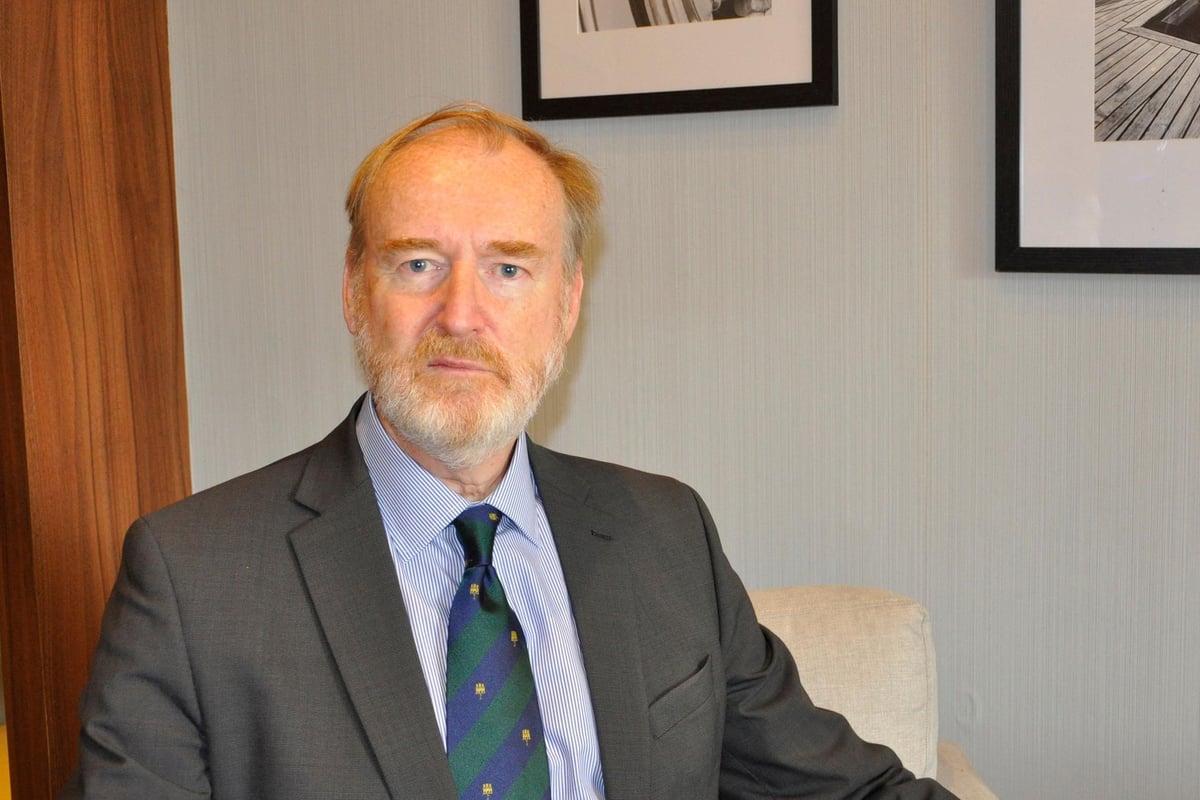
After Benfica’s clash against Real Madrid was halted over alleged racist comments made towards Vinicius Jr, former Premier League referee Mark Clattenburg’s remarks on the matter did not go down well
Mark Clattenburg’s reaction to alleged racism towards Real Madrid forward Vinicius Jr has received strong criticism on social media. The former Premier League referee was providing punditry for Amazon Prime alongside Alan Shearer for the Champions League play-off clash.
Alvaro Arbeloa’s side broke the deadlock shortly after half-time, with Vinicius Junior scoring what went on to be the winning goal in spectacular fashion. The winger bent a shot into the top corner and celebrated enthusiastically by dancing in front of a corner flag.
As he was given a yellow card for his celebration, the Brazilian claimed he had been racially abused. Referee Francois Letexier reacted by activating UEFA’s anti-racism protocol, resulting in a prolonged 10-minute stoppage in play.
READ MORE: Jose Mourinho SENT OFF after furious outburst in Real Madrid v Benfica clashREAD MORE: Vinicius Jr alleges racist abuse as Benfica vs Real Madrid suspended
Sharing his perspective on the situation, Clattenburg implied that Vinicius reporting the alleged remarks had made life ‘very difficult’ for the referee.
He said: “As a referee, I have had this situation before when players have reported a racial comment on the field of play.
“All he (the referee) can do is make the report. Afterwards, then Uefa will look into this. As a referee it is very difficult in this situation.”
He faced widespread condemnation for that analysis on X (formerly Twitter), with numerous viewers expressing their disapproval. @AdamJoseph wrote: “Mark Clattenburg, get a clue. Saying Vinicius Junior has ‘made it difficult’. He can celebrate scoring in front of the crowd.
JOIN US ON FACEBOOK! Latest news, analysis and much more on Mirror Football’s Facebook page
“There is NOTHING wrong with that. In no way does it justify or legitimise alleged racist abuse. This shouldn’t have to be said.”
@AlexisIsKavkas tweeted: “Clattenburg’s comments on TNT are absolutely disgraceful. TNT need to get the mic away from him, he is digging a deeper hole for himself, he isn’t giving enough importance to what was said to Vini.”
@MikeHal08477906 shared: “Honestly, I can’t see Mark Clattenburg being invited onto another show after his antics about Vini Jr. I could feel Alan Shearer cringing through my television and I wonder if he told the director to shut him up.”
Ensure our latest sport headlines always appear at the top of your Google Search by making us a Preferred Source. Click here to activate or add us as Preferred Source in your Google search settings
@RussMCR also said: “Mark Clattenburg has had a stinker,” whilst @jonsheaa simply penned: “Mark Clattenburg? Are you okay?”
The match was halted for approximately 10 minutes before play eventually resumed, with the Real Madrid squad returning to the pitch after initially departing. The exact words directed at Vinicius that triggered the interruption remain unclear, but the allegation came after Gianluca Prestianni had covered his mouth while confronting the Madrid man.
Shearer, who was serving as a pundit alongside Clattenburg, said: “We don’t know what’s been said to him. We can see Jose Mourinho down there and he’s gone speaking to Real Madrid staff and Vini Jr himself to calm him down.
“It’s such a shame, isn’t it? We should be talking about an excellent piece of skill and how he produced a piece of magic which this game needed.”
Following the pause in play, Vinicius was met with jeers from Benfica fans every time he touched the ball. He initially refused to re-enter the pitch but later rejoined the rest of the Real Madrid team.
In the final moments of the match, Benfica manager Mourinho was given his marching orders, in a separate incident, after receiving two yellow cards in rapid succession. In added time, Vinicius was also struck in the head with a bottle of water, thrown from a member of the home fans.
Join our new WhatsApp community and receive your daily dose of Mirror Football content. We also treat our community members to special offers, promotions, and adverts from us and our partners. If you don’t like our community, you can check out any time you like. If you’re curious, you can read our Privacy Notice.
Sky Sports discounted Premier League and EFL package

Sky has slashed the price of its Essential TV and Sky Sports bundle ahead of the 2025/26 season, saving members £336 and offering more than 1,400 live matches across the Premier League, EFL and more.
Sky will show at least 215 live Premier League games this season, an increase of up to 100 more.