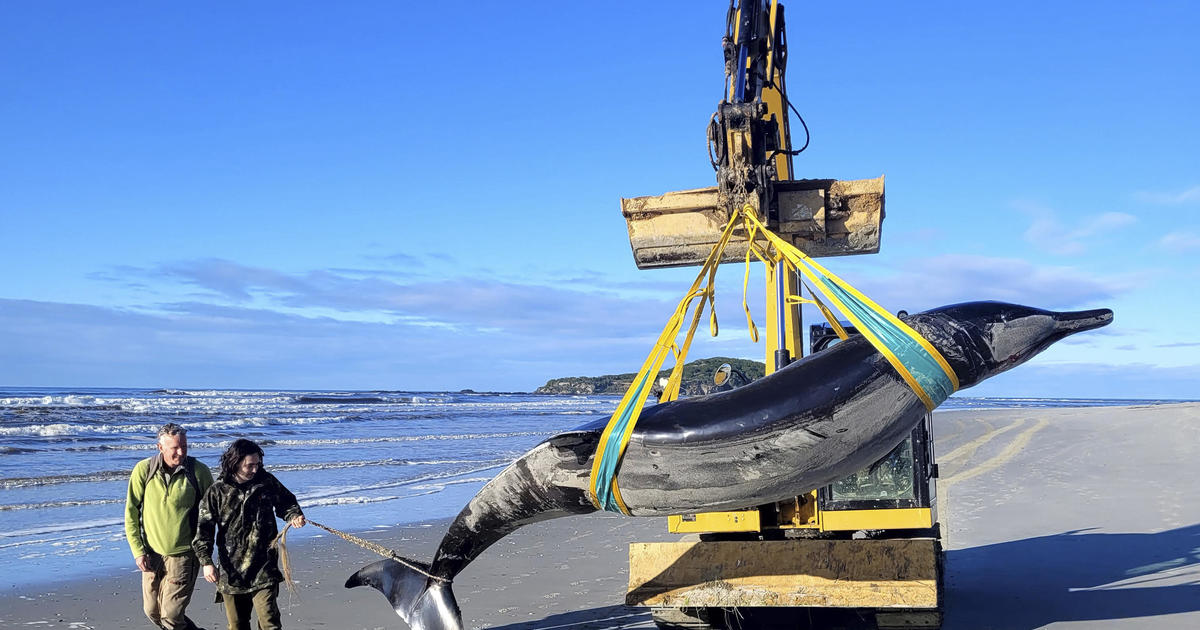

Wellington, New Zealand — Spade-toothed whales are the world’s rarest, with no live sightings ever recorded. No one knows how many there are, what they eat, or even where they live in the vast expanse of the southern Pacific Ocean. However, scientists in New Zealand may have finally caught a break.
The country’s conservation agency said Monday a creature that washed up on a South Island beach this month is believed to be a spade-toothed whale. The five-meter-long creature, a type of beaked whale, was identified after it washed ashore on Otago beach from its color patterns and the shape of its skull, beak and teeth
“We know very little, practically nothing” about the creatures, Hannah Hendriks, Marine Technical Advisor for the Department of Conservation, told The Associated Press. “This is going to lead to some amazing science and world-first information.”
If the cetacean is confirmed to be the elusive spade-toothed whale, it would be the first specimen found in a state that would permit scientists to dissect it, allowing them to map the relationship of the whale to the few others of the species found and learn what it eats and perhaps lead to clues about where they live.
Only six other spade-toothed whales have ever been pinpointed, and those found intact on New Zealand’s North Island beaches had been buried before DNA testing could verify their identification, Hendriks said, thwarting any chance to study them.
This time, the beached whale was quickly transported to cold storage and researchers will work with local Māori iwi (tribes) to plan how it will be examined, the conservation agency said.
New Zealand’s Indigenous people consider whales a taonga – a sacred treasure – of cultural significance. In April, Pacific Indigenous leaders signed a treaty recognizing whales as “legal persons,” although such a declaration is not reflected in the laws of participating nations.
Nothing is currently known about the whales’ habitat. The creatures deep-dive for food and likely surface so rarely that it has been impossible to narrow their location further than the southern Pacific Ocean, home to some of the world’s deepest ocean trenches, Hendriks said.
“It’s very hard to do research on marine mammals if you don’t see them at sea,” she said. “It’s a bit of a needle in a haystack. You don’t know where to look.”
The conservation agency said the genetic testing to confirm the whale’s identification could take months.
It took “many years and a mammoth amount of effort by researchers and local people” to identify the “incredibly cryptic” mammals, Kirsten Young, a senior lecturer at the University of Exeter who has studied spade-toothed whales, said in emailed remarks.
The fresh discovery “makes me wonder – how many are out in the deep ocean and how do they live?” Young said.
The first spade-toothed whale bones were found in 1872 on New Zealand’s Pitt Island. Another discovery was made at an offshore island in the 1950s, and the bones of a third were found on Chile’s Robinson Crusoe Island in 1986. DNA sequencing in 2002 proved that all three specimens were of the same species – and that it was one distinct from other beaked whales.
Researchers studying the mammal couldn’t confirm if the species went extinct. Then in 2010, two whole spade-toothed whales, both dead, washed up on a New Zealand beach. Firstly mistaken for one of New Zealand’s 13 other more common types of beaked whale, tissue samples – taken after they were buried – revealed them as the enigmatic species.
New Zealand is a whale-stranding hotspot, with more than 5,000 episodes recorded since 1840, according to the Department of Conservation.
Science & Environment
Earth will get a second “mini-moon” for 2 months this year

Earth will get a second moon for about two months this year when a small asteroid begins to orbit our planet. The asteroid was discovered in August and is set to become a mini-moon, revolving around Earth in a horseshoe shape from Sept. 29 to Nov. 25.
Researchers at the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System, an asteroid monitoring system funded by NASA, spotted the asteroid using an instrument in Sutherland, South Africa and labeled it 2024 PT5.
Scientists from the Universidad Complutense de Madrid have tracked the asteroid’s orbit for 21 days and determined its future path. 2024 PT5 is from the Arjuna asteroid belt, which orbits the sun, according to their study published in Research Notes of the AAs.
But Earth’s gravitational pull will draw 2024 PT5 towards it and, much like our moon, it will orbit our planet — but only for 56.6 days.
While other non-Earth objects, or NEOs, have entered Earth’s orbit before, some don’t complete full revolutions of Earth. Some, however, do and become so-called mini-moons.
An asteroid called 2020 CD3 was bound to Earth for several years before leaving the planet’s orbit in 2020 and another called 2022 NX1 became a mini-moon of Earth in 1981 and 2022 and will return again in 2051.
2024 PT5, which is larger than some of the other mini-moons, will also return to Earth’s orbit — in 2055.
Earth’s gravity will pull it into its orbit and the asteroid will have negative geocentric energy, meaning it can’t escape Earth’s gravitational pull. It will orbit around Earth in a horseshoe shape before reverting back to heliocentric energy, meaning it will rotate around the sun again, like the other planets and NEOs in our galaxy.
Even after it leaves orbit, it will stay near Earth for a few months, making its closest approach on Jan. 9, 2025. Soon after, it will leave Earth’s neighborhood until its path puts it back into our orbit in about 30 years.
The study’s lead author Carlos de la Fuente Marcos told Space.com the mini-moon will be too small to see with amateur telescopes or binoculars but professional astronomers with stronger tools will be able to spot it.
CBS News has reached out to Marcos for further information and is awaiting response.
Science & Environment
Climate change is making days longer, according to new research

Climate change is making days longer, as the melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets causes water to move closer to the equator, fattening the planet and slowing its rotation, according to a recent study.
Research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences used both observations and reconstructions to track variations of mass at Earth’s surface since 1900.
In the 20th century, researchers found that between 0.3 milliseconds per century and 1 millisecond per century were added to the length of a day by climate-induced increases. Since 2000, they found that number accelerated to 1.3 milliseconds per century.
“We can see our impact as humans on the whole Earth system, not just locally, like the rise in temperature, but really fundamentally, altering how it moves in space and rotates,” Benedikt Soja of ETH Zurich in Switzerland told Britain’s Guardian newspaper. “Due to our carbon emissions, we have done this in just 100 or 200 years, whereas the governing processes previously had been going on for billions of years. And that is striking.”
Researchers said that, under high greenhouse gas emission scenarios, the climate-induced increase in the length of a day will continue to grow and could reach a rate twice as large as the present one. This could have implications for a number of technologies humans rely on, like navigation.
“All the data centers that run the internet, communications and financial transactions, they are based on precise timing,” Soja said. “We also need a precise knowledge of time for navigation, and particularly for satellites and spacecraft.”
Science & Environment
The Buck Moon is almost here. Here’s when and where to see July’s full moon.
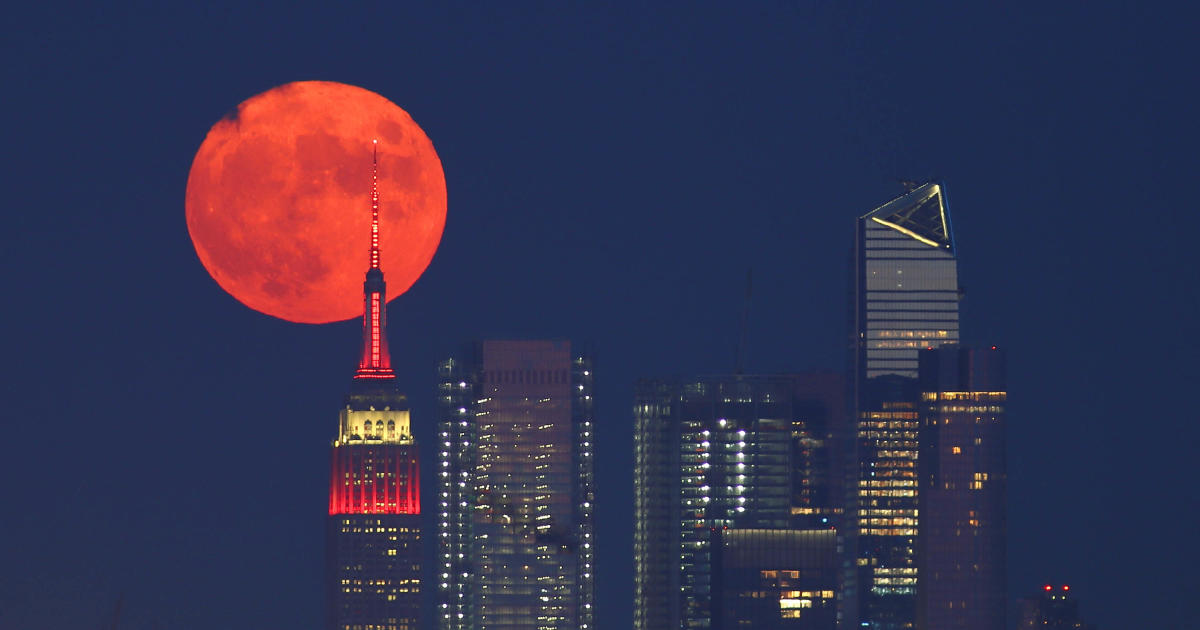

The next full moon is arriving just in time for the weekend. According to NASA, the Buck Moon will make an appearance for three days, from Friday evening to Monday morning, reaching its peak at 6:17 a.m. EDT on Sunday.
The moon is also known as the Thunder Moon, given its overlap with thunderstorm season.
NASA advised viewers to stay safe from the lightning that comes with the storms, but also to indulge in a little fun as the Buck Moon arrives: “As usual, the wearing of suitably celebratory celestial attire is encouraged in honor of the full Moon.”
Why is it called the Buck Moon?
The name stems from a tradition established by the Maine Farmers’ Almanac in the 1930s, according to NASA, when the publication started listing the names of full moons. The Algonquin tribes of the Northeast reportedly called this month’s moon the Buck Moon – a nod to the deer that emerge this time of year.
“Early summer is normally when the new antlers of buck deer push out of their foreheads in coatings of velvety fur,” NASA said.
Other monikers for July’s full moon include Thunder Moon, Asalha Puja, Guru Full Moon, Hay Moon. and Mead Moon.
When will the next full moon take place?
August’s full moon — known as the Sturgeon Moon, according to the almanac.com — will peak on Monday, Aug. 19. This will be the first supermoon of the year, which means it will appear brighter and larger than other full moons.
Another event for stargazers to look forward to is a meteor shower on Saturday, July 31. Those on the East Coast will have to rise early if they want to catch the spectacle of light. According to NASA, the best time to see the shower from Washington, D.C., will be around 2 a.m.
Science & Environment
Secrets of the elephant – CBS News

Watch CBS News
Be the first to know
Get browser notifications for breaking news, live events, and exclusive reporting.
Science & Environment
“Cocaine sharks”: Predators off coast of Brazil test positive for drug, scientists say
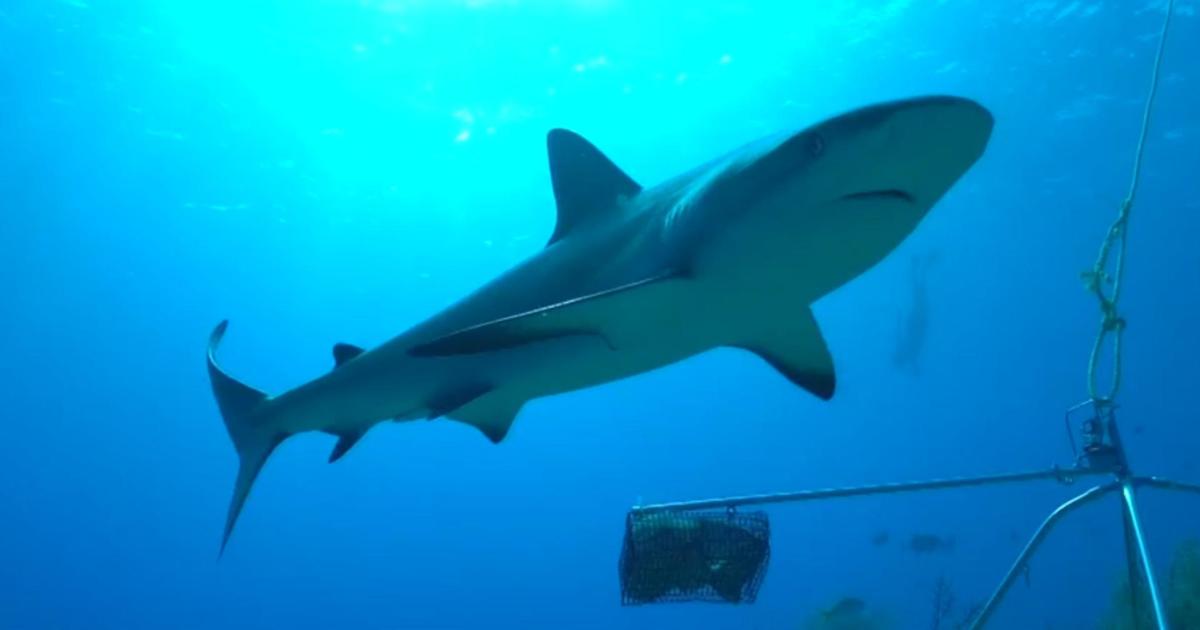

Sharks in the waters off Brazil have tested positive for cocaine, marine biologists said in a new study, marking the first time the drug has been found in the free-ranging predators.
Thirteen sharpnose sharks were taken from the coast off of Rio de Janeiro and tested for the cocaine and benzoylecgonine, the primary molecule in cocaine. Each shark’s liver and muscles tested positive for high levels of cocaine, the study found, and the female sharks tested had higher concentrations of cocaine in their muscles than male sharks.
The scientists — who dubbed the study “Cocaine Shark” — posited that this may show a correlation between a shark’s weight and size and how it metabolizes cocaine, but the study noted that more research was necessary.
CBS News partner BBC News reported that experts have multiple theories on how the illicit substances are entering the water. It’s possible that illegal labs where cocaine is manufactured could be to blame. Scientists also said that it could be entering the waterway through the excrement of drug users. A less likely theory is that packs of cocaine lost or dumped at sea could be to blame. Cocaine and other illicit drugs have previously been found in water drainage systems and in rivers.
It’s the first study to show levels of cocaine and benzoylecgonine in free-ranging sharks. More research is necessary to see how cocaine consumption affects sharks and other wildlife, the scientists said.
It’s not clear how the cocaine consumption affects the sharks, the study said. Some of the female sharks were pregnant at the time of the study, and it remains unclear how the illicit drugs may have affected the fetuses.
The findings are “very important and potentially worrying,” marine eco-toxicologist Sara Novais, from the Marine and Environmental Sciences Centre of the Polytechnic University of Leiria, told Science magazine.
Researchers have tried to study the impact of illicit drugs on sea life in other parts of the world. Last year, Discovery TV aired a show called “Cocaine Sharks” (which was also the title of a 2023 horror movie) that used experiments to show how sharks might be affected by cocaine. Tracy Fanara, an environmental engineer who worked on the show, told CBS News that the experiments and their results were preliminary, but said it’s likely that sharks are coming in contact with the illicit drug.
“My goal of this experiment was to shed light on the real problem of chemicals in our waterways and impacting our aquatic life and then eventually impacting us,” Fanara said in 2023. “But the goal of the study was basically to see if this is a research question worth exploring more. And I would say, yes, it is.”
-

 Sport14 hours ago
Sport14 hours agoJoshua vs Dubois: Chris Eubank Jr says ‘AJ’ could beat Tyson Fury and any other heavyweight in the world
-
 News2 days ago
News2 days agoYou’re a Hypocrite, And So Am I
-

 News15 hours ago
News15 hours agoIsrael strikes Lebanese targets as Hizbollah chief warns of ‘red lines’ crossed
-

 Sport13 hours ago
Sport13 hours agoUFC Edmonton fight card revealed, including Brandon Moreno vs. Amir Albazi headliner
-

 Science & Environment16 hours ago
Science & Environment16 hours ago‘Running of the bulls’ festival crowds move like charged particles
-

 Technology12 hours ago
Technology12 hours agoiPhone 15 Pro Max Camera Review: Depth and Reach
-

 Science & Environment16 hours ago
Science & Environment16 hours agoHow one theory ties together everything we know about the universe
-

 Science & Environment1 day ago
Science & Environment1 day agoSunlight-trapping device can generate temperatures over 1000°C
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoBrian Tyree Henry on voicing young Megatron, his love for villain roles
-
 Science & Environment1 day ago
Science & Environment1 day agoQuantum time travel: The experiment to ‘send a particle into the past’
-
 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours ago2 auditors miss $27M Penpie flaw, Pythia’s ‘claim rewards’ bug: Crypto-Sec
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoBitcoin miners steamrolled after electricity thefts, exchange ‘closure’ scam: Asia Express
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoCardano founder to meet Argentina president Javier Milei
-
 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoDorsey’s ‘marketplace of algorithms’ could fix social media… so why hasn’t it?
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoLow users, sex predators kill Korean metaverses, 3AC sues Terra: Asia Express
-
Business13 hours ago
How Labour donor’s largesse tarnished government’s squeaky clean image
-
 Science & Environment20 hours ago
Science & Environment20 hours agoQuantum ‘supersolid’ matter stirred using magnets
-
News14 hours ago
Freed Between the Lines: Banned Books Week
-

 MMA13 hours ago
MMA13 hours agoUFC’s Cory Sandhagen says Deiveson Figueiredo turned down fight offer
-

 CryptoCurrency13 hours ago
CryptoCurrency13 hours agoEthereum is a 'contrarian bet' into 2025, says Bitwise exec
-

 Science & Environment21 hours ago
Science & Environment21 hours agoA new kind of experiment at the Large Hadron Collider could unravel quantum reality
-
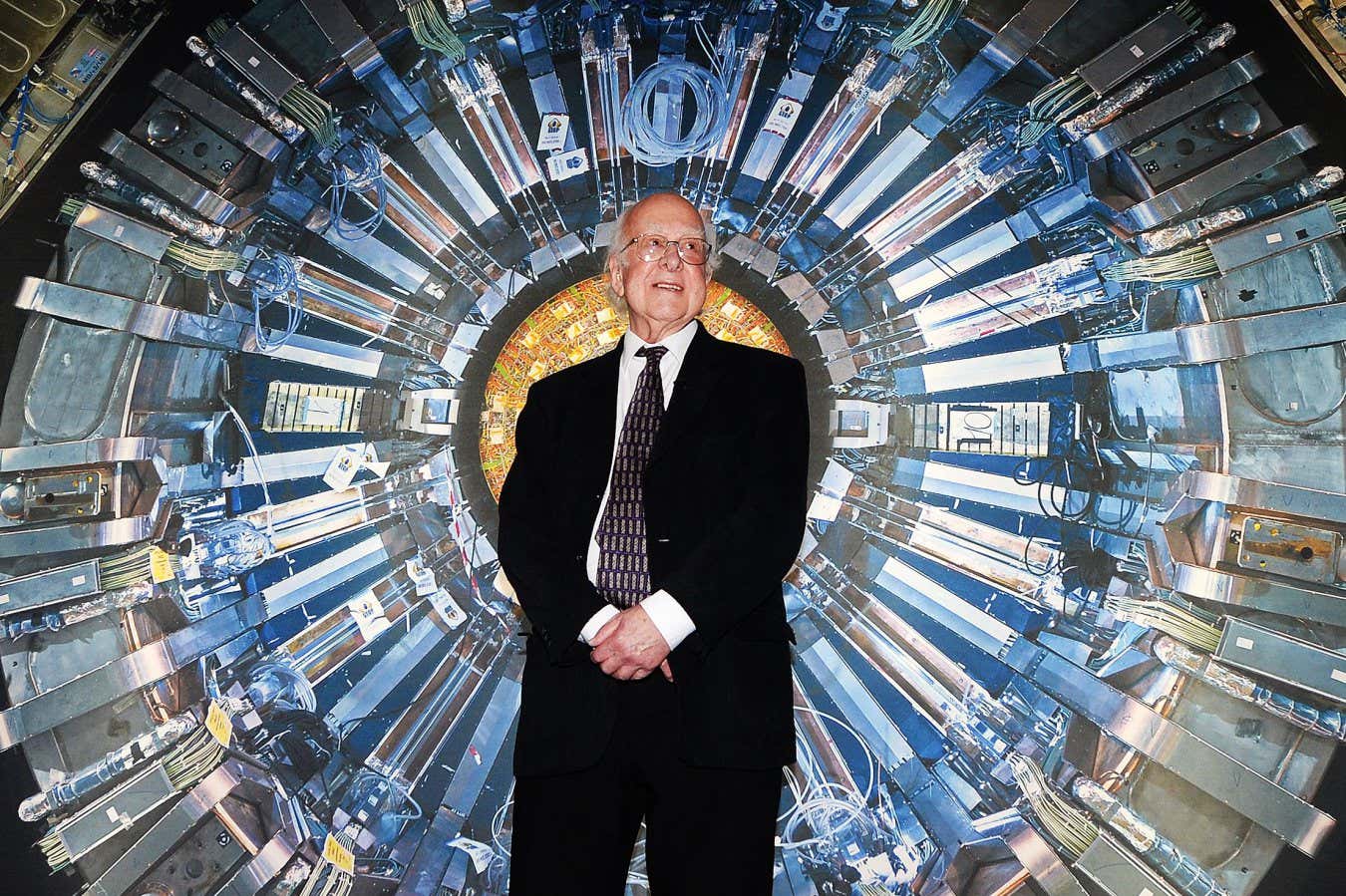
 Science & Environment20 hours ago
Science & Environment20 hours agoHow Peter Higgs revealed the forces that hold the universe together
-

 Science & Environment16 hours ago
Science & Environment16 hours agoRethinking space and time could let us do away with dark matter
-

 Science & Environment14 hours ago
Science & Environment14 hours agoWe may have spotted a parallel universe going backwards in time
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoArthur Hayes’ ‘sub $50K’ Bitcoin call, Mt. Gox CEO’s new exchange, and more: Hodler’s Digest, Sept. 1 – 7
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoTreason in Taiwan paid in Tether, East’s crypto exchange resurgence: Asia Express
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoLeaked Chainalysis video suggests Monero transactions may be traceable
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoJourneys: Robby Yung on Animoca’s Web3 investments, TON and the Mocaverse
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoLouisiana takes first crypto payment over Bitcoin Lightning
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoAre there ‘too many’ blockchains for gaming? Sui’s randomness feature: Web3 Gamer
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoCrypto whales like Humpy are gaming DAO votes — but there are solutions
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoHelp! My parents are addicted to Pi Network crypto tapper
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours ago$12.1M fraud suspect with ‘new face’ arrested, crypto scam boiler rooms busted: Asia Express
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours ago‘Everything feels like it’s going to shit’: Peter McCormack reveals new podcast
-

 Science & Environment17 hours ago
Science & Environment17 hours agoWhy we need to invoke philosophy to judge bizarre concepts in science
-
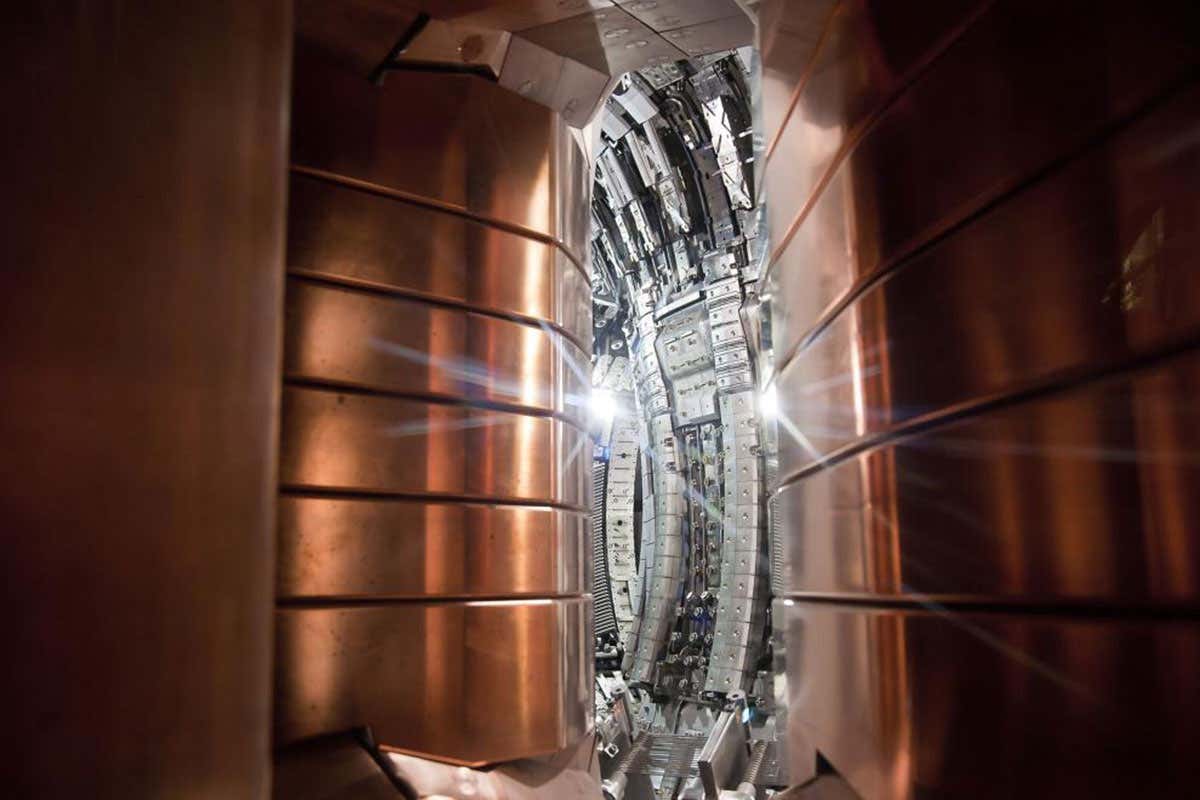

 Science & Environment16 hours ago
Science & Environment16 hours agoFuture of fusion: How the UK’s JET reactor paved the way for ITER
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoSEC sues ‘fake’ crypto exchanges in first action on pig butchering scams
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoFed rate cut may be politically motivated, will increase inflation: Arthur Hayes
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoDecentraland X account hacked, phishing scam targets MANA airdrop
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoCZ and Binance face new lawsuit, RFK Jr suspends campaign, and more: Hodler’s Digest Aug. 18 – 24
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoCertiK Ventures discloses $45M investment plan to boost Web3
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoMemecoins not the ‘right move’ for celebs, but DApps might be — Skale Labs CMO
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoTelegram bot Banana Gun’s users drained of over $1.9M
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoDZ Bank partners with Boerse Stuttgart for crypto trading
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoRedStone integrates first oracle price feeds on TON blockchain
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoBitcoin bulls target $64K BTC price hurdle as US stocks eye new record
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoSEC asks court for four months to produce documents for Coinbase
-

 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours ago‘No matter how bad it gets, there’s a lot going on with NFTs’: 24 Hours of Art, NFT Creator
-

 CryptoCurrency13 hours ago
CryptoCurrency13 hours agoBlockdaemon mulls 2026 IPO: Report
-
Business13 hours ago
Thames Water seeks extension on debt terms to avoid renationalisation
-
Politics13 hours ago
The Guardian view on 10 Downing Street: Labour risks losing the plot | Editorial
-

 Politics13 hours ago
Politics13 hours agoI’m in control, says Keir Starmer after Sue Gray pay leaks
-
Politics12 hours ago
‘Appalling’ rows over Sue Gray must stop, senior ministers say | Sue Gray
-
Business12 hours ago
UK hospitals with potentially dangerous concrete to be redeveloped
-
Business12 hours ago
Axel Springer top team close to making eight times their money in KKR deal
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours ago“Beast Games” contestants sue MrBeast’s production company over “chronic mistreatment”
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoSean “Diddy” Combs denied bail again in federal sex trafficking case
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoSean “Diddy” Combs denied bail again in federal sex trafficking case in New York
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoBrian Tyree Henry on his love for playing villains ahead of “Transformers One” release
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoBrian Tyree Henry on voicing young Megatron, his love for villain roles
-

 CryptoCurrency11 hours ago
CryptoCurrency11 hours agoCoinbase’s cbBTC surges to third-largest wrapped BTC token in just one week
-

 Technology3 days ago
Technology3 days agoYouTube restricts teenager access to fitness videos
-

 News15 hours ago
News15 hours agoChurch same-sex split affecting bishop appointments
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoTrump says he will meet with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi next week
-

 Politics1 day ago
Politics1 day agoWhat is the House of Lords, how does it work and how is it changing?
-

 Politics1 day ago
Politics1 day agoKeir Starmer facing flashpoints with the trade unions
-

 Health & fitness2 days ago
Health & fitness2 days agoWhy you should take a cheat day from your diet, and how many calories to eat
-

 Technology15 hours ago
Technology15 hours agoFivetran targets data security by adding Hybrid Deployment
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoNathan Simpson appears in court over murder of Rachelle Simpson
-

 Science & Environment2 days ago
Science & Environment2 days agoElon Musk’s SpaceX contracted to destroy retired space station
-
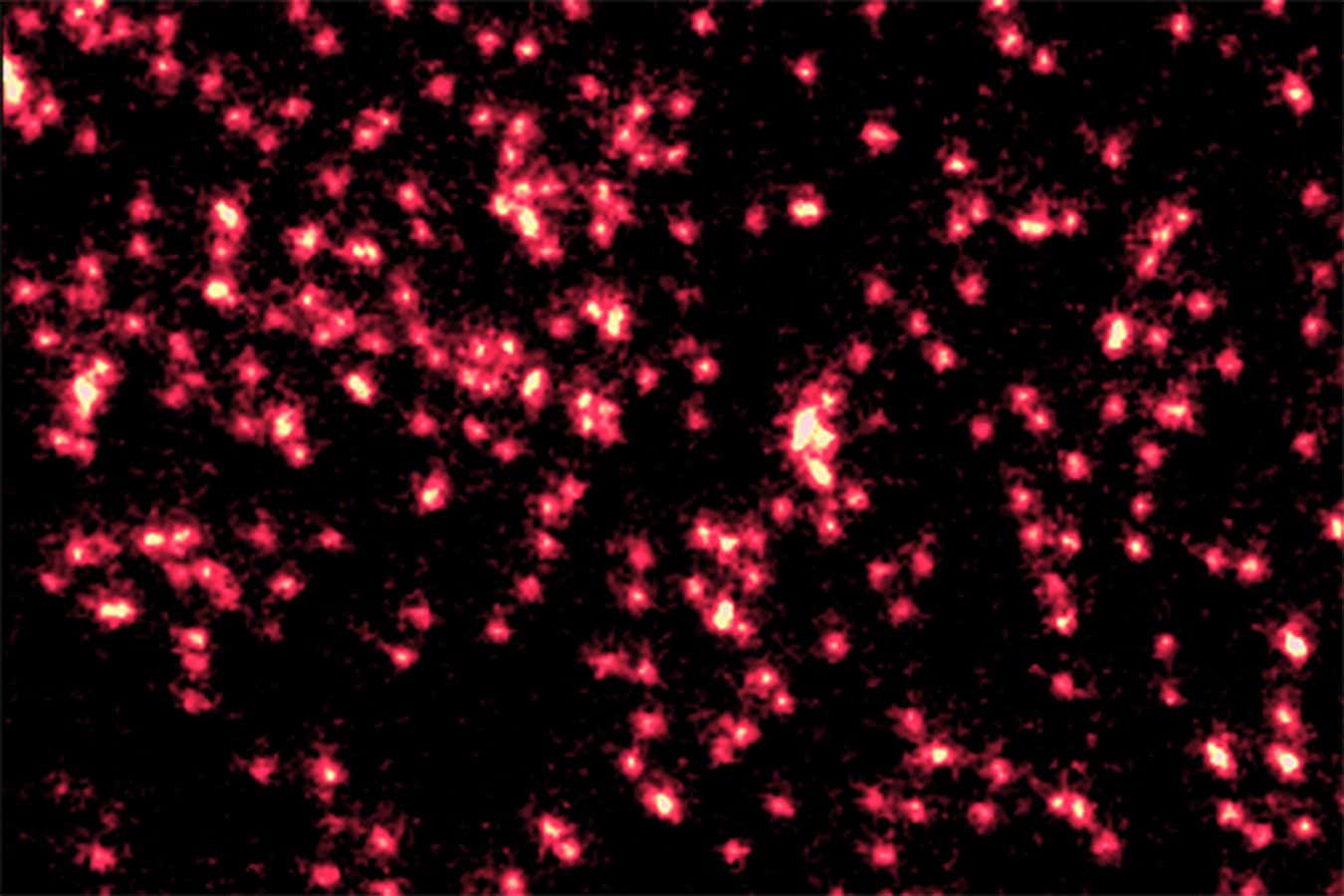
 Science & Environment21 hours ago
Science & Environment21 hours agoSingle atoms captured morphing into quantum waves in startling image
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoGuardian in talks to sell world’s oldest Sunday paper
-

 MMA13 hours ago
MMA13 hours agoDiego Lopes declines Movsar Evloev’s request to step in at UFC 307
-

 Football13 hours ago
Football13 hours agoNiamh Charles: Chelsea defender has successful shoulder surgery
-

 Football13 hours ago
Football13 hours agoSlot's midfield tweak key to Liverpool victory in Milan
-
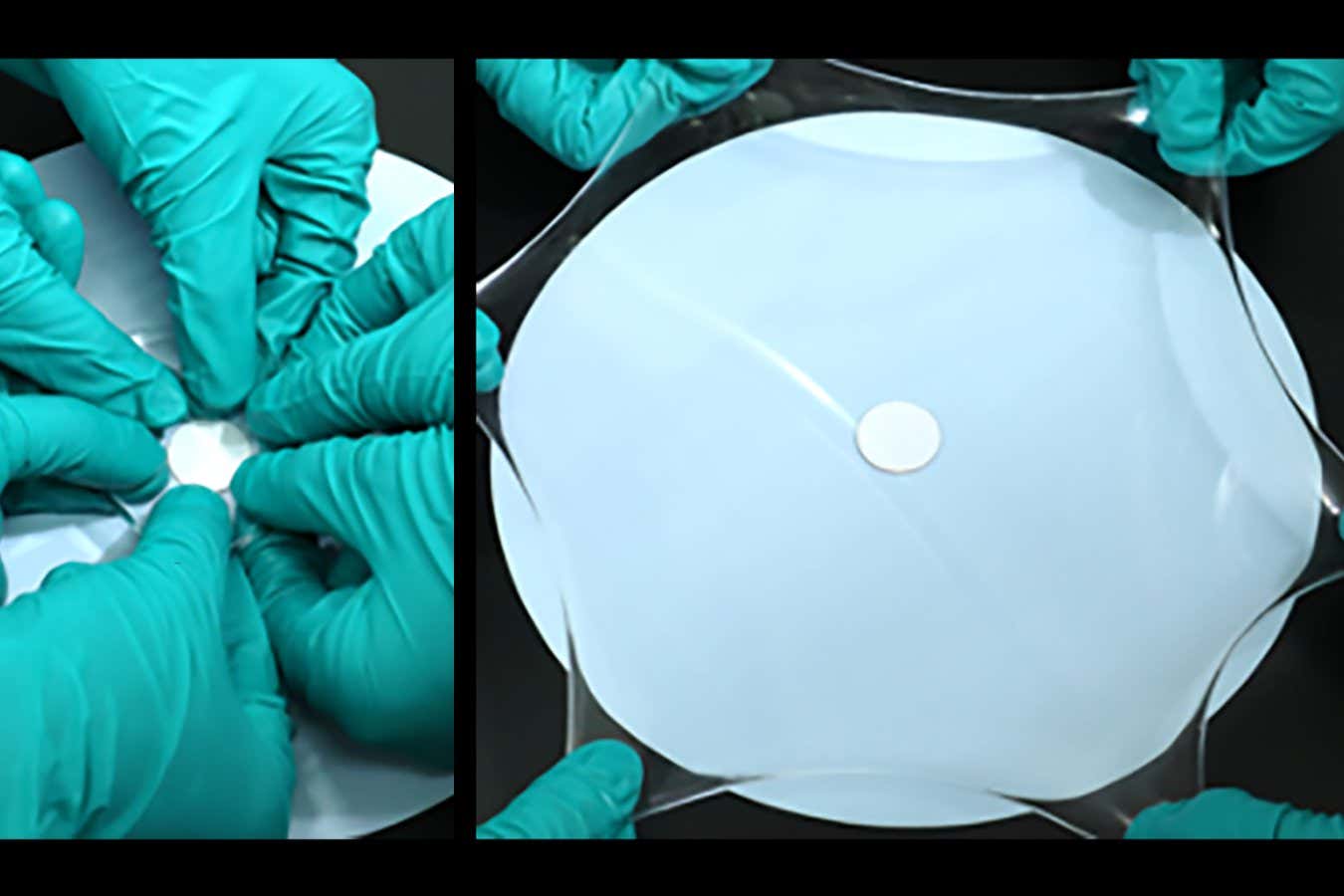
 Science & Environment17 hours ago
Science & Environment17 hours agoHyperelastic gel is one of the stretchiest materials known to science
-

 Science & Environment16 hours ago
Science & Environment16 hours agoHow to wrap your head around the most mind-bending theories of reality
-

 Technology2 days ago
Technology2 days agoCan technology fix the ‘broken’ concert ticketing system?
-

 Fashion Models13 hours ago
Fashion Models13 hours agoMiranda Kerr nude
-

 Fashion Models13 hours ago
Fashion Models13 hours ago“Playmate of the Year” magazine covers of Playboy from 1971–1980
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoDid the Pandemic Break Our Brains?
-

 Health & fitness2 days ago
Health & fitness2 days ago11 reasons why you should stop your fizzy drink habit in 2022
-

 Politics12 hours ago
Politics12 hours agoLabour MP urges UK government to nationalise Grangemouth refinery
-

 Technology2 days ago
Technology2 days agoWhat will future aerial dogfights look like?
-

 Science & Environment15 hours ago
Science & Environment15 hours agoOdd quantum property may let us chill things closer to absolute zero
-

 Science & Environment22 hours ago
Science & Environment22 hours agoQuantum forces used to automatically assemble tiny device
-

 Entertainment11 hours ago
Entertainment11 hours ago“Jimmy Carter 100” concert celebrates former president’s 100th birthday
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoDangers of being a FOMO customer as rates fall
-
 CryptoCurrency14 hours ago
CryptoCurrency14 hours agoSEC settles with Rari Capital over DeFi pools, unregistered broker activity
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoJoe Posnanski revisits iconic football moments in new book, “Why We Love Football”
-
 Health & fitness2 days ago
Health & fitness2 days agoHow to adopt mindful drinking in 2022
-

 Health & fitness2 days ago
Health & fitness2 days agoWhat 10 days of a clean eating plan actually does to your body and why to adopt this diet in 2022
-

 Health & fitness2 days ago
Health & fitness2 days agoWhen Britons need GoFundMe to pay for surgery, it’s clear the NHS backlog is a political time bomb
-
 Health & fitness2 days ago
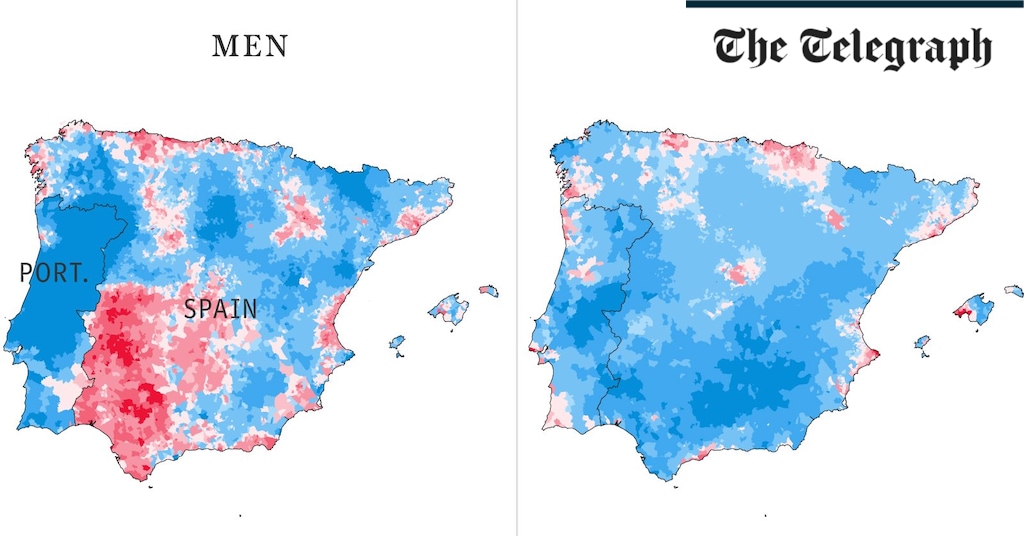
Health & fitness2 days agoThe maps that could hold the secret to curing cancer
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days ago‘I borrowed £44,000 for university and now owe £54,000’
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCan the middle powers save multilateral trade?
-
Health & fitness2 days ago
Covid v flu v cold and how to tell the difference between symptoms this winter
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoAs Democrats fold to GOP on border policy, immigrants pay the price
-

 Science & Environment1 day ago
Science & Environment1 day agoPhysicists determined the paper most likely to give you a paper cut
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoBrits’ favourite history periods revealed – does yours make the list?






You must be logged in to post a comment Login