Tech
Apple ‘Runs on Anthropic,’ Says Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman

Apple “runs on Anthropic at this point” and that the AI company is powering much of what Apple does internally for product development and internal tools, according to Mark Gurman, the most influential reporter on the Apple beat.
Apple had initially pursued an AI deal with Anthropic before the Google partnership came together, but negotiations fell apart over pricing — Anthropic reportedly wanted several billion dollars per year and a doubling of fees over time. Apple’s deal with Google is costing roughly one billion dollars annually.
Tech
Oregon theater marquee joked about ‘Melania’ movie, and manager says Amazon pulled the film


The new “Melania” documentary film was released by Amazon MGM Studios to 1,778 theaters across the country. Make that 1,777 now.
The manager of the Lake Theater & Cafe in Lake Oswego, Ore., just outside of Portland, said a marquee he put up for the theater’s screening of the film about First Lady Melania Trump managed to upset Amazon enough that the company pulled the film.
“To defeat your enemy, you must know them. Melania starts Friday,” read the marquee, as seen in a photograph accompanying a story in The Oregonian.
In an Instagram post on Monday, Lake Theater & Cafe said “the higher ups” at Amazon were upset with the marketing move and that Sunday was the last showing of “Melania” at the theater. A new marquee said Amazon got “mad” and all “Melania” shows were canceled, and that patrons could show their support instead at a nearby Amazon-owned Whole Foods Market.
GeekWire reached out to Amazon for comment, and we’ll update if we hear back.
Marquee messages are apparently a running joke at the Lake Theater. On the theater’s website about page, there are numerous voicemails from passersby reacting to previous messages. The page also has a photo of a marquee that read, “Not getting the Taylor Swift movie because her music’s not even good.”
In a blog post, manager Jordan Perry expounded on why the theater even booked a two-week run of “Melania,” the reaction from both sides of the political spectrum, and how much money the screening made for Amazon founder Jeff Bezos.
“To fill a screen, why not get this inexplicable vanity piece from the current president’s wife?” Perry wrote. “I mean, it just seems so weird that it even exists (who wants a movie about Melania lol?), and wouldn’t it then be exponentially weirder, to the point of being funny, to show it here, at your obviously anti-establishment, occasionally troublemaking, neighborhood cinema?”
Perry said he had no interest in trying to get people to vote one way or another. He said he was more interested in helping people be more “open-minded, compassionate, and well-informed.” He added that for each $11 ticket sold, $5.50 went to Amazon MGM Studios.
“We contributed, in all, $196 to the Jeff Bezos Trust Fund this week (far more to the ‘Hamnet’ Trust Fund, thank you, ‘Hamnet’ lovers),” Perry said.
“Melania” pulled in much more than that in a total weekend box office of $7 million — the largest opening haul for a non-concert documentary in 14 years, according to The New York Times. The film finished third for the weekend behind horror thriller “Send Help” ($20 million) and horror sci-fi mashup “Iron Lung” ($18 million).
Amazon spent $75 million to acquire the rights and market the film, which was directed by Brett Ratner (“Rush Hour,” “X-Men: The Last Stand”) and provides an inside look at the 20 days leading up to the 2025 presidential inauguration.
Backlash around the film was not limited to a small theater in Oregon. Critics torched the film as propaganda in early reviews. Bus stop ads and billboards in Los Angeles have been defaced. And Amazon CEO Andy Jassy and Apple CEO Tim Cook were among those who took heat for attending a private White House screening of the film on the same day protester Alex Pretti was killed in Minneapolis by federal agents.
Watch the “Melania” trailer below:
Tech
The OnePlus 16 could have a much better zoom camera and a massive battery
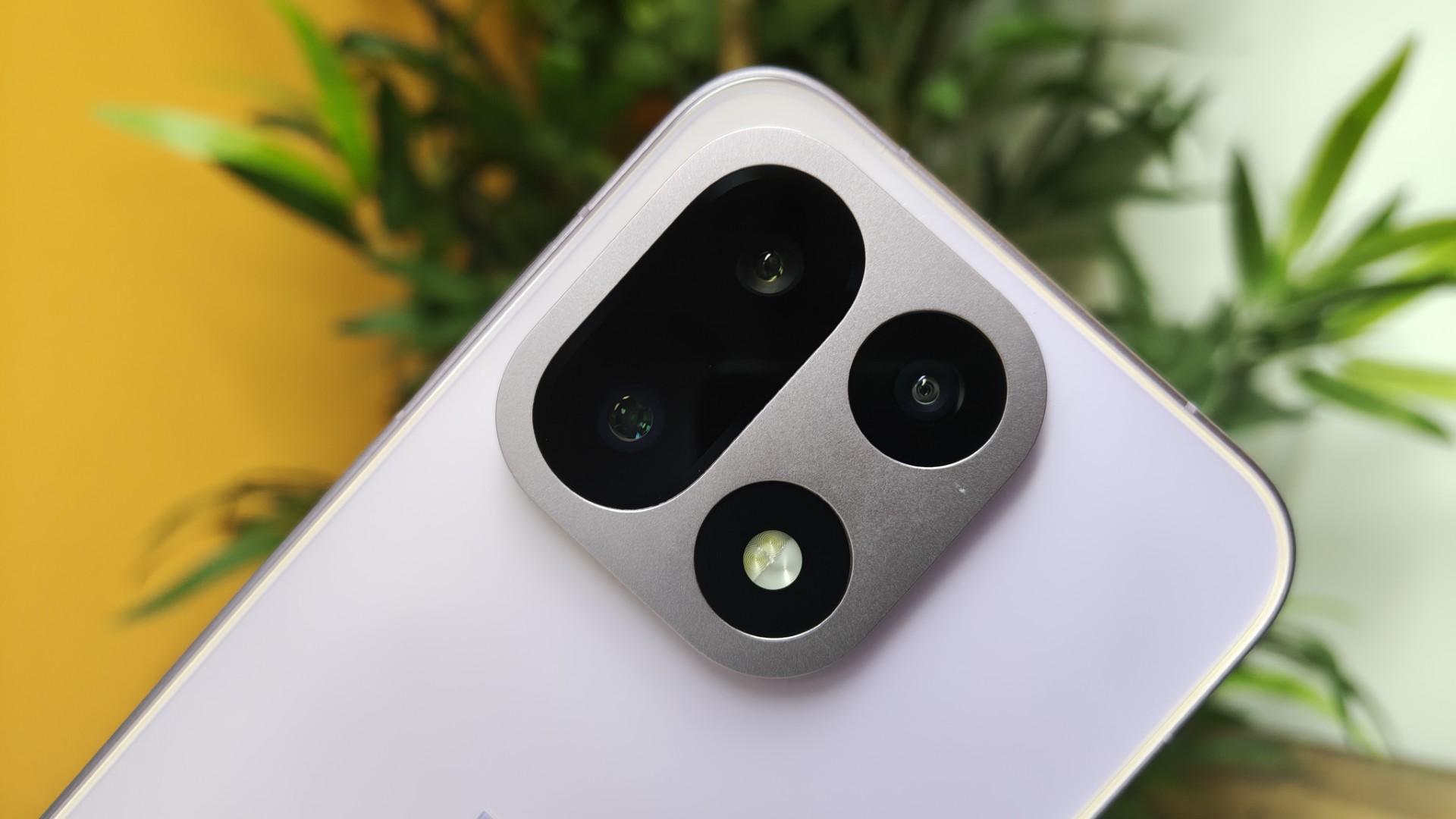

OnePlus is tipped to deliver a major camera upgrade with its upcoming flagship, the OnePlus 16, expected later in 2026.
According to a new leak, the device will feature a 200MP telephoto sensor measuring 1/1.56 inches, a significant jump from the 50MP 1/2.76-inch telephoto lens found on the OnePlus 15. This change could dramatically improve zoom performance and image detail, while also introducing telephoto macro capabilities for close-up shots.
The leak, shared by @OnePlusClub on X, suggests OnePlus is finally addressing criticism of the OnePlus 15’s scaled-down camera system. That model shipped with smaller sensors and lacked Hasselblad colour tuning, leaving photography enthusiasts underwhelmed despite strong performance elsewhere.
The OnePlus 16’s rumoured telephoto upgrade would put it in line with rivals such as Oppo’s Find X9 series, which already offers telephoto macro functionality.
Beyond the camera, the OnePlus 16 is rumoured to pack a 9,000mAh battery, up from 7,300mAh on its predecessor, alongside a display refresh rate exceeding 200Hz. These specifications suggest OnePlus is targeting both endurance and gaming performance.
The handset is also expected to run Qualcomm’s next flagship chipset, though it remains unclear whether it will use the rumoured Snapdragon 8 Gen 6 or the top-end 8 Elite Gen 6. For those weighing up their next upgrade, our best Android phones guide offers a broader look at the competition.
Leaks around the OnePlus 16 highlight a shift in priorities. The OnePlus 15 impressed with raw performance thanks to the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 and a larger battery, but its camera compromises were seen as a step back from the OnePlus 13.
Therefore, the rumoured 200MP telephoto sensor could mark a return to form, especially for users who value versatile photography. However, until OnePlus confirms details, these specifications remain speculative.
These leaks suggest OnePlus is preparing to position the OnePlus 16 as a more balanced flagship, combining performance with meaningful camera improvements. If accurate, the upgrade could make the device one of the most compelling Android options in 2026, particularly for those who demand strong zoom capabilities without sacrificing everyday usability.
Tech
Seeking Candidates for Top IEEE Leadership Positions


Strong leadership is essential for IEEE to advance technology for humanity. The organization depends on the dedicated service of its volunteers to advance its mission.
Each year, the Nominations and Appointments (N&A) Committee is responsible for recommending candidates to the Board of Directors and the IEEE Assembly for volunteer leadership positions, including president-elect, corporate officers, committee chairs, and committee members. See below for the complete list.
By nominating qualified, experienced, committed volunteers, you help ensure continuity, good governance, and thoughtful decision-making at the highest levels of the organization. We encourage nominators to take a deliberate approach and align nominations with each candidate’s demonstrated experience and the specific qualifications of the role.
To nominate a person for a position, complete this form.
The N&A Committee is currently seeking nominees for the following positions:
2028 IEEE President-Elect (who will be elected in 2027 and will serve as President in 2029 )
2027 IEEE Corporate Officers
• Secretary
• Treasurer
• Vice President, Educational Activities
• Vice President, Publication Services and Products
2027 IEEE Committees Chairs and Members
• Audit
• Awards Board
• Collaboration and Engagement
• Conduct Review
• Election Oversight
• Employee Benefits and Compensation
• Ethics and Member Conduct
• European Public Policy
• Fellow
• Fellow Nominations and Appointments
• Governance
• History
• Humanitarian Technologies Board
• Industry Engagement
• Innovations (formerly New Initiatives)
• Nominations and Appointments
• Public Visibility
• Tellers
Deadlines for nominations
15 March
- Vice President, Educational Activities
- Vice President, Publication Services and Products
- Committee Chairs
15 June
- President-Elect
- Secretary
- Treasurer
- Committee Members
Deadlines for self-nominations
30 March
- Vice President, Educational Activities
- Vice President, Publication Services and Products
- Committee Chairs
30 June
- President-Elect
- Secretary
- Treasurer
- Committee Members
Who can nominate
Anyone may submit a nomination. Self-nominations are encouraged. Nominators need not be IEEE members, but nominees must meet specific qualifications. An IEEE organizational unit may submit recommendations endorsed by its governing body or the body’s designee.
A person may be nominated for more than one position, however nominators are encouraged to focus on positions that align closely with the candidate’s qualifications and experience. Nominators need not contact their nominees before submitting the form. The IEEE N&A committee will contact eligible nominees for the required documentation and for their interest and willingness to be considered for the position.
How to nominate
For information about the positions, including qualifications, estimates of the time required by each position during the term of office, and the nomination process check the IEEE Nominations and Appointments Committee website. To nominate a person for a position, complete this form.
Nominating tips
Make sure to check eligibility requirements on the N&A committee website before submitting a nomination as those that do not meet the stated requirements will not be advanced.
Volunteers with relevant prior experience in lower-level IEEE committees and units are recommended by the committee more often than volunteers without such experience.
Individuals recommended for president-elect and corporate officer positions are more likely to be recommended if they possess a strong track record of leadership, governance experience, and relevant accomplishments within and outside IEEE. Recommended president-elect candidates must have served on the IEEE Board of Directors for at least one year.
Contact nominations@ieee.org with any questions.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web
Tech
We Retested Every Meal Kit Service. This Underdog Is Our New Favorite in 2026


Pros
- Thoughtful recipes you won’t find everywhere
- Even the quick recipes felt special
- Extremely fresh ingredients
- Not a lot of plastic waste
Cons
- On the expensive side when you factor in shipping
- Market add-ons are not the best
Meal kits have been around for more than a decade. HelloFresh, Blue Apron, and Home Chef have been the most visible, blasting ads on social media and during your favorite podcast — but are they the best?
After testing and retesting every meal kit service (here’s how we do it), crafting dozens of these meals-by-mail in our own kitchens, we’ve picked a new favorite for 2026, and it’s not one of the “big three.”
If you’re looking for excellent meal kits that are anything but boring, there’s a new top dog in town.
Marley Spoon offers creative and tasty meals, which may come as no surprise when you learn who the woman behind the recipes is: kitchen maven herself, Martha Stewart.
Marley Spoon caters to adventurous home cooks and food enthusiasts with creative recipes that appeal to both beginners and more refined palates. Unlike some meal kit services that target newcomers with straightforward, quick-prep dishes, Marley Spoon offers more elevated fare featuring Martha’s own recipes. Many come straight from her cookbooks or personal collection, yet they remain accessible — you won’t need advanced techniques or professional training to pull them off.
Read more: Your Guide to Meal Kits: The Essential Tools You’ll Need to Get Started
Curious as we are at CNET about all things meal kits, we wanted to know just how good they are — and whether they’re worth the money. We tested a week’s worth of recipes for a third time to bring you this review of Marley Spoon’s meal kit delivery service.
How Marley Spoon works
A selection of Marley Spoon recipes as of 2025.
Marley Spoon operates similarly to most others in the category and offers both meal kits with recipes that you cook and prepared meals that only require reheating.
After choosing between those two options, you will then answer the question, “What kid of meals do you like?” Meal kit options include everyday variety, low calorie, low carb, quick and easy, vegetarian, pescatarian and Mediterranean for two or four people and you can choose between two and six meals per week. The single-serving prepared meal options include everyday variety, low calorie or low carb and you can choose 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 or 18 meals per week.
Your box of meal kit ingredients is delivered once a week — unless you skip a week, which is easy to do — and you can either manually select recipes or let Martha Stewart personally choose them for you. OK, just kidding: She’s not your personal meal concierge, but you can let the brand select meals if you prefer a little mystery. You can select any day of the week for delivery, and the boxes will arrive between 8 a.m. and 9 p.m.
There are now more than 100 recipes each week, ranging in difficulty. Before you choose a recipe for delivery, you’ll see all the steps involved, the estimated time it takes to complete, and detailed nutritional information to help you decide.
Marley Spoon meal kit pricing
Number of people
Recipes per week
Total servings per week
Price per serving
2
2
4
$12.99
2
3
6
$11.99
2
4-6
8-12
$10.99
4
2
8
$10.99
4
3
12
$10.49
4
4-5
16-20
$9.99
4
6
24
$8.99
Prepared meals are $12.99 each and shipping is $10.99 per box.
What are Martha Stewart & Marley Spoon meals like
As you might imagine, since Martha Stewart helped design the concept and created many of the recipes, there are some really interesting, high-end and gourmet dishes to choose from. Luckily, though, most are still fairly simple to make.
There are plenty of healthy recipes, along with dietary preferences to choose from. However, there are only between four and six vegan options each week so if you want more options, Purple Carrot may be a better choice for you. Other services that feature built-in diet meal plans include Green Chef, Home Chef or HelloFresh.
Skillet chicken Parmesan ingredients.
At Marley Spoon, you’ll find plenty of warming comfort dishes like French onion chicken breast and beef stroganoff, plus desserts you can add on to your box, such as baked gingerbread doughnuts and French-style cheesecake.
On the prepared-meal side, the recipes are just as creative. Some meals include tilapia with smoky tomato sauce and black bean street corn and merlot chicken meatballs with orzo pasta and green beans.
How easy are Martha Stewart & Marley Spoon meals to prepare?
The beef empanadas were fun to make from scratch and a new experience for me.
Our meals ran the gamut from the super simple to a bit more complicated and time-intensive, but the good news is that it’s really up to you on how difficult you want the meals to be when you make your recipe selections.
The skillet chicken Parmesan, for instance, had a number of steps like preparing the chicken, cooking it, making the sauce and preparing the pasta (which had its own ingredients). For someone with a decent amount of cooking experience, this isn’t challenging, but some beginners might not be ready for such an involved meal. Other meals, such as the butternut squash pizza, were quite simple, tasty, and perfect for a weeknight when you don’t feel like fussing much or taking time to cook.
Read more: Meal Kits Taught Me How to Cook. Now I Get to Test Them for a Living
What we cooked and how it went
Beef picadillo pockets with bell peppers and cilantro chimichurri: This meal was not only delicious but also fun to make. It was the first time I used raw dough in a meal kit recipe, and the results were well worth the effort. Although the empanadas were filling, I still would have liked it to have come with a side other than the chimichurri sauce.
The beef empanadas were filling and tasty.
Butternut squash pizza with ricotta, almonds and hot honey: I had never had butternut squash on a pizza before this meal, but I can definitely see myself making this again. It was a perfect fall meal with the onions, squash, rosemary and almonds added on top.
The butternut squash used the same type of dough as the empanadas.
Seared salmon and citrus butter sauce with smashed potatoes and shaved Brussels salad: The Brussels sprout salad helped elevate this simple meal and take it to the next level. I cooked the salmon on the stovetop and the smashed potatoes in my air fryer.
I loved making smashed potatoes for this meal.
Skillet chicken Parmesan with casarecce and sautéed spinach: This recipe was good and very comforting, though it certainly had a healthy share of carbs and calories. The red sauce was very simple and the chicken cutlets weren’t breaded so it felt a little healthier than normal chicken Parm but not quite enough to be really, truly healthy. I had lots of leftovers, which was nice.
Honey miso salmon with roasted carrots and Brussels sprouts: This one was great and healthy, but it wasn’t particularly out-of-the-box. The salmon was high-quality and tasted super fresh.
Restorative chicken soup with sweet potato kale and quinoa: A very tasty and hearty soup I made and ate all week. The shredded chicken was already cooked, which surprised me but I appreciated, as it was still moist and flavorful. This entire meal was simple to prepare and felt like nourishing medicine, thanks to all those superfoods.
I was eating chicken Parm and pasta leftovers all week.
Marley Spoon support materials
I found the recipes clear, concise and easy to follow. There’s some nice background on the ingredients, too: my salmon recipe, for instance, provided context on miso for anyone unfamiliar with the fermented paste. The Marley Spoon app is also helpful with lots of information about each recipe and gives you the ability to order, pause, cancel or skip a week right from your mobile device.
All the ingredients for a healthy miso salmon with roasted veggies.
What makes Marley Spoon different from other meal kit services?
One thing to like about this service is it doesn’t try to be anything other than good. There’s no pandering to fad diets or giving users too much autonomy to change recipes or swap out meats. The meal kit service’s proposition is that the culinary team has come up with thoughtful, mostly healthy recipes they think you’ll enjoy — and they ask you to put your trust in them. I wouldn’t go so far as to call it stuffy or stubborn, but there is something very Martha Stewart about it.
In that respect, it reminds me a bit of Sunbasket. That meal kit service also tries to keep the integrity of the original recipes they’ve created and while it might not please everyone, I think it pays off in the end for those who appreciate good food.
The finished product.
Who is Marley Spoon good for?
This is one of the best meal kit services for foodies and experienced cooks looking to shake up their weeknight dinner rotation. If you’re looking for interesting new recipes that are both gourmet and approachable, Martha Stewart’s meal kits are a good pick. It’s also a solid choice for a home cook who’s looking to hone new skills or work with new ingredients.
A lot of the recipes are kid-friendly, so these meal kits would also work well for families of up to four people. And with as many as seven plant-based recipes each week, this is a good meal kit service for vegans, vegetarians or those trying to sprinkle in a few more non-meat dinners per week.
A healthy chicken soup that fed me for a few days.
Who is Martha Stewart & Marley Spoon not good for?
If you’re an extremely picky eater, a very new cook, or are trying to keep a gluten-free diet, I would not suggest this meal kit. It’s also not a good meal delivery service if you’re simply looking to get dinner on the table each week and don’t care about the cooking process, since some of the recipes are involved.
Packaging and environmental friendliness
I found Martha Stewart & Marley Spoon to be on the eco-friendly side of the meal kit spectrum. There was some single-use plastic waste, as there always is, but nothing excessive — and the ingredients were not individually packed in disposable bags as of 2025. The boxes, coolers and ice packs were also recyclable.
Changing, skipping or canceling your meal kit order
Between the website and mobile app, Marley Spoon makes it very easy to skip weeks, change out recipes or pause your subscription. Any changes must be made six days prior to the delivery date.
The final verdict on Martha Stewart & Marley Spoon
Being a Martha Stewart-conceived meal kit project, I had lofty expectations for this service and it mostly met them. When I flip through the menu each week, it boasts one of the highest percentages of recipes that make me go “ooh, that sounds good” right up there with Sunbasket. Most importantly, all the recipes we made delivered on the promise of a tasty and interesting meal. There wasn’t much blah factor, and we very much appreciate that.
The meal kit service also includes some thoughtful touches that others don’t, like quick ingredient explainers for new chefs and different chefs behind some of the recipes. The produce, meats and fish were also some of the freshest we’d received from a meal kit service and that goes a long way in creating a truly delicious dinner. The pricing is fair for what you get, and if you’re cooking for a large group, it actually gets rather affordable per serving. The market add-ons have also grown over the years.
If you’ve been wanting to try a meal kit service with a range of healthy, hearty and comforting meals and you already have the cooking basics down, I’d say give Martha’s meals a whirl.
Tech
The best VR headsets for 2026

Stepping into VR is about more than strapping on a headset and loading a game. The best VR headsets today are gateways to fully realized experiences, whether that’s gaming, fitness, creative work or simply spending time inside a richly rendered virtual world. As the hardware has improved, so has the sense of presence, with sharper displays, wider fields of view and tracking systems that make movement feel more natural and responsive. The result is VR that feels less like a novelty and more like a platform you can actually spend time in.
That said, not every headset is built for the same function. Some prioritize ease of use and standalone play, while others demand a powerful PC in exchange for higher fidelity. Compatibility also matters more than ever, especially as VR begins to overlap with mixed reality and early smart glasses experiments. Whether you want a simple way to explore virtual spaces or a high-end rig that pushes immersion as far as possible, this guide breaks down the best VR headsets you can buy in 2026 and explains who each one is really for.
Table of contents
Best VR headsets for 2026
Read our full Meta Quest 3 VR headset review
Storage capacity: 128GB | Battery life: 2.2 hours | Field of view: 110 degrees (horizontal), 96 degrees (vertical) | Max refresh rate: 120Hz
The long-awaited follow-up to the Quest 2 is an upgrade in every respect: It’s more comfortable to wear, it has higher quality screens and it has full-color mixed reality cameras, allowing you to see the real world alongside virtual elements. While it’s more expensive at $500, it’s also a far more capable headset than the Quest 2 and the new Quest 3S, with hardware and optics that will keep you happily immersed in VR for years.
The Quest 3 is powered by Qualcomm’s Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 chip, which Meta says has double the graphics power of the Quest 2. That additional power is noticeable in games like Red Matter 2, which feature updated textures that deliver an experience closer to PC VR. The Quest 3’s new displays run at 2,064 by 2,208 pixels per eye, offering an even better experience than the PlayStation VR2. Its mixed reality cameras also let you easily see the real world, in case you need to quickly answer a text or Slack message. And they enable games that can be built around your room.
What makes the Quest 3 interesting is that it offers more than just solid VR: It also gives you a glimpse at what a mixed reality future could be, blurring the line between the real world and a virtual world. While it’s not as sharp or capable as Apple’s Vision Pro, that’s understandable. And just like previous Quest headsets, you can also plug it into a gaming PC for higher quality VR experiences, expanding its compatibility beyond standalone use.
- Sharp new screens and lenses
- Faster performance
- Mixed reality cameras make it easier to see the real world
- Adjustable for glasses
- More expensive than before
- Only 128GB of storage to start
- No battery life improvements
Read our full Apple Vision Pro M5 review
Storage capacity: Up to 1TB | Battery life: 2.5 hours | Field of view: 100 degrees | Max refresh rate: 120Hz
Apple’s first update for the Vision Pro is basically just a spec bump, but it’s at least a sign that the company hasn’t forgotten about its whole spatial computing endeavour. It’s faster and more power efficient, thanks to the M5 chip, and it also ships with a more comfortable Dual Knit Band that does a better job of balancing such a heavy headset.
With its additional power, the M5 Vision Pro can render 10 percent more pixels than the original model, and it can reach up to a faster 120Hz refresh rate for smoother scrolling. I couldn’t see a major difference in our testing, but I can confirm its Micro OLED screens still look phenomenal. They’re crisp enough for reading text on websites and a mirrored Mac, plus can also scale to extreme heights for stunning Immersive Video content.
Given its high $3,500 price and limited content, though, the Vision Pro is still clearly not meant for typical consumers, with its primary function leaning more toward development and experimentation than everyday VR use. Instead, like the original, it’s basically just a highly polished developer kit for people interested in building visionOS apps. Apple diehards will likely get a kick out of it too, but practically most people interested in AR and VR are better off buying a Meta Quest 3 alongside a gaming PC, especially as lighter smart glasses concepts continue to evolve separately from full headsets.
- Faster M5 chip
- Excellent displays
- Hand and eye tracking work well
- Support for PS VR2 controllers
- Expensive
- Limited immersive video and apps
- Relatively heavy
Read our full Meta Quest 3S VR headset review
Storage capacity: 128GB, 256GB | Battery life: 2-3 hours | Field of view: 96 degrees | Max refresh rate: 120Hz
The Quest 3S is Meta’s latest entry-level VR headset, but don’t let its reasonable $300 price fool you: It’s also a remarkable achievement for the company. It sports the same Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 chip as the Quest 3, as well as a healthy 8GB of RAM, allowing it to power the same experiences as its pricier sibling. It also features Meta’s excellent Touch Plus controllers, which deliver solid motion controls, as well as responsive joysticks and buttons.
The only major downside is that the Quest 3S isn’t nearly as sharp as the Quest 3. It features the same 1,830 by 1,920 pixel per eye screen from the Quest 2, while the Quest 3’s screen offers 30 percent more pixels (2,264 by 2,208 pixels per eye), to deliver a sharper and more realistic image.
VR newbies probably won’t notice the difference much though, and that’s what really matters. The Quest 3S is just as comfortable as the Quest 3 to wear, and it can easily access the same apps and games on the Meta Quest Store. There’s no headphone jack either, but its built-in speakers deliver solid enveloping audio for games like Maestro, and you could also plug in a USB-C to 3.5mm adapter, or just pair wireless headphones.
The Quest 3S can connect to gaming PCs over USB-C or wirelessly to play more intense VR experiences, giving it strong compatibility with both standalone and PC-based setups. It can also wirelessly stream your gameplay to Chromecast devices, or to AirPlay devices by mirroring the Quest app from an iPhone. If you’re still holding onto the Quest 2, or an original Quest, the Quest 3S is precisely the inexpensive upgrade you’ve been waiting for.
- Fast performance
- Comfortable to wear
- Excellent controllers
- Large app library
- Older Fresnel lenses lead to artifacts
- No headphone jack
- Average mixed reality cameras
Read our full PlayStation VR2 headset review
Storage capacity: 128GB, 256GB | Battery life: 3 hours | Field of view: 110 degrees | Max refresh rate: 120Hz
The PS VR2 is one of the best headset we’ve tested. It offers dual 2K OLED HDR screens, effectively giving you 4K quality. It’s one of the most comfortable headsets around. And it has some genuinely refreshing new features, like eye tracking and headset haptics. (Yes, it can literally rock your noggin.) Best of all, the PS VR2 delivers high-quality virtual reality without the need for a $1,000+ gaming PC – all you need is a PlayStation 5, making its core function tightly focused on console gaming.
Now, our recommendation comes with a few caveats. At $550, the PS VR2 is more expensive than the PS5 itself. And it’s unclear how quickly its game library will fill up. The initial run has only a few exclusives, like Horizon VR and Gran Turismo 7, and we haven’t seen many new titles since then. But it’s still the easiest way to experience high-end VR, and it’s a major upgrade over the original PS VR.
- Excellent OLED displays
- Comfortable fit
- Headset haptics feel immersive
- Sense controllers are solid
- Incredibly high launch price
- Limited new titles
- Long term development is suspect
Read our full Valve Index VR kit review
Storage capacity: N/A | Battery life: 7 hours | Field of view: 108 degrees | Max refresh rate: 120Hz
Valve’s Index kit remains one of the best high-end solutions on the market that provides a truly immersive VR experience. For $999 you get the Index headset, Valve’s finger tracking controllers and two SteamVR base stations. While we’ve seen higher-resolution headsets arrive in the last two years, it’s still a very solid option, with a 1,440 by 1,600 pixel resolution, an eye-watering 144Hz refresh rate and a massive 130-degree field of view. I’d gladly lose a few pixels for the Index’s smoother and more expansive screen, which are still far beyond most other consumer headsets.
As a SteamVR product, the Index requires installing two sensors at opposite corners of your room, which limits its compatibility but enables extremely precise tracking. And of course, it’s wired to your PC. But that clunkiness is worth it for the higher refresh rate and more accurate tracking, especially if you want the deepest possible sense of immersion in a virtual world. Sure, it’s not as easy to use as the Quest 3S, but at this price range, we assume you’ll suffer a bit of inconvenience to get a truly high-quality VR experience.
Valve’s finger tracking controllers are fantastic as well, with a convenient strap that locks them onto your hands. They make playing Half-Life: Alyx feel like a dream. It’s unfortunate that other VR games haven’t fully taken advantage of the finger tracking though.
- 144Hz refresh rate with a 130-degree field of view
- Excellent finger-tracking controllers
- Stellar performance
- Requires installing sensors in your room
- Wired design
Read our full Bigscreen Beyond VR headset review
Storage capacity: N/A | Battery life: 2 hours | Field of view: 102 degrees | Max refresh rate: 90Hz
Essentially an upgrade for the Index, the Beyond is a unique spin on a VR headset from Bigscreen, with a function that prioritizes comfort and visual fidelity over convenience, the developer of a popular app for watching video in VR. It looks more like an oversized pair of goggles than a massive VR headset. The $999 Beyond is the lightest VR option we’ve ever seen (it weighs a tad more than a deck of playing cards), and its Micro-OLED screens are sharp and offer near-perfect contrast. Unlike LCD screens, black can look genuinely black with the Beyond.
The downside, though, is that the Bigscreen Beyond is expensive. It’s $999 on its own if you’re just upgrading a Valve Index setup. If you’re starting from scratch, though, you’ll also need to buy two Steam VR base stations and a pair of Index controllers. That adds up to a whopping $1,578.
The Bigscreen Beyond also requires a custom face cushion, which is built from a 3D facescan when you place your order. Unfortunately, that makes it harder to share than other headsets. There’s also no room for glasses, since it’s so slim. You can buy prescription lens inserts from Bigscreen for an additional fee. And of course, you’ll have to live with a cable tethered to your PC, there’s none of the freedom of the cordless Meta Quest headsets.
For all of its complexity, though, the Bigscreen Beyond delivers the most immersive PC VR experience I’ve ever seen. Since it’s so light, you can easily wear it for hours. Together with its glorious screens, it’s the best option for VR enthusiasts who don’t mind dealing with cost and complexity for true immersion.
- Incredibly light and comfortable
- Sharp and bright Micro-OLED screens
- Works alongside existing Valve Index accessories
- Expensive
- No built-in audio
- Still exhibits artifacting like other VR headsets
How we test VR headsets
I tend to judge candidates for the best VR headset on a few basic criteria: Ergonomics, immersion and controls. It’s not that hard to shove a mobile display into a plastic headset and strap some cheap elastic headbands onto it. But it takes real design skill to craft something that’s well balanced, includes a supportive headstrap, and doesn’t feel uncomfortable after 30 minutes.
My test for ergonomics is fairly simple: How long can I wear a headset until I start to feel discomfort? For the most ergonomic devices, like the Quest 3, that could easily be an hour or two. But heavier PC hardware often feels cumbersome after just 15 minutes — you won’t find those kinds of devices in our list of the best VR headsets.
Immersion, meanwhile, comes from having high resolution screens with fast refresh rates, like a 120Hz refresh rate, helping users feel fully present inside a virtual world. Field of view is also a major element, as it describes how well VR screens can cover what you see. A narrow FOV makes it feel like you’re peering through a pair of binoculars, which limits your sense of “presence.” The best VR headsets aim for a wider field of view, helping virtual environments feel more natural and fully surround you.
A wide field of view, on the other hand, can make it seem like you’re actually flying over the globe in Google Earth. We look at a few popular video games, like Superhot, Beat Saber and Pistol Whip, on every headset to judge how immersed we feel and how enjoyable the gaming experience is overall.
The best controllers fit naturally in your hands and offer accurate tracking. The industry has basically adopted the design of Meta’s excellent touch controllers, but we’re also seeing intriguing leaps forward like Valve’s finger tracking gamepads. We judge controllers based on how easy they are to hold, how they hold up to sweaty gameplay sessions and how easily headsets can track their position in space.
However, it’s important to look at a virtual reality headset’s specs as a whole, including compatibility with your existing hardware and the kind of experiences you plan to use it for. Depending on what you’re looking for in yourVR headset, you’ll want to consider factors like your PC’s CPU and graphics card if you plan to use the headset to play the best VR games. You might not need a super powerful PC, but you should check the minimum requirements for the headset you’re looking to purchase. If you’re not looking to invest in a VR headset solely for gaming, features like head tracking allow you to explore your environment just by simply moving your head in the simulator. This often results in a more immersive and realistic experience.
Other VR headsets we’ve tested
HTC Vive Focus Vision
The Vive Focus Vision is a sleek premium standalone VR headset that can also deliver solid PC VR. But it’s also running aging hardware, it’s riddled with software issues and it’s expensive compared to the Meta Quest 3.
Meta Quest Pro
As great as the Meta Quest 3 is, the Quest 2 is still a very good entry-level VR headset, and it’s worth considering if it’s on sale below its current $250 list price. The Meta Quest Pro, on the the hand, is an expensive boondoggle best ignored.
HTC Vive Pro 2
Outside of Meta’s hardware, the HTC Vive Pro 2 remains a fantastic PC headset, but it’s far more expensive than the Valve Index, which is more comfortable and offers better audio.
VR headset FAQs
How do VR headsets work?
At the most basic level, a VR headset is simply a high quality screen that you’re holding up to your face. For a wired headset, the actual work of rendering a game is done on either a PC or game console. For completely wireless devices, like the Meta Quest 3, that work is handled right on the headset. They rely on either external sensors, or sensors built into the headsets, to map your physical space. While you can use a traditional gamepad or keyboard and mouse in VR, they typically use motion tracking controllers to immerse you in their 3D environments.
What VR headset is best for full body tracking?
While we’re still waiting for a truly great haptic VR bodysuit to arrive, you can still achieve accurate body tracking with most Steam VR-compatible PC headsets. The Valve Index and HTC Vive Pro 2 both rely on room-tracking sensors that can map your body more effectively than the built-in sensors on competitors. You can also add HTC Vive Trackers to wrist and leg straps, as well as belts, for even better coverage. The Meta Quest 3 doesn’t have any easy body tracking solutions, but you can add Vive trackers when it’s plugged into your PC to mimic a Steam VR headset.
Only a few experiences, like VRChat, take advantage of full body tracking at the moment. Currently there aren’t any body tracking solutions for the PlayStation VR and VR2, but we’re intrigued by the company’s Mocopi body trackers, which were really announced in Japan.
What VR headsets are better than Oculus?
Oculus is the previous name for Meta’s VR hardware. Currently, Meta only supports the Quest 3, Quest 3S and Quest Pro, all of which are wireless headsets. As we explain above, PC VR headsets can generally achieve better quality virtual reality, since they rely on more powerful graphics hardware.
What VR headsets work with Xbox?
Currently, Microsoft’s Xbox consoles don’t support any VR headsets.
Recent updates
November 2025: Updated to include the Apple Vision Pro M5.
April 2025: Updated to include review scores for our top picks, where applicable.
November 2024: Added the HTC Vive Focus Vision to the “others we tested” section.
October 2024: Updated our “best cheap VR headset” top pick to be the Meta Quest 3S.
Tech
Xbox Cloud Gaming Ad-Supported Tier: When Does It Start, How Much Will It Cost and More
Xbox Cloud Gaming is one of the key selling points of Xbox Game Pass, and it generally works well. The service lets gamers stream Xbox titles to a wide range of devices, including phones, tablets, handhelds and select smart TVs from Samsung, LG and Hisense. However, following the Xbox Game Pass price increase from November, streaming alone may not be enough to keep some subscribers on board, which is where an ad-supported tier could come into play.
Microsoft confirmed the existence of an ad-supported tier last year but has not shared details on when it will launch or what it will include. New screenshots shared by players suggest the tier may be arriving soon, though questions remain about how it will work and what limitations it may have.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
When will the Xbox Cloud Gaming ad-supported tier launch?
Microsoft hasn’t made an official announcement yet, but it’s expected to roll out sometime this year, according to Windows Central. Last month, some gamers saw a different loading screen for Xbox Cloud Gaming with a message saying “1 hour of ad-supported play time per session,” which would point to the ads coming soon.
looks like ad-supported Xbox Cloud Gaming is coming soon 👀 pic.twitter.com/c8hAERrVB9
— Tom Warren (@tomwarren) January 17, 2026
How much will the Xbox Cloud Gaming ad-supported tier cost?
In October, Microsoft confirmed it was internally testing the ad-supported tier, and at the time, said it would be free. Going by the load screen message I mentioned earlier, there will likely be a limit on how long people can play on the tier and during internal testing, players would have to watch a 2-minute ad.
What games will be available on the ad-supported tier?
Rumors about the internal testing suggested players would only have access to certain games for free, but the question is, which ones? Microsoft has a significant number of games available to stream, whether it’s purchased digital games or those available with an Xbox Game Pass subscription. Microsoft may allow all the digital games in a player’s library to be streamed and might make a few games available for free on a weekly or monthly basis, similar to the Free Play Days games.
Tech
ARCAM Expands Radia Series With New AVAs, Power Amps and Preamp at ISE 2026

ARCAM is pushing the Radia Series beyond two-channel and straight into serious home theater territory. At ISE 2026 in Barcelona, the brand will debut its new Radia AV lineup—AVA15, AVA25, AVA35, and the AVP45 sixteen-channel AV processor, along with PA4 and PA9 power amplifiers.
The three new AVA models are essentially A/V receivers. However, because they do not include traditional AM/FM radio tuners, ARCAM has chosen to label them AVA (Audio/Video Amplifiers) rather than AVR (Audio/Video Receivers). AVP, meanwhile, stands for Audio/Video Preamp or Processor, a term commonly used to describe surround processors that require external power amplification.
The new lineup replaces the AVR11, AVR21, AVR31, and AV41 models introduced in 2022, delivering a full design refresh that brings ARCAM’s home theater components into visual alignment with the existing Radia Series hi-fi models. More importantly, the new AVA and AVP models add support for Dirac Live Active Room Treatment (Dirac ART), a notable step forward over the previous generation, which was limited to Dirac Live and Dirac Bass Control room correction upgrades.
The move positions ARCAM’s new AV components as fully modern cinema hubs, combining Dirac Live room correction with optional Dirac Live Bass Control and Dirac Live Active Room Treatment (ART) upgrades to actively manage low-frequency resonances and reflections. The result is tighter, more controlled bass, improved dialogue clarity, and a wider, more consistent sweet spot—even in asymmetrical or acoustically challenging rooms where traditional correction methods start to show their limits.

What the ARCAM AVA & AVP Models Share
- Dirac: Dirac Live Room Correction is standard, with optional upgrades for Dirac Live Bass Control and Dirac Live Active Room Treatment (ART).
- Dolby Atmos: Industry-standard immersive surround sound support.
- DTS:X: Immersive surround format offering more flexible speaker layout options than Dolby Atmos.
- Remote Control: Included Bluetooth remote operates without line-of-sight requirements.
- App Control: AVA and AVP models work with the ARCAM Radia app for setup, control, Internet Radio, podcasts, and UPnP playback on iOS, Android, and Windows PCs.
- Streaming Support: Apple AirPlay, Google Cast, Spotify Connect, TIDAL Connect, Qobuz Connect, and Roon support are all included, enabling direct streaming from lossless music services on Apple and Android devices.
- Bluetooth Support: Built-in Bluetooth with Snapdragon Sound and Auracast support.
- Front Panel Display: Large, high-resolution front-panel display provides clear system status and metadata visibility from the listening position.
- Form Factor: The AVA15, AVA25, AVA35, and AVP45 all share the same chassis dimensions.
What’s New?
The biggest changes over the previous generation of ARCAM AVRs are the new Radia Series design, added support for Dirac Live Active Room Treatment (ART), and an increase from seven to nine built-in amplified channels. These upgrades, however, come with a notable price increase, and both Dirac Live Bass Control and Dirac Live Active Room Treatment remain paid upgrades rather than standard features.
AVA15
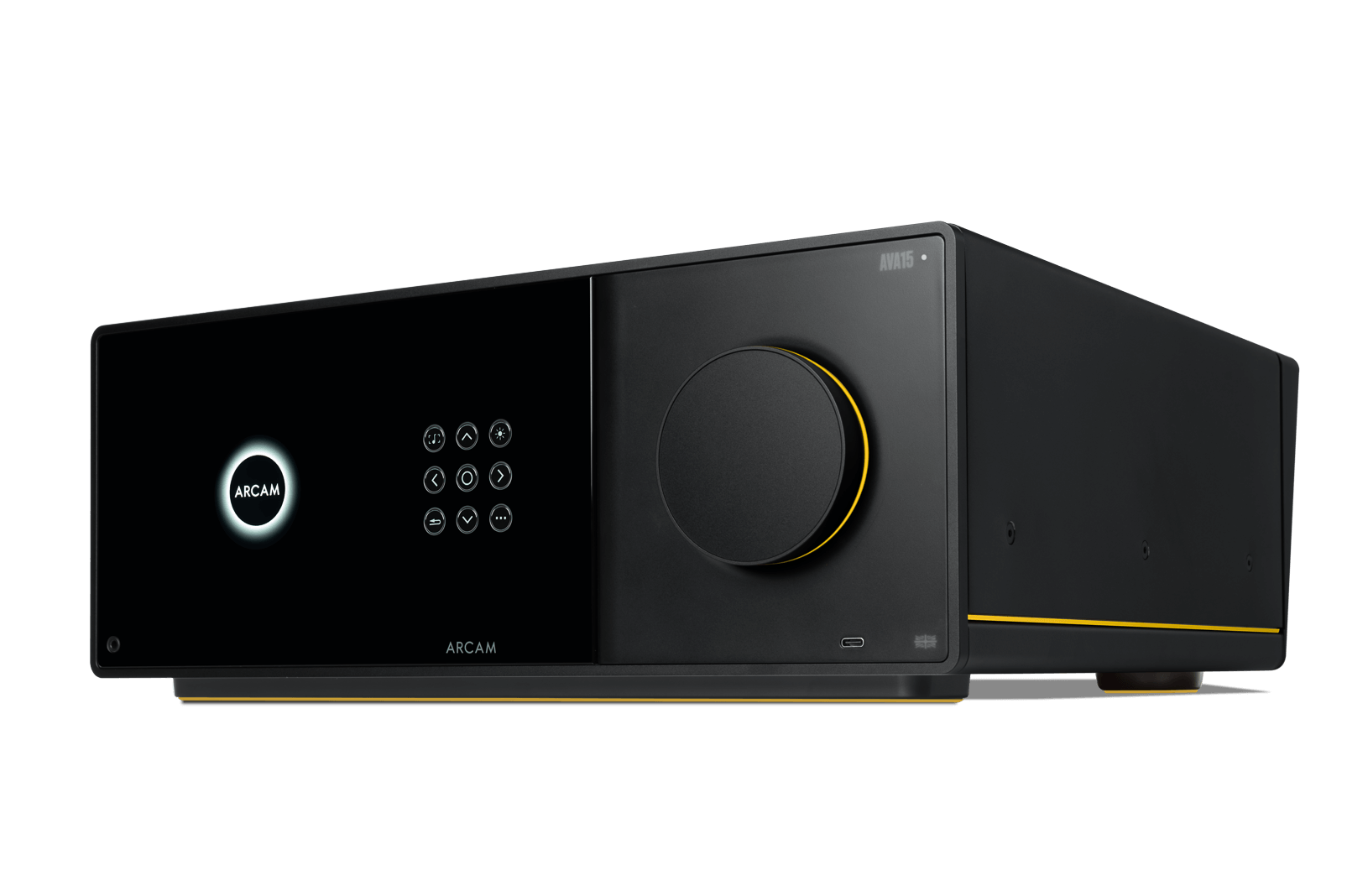

This AVA15 sits in the entry-level position within ARCAM’s lineup, but the feature set is anything but basic. It delivers nine channels of built-in Class D amplification, with the ability to expand to twelve channels through the use of external power amplifiers. This enables 7.1.2 or 5.1.4 speaker configurations using onboard amplification alone, while adding external amplification opens the door to 9.1.2 layouts. Additional system flexibility is available through configurable speaker assignments for extra subwoofers, height, or surround channels. For users seeking flexible Dolby Atmos and DTS:X support without jumping to a full separates setup, the AVA15 covers a lot of ground.

AVA25
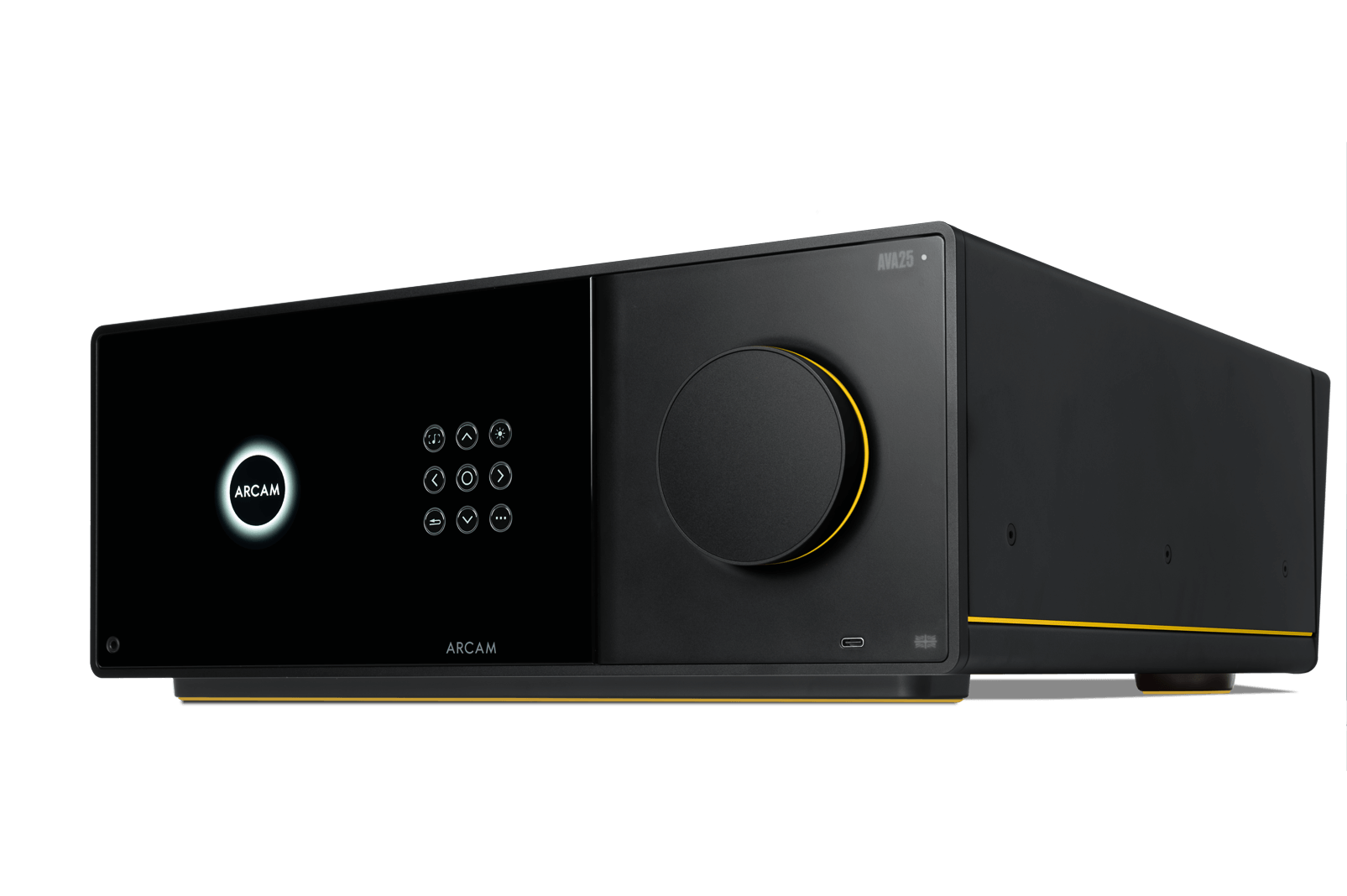

The AVA25 steps things up with more robust amplification and enhanced audio decoding and processing, featuring nine channels of built-in Class A/B amplification rated at 100 watts per channel for greater control in larger rooms or with more demanding loudspeakers. In addition to Dolby Atmos and DTS:X support, it adds Auro-3D surround sound, includes a Zone 2 output for multi-room configurations, and employs a toroidal linear power supply to deliver stable, consistent power under load.

AVA35
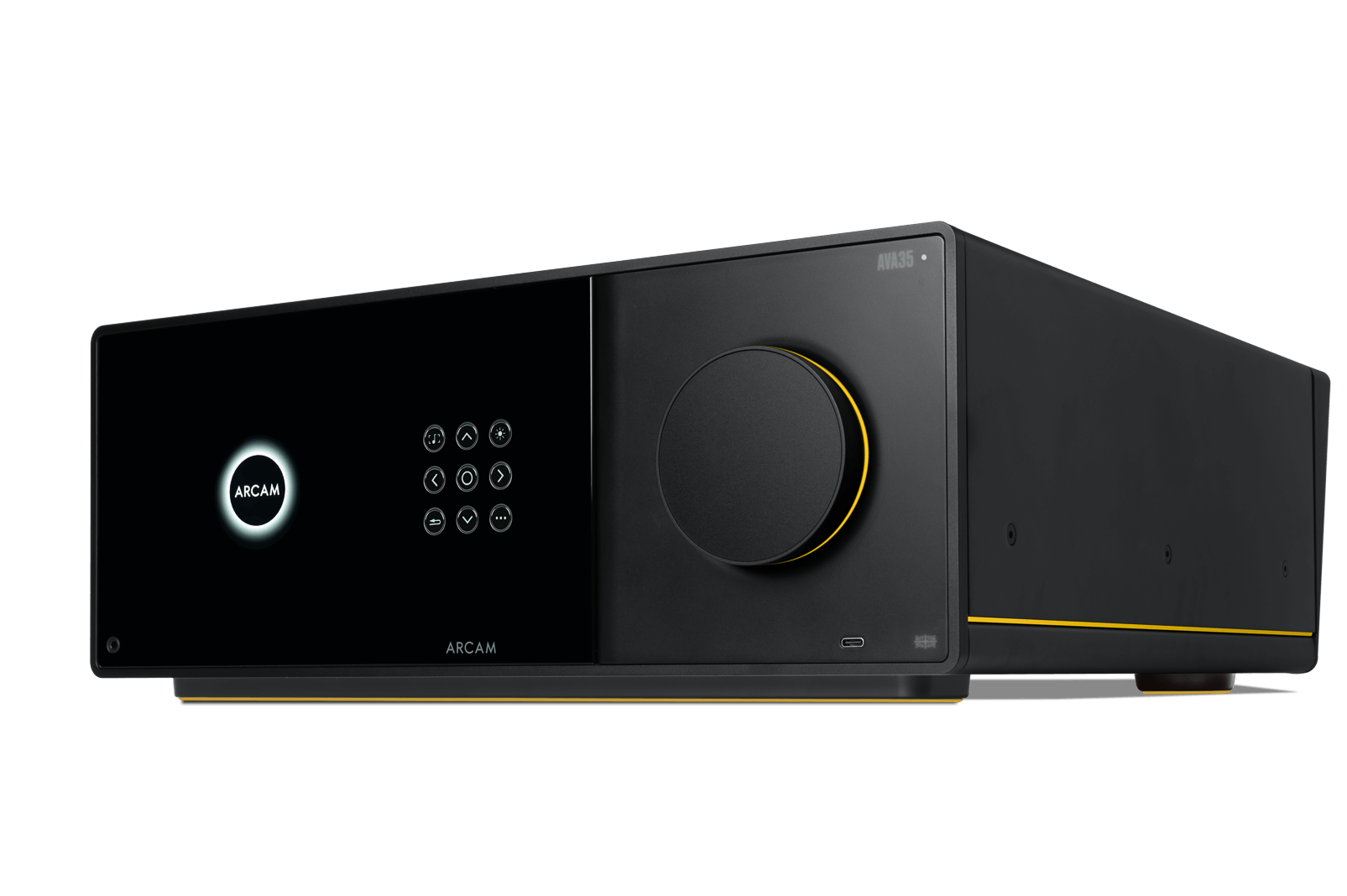

The top-of-the-line AVA35 also delivers nine channels of built-in amplification but moves to Class G topology, which ARCAM claims offers roughly twice the efficiency of the AVA25’s Class A/B design. According to ARCAM, this results in more controlled, precise performance with greater consistency across the full dynamic range. The AVA35 also benefits from an upgraded DAC architecture borrowed from the Radia Series hi-fi lineup, positioning it as the strongest option of the three for two-channel music listening as well as home cinema duties.

AVP45
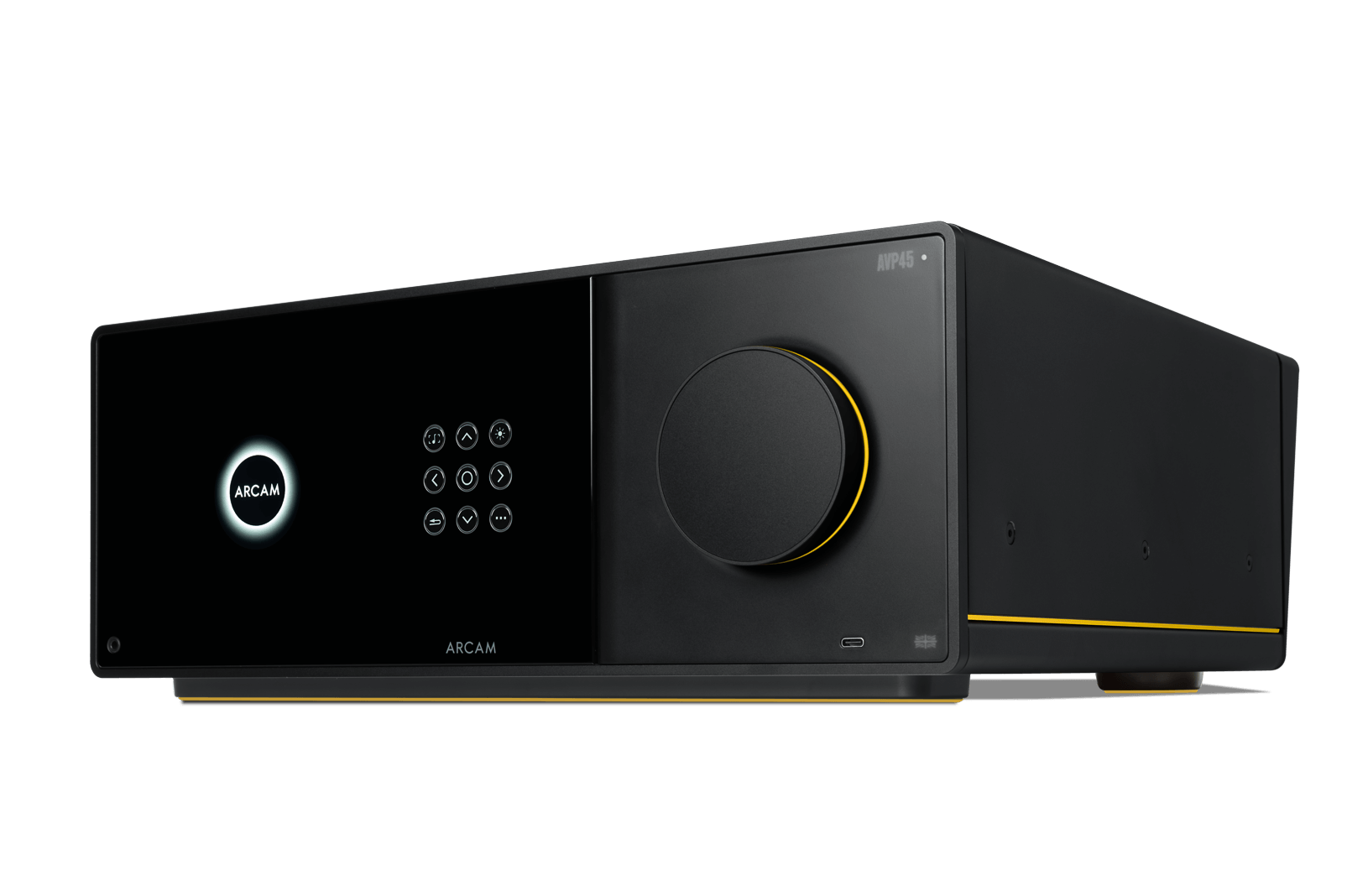

For those who prefer a separates-based approach, the ARCAM AVP45 is designed to serve as the central hub of a home cinema system, offering sixteen unamplified channels of decoding with support for Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, Auro-3D, and IMAX Enhanced. Balanced outputs ensure a clean signal path, while Matrix Channel Assignment enables flexible speaker configurations and includes Zone 2 output for multi-room integration.
As a preamp/processor, the AVP45 requires external power amplification to deliver sound, but that flexibility allows users to choose amplification that best matches their speakers and listening priorities.

PA4
Housed in a slimline 1U chassis, the PA4 power amplifier provides four channels of Class D amplification. It can be paired with any multi-channel preamp/processor but is specifically designed to expand ARCAM Radia AV systems. The PA4 can be used to add additional channels to the AVA15, AVA25, and AVA35, or to offload the most demanding power requirements to the front main channels in a home theater setup.
PA9
Designed to partner with the AVP45 processor, the PA9 provides nine channels of Class D amplification, delivering controlled, effortless power across all channels. Built for high-channel-count immersive systems, the PA9 allows Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, and Auro-3D setups to perform at their best when paired with a dedicated processor-based configuration.
Comparison
| AVA15 | AVA25 | AVA35 | AVP45 | |
| Product Type | Audio/Video Amplifier | Audio/Video Amplifier | Audio/Video Amplifier | Audio/Video Processor |
| Price | $4,499.95 | $5,499.95 | $6,999.95 | $5,999.95 |
| Amplified Channels | 9 | 9 | 9 | N/A |
| Channels/Pre-outs | 12/RCA | 16/RCA | 16/RCA | 16/RCA/XLR |
| Reassignable Channels | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Amplifier Type | Class D | Class AB | Class G | N/A |
| Power | 75W (20Hz – 20kHz, 9 channels driven, 8 ohms) | 100W (20Hz – 20kHz, 9 channels driven, 8 ohms) | 100W (20Hz – 20kHz, 9 channels driven, 8 ohms) | None |
| HDMI Inputs/Outputs | 7/2 | 7/2 | 7/2 | 7/2 |
| HDR Support | HDR10 HDR10+ HDR10+ Gaming Dolby Vision HLG |
HDR10 HDR10+ HDR10+ Gaming Dolby Vision HLG |
HDR10 HDR10+ HDR10+ Gaming Dolby Vision HLG |
HDR10 HDR10+ HDR10+ Gaming Dolby Vision HLG |
| Surround Sound Support | Dolby Atmos Dolby TrueHD Dolby Atmos Height Virtualization Dolby Surround DTS:X DTS HD Master Audio DTS Neural:X DTS Virtual:X MPEG H |
Dolby Atmos Dolby TrueHD Dolby Atmos Height Virtualization Dolby Surround DTS:X DTS HD Master Audio DTS Neural:X DTS Virtual:X MPEG H IMAX Enhanced Auro 3D |
Dolby Atmos Dolby TrueHD Dolby Atmos Height Virtualization Dolby Surround DTS:X DTS HD Master Audio MPEG H DTS Neural:X DTS Virtual:X Auro 3D |
Dolby Atmos Dolby TrueHD Dolby Atmos Height Virtualization Dolby Surround DTS:X DTS HD Master Audio DTS Neural:X DTS Virtual:X MPEG H Auro 3D |
| App Support | ARCAM Radia Control | ARCAM Radia Control | ARCAM Radia Control | ARCAM Radia Control |
| Bluetooth Version | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.4 |
The Competition
There’s no avoiding the fact that the new Radia Home Theater lineup is expensive, with pricing ranging from $4,500 to $7,000. That said, it’s largely in line with competing high-end options, including Denon’s $5,200 AVR-A10H and $7,200 AVR-A1H, as well as the $4,700 Marantz Cinema 30. On the AV preamp/processor side, the AVP45 faces direct competition from Marantz’s $8,000 AV10, $6,000 AV20, and $4,000 AV30.
The Bottom Line
ARCAM’s decision to bring Dirac Live Active Room Treatment to the Radia AV lineup is the defining upgrade. This is not a checkbox feature or marketing noise—it’s a real performance tool that elevates the AVA15, AVA25, AVA35, and AVP45 into serious home cinema territory for listeners who understand that the room is part of the system. What’s new is substantial: the Radia design language, higher channel counts, optional Dirac ART, Bluetooth with Snapdragon Sound and Auracast, HDR10+ Gaming support, and streamlined setup and control via the Radia Control app. What’s missing is equally clear: there’s no AM/FM radio tuner, and Dirac’s advanced processing options remain paid upgrades.
This lineup is aimed at buyers moving beyond mass-market AVRs—people building modern, immersive systems who care about bass control, timing, and consistency across multiple seats, not just a single sweet spot. With the simultaneous launch of the new ARCAM Radia Series loudspeakers at ISE 2026, ARCAM is making a coordinated push into high-performance home theater, offering a complete ecosystem designed for listeners who expect precision, not compromises.
Pricing & Availability
The ARCAM Radia AVA and AVP models will be available from authorized ARCAM dealers from Q3 2026. The PA amplifiers are scheduled for Q4 2026.
- ARCAM Radia AVA15: £2,599 / €2,999 / $4,499.95
- ARCAM Radia AVA25: £4,499 / €4,999 / $5,499.95
- ARCAM Radia AVA35: £5,999 / €6,999 / $6,999.95
- ARCAM Radia AVP45: £5,299 / €5,999 / $5,999.95
- ARCAM Radia PA4: £899 / €999 / $1,499.95
- ARCAM Radia PA9: £3,499 / €3,999 / $4,999.95
Related Reading:
Tech
Turns Out They Didn’t Really Want You To Bring Your Whole Self To Work

from the incentives-are-everything dept
For years, we watched Silicon Valley executives perform elaborate corporate theater about “values” and “belonging” and “bringing your whole self to work.” If you were skeptical that any of that was real, well, congrats.
Aaron Zamost, a longtime tech communications exec, has a piece in the NY Times that should be required reading for anyone trying to understand the tech industry’s sudden, conspicuous rightward lurch. His argument is refreshingly blunt: this isn’t about ideology. It never was. It’s about leverage.
There are many theories about Silicon Valley’s swift, and very conspicuous, rightward turn. Tech leaders course-corrected from an overly permissive era. The Trump administration demands fealty in exchange for critical regulatory favors. Mr. Trump’s re-election reshaped the national climate and reoriented the values of tech leadership.
Each of these explanations is convenient, but none are correct. I’ve worked in tech for 20 years, across both Big Tech and venture-backed start-ups, and I can tell you the truth is much more mundane. Silicon Valley’s chief executives have always been driven by economics, not ideology. As Michael Corleone put it: It’s not personal — it’s strictly business.
This tracks with everything we’ve observed about how these companies actually operate. The notion that tech CEOs underwent some kind of ideological awakening—either leftward in 2020 or rightward in 2024—always gave them way too much credit for having coherent beliefs about anything other than what would help them with Wall Street in the long run.
What actually happened? This is where my undergrad degree in labor relations actually comes in handy: because, as Aaron notes: labor economics happened. When you’re in a vicious war for talent and engineers have infinite options, you do whatever it takes to keep them happy. And if that means mental health stipends and letting employees “bring their whole selves to work,” then that’s what you do. Not because you believe in it. Because replacing a top engineer costs a fortune.
Big tech companies and growing start-ups are in constant, vicious competition with one another to hire and retain the best employees, especially in product and engineering roles. When these companies are in hypergrowth mode, and particularly when the job market is tight, hiring top talent can be nothing short of a matter of survival. And they are fishing in a largely progressive pond: Political donation data shows tech employees are predominantly Democratic-leaning.
The late 2010s and early 2020s were a particularly intense period in the industry’s war for talent. Hiring exploded. Meta nearly doubled to 86,000 employees in 2022 from approximately 45,000 three years earlier. Amazon added over 400,000 employees in 2020 alone. As Silicon Valley recruiting teams relentlessly poached one another’s people, tech labor had infinite choices and all the leverage.
So what did companies do when a generous compensation package was no longer enough to win over candidates? They instead sold a sense of belonging. Amid fierce competition, many companies realized that encouraging workers to bring their perspectives and passions to the office could increase their loyalty and their willingness to work hard. That, in turn, served the real financial objective: higher job acceptance rates, lower employee attrition and faster growth.
So when tech companies said all those nice things about diversity and belonging and employee voice, it was merely a calculated business decision to attract and retain workers in a brutally competitive labor market. The “whole self” culture wasn’t a political movement. It was, as Zamost puts it, “a labor-market artifact where talent war conditions made employee empowerment economically rational.”
And then the market shifted.
Growth slowed. Interest rates rose. Suddenly companies didn’t need to compete for labor at any cost. And the moment that leverage flipped back to management, all those “values” evaporated faster than you can say “return to office mandate.”
It’s worth asking whether many tech companies’ professed values were ever real. We’ve seen leaders who built their reputations on defying authority become foot soldiers for the administration. The same elasticity informs their rollback of the culture they once championed.
Four years ago, Marc Benioff, the Salesforce boss, said, “Office mandates are never going to work.” He now works from home in Hawaii much of the time while most of his employees are required to be in-office three to five days a week. In 2020, Mark Zuckerberg announced that Facebook would donate $10 million to groups working on racial justice. Last year he rolled back Meta’s D.E.I. programs. Did his values change? Or did the power dynamics?
The answer, obviously, is the power dynamics. And this isn’t a particularly controversial thing to say. The thing that gets lost in all the discourse about tech’s “MAGA turn” is how utterly banal the explanation actually is. It’s got nothing to do with ideology. These are business actors responding to incentives. When employees had leverage, executives catered to them. When executives got leverage back, they stopped.
Zamost makes an important point that may get buried by the rest of the article though: the response to all this from tech workers hasn’t been outrage. It’s been detachment. And that’s going to boomerang back on these tech leaders.
This about-face will prove counterproductive over the long term. In my conversations with tech employees, the result hasn’t been anger at hypocrisy so much as detachment — a loss of tribal loyalty (fewer T-shirts emblazoned with tech company logos), and a clearer understanding of the limits of corporate idealism.
This is the part that should worry these executives. They’ve revealed the game. They’ve shown that all the talk about values and culture and belonging was contingent on market conditions. And employees noticed. They’re not mad—they’re just not going to forget.
And, yes, the cynical among you will say “come on, no one ever believed these companies were serious” and perhaps that’s true. But there was a time when Silicon Valley employees really liked where they were working and really felt like, as a team, they were achieving stuff.
That’s gone.
Labor markets are cyclical. At some point, these companies will need to compete for talent again. And when they do, they’re going to discover that the employees they’re trying to recruit remember what happened. They remember that the “values” disappeared the moment they became inconvenient. They remember which executives lined up behind Trump. They remember the layoffs and the return-to-office mandates and the sudden silence when it actually mattered.
The recent reassertion of managerial prerogative was only possible in an economic environment where top executives could flex their muscles like a boss. It won’t last forever. When labor is scarce again, many of these companies will rediscover the values they abandoned. The question is whether employees will forget just as quickly.
The optimistic read is that employees won’t forget. That this period will serve as a permanent reminder that corporate values are, at best, marketing. That the next generation of tech workers will enter these companies with clear eyes about what the relationship actually is: transactional.
The pessimistic read is that Zamost is right to pose it as a question. Because companies have been pulling this bait-and-switch for decades, and workers keep falling for it. Maybe the cycle just repeats.
Either way, the lesson isn’t really about politics. It’s about understanding what these companies actually are. They’re not movements. They’re not communities. They’re not families. They’re businesses that will say whatever they need to say to achieve their business objectives. And right now, the (somewhat short-sighted) business objective is staying in the good graces of an administration that has made clear it rewards loyalty and punishes dissent.
So no, they didn’t really want you to bring your whole self to work. They wanted you to bring the parts that were useful to them, for exactly as long as it was useful to them. The “whole self” thing was just the price of admission in a seller’s market. Now that it’s a buyer’s market, they’d prefer you just shut up and (use AI to write) code.
The irony is that employees who actually believe in what they’re building tend to build better things. These executives may have just taught an entire generation of workers that the relationship is purely transactional. When the labor market tightens again—and it will—they might find that lesson stuck.
Filed Under: hiring, labor economics, politics, retention, silicon valley, values
Tech
Onkyo TX-RZ30 9.2-Channel A/V Receiver Review: Sound Matters

Growing up in the 80s, everybody wanted a stereo system. The older guys called it a “HiFi” but we kids just wanted something that could play our records (and eventually tapes and CDs) loud and clear. That system usually included a receiver or integrated amp, a pair of speakers (the bigger, the better) and a turntable.
Over time, listening to music migrated to headphones and earbuds. Those who wanted to listen to music out loud maybe bought wireless speakers and those who were serious about it might have invested in a whole home music system like a Sonos.
TVs got bigger and cheaper while picture quality began to rival – or even exceed – that of local movie theaters. But TV sound really never improved that much. So the soundbar market was born for those who wanted better sound from movies and TV shows. Soundbars can play music too, of course, but mostly they just serve the singular purpose of making terrible-sounding TVs sound less terrible.
Receivers never really went away. They just faded into the background.

Then a global pandemic happened. People stopped going out to dinner or to the movies, to concerts or sporting events. They stopped traveling, too, or at least cut way back. Suddenly people were spending a lot more time at home and found they had a little extra disposable income. Now instead of going out to the movies or concerts, they were watching movies – and concerts – and listening to more music at home. And that’s when many noticed that their little wireless speakers and puny soundbars didn’t actually sound that great.
Since then, receivers have made a comeback. In 2020-2021, many retailers couldn’t keep popular models in stock as demand exceeded supply. Companies who hadn’t released new models in years started doing exactly that. Brands like Denon, Marantz and Sony all began gearing up production and releasing new models. But this surge in popularity didn’t save Onkyo. On May 13, 2022, Onkyo, one of the top Japanese HiFi brands since 1946, declared bankruptcy. It was a sad day for audiophiles and home theater aficionados.
But dry those eyes, dear readers, because Premium Audio Company, a joint venture between VOXX International and Sharp, stepped in to rescue Onkyo, Integra and Pioneer from oblivion and obscurity. Last year, VOXX was itself acquired by Gentex, and, sadly, Pioneer exited the A/V receiver market as a result. However, Onkyo is still going strong with several new models introduced in the past three years. The Onkyo TX-RZ30 is the latest model from this revitalized brand.
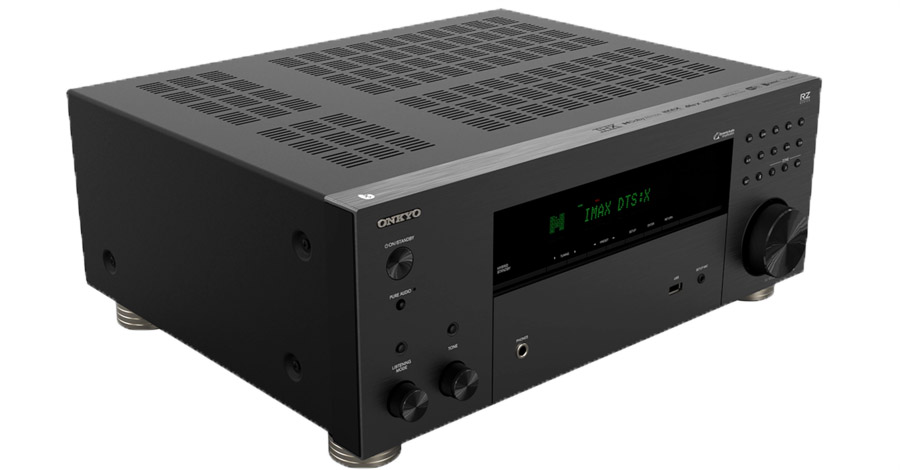

What Is It?
The Onkyo TX-RZ30 is a home theater receiver or audio/video receiver (AVR). As such, it includes a built-in AM/FM tuner, audio and video decoding, processing and switching, and built-in power amplifiers to drive a multi-channel fully immersive surround sound speaker system. The RZ30 specifically can drive up to nine channels (nine speakers) plus two powered subwoofers with a power rating of 100 Watts/Channel. This means it can power a 5.2.4-channel or 7.2.2-channel Dolby Atmos or DTS:X immersive surround system. Of course, you may not need this many speakers in your specific room, but it’s nice to have the option to expand and upgrade over time. If your system needs are smaller, then you can use the built-in amps to power speakers in a second or even third zone or room.
In addition to the essentials like Dolby Atmos, multi-channel PCM and DTS:X decoding, the TX-RZ30 is also IMAX-Enhanced Certified which means it can reproduced the full visual and audio bandwidth of IMAX Enhanced content on Blu-ray Disc, UHD Blu-ray and on streaming services such as Disney+ and Sony Pictures Core. The RZ30 also features full-bandwidth Dirac Live optimization and room correction, built-in at no additional charge. This advanced speaker calibration software adjusts speakers in both the level (magnitude) and time (phase) domains so they’ll provide the optimum performance in your specific room. It used to be that Dirac Live was only available in very high end gear or incurred a separate fee, but we’re starting to see this in more budget-friendly products, including the RZ30.
The RZ30 lacks decoding for Sony 360 Reality Audio, MPEG-H immersive audio and Auro-3D. While none of these codecs are currently that widely used, it’s worth mentioning their lack in case you’re looking for any of these formats in a receiver.
Originally priced at $1,199 (MSRP), but recently lowered to $999, the RZ30 is currently the “entry-level” receiver in Onkyo’s high-end RZ line-up. The “RZ” doesn’t seem to stand for anything official, so I’m going to call it the “Reference Zeries” because it sounds fancy, and maybe slightly French. It joins the RZ70 introduced in 2023 and the RZ50, introduced in 2021. You can find out more about the differences among these models (including a comparison chart) in our earlier news post about the RZ30.
For music, the RZ30 supports high resolution audio playback up to 24-bit/192kHz. Digital audio file format compatibility includes MP3, WMA, WAV, MPEG-4/AAC, FLAC, and ALAC. The RZ30 also includes several streaming music services built-in, including Apple Music, Amazon Music HD, Spotify Connect, Tidal, Deezer, Pandora and Tune-In. Additional third party audio networking integration includes DTS Play-Fi support, “Works with Sonos” certification and “Roon ready” certification. Wireless connectivity for the RZ30 includes Bluetooth (aptX HD), AirPlay 2, Chromecast Built-in, and Wi-Fi networking. An ethernet port is also included for those who prefer a hard-wired network connection.
Weighing in at 11.5 kilograms (about 25.4 pounds), the RZ30 feels substantial, and a peek inside its cover shows some pretty solid components including beefy transformers and thick aluminum heat sinks. The unit features Class A/B amplification which means it runs a bit warmer than Class D amps would, but it never got excessively warm during our testing. We sure to leave it some room to breathe in your A/V cabinet and it should be fine.
The Ins and Outs
The TX-RZ30 includes six HDMI inputs and two HDMI outputs. It supports HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) and eARC and provides HDMI 2.1a and HDCP 2.3 compatibility. It can handle gaming and other video source devices at 4K/120Hz or 8K/60Hz with up to 40 Gbps transfer rate, VRR (Variable Refresh Rate), ALLM (Auto Low Latency Mode), QFT (Quick Frame Transport), SBTM (Source-based Tone Mapping) and Dynamic HDR. Pass-through support is provided for virtually all the HDR formats, including Dolby Vision, HDR10+, HDR10 and HLG (Hybrid Log Gamma).

The RZ30 supports legacy gear, too with one component video, two composite video, six analog audio, one coax digital audio, one fiberoptic digital audio and one USB input. Analog video sources are converted to digital for output over the HDMI port. Your old laserdisc player and VHS deck are welcome here. There’s also a phono input for moving magnet cartridges, in case you’re still rocking that vintage (or not so vintage) turntable.
Outputs include the afore-mentioned two HDMI outputs, speaker level outputs for up to nine speakers, two independently adjustable subwoofer outputs, nine channels of preamp out (in case you want to use separate power amps) and a quarter-inch analog headphone output.
To operate the myriad features that the RZ30 has to offer, Onkyo has provided several control options, including a standard remote control, a smartphone app, voice control via Google Assistant and Siri, and third-party CI control via an RS232 connection. Home automation and control standards like Control4, Crestron, Savant, URC, Elan and RTI are all supported.
All things considered, the RZ30 certainly lives up to its “smart receiver” name and provides enough features, inputs, outputs, decoders, processing and third party integration options to satisfy the needs of even the most demanding consumers.
The Set-Up
A receiver does take a bit more effort to install than most soundbars, but the Onkyo set-up wizard does a decent job walking you through it. There are so many speaker configuration options that you will want to pay attention to plug each speaker into the appropriate output. Also, be sure to keep phase (black and red) consistent for all speakers. Every speaker wire comes with a marked side and an unmarked side in the pair. I usually use the marked side for red (+) and the unmarked side for black (-) on both the receiver and speaker ends of each wire.
If you make any mistakes connecting the speakers, you may find out about phase errors or incorrectly attached speakers during the calibration. If you make phase mistakes, you will still get sound from all speakers but it will affect imaging and tonal balance across the system as some speakers will be canceling each other out at some frequencies.

With the speakers and subwoofers connected, it’s time to connect your TV to the receiver using a high speed HDMI cable. Use the HDMI ports labeled “eARC” or “ARC” on both the TV and receiver for this connection, if possible. Also, connect any analog source components like a turntable or cassette deck to the receiver. With HDMI eARC, you can connect any video components to the TV and the TV will pass the audio (even lossless multi-channel PCM, Dolby Atmos or DTS:X audio) to the receiver for processing. An exception would be if you’re using a projector or a TV with the older ARC type of HDMI connection. In this case, it’s probably best to connect all components (digital, analog, video and audio) directly to the receiver and just send the video signal to your TV or projector over the HDMI output.
Corrections Corner
Once all the connections are made, it’s time for some corrections. And no, I’m not talking about factual errors or typos (please!). I mean room correction of course. Most receivers come with some sort of speaker calibration routine (with Audyssey being the most popular in AV Receivers). Onkyo offers its own home-grown calibration software called “AccuEQ Room Calibration.” This can take care of the basics like adjusting EQ, crossover points and distance settings for the speakers. But the RZ30 includes Dirac Live, a much more advanced software package which compensates for anomalies in the room itself which can impact the overall sound.
Dirac Live full bandwidth control handles adjustments to all speakers. If you opt for a second subwoofer for deeper, more extended bass response and better bass uniformity throughout your listening room, then you may want to purchase the optional DIRAC Live Bass Control upgrade, which is an additional $299, directly from DIRAC. The RZ-30 is one of most affordable receivers on the market that can even handle Dirac Bass Control and which includes dual independently adjustable subwoofer outputs.
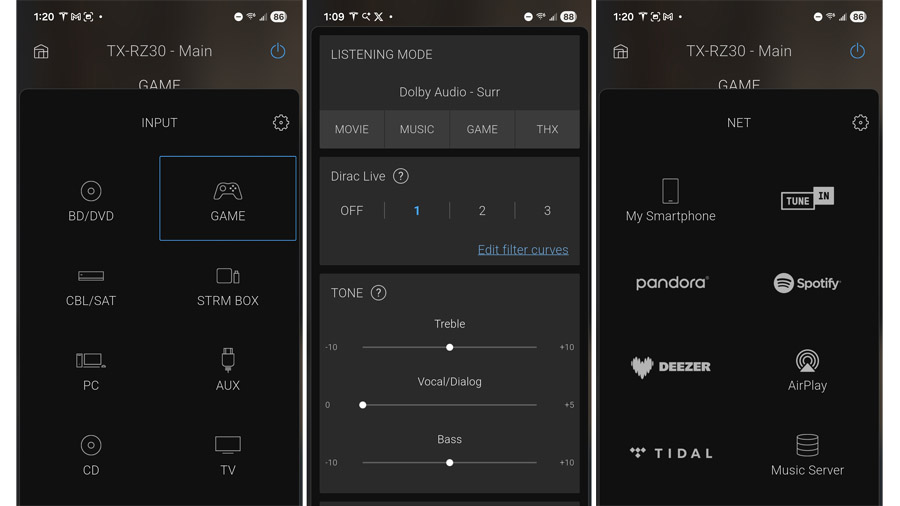
To perform Dirac room correction, you’ll need to install the Onkyo Controller app, available in Apple’s App Store and in the Google Play Store. Plug in the included calibration mic to the receiver’s front panel, then click through the instructions in the app. You can perform a basic correction using three measurement points or a full correction using nine measurement points. I opted for the basic 3-point correction, which took less than 30 minutes to complete. I found that Dirac was a bit more sensitive to ambient noise and subwoofer level settings than its competitor, Audyssey, so we had to restart the calibration a couple of times. But once it successfully completed, the results were obvious: better imaging specificity, clearer, more natural sounding dialog, more natural tonal balance overall and smoother transitions from main speakers to the powered subwoofer.
If you prefer, you can also perform Dirac Live room correction on a laptop by downloading the Dirac software and plugging in a compatible microphone like a miniDSP UMIK-1. Doing DIRAC calibration this way can be more accurate and effective as each miniDSP mic has its own unique measurement signature which you identify to Dirac so it can compensate. After performing the calibration, you can then download these Dirac profiles from your laptop to the RZ30 to apply the profile or profiles to the receiver.
Listening Notes
I evaluated the Onkyo TX-RZ30 with a 5.1.4-channel Klipsch reference speaker system I had previously been using with a Denon AVR-X3800H receiver. I hit the system with dozens of my favorite movie clips as well as several music tracks mixed in Dolby Atmos immersive surround as well as some stereo music tracks. I did some listening pre-calibration, but with the big improvement added with DIRAC Live, I left that applied for the remainder of testing.

The RZ30 has a wealth of different listening options, accessible by hitting the “Music” and “Movie/TV” buttons on the remote. Want to listen to your music in Dolby Surround in an orchestral concert hall? No problem! For stereo material, you can choose between Dolby Surround or DTS: Virtual:X to expand the soundstage to fill the room, or select “Direct” or “Stereo” modes for a more purist 2-channel approach. There’s also an “All Channel Stereo” mode if you want to fill a room with background music like for a party or gathering. I found Dolby Surround to work pretty well to expand the soundstage on most stereo music.
Dolby Atmos and DTS:X content in particular sounded wonderfully immersive through the RZ30. Sound objects that traveled around in space moved seamlessly from front to back, side to side and top to bottom. The Dolby Atmos mix of KX5/Deadmau5 “Alive” presented a huge soundstage and the rhythmic synth snare drum roll around 4 minutes into the song presented a nicely defined circle as it moved all around the room. And when the chorus of the Dolby Atmos mix of Elton John’s “Rocket Man” came along, the room came alive with instruments and vocals placed in a virtual dome that expanded beyond the borders of the room. This is an extremely effective mix for those who like to be brought inside the music mix and it was very well represented on the RZ30.
Moving onto IMAX content, the RZ30, with its IMAX Enhanced certification, is able to identify IMAX Enhanced DTS:X content from UHD Blu-ray Disc and from streaming services such as Disney+ and Sony Pictures Core, decode the DTS:X soundtrack and apply the IMAX EQ and processing. This gives IMAX movies a more theatrical sound as it uses the far-field IMAX cinematic mix, which results in more impactful bass, extended dynamic range and, in some cases, more pronounced height effects.
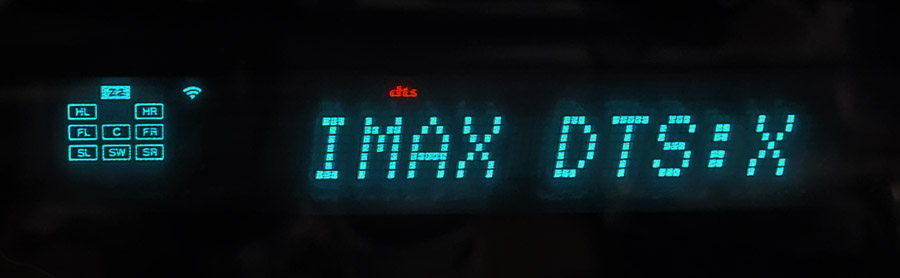
The RZ30 delivers these IMAX Enhanced DTS:X soundtracks as expected showing IMAX DTS:X on the front panel display. And the sound on the few titles I was able to test was quite bombastic with deep rumbling bass and enveloping height effects. “Zombieland: Double Tap” is one of the few UHD Blu-ray Discs with IMAX Enhanced certification and a lossless DTS:X soundtrack. Both the RV zombie attack scene and the final battle scene provided great examples of DTS:X IMAX Enhanced audio with gunshots, shuffling zombie growls and other sonic mayhem exploding into the room. And over on Disney+, the “Queen Rock Montreal” IMAX film had a raw power and immediacy in IMAX Enhanced DTS:X making the viewer feel like he (or she) was there in the audience. Marvel IMAX Enhanced titles like “The Fantastic 4” and “Guardians of the Galaxy Volume 3” also sounded dynamic and engaging with their IMAX/DTS:X soundtracks activated.
Sadly, actually finding this IMAX Enhanced content with a DTS:X soundtrack is tricky. There are only a handful of IMAX Enhanced titles on UHD Blu-ray Disc, and only two streaming services — Disney+ and Sony Picture Core — can deliver the necessary DTS:X soundtracks. And DTS:X support on Disney+ is currently limited to select TVs from Hisense, TCL and Sony. Though we were happy to see that the Disney+ app on the Valerion Max projector’s Google TV OS, also supports DTS:X/IMAX Enhanced audio output. This is the first projector we’ve tested that supports the feature.
Comparisons
The Denon AVR-X3800H ($1,699) offers similar features and functionality to the Onkyo TX-RZ30 ($999). They both include nine channels of amplification, but the Denon can be expanded to 11 channels by connecting an external 2-channel amplifier and using the preamp outputs. The Denon also offers Dirac Room Correction, but at an additional cost (ranging from $259 for the basic limited bandwidth DIRAC Live version to $799 for a full license with Bass Control and ART included). To get the same level of Dirac room correction on the Denon vs. the Onkyo would require spending an additional $349 on the full bandwidth Dirac version on the Denon, bringing its price (with Dirac) up to $2048 (MSRP), roughly twice the price of the Onkyo TX-RZ30. However, the 3800H includes four independently adjustable subwoofer outputs compared to the Onkyo TX-RZ30’s two so it can work better in larger or problematic rooms where more subwoofers are preferred.
Sound quality-wise, the Denon 3800H and Onkyo RZ30 are not far off. Both offer excellent dynamics and cohesiveness of sound. The Denon may have a slight warmth compared to the RZ30’s more neutral sonic signature but both can create an outstanding immersive soundstage, particularly on Dolby Atmos and DTS:X content, particularly after DIRAC calibration and room correction. The Denon receiver does add decoding for Sony 360 Reality Audio, MPEG-H immersive sound and Auro 3D, none of which are particularly popular but which may appeal to those who want universal format support.
Compared to the similarly priced Denon AVR-X2800H ($1,199), the Onkyo TX-RZ30 represents a clear upgrade with more channels, more features, a full set of preamp outputs, dual independent subwoofer outputs and Dirac Live room correction.
Onkyo’s own TX-NR7100 may be a more likely competitor to the TX-RZ30 as it also includes nine channels of amplification and has Dirac Live full bandwidth room correction built-in. However, the 7100 does not offer preamp outputs so you can’t upgrade the on-board amplification. Also, the two subwoofer outputs on the NR7100 are identical and not independently adjustable and the 7100 has no option to add Dirac Bass Control. Still, at a street price now of around $750, the TX-NR7100 offers a very compelling value proposition for a 9.2-channel receiver and offers a fine choice if you’re on a more limited budget.

The Bottom Line
Onkyo’s TX-RZ30 is built to satisfy even the pickiest audiophiles and home theater aficionados with a strong feature set, excellent sonics and best-in-class Dirac Live room correction. It may not offer the upgradability of the Denon AVR-X3800H but it sells for a significantly lower price, particularly when you consider that the Onkyo includes Dirac Live full bandwidth room correction, while that option adds $349 to the cost of the Denon. Its only real competition is from Onkyo itself, in the TX-NR7100, but that unit is less flexible, older and less upgradeable.
If you’re looking for a solid 9-channel A/V receiver with excellent sound quality, best-in-class Dirac Live room correction built-in and a path toward upgrade, the Onkyo TX-RZ30 should definitely be on your short list.
Pros:
- Full bandwidth Dirac Live room correction included, with upgrade to Direct Live Bass Control available
- 9 channels of power with full set of preamp outputs for use with external amps
- Intuitive operation
- Transparent, neutral sound
- Dual independently adjustable subwoofer outputs
- A plethora of analog audio and video inputs including phono input, component and composite video
Cons:
- Cannot be expanded beyond nine channels (maxes out at 5.2.4 or 7.2.2)
- Lacks Sony 360RA, MPEG-H and Auro 3D audio decoding and processing
- No option to upgrade to DIRAC ART
- Basic remote lacks backlighting
Where to Buy
Onkyo TX-RZ30 9-channel AV Receiver with Dirac Live on Amazon.com or Crutchfield.
Related Reading:
Tech
6 Must-Have WordPress Backup Plugins for Website Safety


Have you ever woken up in a cold sweat, panicking that your website is gone overnight? Whether a technical error, a deliberate attack, or your server gave up on itself, it happens more than you think. Just imagine all your time and hard work poured into your site, only for it to disappear within seconds. Quite terrifying, no? That’s why having a solid backup plan is not just an option but a must-have.
The good news is that WordPress offers several backup and recovery plugins to protect your site. These plugins act as digital guardians for your content making sure you can recover from any unexpected disasters. In this post, we’ll explore the top WordPress backup plugins that simplify site recovery. Let’s begin strengthening your online presence!
Top 6 WordPress Backup Plugins to Secure Your Site
1. UpdraftPlus
UpdraftPlus is a popular WordPress backup plugin used by millions. It keeps your website safe from accidental deletions, server problems, and hacking. Its easy-to-use interface makes backing up and restoring your site a breeze.
You can manually or schedule backup on your entire WordPress site with several storage options, including but not limited to, Google Drive, Dropbox, and others. The Premium version gives you a little more, with features like incremental backups, widely varying storage choices, automatic backups before updates, and elaborate reports. It’s an excellent choice for keeping your WordPress site secure.
Key Features:
- Choose to back up your site hourly, daily, weekly, or set your own custom schedule.
- Quickly restore your site directly from the WordPress control panel.
- Save only the changes made since the last backup, reducing server load.
- Save your backups to Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon cloud, and more.
Pros:
- Very easy to use, in fact, even beginners can handle it.
- There are various ways in which you can do remote storage backups, for example, Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon S3.
Cons:
- Certain advanced features are exclusively accessible in the Premium version.
Pricing: You can get this plugin for free. Its premium version starts from $70 annually.
2. Duplicator
Duplicator is among the more popular ones with over 1 million and a half users and a very good usability experience. In addition to database file, themes, and plugins, it provides complete backup capabilities for a WordPress site. Once backup is done, it can be uploaded and stored in any other locations like other cloud services with services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and Amazon S3.
Duplicator also makes site migration between servers or domains effortless, saving you time and reducing complexity. Key features include a 1-click restore function and a Migration Wizard that makes transferring your website a breeze.
In addition, it allows for larger WordPress migrations, making it a suitable option for anyone determined to keep their site safe and easily transferable. If you need customised solutions, custom WordPress plugin development makes sure they tailor features suited towards their needs.
Top Features:
- Make full backups of the entire WordPress site, including databases, files, themes, and plugins.
- Store the backups on remote cloud platforms such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon S3.
- It enables easy one-click restoration of your site to a previous state.
- Simplifies website transfers, with an intuitive process to make quick migrations.
Pros:
- It makes sure the process of backup and restoration is really easy and straightforward-just for a beginner.
- Multiple storage options are provided, so that you don’t run any risk of data loss due to server outages.
Cons:
- Larger sites may face issues with file size limits during backups and migrations
Pricing: The free version is available. Its premium version starts from $69 annually.
3. BlogVault
BlogVault is a great backup plugin for WordPress that provides extremely fast and secure backups for types of websites. It eliminates all usual backup problems such as friction in backup operations and straining your server by performing the backups on its own servers, offsite. Therefore, your website remains fast and smooth.
With BlogVault, you will back up all your WordPress site-assets-your files, themes, plugins, databases, and media- without putting pressure on your web hosting. It can handle very large websites, up to 500 GB, and operates on incremental backup, in such a way that it only saves changes made. This makes it efficient and stable as a berry, giving you great assurance.
Main Features:
- Ensuring secure and reliable backups for large sites.
- Backing up only site-made changes, saving resources, and speeding up the process.
- Advanced data protection for backups.
- Single-click site restoration for minimal downtime.
- Changes are tested in the staging environment before being applied to the live site.
- Real-time backup support for WooCommerce sites.
- Supports backup and migration for WordPress Multisite networks.
- Continuous website monitoring for health and security.
Pros:
- Offloads backup process to external servers for website stability.
- Capable of backing up sites up to 500 GB.
- Minimizes resource usage by only backing up site changes.
- Offers quick recovery from errors or hacks.
- Compatible with over 5000+ web hosting providers.
Cons:
- Offers a free trial, though no free version is available.
- Higher cost compared to simpler backup plugins.
Pricing: The plugin costs $89 annually for a single site.
4. Solid Backups
Solid Backups is a highly reliable and super-secure backup solution for WordPress installations. It does not use regular plugins, but rather the SolidWP cloud itself, ensuring that the performance of the site is not adversely affected during backups. With a cloud-first approach towards backups, the operations are faster and more efficient and require less space on the hosting server.
Incremental backups imply that only changes are saved since the last full backup. It also includes a one-click restore feature for easy recovery from any errors or security incidents. Your management dashboard allows centralized management of backups, monitoring of the activity logs, and performing restores. It makes Solid Backups a perfect tool for anyone who needs speed with their safety.
Key Features:
- Uses SolidWP’s cloud infrastructure to ensure your site’s performance isn’t affected during backups.
- Optimizes storage and processing time by only backing up changed files after the initial full backup.
- Allows for fast and simple site restoration with a single click.
- Provides detailed information about each backup, including posts, pages, and uploads.
Pros:
- Ensures quick backups without server overload.
- Saves time and resources by only backing up changed files after the initial backup.
Cons:
- There is no free plan available for Solid Backups.
Pricing: This plugin costs $8.25 per year for 1 site.
If you know exactly what you want from a backup solution plugin, WooCommerce development company creates it in reality, implementing the unique features that meet your exact needs.
5. BackWPup
BackWPup is an extremely popular WordPress backup solution with more than 12 million downloads. It’s also simple to set backups on automatic scheduling and supports a variety of cloud storage services. What really sets BackWPup apart is the combination of its ease of use along with more powerful management tools.
It backs up your website, which means everything from files, themes, to databases, on its own or through popular services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and more. But the Pro version offers unique features for those who would like to have even more control. Whether you’re running a single personal blog or multiple sites, BackWPup is a versatile and powerful solution for WordPress backup, tickling your fancy for a small or large site.
Best Features:
- Backup your site with one of the following cloud applications: Amazon S3, Dropbox, Google Drive, Microsoft Azure.
- Protect with the security of an encrypted backup.
- Allow backup to automatically run at the time you choose so you can start your worries.
- Great for WordPress multisite networks, letting you backup more than one site in no time.
Pros:
- The interface is easy, even for beginners.
- Provides various cloud storage solutions for backups to offer flexibility and security.
Cons:
- Backing up large sites can strain server resources.
Pricing: The free version is available. The pro version starts from $69 annually.
6. WP Time Capsule
WP Time Capsule is an intelligent WordPress backup plugin which uses an incremental backup system that means only qualifying changes made to the site are backed up and not the whole site so that the server runs smoothly. It works with cloud storage such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon S3, so your backups stay safely stored offsite.
WP Time Capsule offers real-time backups, enabling you to re-establish your site quickly should anything go wrong. There’s a one-click staging feature to test changes without having to disturb your live site. It is a lightweight yet very powerful plugin to take care of your website restoration and staging requirements.
Key Features:
- This means that it will only backup the changed files and database entries thus saving server resources and speeding up the backup process.
- Also, it already has reinforcement for offsite storage via Google Drive, Wasabi, and Backblaze.
- The staging environment allows you to test changes or updates without affecting the actual site.
- Ensure that your website data is compliant with GDPR and thus secure.
Pros:
- Incremental backups minimize server load and storage use.
- Ensures users can revert to the most recent version of their website quickly.
Cons:
- Relying on third-party cloud storage might result in extra expenses.
Pricing: You can get this plugin for free. Its premium version starts from $49 annually.
Final Words
To wrap up, protecting your WordPress site with a trustworthy backup plugin is essential for anyone who owns a website. The appropriate plugin makes sure your data stays safe and allows for quick recovery if unexpected problems occur. We’ve looked at seven excellent WordPress backup plugins, each offering special features to suit different requirements. Whether you value simplicity advanced capabilities, or affordability, you’ll find a plugin that’s just right for you. Don’t wait for something bad to happen—take action now to protect your site and rest easy knowing your hard work has protection.
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoSmart energy pays enters the US market, targeting scalable financial infrastructure
-
Crypto World6 days ago
Software stocks enter bear market on AI disruption fear with ServiceNow plunging 10%
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy is the NHS registering babies as ‘theybies’?
-
 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoAdam Back says Liquid BTC is collateralized after dashboard problem
-

 Video2 days ago
Video2 days agoWhen Money Enters #motivation #mindset #selfimprovement
-

 Tech5 hours ago
Tech5 hours agoWikipedia volunteers spent years cataloging AI tells. Now there’s a plugin to avoid them.
-

 NewsBeat5 days ago
NewsBeat5 days agoDonald Trump Criticises Keir Starmer Over China Discussions
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoSky News Presenter Criticises Lord Mandelson As Greedy And Duplicitous
-

 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoU.S. government enters partial shutdown, here’s how it impacts bitcoin and ether
-

 Fashion5 days ago
Fashion5 days agoWeekend Open Thread – Corporette.com
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoSinner battles Australian Open heat to enter last 16, injured Osaka pulls out
-
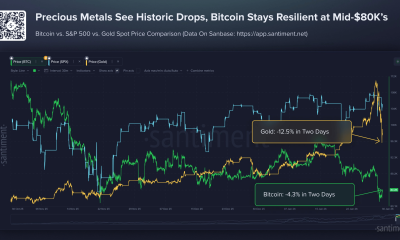
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoBitcoin Drops Below $80K, But New Buyers are Entering the Market
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoMarket Analysis: GBP/USD Retreats From Highs As EUR/GBP Enters Holding Pattern
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoKuCoin CEO on MiCA, Europe entering new era of compliance
-
Business5 days ago
Entergy declares quarterly dividend of $0.64 per share
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoShannon Birchard enters Canadian curling history with sixth Scotties title
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoUS-brokered Russia-Ukraine talks are resuming this week
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoGAME to close all standalone stores in the UK after it enters administration
-

 Crypto World14 hours ago
Crypto World14 hours agoRussia’s Largest Bitcoin Miner BitRiver Enters Bankruptcy Proceedings: Report
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoWhy AI Agents Will Replace DeFi Dashboards






