Crypto World
Here’s why Bitcoin price is crashing today (Jan. 31)
Bitcoin price continued its strong downward trend as ETF outflows accelerated, geopolitical risks rose, and the government shutdown continued.
Summary
- Bitcoin price continued its strong downward trend on Saturday.
- The crash happened after Donald Trump nominated Kevin Warsh to be the next Fed Chair.
- It also dropped due to geopolitical risks, and the government shutdown started.
Bitcoin (BTC) dropped below the key support level at $81,000 and hit its lowest level since October last year. It has moved into a bear market by falling by 35% from its highest point in 2025.
BTC dropped as third-party data shows that ETF outflows continued. It shed over $509 million in assets last Friday, after losing $817 million on Thursday. They have shed assets in the last four consecutive days, bringing the monthly outflow to over $1 billion. It was the third consecutive month of outflows.
Bitcoin price also slumped after President Donald Trump nominated Kevin Warsh to become the next Federal Reserve Chairman. Warsh is widely seen as a hawk who has criticized the Federal Reserve for cutting interest rates. Therefore, there is a likelihood that he will embrace a more hawkish view at the Fed.
Meanwhile, there is a possibility that Trump will attack Iran. According to the WSJ, Trump is considering a kinetic attack that will avoid a prolonged war in the country.
On the other hand, Iran has warned that it may hit Israel, US installations in the region, and shut the Strait of Hormuz, a move that will disrupt the energy market.
Bitcoin has constantly proven that it is not a safe-haven asset. Instead, investors have embraced other assets like gold and the Swiss franc as risks have continued rising. Bitcoin also slipped as the US government moved to a shutdown.
Bitcoin price technical analysis
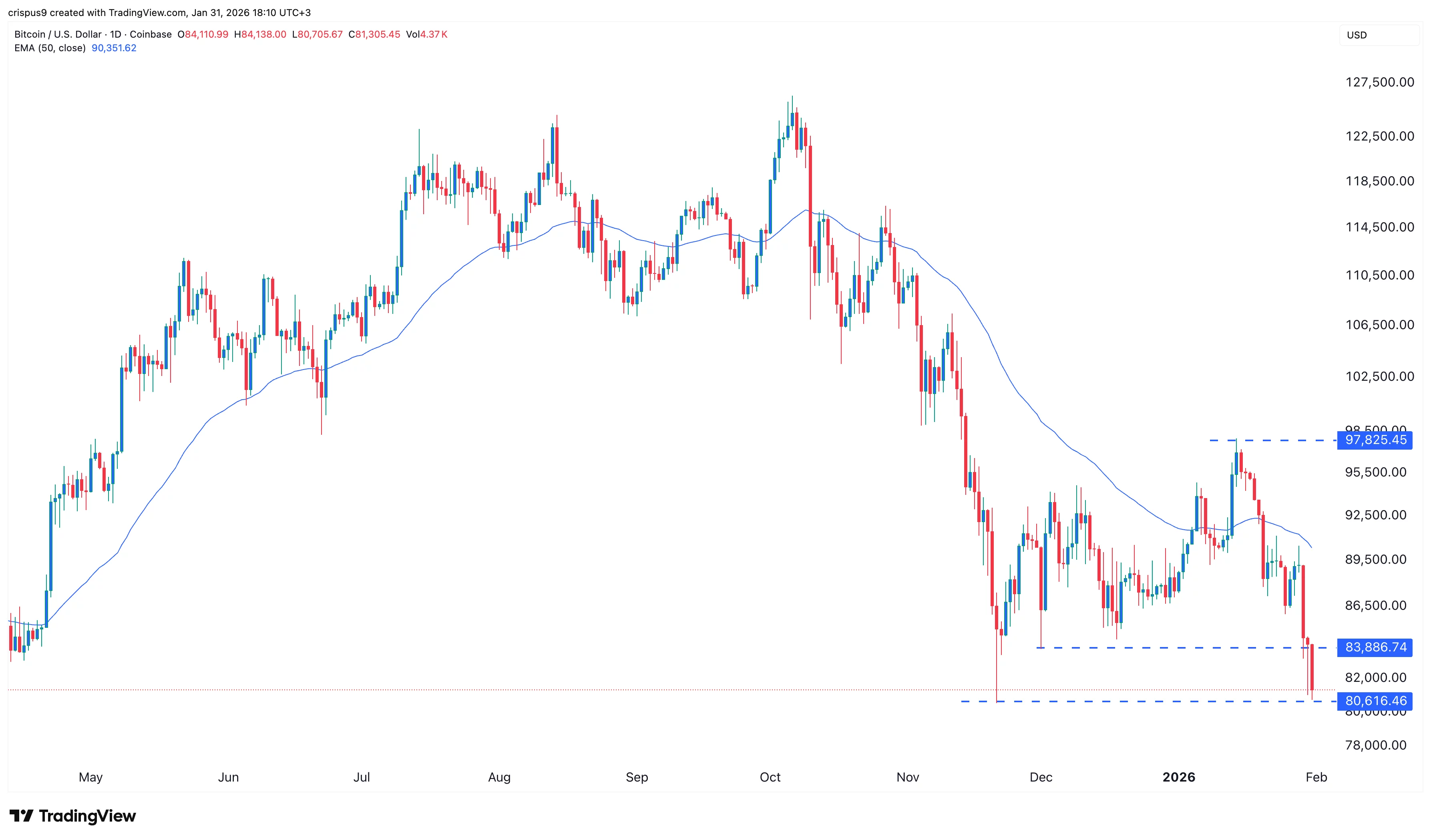
The daily timeframe chart shows that the BTC price has crashed and erased all the gains it made earlier this year. It has now slipped below the psychological point at $85,000 and the key point at $83,885, its lowest level in December last year.
Bitcoin price has crashed below the 50-day and 100-day moving averages and the Supertrend indicator. It dropped below the Ultimate Support of the Murrey Math Lines tool.
The Average Directional Index has continued rising, a sign that the momentum is continuing. Therefore, the most likely BTC price forecast is bearish, with the next key target being at $80,000. A drop below that level will point to more downside to last year’s low of $74,000.
Crypto World
Solana Price Could Fall to $65 as Unstaking Surges 150%
The Solana price remains under heavy pressure in early February, with the token down nearly 30% over the past 30 days and trading inside a weakening descending channel. Price continues to grind toward the lower boundary of this structure as long-term conviction fades.
At the same time, net staking activity has collapsed, exchange buying has slowed, and short-term traders are building positions again. Together, these signals suggest that more SOL is becoming available for potential selling just as technical support weakens.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Staking Collapse Meets Descending Channel Breakdown Risk
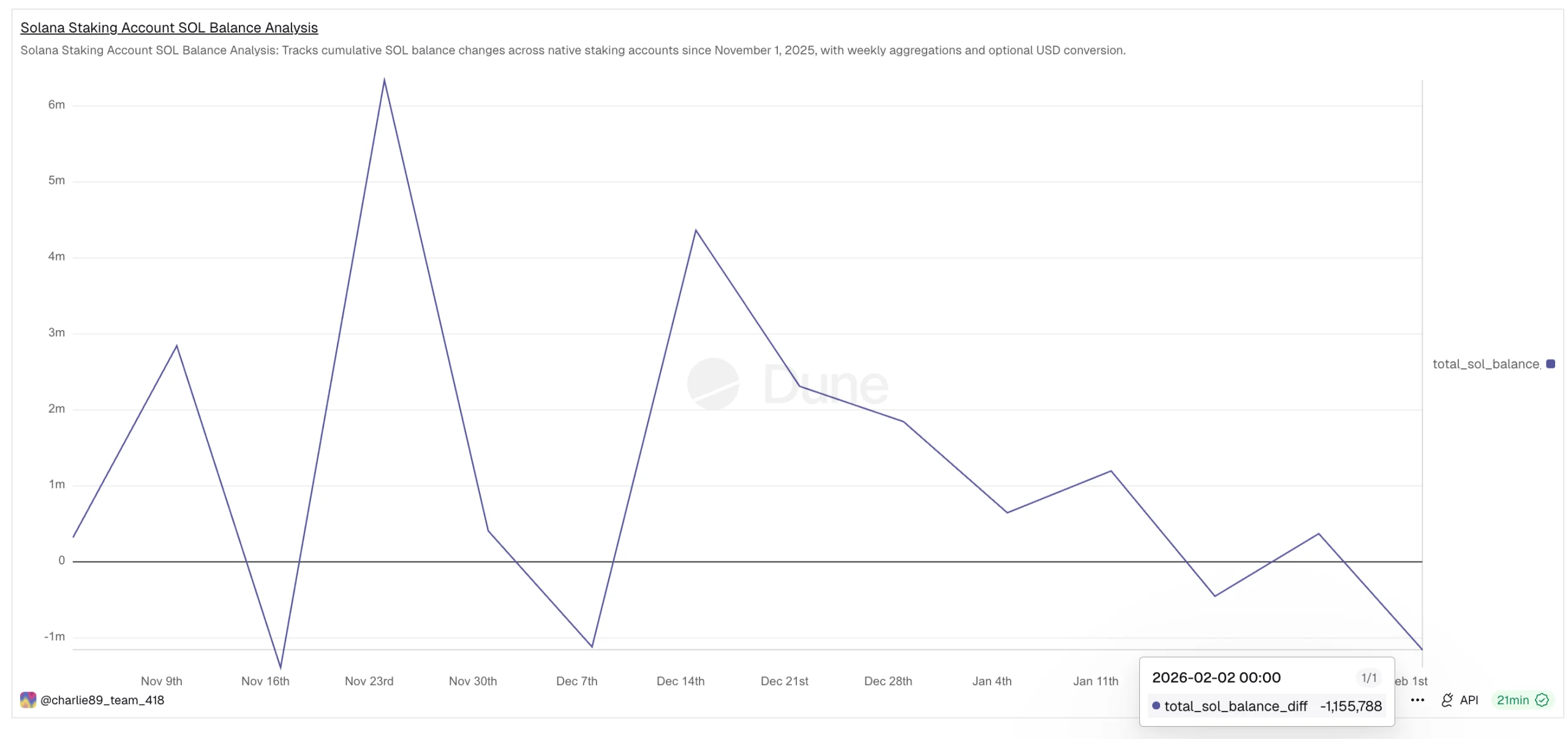
Solana’s latest weakness is being reinforced by a sharp drop in staking activity. The Solana staking difference metric tracks the weekly net change in SOL locked in native staking accounts. Positive values show new staking, while negative readings indicate net unstaking.
In late November, long-term conviction was strong. During the week ending November 24, staking accounts recorded net inflows of over 6.34 million SOL, marking a major accumulation phase.
That trend has now fully reversed. By mid-January, weekly staking flows had turned negative. The week ending January 19 showed net unstaking of around –449,819 SOL. By February 2, this had worsened to –1,155,788 SOL, a surge of roughly 150% in unstaking within two weeks.
Want more token insights like this? Sign up for Editor Harsh Notariya’s Daily Crypto Newsletter here.
This means a growing amount of SOL is being unlocked from staking and returned to liquid circulation. Once unstaked, these tokens can be moved to exchanges and sold immediately, increasing downside risk.
This collapse is happening as price trades near the lower edge of its descending channel with a 30% breakdown possibility in play.
Sponsored
Sponsored
With SOL hovering near $96, the combination of technical weakness and rising liquid supply creates a dangerous setup. If selling accelerates, the channel support may not hold.
Exchange Buying Slows as Speculators Increase Exposure
Falling staking activity is now being reflected in exchange flows. Exchange Net Position Change tracks how much SOL moves onto or off exchanges over a rolling 30-day period. Negative values indicate net outflows and accumulation, while rising readings signal slowing demand.
On February 1, this metric stood near –2.25 million SOL, showing strong buying pressure. By February 3, it had weakened to around –1.66 million SOL. In just two days, exchange outflows dropped by nearly 26%, signaling that accumulation has slowed.
Sponsored
Sponsored
This decline in buying is occurring as unstaking accelerates, increasing the amount of SOL available for trading. When supply rises while demand weakens, the price becomes more vulnerable to sharp declines.
At the same time, speculative activity is rising.
HODL Waves data, which separates wallets based on holding time, shows that the one-day to one-week cohort increased its share from 3.51% to 5.06% between February 2 and February 3. This group represents short-term Solana holders who typically enter during volatility and exit quickly.
Similar behavior appeared in late January. On January 27, this cohort held 5.26% of the supply when SOL traded near $127. By January 30, their share dropped to 4.31% as the price fell to $117, a decline of nearly 8%.
This pattern suggests that speculative money is positioning for short-term bounces rather than long-term holding, increasing the risk that bounces will fade.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Key Solana Price Levels Still Point to $65 Risk
Technical structure continues to mirror the weakness seen in on-chain data. SOL remains locked inside a descending channel that has guided price lower since November. After losing the critical $98 support zone, the price is now trading near $96, close to the channel’s lower boundary.
If this support fails, the next major downside target lies near $67, based on Fibonacci projections. A deeper move could extend toward $65, aligning with the full measured 30% breakdown of the channel.
On the upside, recovery remains difficult. The first level that Solana must reclaim is $98, followed by stronger resistance near $117, which capped multiple rallies in January. A sustained move above $117 would be required to neutralize the bearish structure.
Until then, downside risks remain elevated.
With staking collapsing, exchange buying weakening, and speculative positioning rising, more SOL is entering circulation just as technical support weakens. Unless long-term accumulation returns, Solana remains vulnerable to a deeper correction toward $65.
Crypto World
Lawsuits are piling up against Binance over Oct. 10
Social media sentiment continues to turn against Binance for its alleged role in crypto liquidations on October 10.
Immediately after October 10, traders were already threatening legal action. However, this year, new lawsuits and arbitrations look to be underway, along with numerous other complaints and legal setbacks.
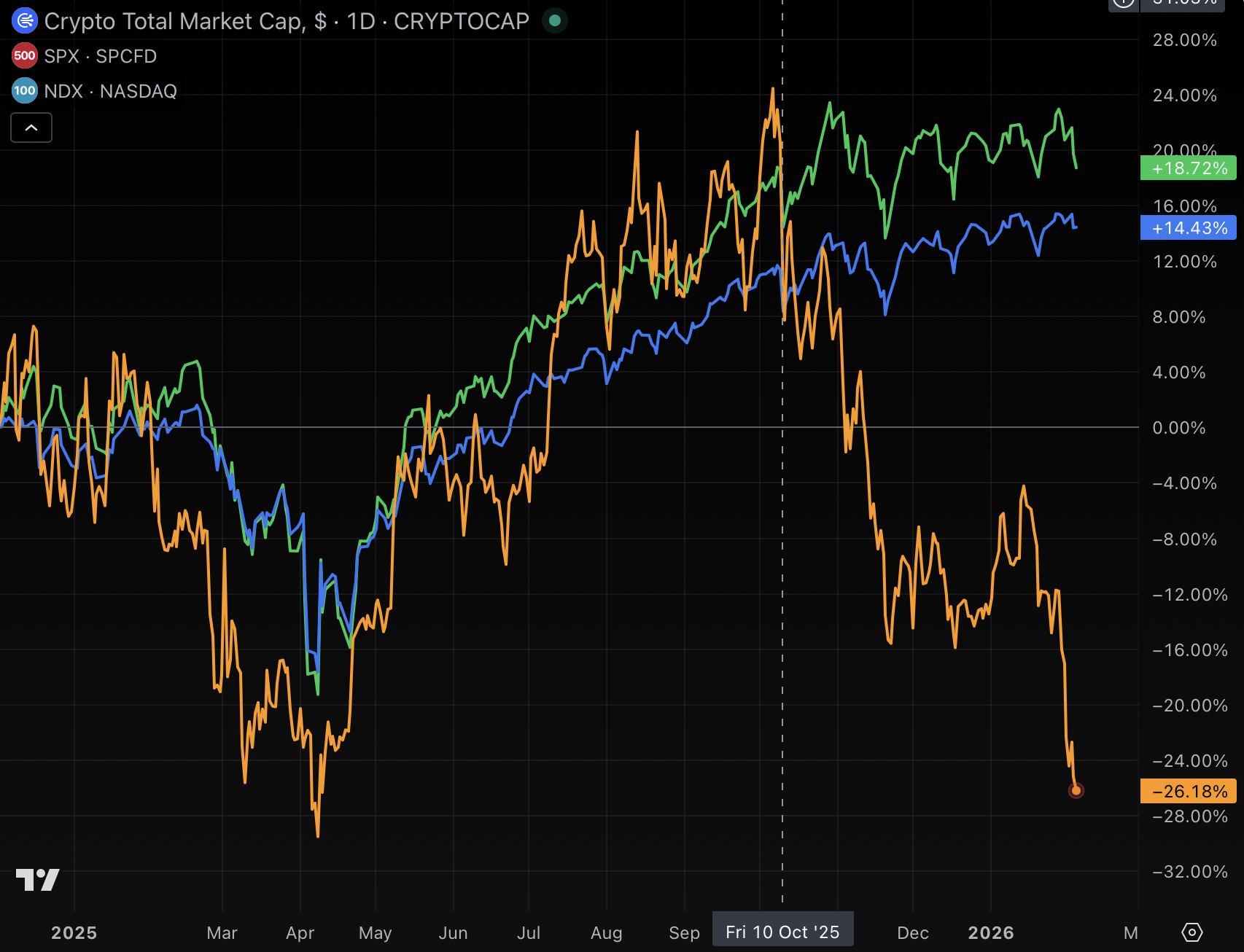
A simple chart of crypto asset prices illustrates the reason for the dogpile of complaints against Binance.
Following months of clear correlation with broad indices like the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100, crypto decoupled precisely on October 10 — and has trended downward ever since.

Read more: Binance’s $1B BTC buy fails to win back trust after Oct. 10
October 10 auto-deLeveraging
As the world’s largest crypto exchange, Binance had a unique role to play in October 10.
For example, flash-crash prices as low as 99.9% existed only on the exchange on that date, and it had just changed its pricing feeds and treatment of a major stablecoin, Ethena USDE.
Wintermute CEO Evgeny Gaevoy called Binance’s Auto-DeLeveraging prices “very strange,” while Ark Invest’s Cathie Wood blamed billions in crypto liquidations on a Binance “software glitch.”
A post with millions of impressions also called out errors in Binance’s pricing oracles for cross-margin unified accounts.
Ethena USDE played a particularly important role in Binance’s October 10 liquidations. After crashing to less than $0.67 on Binance, USDE has regained its $1 peg but has shed more than half its market capitalization since 10/10.
Binance attempts to restore confidence
Without admitting to responsibility, Binance nonetheless quickly — and voluntarily — agreed to pay huge sums of money to customers that suffered losses on that date.
Shortly after the event, Binance announced $328 million in compensation plus another $400 million worth of loans and vouchers.
In another attempt restore confidence amid the bearish knock-on effects of October 10, Binance announced in late January 2026 that it would use its entire $1 billion SAFU (Secure Asset Fund for Users) emergency reserve to buy bitcoin (BTC) over a 30-day period.
It has not helped much. The giant BTC buy failed to win back its fans-turned-critics, with negative topics about Binance still trending on social media on a nearly daily basis.
As pressure continues to build over the exchange’s role in the historic liquidation event, founder Changpeng Zhao has blamed fake social media and unrelated bitcoin traders for bearishness.
He also attempted to divert blame from Binance onto Donald Trump for the crash, saying, “It’s pretty clear that the tariff announcements preceded the crash, not Binance system issues or Binance doing anything.”
Got a tip? Send us an email securely via Protos Leaks. For more informed news, follow us on X, Bluesky, and Google News, or subscribe to our YouTube channel.
Crypto World
Wall Street giant CME Group is eyeing its own ‘CME Coin,’ CEO says


CME Group CEO Terry Duffy has suggested the derivatives giant is exploring launching its own cryptocurrency.
In response to a question from Morgan Stanley’s Michael Cyprys during the company’s latest earnings call, Duffy confirmed the firm is exploring “initiatives with our own coin that we could potentially put on a decentralized network.”
The comment was brief and came in response to a question about the role of tokenized collateral. In response, Duffy first noted that the world’s largest derivatives exchange is carefully reviewing different forms of margin.
“So if you were to give me a token from a systemically important financial institution, I would probably be more comfortable than maybe a third or fourth-tier bank trying to issue a token for margin,” Duffy said. “Not only are we looking at tokenized cash, we’re looking at different initiatives with our own coin.”
The company is already working on a “tokenized cash” solution with Google that’s set to come out later this year and will involve a depository bank facilitating transactions. The “own coin” Duffy referenced appears to be a different token that the firm could “potentially put on a decentralized network for other of our industry participants to use.”
The CME declined to clarify whether this “coin” would function as a stablecoin, settlement token or something else entirely when asked by CoinDesk.
However, if such an initiative goes through, the implications are significant.
While CME Group has previously flagged tokenization as a general area of interest, CEO Terry Duffy’s comments this week mark the first time the exchange has explicitly floated the concept of a proprietary, CME-issued asset running on a decentralized network.
The firm is set to launch 24/7 trading for all crypto futures in the second quarter of the year, and is also set to soon offer cardano, chainlink and stellar futures contracts.
CME’s average daily crypto trading volume hit $12 billion last year, with its micro-ether and micro-bitcoin futures contracts being top performers.
The launch wouldn’t make CME the first traditional finance giant to launch its own token. JPMorgan has recently rolled out tokenized deposits on Coinbase’s layer-2 blockchain Base via its so-called JPM Coin (JPMD), quietly rewiring how Wall Street moves money.
Crypto World
Bitnomial Lists First US-regulated Tezos Futures
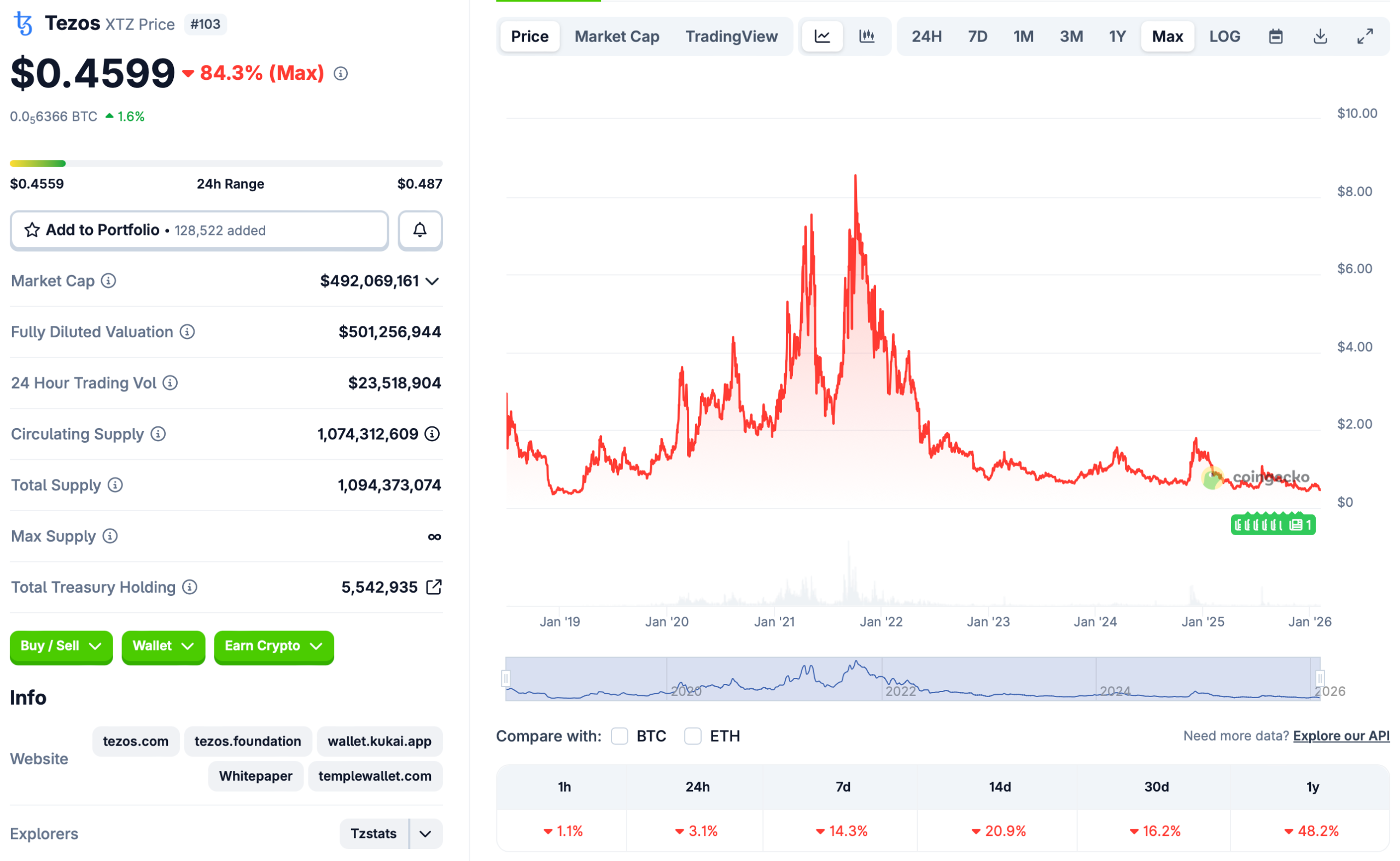
The Chicago-based cryptocurrency exchange Bitnomial has launched futures tied to Tezos’s XTZ token, marking the first time the asset has a futures market on a US Commodity Futures Trading Commission-regulated exchange.
According to Wednesday’s announcement, the futures contracts are live and allow institutional and retail traders to gain exposure to XTZ (XTZ) price movements using either cryptocurrency or US dollars as margin.
Futures contracts let traders hedge risk or gain price exposure by agreeing to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a future date, without holding the asset itself.
Regulated futures markets are often viewed as a prerequisite for broader institutional participation in the US, including potential spot exchange-traded funds (ETFs), because they provide standardized price discovery and oversight under the CFTC.
“CFTC-regulated futures market with six months of trading history checks a key box under the SEC’s generic listing standards for spot ETFs,” Bitnomial president Michael Dunn said.
Dunn told Cointelegraph the company is “actively looking at new tokens” for potential US institutional and retail derivatives markets, but declined to comment on specific assets.
Previously, Bitnomial listed US-regulated futures tied to assets including Cardano (ADA), XRP (XRP) and Aptos (APT), positioning it among the few venues offering regulated crypto derivatives beyond Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether (ETH) in the US.
Bitnomial’s push to list futures tied to altcoins has not been without regulatory hurdles. In August 2024, the exchange sought to self-certify XRP futures with the CFTC, but the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) objected, arguing the contracts required registration as a securities exchange.
After suing the SEC in October 2025 and later dropping the case, Bitnomial launched XRP futures in March, citing the agency’s evolving approach to crypto policy.
Related: CFTC issues no-action letter to Bitnomial, clearing way for event contracts
A brief history of Tezos
Tezos’ mainnet launched in June 2018 following a 2017 initial coin offering that raised about $232 million in Bitcoin and Ether. While not the first proof-of-stake blockchain, Tezos was among the earliest layer-1 networks to combine proof-of-stake with formal onchain governance, enabling token holders to approve protocol upgrades that allowed the network to evolve without hard forks.
During the 2021–2022 non-fungible token boom, the blockchain carved out a niche as a lower-cost, energy-efficient alternative to Ethereum for minting and trading NFTs. As Ethereum gas fees surged, artists and game publishers such as Ubisoft gravitated to Tezos, citing lower transaction costs and the network’s proof-of-stake design.
During these years, Tezos also secured high-profile sports partnerships with Red Bull Racing and McLaren Racing, and was later reported to be preparing a multi-year training kit sponsorship with Manchester United valued at more than $27 million per year.
Tezos’ native token, XTZ, hit an all-time high of $9.12 in October 2021, according to CoinGecko data, but has since fallen about 95% and is now trading around $0.46.
On Jan. 25, Tezos implemented its Tallinn protocol upgrade, cutting base-layer block times to six seconds as part of the network’s 20th onchain upgrade.

Magazine: Bitcoin is ‘funny internet money’ during a crisis: Tezos co-founder
Crypto World
Can DOGE and SHIB Crash to $0 in 2026? 4 AIs Make Predictions


Can 2026 turn out to be a devastating year for the biggest meme coins?
The meme coin sector has been deeply impacted by the latest crypto collapse, with its market capitalization plummeting below $40 billion.
We consulted four of the most popular AI-powered chatbots about whether the crisis will continue and specifically asked whether Dogecoin (DOGE) and Shiba Inu (SHIB) could crash to $0 sometime this year.
The Chances are Small
According to ChatGPT, there is a theoretical possibility, although it is extremely doubtful, for the biggest meme coins (in terms of market cap) to nosedive to zero.
It reminded that the tokens trade actively on major exchanges and have millions of holders, and that is unlikely to change in 2026. At the same time, given current market conditions, ChatGPT suggested that a deeper crash could occur in the following months.
“DOGE and SHIB are among the most widely held cryptocurrencies in the world. Millions of wallets hold these assets, many with no intention of selling at extremely low prices. This creates a distributed supply base, reducing the odds of a total demand vacuum. Even during prolonged bear markets, a subset of holders continues to transact, stake (where applicable), or speculate,” it stated.
Grok – the chatbot integrated within X – claimed a collapse to $0 can’t be ruled out in extreme scenarios. However, it predicted that DOGE and SHIB can stabilize later in 2026 if Bitcoin (BTC) rebounds and hype returns.
“DOGE might hover around $0.10–$0.15, and SHIB could aim to “delete a zero” (reach $0.00001+) with burns and upgrades,” it forecasted.
Not a Chance at All
Google’s Gemini explained that for a cryptocurrency to hit zero, it must have zero buyers and be delisted from all leading exchanges. It stated that such a development is unlikely for several reasons.
First, Dogecoin has made significant progress in the past years, and there are even approved spot DOGE ETFs in the US. It is also Elon Musk’s favorite cryptocurrency, while Shiba Inu has evolved into a complex ecosystem with a vast and devoted community.
You may also like:
Perplexity predicted that smaller meme coins may plummet to $0 in 2026, but it won’t be DOGE or SHIB. The chatbot even envisioned a potential spike to $0.50 and even $1 for Dogecoin in the coming months should hype return. It outlined a less bullish prediction for SHIB, assuming that its price may pump by a maximum of 20% this year.
SECRET PARTNERSHIP BONUS for CryptoPotato readers: Use this link to register and unlock $1,500 in exclusive BingX Exchange rewards (limited time offer).
Crypto World
Bitcoin Slides to Lower Lows After Failed $76,000 Relief Bounce
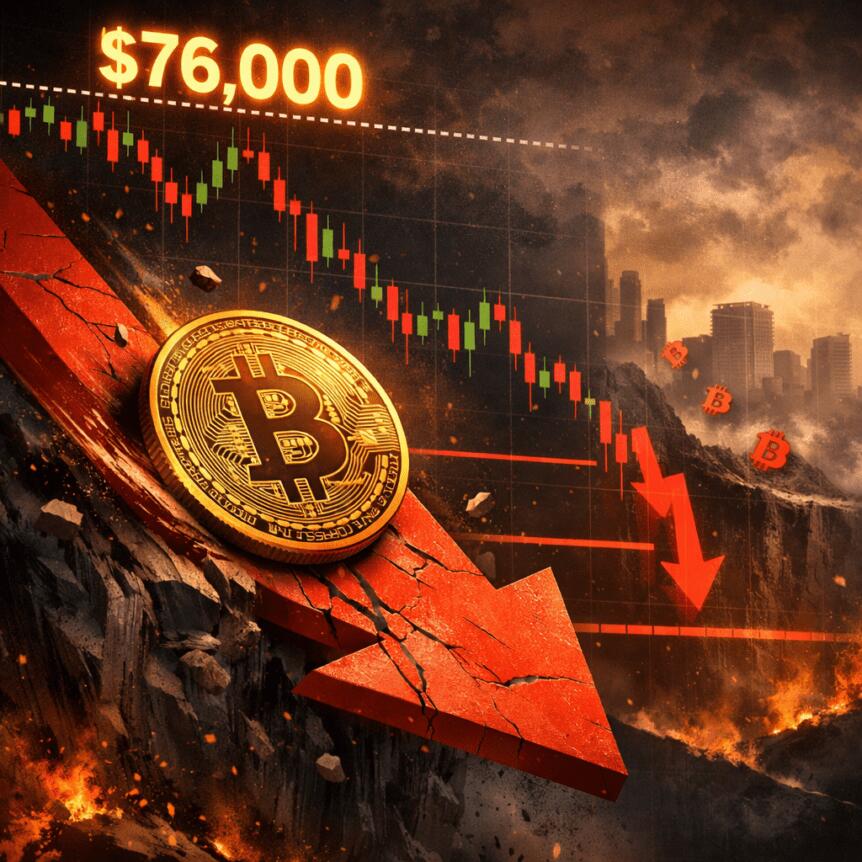

Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) slipped to fresh lows not seen since late 2024 after a wavering relief bounce failed to sustain momentum, with the asset testing new pressure near the $72,000 area as US traders returned to the desk. Data feeds from TradingView highlighted weakness in the US session, with dips briefly pushing BTC beneath $73,000 and lighting up the $72,000 mark on major venues such as Bitstamp. The move underscored a broader risk-off tone in macro markets, where gold struggled to reclaim lofty levels and equities drifted lower at the open. Traders and analysts alike flagged a potential safety net around the 200-week exponential moving average (EMA) near $68,000, a level that has historically been watched as a long-term anchor during drawdowns.
Key takeaways
- Bitcoin breached the previous Tuesday low, slipping to a sub-$73,000 print as Wall Street opened and sellers resurfaced.
- The broader macro backdrop cooled, with precious metals giving back gains and equity indices under pressure in the early session.
- Analysts emphasized the importance of the 200-week EMA around $68,000 as a potential long-term support line, should selling intensify.
- Market participants warned that ongoing volatility could push BTC toward psychological and technical levels that have historically invited capitulation bids or further setbacks.
- Uncertainty surrounding U.S. fiscal policy—specifically government funding deadlines—kept headlines active and contributed to headline risk over the near term.
Tickers mentioned: $BTC
Sentiment: Bearish
Price impact: Negative. The slide into sub-$73,000 territory and the failure of a relief rally reinforce a cautious to bearish stance among traders.
Trading idea (Not Financial Advice): Hold. The market is weighing potential further downside against possible stabilizations near key moving averages, warranting patience before committing to new longs.
Market context: The move comes as a broader risk-off environment takes hold, with macro assets showing renewed sensitivity to headlines and policy signals. Traders will be watching for continued liquidity shifts, near-term fiscal risk headers, and how these factors affect risk assets across crypto and traditional markets.
Why it matters
The latest price action illustrates how Bitcoin continues to trade in a high-volatility regime where macro headlines and on-chain signals interact in real time. The retreat below $73,000, following a brief relief rally above $76,000, signals that buyers are not yet reclaiming the recent highs with sustained force. Technical observers point to the 200-week EMA near $68,000 as a possible anchor if selling accelerates, given its historical role as a gravity point during prolonged pullbacks. The market’s attention on long liquidations—signaling aggressive positioning by leveraged traders—also underscores the fragility of near-term upside scenarios as risk appetite remains fragile.
Beyond price levels, the narrative is shaped by the broader macro context. Gold’s inability to recapture higher ground and the mixed performance of U.S. equities in early trading echo a risk-off mood that often spills into crypto markets. The scene is further complicated by a shifting policy backdrop in Washington. While a fresh government shutdown was avoided in the near term, the funding deadline extended only through mid-February keeps policymakers in the spotlight and potentially adds a layer of headline risk for financial assets, including BTC. In such moments, traders often search for wall-based support from familiar levels or moving averages, while hedging strategies come into play as a counterbalance to drawdown risk.
Industry commentary has reflected the ongoing difficulty of sustaining relief rallies in a market dominated by uncertain macro cues. Notably, market participants have flagged that recent price behavior resembles “bear market price action” rather than a durable bottoming process. The sense of urgency around downside risk was palpable across trading desks, with some analysts forecasting the next target in a scenario of continued weakness around the $50,000 to $60,000 region if macro conditions deteriorate further. The debate underscores how crypto markets are increasingly responsive to cross-asset dynamics, including shifts in precious metals, equities, and macro policy signals that set the tone for liquidity and risk tolerance across the sector.
What to watch next
- Watch BTC’s weekly close relative to the key levels around $74,000 and $68,000 (the latter aligning with the 200-week EMA) to gauge whether downside pressure accelerates or subsides.
- Observe liquidity and leverage indicators, including any uptick in long liquidations near the $72,000–$73,000 area, which could signal renewed selling pressure.
- Monitor macro headlines, especially any updates on U.S. fiscal policy deadlines (Homeland Security funding extended through February 13) that could reframe risk sentiment in both crypto and traditional markets.
- Track relief-bounce dynamics: a sustained move back above the $76,000–$77,000 zone would be a meaningful sign of a shifting intraday risk appetite, while failure to do so could reinforce the bear case.
- Pay attention to data from on-chain analytics and market commentators who tie volume patterns to potential trend reversals; sustained high-volume declines typically indicate persistent selling pressure.
Sources & verification
- BTC price action and levels referenced via analyses that cite TradingView price feeds and Bitstamp data.
- Historical reference to the 200-week EMA near $68,000 as a potential long-term anchor.
- Market comments from QCP Capital’s Asia Color update on volatility and headline risk.
- Market commentary from traders on social channels and related coverage discussing bear-market price action and resistance levels.
- Liquidation metrics from CoinGlass indicating ongoing long liquidations and total crypto liquidations.
Bitcoin price action and macro backdrop
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) faced renewed selling pressure after briefly testing higher ground, with the asset sliding back toward the lower end of the recent trading band as the U.S. market reopened. The intraday trajectory pointed to a deeper tilt toward risk-off dynamics that have characterized much of the recent price action in crypto, equities, and precious metals. A key focus for traders has been whether BTC can sustain any bounce above the $76,000 level or if sellers reassert themselves and push the price toward the next major magnetic price point around $68,000—the approximate footprint of the 200-week EMA that market technicians often monitor for long-term support.
TradingView data showed the weakness extended into a sub-$72,500 print on main venues, reinforcing the idea that relief rallies have struggled to gain traction in the current environment. The pattern aligns with a broader narrative in which macro assets give back gains after brief recoveries, as evidenced by gold failing to reclaim a higher plateau and U.S. stocks trading lower at the open. Within this framework, traders have looked to various anchors—technical, on-chain, and sentiment-based—to price the probability of further downside versus a potential stabilization or rebound.
Several observers have emphasized the persistence of bear-market price action, citing high-volume moves down as a signal that selling pressure remains dominant when price moves lower. A popular chart-focused view suggests that if BTC closes under the $74,000 threshold, the next meaningful objective could shift toward the $50,000–$60,000 area, a scenario that several analysts deem plausible given the current macro setup. In the meantime, market participants cited a potential safety net around $68,000, anchored by the 200-week EMA, a level that has historically attracted buyers during extended retreats. The market’s mood remains cautious, with risk tolerance tightly tethered to evolving macro headlines and policy signals.
“Ugly interim weekly candle for bulls. IF we close sub 74k – its safe to say 50k area is next,” trader Roman wrote in his latest analysis on X.
Beyond the price action, the market remains sensitive to policy developments and funding timelines, with headlines about government funding continuing to influence risk appetite. In a related note, the broader crypto ecosystem continues to digest liquidity dynamics, with long-liquidation pressure mounting whenever price breached key support zones. The combined effect is a landscape where investors weigh the probability of a sharp drawdown against the possibility of a sustained base-building phase that could set the stage for a longer-term recovery should macro conditions cool and liquidity improve.
Crypto World
XRP price risks drop below $1.50 amid crypto market crash


- Ripple’s XRP dropped nearly 5% in 24 hours and 20% in the past week.
- Bitcoin’s dip to $72,900 saw XRP come close to breaking below $1.50.
- XRP saw over $19 million in ETF inflows on February 3, 2026.
XRP has fallen sharply, shedding about 20% over the past week to trade near the critical $1.50 level.
The Ripple cryptocurrency, which has declined by about 5% over the past 24 hours amid a broader crypto market downturn, risks dipping below a key level despite witnessing a fresh uptick in exchange-traded fund inflows.
Overall bearish pressure has led the cryptocurrency market cap to drop to $2.66 trillion, with the crash on “Black Sunday II” having plummeted Bitcoin to under $73,000 on Wednesday.
Meanwhile, top altcoins such as Ethereum, BNB, and Solana have also sold off significantly.
ETH, SOL and BNB dropped to $2,100, $91 and $727 respectively on Wednesday.
Key triggers include President Trump’s tariff threats, panic sell-offs amid a risk asset dip, and negative reaction to Federal Reserve policy fears and the recent nomination of Kevin Warsh as the next Fed chair.
Institutional ETF inflows have failed to stem the downside action.
XRP price slips towards $1.50
XRP’s slide to near $1.53 across major exchanges amid risk-off sentiment means that another slip could push prices lower.
Data shows Ripple futures open interest currently averages $2.53 billion, and aligns with the shrinking retail demand and trader caution.
Per CoinGlass data, OI has shrunk from over $8.3 billion on October 10, when a bloodbath pushed XRP price from above $2.80 to under $2.30.
Sellers have since seen prices hit lows under $1.55, with the downside accelerating since January 6, 2026, when prices retested the $2.30 level.
A dip in OI points to a sustained decline in retail interest, which has previously impacted bulls.
The trend holds despite digital asset investment products, including spot XRP ETFs, seeing notable cumulative inflows over the past week.
Spot XRP ETFs also attracted net inflows on Tuesday, with about $19.4 million in net inflows.
What’s next for the Ripple (XRP) price?
Bitcoin’s drop to $72.8,000 exacerbates the bearish outlook, despite the swift bounce as investors reacted to developments that prevented a US government shutdown. However, bears are still in control.

XRP has lost over 33% in the past month, hitting $1.53 on February 4 and extending declines from January highs around $2.35.
Analysts say $1.53-$1.50 is a potential key reload zone, but buyers must absorb the likely pressure.
Bearish risks persist amid macro caution, and another leg down might potentially see sellers test lows of $1.25. However, the upside amid a bullish divergence has $1.59 as a key pivot towards $2.00.
Crypto World
Cardano Founder Clashes With Ripple CEO Over US Crypto Bill
Join Our Telegram channel to stay up to date on breaking news coverage
Cardano founder Charles Honskinson recently criticized Ripple CEO Brad Garlinghouse in a January 18 video, focusing on what he framed as an industry push to accept the US Clarity Act on terms that would expand the Securities and Exchange Commission’s authority over new projects.
According to Hoskinson, the CLARITY Act can be useful to some companies while being the opposite for others. He went on to warn that blindly supporting the bill could confuse the public and also reduce growth in the crypto market.
Hoskinson said that “the law is not perfect, and favoring one company over another can backfire.”
🚨CHARLES HOSKINSON MOCKS XRP CEO & DRAFT BILL IN LATEST SUNDAY RANT
Cardano founder Charles Hoskinson criticized Ripple CEO Brad Garlinghouse in a latest video, taking aim at his support for the draft bill of the CLARITY Act. pic.twitter.com/4qKk7FTPtB
— Coin Bureau (@coinbureau) January 19, 2026
However, Garlinghouse has been backing the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act. In the video, Hoskinson acknowledged that Garlinghouse is acting from what he sees as genuine conviction.
“He’s being principled. That’s genuine passion and concern. He got into the space as a cypherpunk from the early days. He’s trying to support what this technology was meant to be about and for,” he said.
The XRP community has attacked Hoskinson for supposedly “crashing out,” arguing that he is undermining regulatory progress. Others have also backed this skeptical stance, reflecting the growing divide in industry opinion over the bill’s merits.
Crypto Industry Eyes Lawmakers on Market Structure Bill
The exchange between Hoskinson and Garlinghouse underscores how crypto policy has become more polarized as lawmakers weigh the Digital Asset Clarity Act. However, both sides agree that the stakes for US market structure, investor protection, and innovation are significant.
The CLARITY ACT was proposed to classify digital assets and provide regulatory clarity. This draft law is currently under discussion in the US to provide clearer rules for digital assets and cryptocurrencies.
However, the Senate Banking Committee delayed the markup of the crypto market structure bill after crypto exchange Coinbase publicly withdrew its support for the legislation on Wednesday, January 14, and the White House is now considering dropping support.
🚨SCOOP: The White House is considering pulling its support for the crypto market structure bill entirely if @coinbase does not come back to the table with a yield agreement that satisfies the banks and gets everyone to a deal, a source close to the Trump administration tells me.…
— Eleanor Terrett (@EleanorTerrett) January 17, 2026
Despite the delay, the Committee’s Chair, Tim Scott, reaffirmed that negotiations would continue in good faith, saying he had conversations with leaders across the crypto industry and the financial sector, as well as with both parties in Congress.
If enacted, the bills would become the first comprehensive federal statutes to offer a clear picture of the crypto market structure, thereby replacing reliance on regulatory guidance and litigation.
Related News:
Best Wallet – Diversify Your Crypto Portfolio
- Easy to Use, Feature-Driven Crypto Wallet
- Get Early Access to Upcoming Token ICOs
- Multi-Chain, Multi-Wallet, Non-Custodial
- Now On App Store, Google Play
- Stake To Earn Native Token $BEST
- 250,000+ Monthly Active Users
Join Our Telegram channel to stay up to date on breaking news coverage
Crypto World
DOJ emails show Coinbase co-founder discussed meeting Jeffrey Epstein during 2014 investment talks


Newly unsealed Justice Department documents reveal that Coinbase co-founder Fred Ehrsam was involved in emails regarding a $3 million investment from Jeffrey Epstein in 2014, long after Epstein’s initial conviction.
While Epstein’s stake was less than 1% and he held no governance role, the records show Ehrsam expressed interest in a meeting during the funding round.
The files show that Epstein’s team had direct communication with Ehrsam, a member of the Coinbase Board of Directors and co-founder, who discussed a possible meeting in New York related to a $3 million investment.
“I have a gap between noon and 3 PM today, but again, not crucial for me, but would be nice to meet him if convenient. Is it important for him?” Ehrsam wrote in an email chain that included representatives from crypto entrepreneur Brock Pierce’s VC firm, Blockchain Capital. In the same thread, another email states that Epstein was “in a full afternoon board meeting yesterday.”
Coinbase did not return a request for comment.
In an email dated Dec. 2, 2014, Pierce — the child actor turned entrepreneur who later co-founded Block.one, which in turn launched CoinDesk parent Bullish Global in 2021 — contacted Epstein about an opportunity to invest in Coinbase’s Series C fundraising round.
Pierce, who also co-founded Tether and reportedly had a lengthy relationship with Epstein, wrote, “On another diligence call with the co-founder. First close happened today. Round should be fully committed by Wednesday. $12M / 20% of the round can be taken. This is the most platinum-plated deal in the space.”
That same day, Epstein sought advice from LinkedIn co-founder Reid Hoffman on whether to participate in the round. Hoffman replied that he did not have deep insight into Coinbase and advised against participating, writing, “I probably wouldn’t play.”
But Epstein ended up investing in the company separately from Blockchain Capital.
Emails from Blockchain Capital co-founder W. Bradford Stephens dated Dec. 3, 2014, state that Blockchain Capital intended to invest approximately $3.25 million in Coinbase, spread across three affiliated entities.
Within the same email chain, Epstein’s longtime associate Darren Indyke identified the investing entity as “IGO Company, LLC, which is a USVI limited liability company.”
A valuation report dated Dec. 31, 2014, included in the DOJ release lists a transaction described as “Purchase of Coinbase via IGO LLC (3,001,000),” and lists Coinbase as an investment held through IGO LLC in that amount.
‘Opportunity to invest’
As more businesses and individuals named in the Epstein documents have sought to distance themselves from him, legal and reputational risk has become a key concern. In 2023, JPMorgan Chase and Deutsche Bank paid a combined $365 million to settle lawsuits brought by Epstein’s victims, who alleged the banks enabled his sex-trafficking operation by providing financial services.
Against that backdrop, Blockchain Capital, which is widely referenced in the documents, said the original fund investment was never completed.
Blockchain Capital did not respond to a CoinDesk request for comment, but in an emailed statement to Decrypt, a representative said, “In 2014, Brock Pierce was in contact with Mr. Epstein in relation to fundraising. As part of those discussions, an opportunity to invest in Coinbase’s Series C was also discussed via email.”
The representative added that a fund investment “was never consummated,” and that Epstein instead invested independently through IGO Company LLC.
However, a few years later, Blockchain Capital attempted to buy Epstein’s stake in the crypto exchange.
In January 2018, Blockchain Capital initiated discussions with Epstein’s associate, Indyke, about purchasing the Coinbase position held through the LLC. “We would be willing to buy the position from you at a $2b [billion] valuation,” Stephens wrote, adding that Blockchain Capital would pay roughly $15 million for the stake.
Later emails show negotiations focused on selling half of the Coinbase position held in IGO LLC. Indyke wrote that Epstein believed the company’s value exceeded $3 billion and that he had received “two other bids” for the stake.
On Jan. 31, 2018, Stephens responded that Blockchain Capital’s offer to buy 50% of the position at a $4 billion valuation remained open.
“The price for the 50% interest is $14,666,667,” Stephens wrote, a price that would imply a gain of more than $11 million on the portion of the Coinbase stake sold, according to the emails. In a Feb. 1, 2018 email, Indyke confirmed agreement to the transaction, writing, “Jeffrey agrees that he will sell you 50% of his LLC.”
A valuation report dated Aug. 31, 2018, said Epstein had sold half of his Coinbase stake, saying “50% sold for $15mm [million] Feb 2018.”
Epstein was arrested on federal sex trafficking charges on July 6, 2019, and was held at the Metropolitan Correctional Center in New York City. He died by alleged suicide on Aug. 10, 2019, after being found unresponsive in his cell.
Crypto World
What It Means for Regulated Crypto

Dubai’s January 2026 regulatory shift targets anonymity-focused tokens within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), signaling a recalibration of how regulated markets balance innovation with scrutiny. The Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) moved to bar licensed venues from trading, marketing, or packaging privacy-oriented assets such as privacy coins, within the DIFC’s regulated ecosystem. Ownership in personal wallets remains possible, but access through institution-friendly platforms will be restricted. The move centers on Monero and Zcash, two prominent privacy-focused projects, underscoring a broader push toward transparency that mirrors evolving global standards in AML and sanctions enforcement. While the emirate continues to position itself as a hub for compliant digital finance, the policy crystallizes the friction between private transaction confidentiality and the interests of regulated financial intermediaries.
In the broader crypto landscape, liquidity and institutional appetite are increasingly tethered to traceability and verifiability. The Dubai policy arrives amid a global debate about how much privacy should be permissible within regulated markets, particularly as overt privacy capabilities clash with anti-money-laundering and counter-terrorism financing obligations. The decision is also a reminder that, even in a jurisdiction keen on attracting regulated innovation, privacy-centric architectures face structural headwinds when verticals like exchanges and custodians must meet rigorous reporting and auditing standards. The policy’s implications extend beyond the emirate, fueling ongoing conversations about the future of privacy tooling in an era of expanding regulatory clarity.
Key takeaways
- The DFSA policy applies specifically to activities “in or from” the DIFC, restricting trading, marketing, listing, and fund-related services tied to privacy tokens within this regulated zone.
- From a compliance perspective, privacy-by-default designs clash with AML and sanctions regimes that require visibility into counterparties and transaction flows.
- The Dubai move aligns with a broader, cross‑regional trend as regulators in Europe and North America tighten stance on privacy-focused assets on licensed platforms and within financial institutions.
- Dubai’s stance signals that future growth in regulated crypto markets will prioritize financial transparency, while privacy-first innovation may gravitate toward non-institutional or decentralized channels.
- The rule is narrowly scoped to the DIFC; it does not equate to a UAE-wide prohibition on ownership of privacy coins, which remains allowed in personal wallets but not facilitated by DFSA-regulated venues.
Tickers mentioned: $XMR, $ZEC, $BTC, $ETH
Price impact: Positive. Privacy tokens rose in value around the announcement as traders repositioned toward assets emphasizing anonymity within a constrained regulatory framework.
Market context: The Dubai move sits within a tightening regulatory milieu that favors traceability and compliance, echoing developments across the EU and the US where privacy-oriented assets face enhanced scrutiny and, in some cases, restricted access on regulated surfaces.
Why it matters
The DFSA’s stance marks a notable inflection in how jurisdictions balance crypto innovation with the expectations of traditional financial markets. By narrowing the channels through which privacy-focused tokens can be accessed via regulated venues, Dubai signals that any pathway into institutional finance will demand greater visibility and governance. For exchanges operating in financial hubs, the policy translates into a discriminating gatekeeping standard: assets with built-in obfuscation features are less likely to receive licensing or ongoing approval for listing and market making. In practical terms, this could shift capital toward assets that offer transparent architectures or adjustable privacy layers that maintain regulatory compliance while preserving some user protections.
From a design and engineering perspective, the policy incentivizes builders to explore privacy features that do not undermine auditability and travel-rule compliance. Developers targeting institutional use may pivot toward modular privacy tools, opt-in privacy shields, or verifiable-zero-knowledge frameworks that align with regulatory expectations. Meanwhile, privacy-first projects that rely on complete concealment of transaction data could be relegated to peer-to-peer ecosystems or entirely unregulated realms. These dynamics reflect a broader calculus about where capital should flow if regulators insist on traceability and accountability as prerequisites for market participation.
The policy also feeds into a broader debate about the proper scope of privacy in finance. Some policymakers argue that robust monetary tracking can coexist with privacy-preserving technologies, provided there are safeguards and auditable surfaces. Others contend that anonymity, by design, inherently challenges enforcement of sanctions and anti-fraud safeguards. The reality in practice appears to be an ongoing tension: privacy tools can offer legitimate protections against data breaches and surveillance, but they complicate the ability of institutions to monitor for illicit activity. The Dubai approach embodies a pragmatic stance—prioritize compliance through regulated channels, while allowing private ownership to persist outside those channels.
In the same breath, the policy highlights a historical pattern: when regulated markets require per-transaction visibility, governance and product design naturally migrate toward models that balance privacy with accountability. This is not a wholesale rejection of privacy innovations but a reordering of where and how they can be deployed at scale.
What to watch next
- European Union: The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) framework plus the AML Regulation will effectively restrict privacy coins on regulated EU exchanges by July 1, 2027.
- United States: The ongoing scrutiny of privacy tooling and infrastructure, including liability discussions around developers of open-source privacy protocols, continues to shape permissible use in regulated settings.
- Dubai/DIFC: Further regulatory updates and licensing expectations for crypto firms operating within the DIFC, particularly around token risk assessment and compliance review processes.
- Industry design choices: Token projects may increasingly favor transparent core designs with optional privacy enhancements designed for compliance, rather than opaque transaction models.
- Market structure: Expect continued divergence between regulated, institution-oriented markets and unregulated or decentralized ecosystems that host privacy-centric assets.
Sources & verification
- DFSA notice amendments, December 2025: https://www.dfsa.ae/news/notice-amendments-legislation-december-2025-2
- DFSA policy restricting privacy tokens in DIFC (January 2026) as described in the reporting context
- European Union MiCA and AML Regulation implications for privacy coins on regulated exchanges, 2027
- Tornado Cash regulatory discussion and developer liability (2025): https://www.reuters.com/practical-law-the-journal/litigation/tornado-cash-verdict-developer-liability-implications-2025-11-01/
- Privacy-token market activity and rally coverage: https://sg.finance.yahoo.com/news/privacy-tokens-rally-xmr-breaks-043123462.html
Dubai’s privacy-token stance reshapes the regulated crypto landscape
The DFSA’s January 2026 decision to curb privacy-focused assets within the DIFC does not eradicate privacy technologies from the crypto ecosystem; it confirms that regulated financial markets will demand traceability as a precondition for access. While ownership remains possible outside regulated channels, the constraint on interaction with DFSA-regulated venues nudges institutional players toward assets with clearer audit trails and standardized reporting. The move also serves as a bellwether for other financial centers weighing similar questions: how to foster innovation while maintaining governance that can satisfy banks, custodians, and compliance regulators. In a market where public blockchains routinely intersect with regulated finance, Dubai’s stance underscores a growing bifurcation—one path built for compliance, another for censorship resistance. For investors and developers, the evolving regime means clearer rules, but also a narrowing of on‑ramp options for privacy-centric instruments within mainstream, regulated markets.
What to watch next
- July 1, 2027 — EU regulation will progressively restrict privacy coins on regulated trading venues under MiCA/AML rules.
- 2025–2026 — Ongoing regulatory debates in the US around liability for developers of privacy tooling and open-source privacy gateways.
- 2026–2027 — DIFC licensing and compliance frameworks to be updated, influencing which assets qualify for regulated listing and market making.
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoSmart energy pays enters the US market, targeting scalable financial infrastructure
-
Crypto World6 days ago
Software stocks enter bear market on AI disruption fear with ServiceNow plunging 10%
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy is the NHS registering babies as ‘theybies’?
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoAdam Back says Liquid BTC is collateralized after dashboard problem
-

 Video2 days ago
Video2 days agoWhen Money Enters #motivation #mindset #selfimprovement
-

 Tech11 hours ago
Tech11 hours agoWikipedia volunteers spent years cataloging AI tells. Now there’s a plugin to avoid them.
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoDonald Trump Criticises Keir Starmer Over China Discussions
-

 Fashion5 days ago
Fashion5 days agoWeekend Open Thread – Corporette.com
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoSky News Presenter Criticises Lord Mandelson As Greedy And Duplicitous
-

 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoU.S. government enters partial shutdown, here’s how it impacts bitcoin and ether
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoSinner battles Australian Open heat to enter last 16, injured Osaka pulls out
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoBitcoin Drops Below $80K, But New Buyers are Entering the Market
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
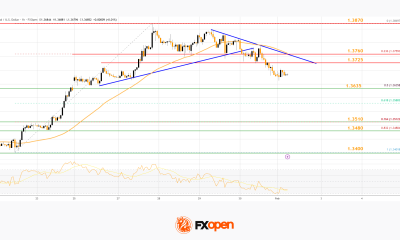
Crypto World2 days agoMarket Analysis: GBP/USD Retreats From Highs As EUR/GBP Enters Holding Pattern
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoKuCoin CEO on MiCA, Europe entering new era of compliance
-
Business5 days ago
Entergy declares quarterly dividend of $0.64 per share
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoShannon Birchard enters Canadian curling history with sixth Scotties title
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoUS-brokered Russia-Ukraine talks are resuming this week
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoGAME to close all standalone stores in the UK after it enters administration
-

 Crypto World20 hours ago
Crypto World20 hours agoRussia’s Largest Bitcoin Miner BitRiver Enters Bankruptcy Proceedings: Report
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoWhy AI Agents Will Replace DeFi Dashboards










