Crypto World
Aave Founder Unveils $50 Trillion Solar Financing Vision Through Tokenized Infrastructure

TLDR:
- Aave could expand collateral by $1.5-5 trillion capturing just 10% of solar financing market share by 2050
- Global solar investment needs $10-50 trillion through 2050, with current annual investment at $420 billion
- Tokenized solar debt enables developers to borrow $70 million in minutes versus months with traditional finance
- Five percent bond market reallocation to solar would inject $6.5 trillion, advancing net zero by 10-15 years
Aave founder Stani Kulechov has published a comprehensive vision for onchain lending to capture a substantial portion of the global energy transition market.
The proposal centers on tokenizing solar energy infrastructure and battery storage projects as collateral. Kulechov estimates the total addressable market at $30 to $50 trillion between now and 2050.
The strategy positions decentralized finance protocols to compete directly with traditional infrastructure funds and development banks in financing renewable energy deployment.
Global Solar Investment Requirements Create DeFi Opportunity
Kulechov frames the opportunity in transformative terms, stating the industry is approaching “a 30 to 50 trillion dollar value capture market for Aave between now and 2050.”
Current solar energy investment stands at approximately $400 to $420 billion annually as of 2024. However, reaching net zero emissions by 2050 requires installing between 14,000 and 15,500 gigawatts of solar capacity.
With roughly 1,700 gigawatts currently deployed, the remaining gap demands $10 to $12 trillion in conservative scenarios.
More aggressive projections accounting for artificial intelligence growth and emerging market development push requirements to $15 to $20 trillion.
The Aave founder argues that energy abundance creates positive feedback loops rather than market saturation. As solar costs decline through economies of scale, cheaper energy stimulates additional economic activity. This increased activity drives higher electricity demand, requiring further solar deployment.
Traditional infrastructure capital currently comes from specialized funds managing $300 to $400 billion annually. Meanwhile, global bond markets exceed $130 trillion, and equity markets reach $110 trillion.
Even capturing five percent of bond capital allocation to solar would inject $6.5 trillion into the sector. This represents roughly 15 times current annual investment levels and could accelerate net zero timelines by 10 to 15 years.
Tokenization Addresses Illiquidity Premium in Infrastructure Assets
Solar projects typically structure with 30 percent equity and 70 percent senior debt components. Equity sponsors target 8 to 15 percent returns, while senior debt offers 5 to 8 percent yields in mature markets.
These cash flows come from power purchase agreements spanning 15 to 25 years with creditworthy counterparties. The predictability creates bond-like characteristics, yet infrastructure funds face illiquidity constraints that limit capital deployment.
Kulechov emphasizes that “every dollar invested in solar manufacturing drives costs down further through learning curves, making the next dollar more productive.”
Pension funds typically allocate only 3 to 5 percent to illiquid infrastructure despite potentially allocating 15 to 20 percent to liquid equivalents.
Tokenizing solar assets on blockchain networks enables continuous secondary market trading. An identical project might require 10 percent returns as an illiquid asset but only 6 percent when tokenized.
Aave Protocol can accept tokenized solar debt as collateral for stablecoin borrowing. A developer holding $100 million in tokenized project debt could borrow $70 million in stablecoins within minutes rather than months.
This capital velocity allows immediate redeployment into new projects. Simultaneously, Aave depositors gain access to diversified, geographically distributed yield backed by physical infrastructure rather than government debt or cryptocurrency volatility.
Market Share Projections Position Protocol as Major Financier
Kulechov projects that capturing just 10 percent of the solar financing market would expand Aave’s economic collateral by $1.5 to $5 trillion through 2050. A 25 percent market share scenario grows this to $3.75 to $12.5 trillion.
For context, JPMorgan manages $4.5 trillion in assets while BlackRock oversees $14 trillion. The abundance financing thesis positions decentralized protocols to compete at comparable scale with the largest traditional financial institutions.
The strategy extends beyond dollar-denominated markets. Solar farms exist across multiple jurisdictions, creating natural demand for euro, pound, and other local currency stablecoins.
Developers in Europe could tokenize euro-denominated senior debt and borrow in euros against that collateral. This solves persistent demand-side problems for non-dollar stablecoins while creating local currency yield opportunities.
Distribution channels include Aave App for retail users, Aave Pro for institutional participants, and Aave Kit for fintech integration. Kulechov declares that “funding energy transitions is by far the largest opportunity for Aave,” framing the approach as explicitly opinionated capital allocation.
Rather than offering neutral access to all asset classes, the protocol would prioritize future-proof abundance assets over legacy scarcity-based instruments like government bonds or mortgages.
Crypto World
Apollo to acquire Up to 90M MORPHO tokens in strategic deal


Apollo Global Management is moving to deepen its involvement in decentralized finance through a long-term collaboration with the Morpho Association.
Summary
- Apollo Global Management will acquire up to 90 million MORPHO tokens over 48 months.
- The partnership follows institutional integrations with Bitwise, which launched a USDC yield vault, and Flare, which enabled XRP-linked lending.
- The deal strengthens Morpho’s on-chain lending infrastructure and gives Apollo long-term governance influence.
The partnership was announced on Feb. 13, with the Morpho Association confirming that it had signed an agreement with Apollo affiliates.
Over the next 48 months, Apollo and its related entities will have the option to acquire up to 90 million Morpho (MORPHO) tokens.
Agreement outlines token purchase plan
These tokens may be obtained through a mix of open-market purchases, over-the-counter transactions, and other negotiated arrangements. To promote market stability, the agreement includes ownership caps as well as specific transfer and trading restrictions.
These safeguards were built into the structure of the deal to limit sudden supply increases and reduce the likelihood of sharp price swings.
If the full allocation is purchased, Apollo’s holdings would represent about 9% of Morpho’s total governance token supply.. At recent prices ranging between $1.19 and $1.37 per token in mid-February, the full cap would be valued at approximately $107 million to $115 million.
Galaxy Digital UK Limited acted as the exclusive financial adviser to Morpho during the negotiations. Morpho said the cooperation will support the development of lending markets, credit infrastructure, and curator-managed vaults across its protocol.
Agreement outlines token purchase plan
The Apollo deal follows several high-profile institutional partnerships that have helped Morpho strengthen its position in decentralized lending.
In late January 2026, Bitwise Asset Management introduced its first on-chain vault on Morpho, offering USDC deposits with yields of up to 6%. The launch marked Bitwise’s first move into non-custodial DeFi yield strategies.
Shortly after, in early February 2026, Morpho expanded its platform by integrating with the Flare blockchain. This integration made it possible for users to lend and borrow XRP-linked assets, such as FXRP. The rollout included vaults backed by FXRP, FLR, and USDT0, all accessible through the Mystic app.
Coinbase made major strides in 2025 when it integrated Morpho’s infrastructure to support its crypto-backed lending services. The integration supported over $960 million in active loans, $1.7 billion in collateral, primarily backed by Ethereum and Bitcoin, and over $450 million in USDC earning yield.
Morpho has been also able to reach a wider audience by offering lending, borrowing, and yield products to both individual and institutional customers through other partnerships with Bitget, Société Générale Forge, Gemini, and Crypto.com.
Ongoing protocol improvements have enabled this expansion. Morpho Vaults 1.1, which was released in 2025, improved risk management. In the meantime, the development of Morpho V2 is one of the main objectives for 2026. Future iterations will include fixed-rate and fixed-term loans with decentralized risk controls.
Market observers see the Apollo deal as evidence of growing institutional confidence in on-chain credit markets. Partnerships such as these are becoming more common as traditional asset managers look for more direct access to blockchain-based financial infrastructure.
Crypto World
Aave Founder Wants DeFi to Tokenize $50T Abundance Assets
Stani Kulechov, the founder of decentralized lending platform Aave, said DeFi could benefit from $50 trillion worth of “abundance assets” such as solar through tokenization by 2050, opening a new class of onchain collateral.
Data from RWA.xyz shows that nearly $25 billion worth of real-world assets have been tokenized onchain, but they are mostly in the form of US Treasury bonds, stocks, commodities, private credit and real estate.
In a post to X on Sunday, Kulechov said he expects these scarce assets to continue growing but that the “biggest impact from tokenization can be achieved by tokenizing abundance assets.”
“Capital is hungry for new collateral, and the world is ready for a transformation that onchain lending can capture and accelerate,” the Aave Labs boss said, while adding that solar could account for $15-$30 trillion of the $50 trillion “abundance asset” market by 2050.

Kulechov said solar debt financiers could tokenize a $100 million solar project while borrowing $70 million to redeploy into new projects, while onchain depositors would have “access to enormously scalable, low-risk yield that is well diversified.”
“An investor might buy tokenized solar, hold for three years, sell at a profit, and immediately redeploy into new development,” Kulechov added, arguing that such a model could significantly increase capital efficiency.
“Traditional infrastructure capital locks up for decades. Tokenized assets allow continuous trading, meaning the same dollar can finance multiple projects over time.”
Kulechov said the same idea extends to batteries for energy storage, robotics for labor, vertical farming and lab-grown food for nutrition, semiconductors for computation and 3D printing for materials.
Abundance assets could offer better returns
Kulechov said these abundance assets could offer higher returns than scarce assets, which he said are heading down “a road toward low, thin margins and diminished profitability.”
“Abundance-backed products offer better returns, better risk characteristics, and better values alignment. They win in the market because they are superior products.”
Aave is the largest DeFi protocol by total value locked, at $27 billion for borrowing and lending, DeFiLlama data shows.
The Tether-issued USDt (USDT) stablecoin, Ether (ETH) and wrapped Ether (wETH) are the most lent and borrowed assets on the platform.
AAVE down 15.2% in 2026
Aave’s native token Aave (AAVE) has not managed to stave off the recent crypto market slump, falling another 1.6% over the last 24 hours, CoinGecko data shows.
Related: Aave winds down Avara, phases out Family wallet in DeFi refocus
AAVE has fallen 15.2% so far in 2026 to $125.98 and is now 81% off its $661.70 all-time high set in May 2021.

Magazine: A ‘tsunami’ of wealth is headed for crypto: Nansen’s Alex Svanevik
Crypto World
Coinbase Retail Users Increase BTC and ETH Holdings During Market Downturn, Armstrong Reports

TLDR:
- Coinbase retail users accumulated more Bitcoin and Ethereum in native units during recent market volatility
- Platform data shows vast majority of customers maintained or increased holdings between December and February
- CEO Brian Armstrong confirmed retail investors bought the dip rather than panic selling during downturns
- Native unit measurements reveal investor conviction independent of fiat currency price fluctuations
Coinbase retail users have maintained strong purchasing activity during recent market volatility, according to data shared by CEO Brian Armstrong.
The exchange platform recorded increases in native unit holdings for both Bitcoin and ETH among retail customers.
Armstrong’s analysis revealed that most customers demonstrated long-term holding patterns, with February balances matching or exceeding December levels across major digital assets.
Retail Investors Increase Native Unit Holdings
Armstrong disclosed the trading patterns through his official Twitter account on February 16, 2026. According to his statement, “Retail users on Coinbase have been very resilient during these market conditions, according to our data.” The CEO noted that customers actively purchased digital assets during price declines.
Armstrong specifically stated that “they’ve been buying the dip” in his public announcement. Platform data confirmed this behavior through measurable growth in cryptocurrency holdings.
The Coinbase executive further explained that “we’ve seen a native unit increase for retail users across BTC and ETH.”
This buying behavior contrasts with traditional market panic selling during downturns. Retail investors on Coinbase chose to accumulate more tokens as prices dropped.
The pattern suggests confidence in long-term value appreciation despite short-term market fluctuations. The data represents actual customer holdings tracked across the Coinbase platform.
Long-Term Holding Patterns Emerge
Armstrong described the customer base using a popular market term in his tweet. He stated that “they have diamond hands” when characterizing their holding behavior. The phrase refers to investors who maintain positions through market volatility without selling.
The data backed up this characterization with concrete numbers. Armstrong noted that the “vast majority of customers had native unit balances in Feb equal to or greater than their balances in December.” This two-month period captured behavior through significant market volatility and price fluctuations.
The holding pattern indicates retail investors are not engaging in panic selling during downturns. Instead, customers are either maintaining existing positions or adding to them strategically.
Platform data tracked individual account balances to measure this retention behavior across the entire user base.
Market observers often question retail investor resilience during extended price declines. However, Coinbase data suggests this demographic is exhibiting patience and long-term thinking.
Armstrong’s public disclosure of internal platform metrics offers transparency into retail trading patterns. The findings challenge common assumptions about retail capitulation during market stress periods and demonstrate sustained conviction among individual investors.
Crypto World
Binance Battles Explosive Iran Claims in $1 Billion Allegation


Binance is forcefully rejecting allegations that its internal investigators uncovered more than $1 billion in Iran-linked transactions and were subsequently dismissed.
The pushback escalates tensions between the world’s largest crypto exchange and sections of the financial press.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Binance Rejects Allegations and Defends Compliance Record
The controversy stems from a February 13 investigative report by Fortune, which alleged that compliance investigators identified over $1 billion in transactions tied to Iranian entities between March 2024 and August 2025.
The transfers reportedly involved Tether (USDT) on the Tron blockchain, an ecosystem frequently scrutinized by regulators for sanctions-related activity.
According to the report, at least five members of Binance’s compliance investigations team were dismissed after raising concerns internally.
Several of the affected staff were described as senior investigators with law enforcement backgrounds. Additional compliance personnel were also said to have departed in recent months, though the precise reasons for their exits were not publicly confirmed.
Binance Says “The Record Must Be Clear”
In a public statement, Binance Co-CEO Richard Teng directly refuted the allegations.
“The record must be clear. No sanctions violations were found, no investigators were fired for raising concerns, and Binance continues to meet its regulatory commitments. We’ve asked for corrections to recent reporting,” Teng wrote.
Sponsored
Sponsored
In a formal letter addressed to Fortune, Binance Communications stated that the article contained “gross material inaccuracies and misleading implications.” The company articulated that:
- No personnel were terminated for reporting sanctions concerns.
- No personnel decisions or terminations are related to the reporting of alleged sanctions violations.
Binance further asserted that a full internal review, conducted alongside external legal counsel, found no evidence of sanctions breaches related to the referenced activity.
The letter emphasized that the exchange operates under whistleblower protections and strict employment laws across multiple jurisdictions.
Binance also pushed back against suggestions it had reneged on regulatory commitments stemming from its 2023 settlement with US authorities.
Sponsored
Sponsored
The exchange has committed to fully cooperate with monitorship requirements. Reportedly, they have also “significantly strengthened” their sanctions screening, monitoring, and compliance infrastructure since the resolution.
Heightened Sensitivity Post-Settlement
The allegations are particularly sensitive given Binance’s 2023 $4.3 billion settlement over anti-money laundering and sanctions violations. Since then, the exchange has operated under enhanced compliance obligations and increased regulatory scrutiny.
However,beyond the dispute itself, the incident highlights broader concerns about stablecoins and sanctions evasion.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Blockchain analytics firms, including TRM Labs, Chainalysis, and Elliptic, have previously reported growing use of USDT by Iranian-linked actors to move funds outside traditional banking channels.
US authorities, including the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), have sanctioned other exchanges over similar Iran-linked activity involving USDT on Tron.
The standoff remains a battle of narratives, with anonymous-source allegations meeting categorical corporate denials.
With no new enforcement action announced, the question shifts from whether violations occurred to how transparency, compliance, and investigative reporting intersect in an industry still fighting to rebuild trust.
Crypto World
Saylor’s 3-6 Year Strategy to Equitize Convertible Debt

Strategy founder Michael Saylor unveiled a plan to convert roughly $6 billion of convertible debt into equity, a move designed to ease balance‑sheet pressure while preserving the firm’s Bitcoin holdings. The company maintains a Bitcoin treasury of about 714,644 BTC, valued at roughly $49 billion at current prices, a substantial cushion for its leverage profile. Equitizing the debt—converting bonds into equity rather than repaying cash—would turn bondholders into shareholders and reduce near‑term debt obligations. The announcement, prompted by a Sunday post on X, followed a public assertion that the plan could withstand a dramatic BTC price drop and still fully cover the debt, a claim the firm made in a message linked to a Saylor post. The news comes as the market contends with sharp volatility and a price environment that has kept BTC trading in a wide range around the high 60,000s.
Key takeaways
- Strategy plans to convert about $6 billion of convertible debt into equity, reducing debt exposure without a cash repayment.
- The firm’s Bitcoin treasury stands at approximately 714,644 BTC, underpinning the balance sheet with a sizeable asset base worth tens of billions of dollars at current prices.
- Bond-to-equity conversion hinges on BTC price sensitivity; the firm argues that BTC would need to fall about 88% for the debt and equity to be equivalent on a value basis.
- Equitization could dilute existing shareholders by issuing new stock, though it also eases pressure on cash flow and debt servicing.
- The company has continued accumulating BTC, signaling a persistent long‑term thesis even as market prices dip.
- Strategy’s stock has fallen roughly 70% from its all‑time high, reflecting broader declines in crypto markets and investor sentiment as BTC fluctuates near $68,000–$70,000.
Tickers mentioned: $BTC, $MSTR
Sentiment: Neutral
Price impact: Neutral. The described debt conversion is a balance‑sheet adjustment rather than a direct price move.
Trading idea (Not Financial Advice): Hold. The company is pursuing structural relief through equity issuance while continuing to accumulate BTC, which could support downside protection if BTC stabilizes or recovers.
Market context: The strategy reflects a broader approach among BTC‑heavy firms to balance debt with control over equity issuance, as crypto markets experience episodic volatility and shifting investor risk appetite.
Why it matters
The move to convert debt into equity spotlights a pragmatic path for crypto‑native companies seeking to de‑risk their balance sheets without selling large BTC holdings into a volatile market. If successful, the conversion could limit cash obligations and preserve a strategic BTC reserve that could support future liquidity needs. For investors, the key question is how the equity dilution will affect existing shareholders and whether the new capital structure will provide a clearer path to profitability as BTC remains a cornerstone of Strategy’s balance sheet.
From a market perspective, Strategy’s strategy tests how far a BTC‑backed business can lean on its crypto reserves while weathering price swings and volatility in both digital assets and traditional equity markets. The company contends its BTC hoard provides a robust cushion, even if the price of BTC experiences extended drawdowns. The dynamic between debt relief and equity dilution will be watched closely by investors and analysts, particularly as BTC prices hover in a historically elevated but highly cyclical band and as the broader market evaluates the durability of corporate treasury strategies tied to crypto assets.
What to watch next
- Details on the final terms of the debt‑to‑equity conversion, including any changes to voting rights, dilution thresholds, and timing of the issuance.
- Any updates to the BTC accumulation program, including changes to the size of the reserve and the cadence of purchases.
- Regulatory developments around convertible notes and crypto treasuries that could influence balance‑sheet choices for BTC‑heavy companies.
- Further commentary from Michael Saylor or Strategy on future buy signals or treasury strategy, including additional posts on X.
Sources & verification
- Strategy’s official posts and remarks on X detailing the debt conversion and BTC holdings.
- Historical data on Strategy’s stock price (MSTR) and Bitcoin price data from referenced sources (Google Finance, CoinGecko).
- Previously published articles referenced in the original piece about Saylor’s buy signals and prior accumulation episodes.
Strategy’s balance sheet reshaped by a debt-to-equity plan
Strategy’s planned move to convert about $6 billion of convertible debt into equity reflects a deliberate effort to pare back leverage while preserving governance and the strategic advantage of its bitcoin reserves. Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) is central to this approach, and the company publicly states that its 714,644 BTC stack creates a substantial cushion that could sustain debt obligations even as market prices swing. The conversion turns creditors into shareholders, realigning incentives with long‑horizon investors who expect the BTC treasury to underpin future growth and liquidity.
From a structural standpoint, the strategy has a double effect. On the one hand, it reduces the near‑term debt load on the balance sheet and eliminates cash interest obligations tied to the convertible notes. On the other hand, it introduces equity dilution, which can dilute existing owners’ ownership and shareholder earnings per share if the new stock issuance expands the float. The firm emphasizes that the conversion would be fully backed by BTC reserves; in other words, the risk on debt coverage remains anchored by the crypto asset base, even if BTC experiences a meaningful price correction.
The financial calculus is anchored to a striking data point: the conversion would effectively require an 88% drop in BTC price for the debt and the resulting equity to be value‑balanced. The math underscores how much the reserve acts as a backstop and also highlights the sensitivity of the plan to BTC’s price trajectory. The firm’s public statements to date suggest that even under severe stress scenarios, the strategy could sustain debt coverage while giving bondholders an ownership stake rather than a cash repayment at maturity, thereby avoiding forced sales in a downturn.
Meanwhile, Strategy has continued to accumulate BTC, a pattern that has persisted through recent market turbulence. The company’s average entry price for Bitcoin sits around $76,000, implying that even with current prices near $68,400, the overall position remains underwater on a cost basis. The ongoing accumulation is part of a broader narrative wherein the company uses its treasury not simply as a reserve but as a cornerstone of its equity‑backed financial stance. The public posts and related coverage indicate a steady cadence of purchases, including mentions of multiple weeks of continued accumulation as BTC price action fluctuates.
Beyond the internal balance‑sheet mechanics, the market response to Strategy’s leadership has been a mix of caution and curiosity. Strategy’s stock (MSTR) has endured a significant drawdown from its all‑time high, illustrating how crypto equities can decouple from the performance of BTC during periods of broad risk aversion. The latest trading, with shares near a fraction of the peak, showcases the tension between a potentially stabilizing balance‑sheet strategy and the market’s perception of dilution risk and growth prospects. As BTC attempted to reattain key levels in late trading and again faced pressure, investors weighed whether the new equity issuance would unlock a clearer path to profitability or simply reset the capital structure without delivering immediate earnings momentum.
The ongoing narrative also intersects with broader market sentiment about crypto treasuries and convertible debt, a topic covered in prior industry discussions. The company’s approach, while tailored to its own assets and obligations, mirrors a broader trend in which BTC‑centric businesses seek structural options to weather cycles of drawdown without sacrificing long‑term exposure to the asset that forms the core of their strategic thesis.
Crypto World
USD1 Stablecoin Surges to $5 Billion Market Cap as Wall Street CEOs Schedule Florida Summit

TLDR:
- USD1 achieved over $5 billion market capitalization within initial phase, ranking among top stablecoins globally.
- Platform recorded $300 million total value locked with yields reaching 13% on USDC and 7% on USD1 holdings.
- Major financial CEOs from Goldman Sachs, Coinbase, Franklin Templeton attend February 18 Mar-a-Lago meeting.
- Developer plans target $9 trillion daily FX market, positioning USD1 as potential settlement infrastructure.
USD1 has reached a market capitalization exceeding $5 billion within its initial phase, positioning itself among the largest stablecoins in the global market.
The token, associated with World Liberty Financial, has attracted attention from traditional finance leaders ahead of a scheduled February 18 gathering at Mar-a-Lago.
Capital flows into the platform have accelerated despite broader market volatility, with early metrics showing substantial total value locked and competitive yield rates.
Platform Metrics Show Early Traction
The stablecoin recorded approximately $300 million in total value locked during its first month of operation. Users can access yield rates reaching around 13 percent on USDC deposits through the platform.
USD1 itself offers roughly 7 percent returns to holders, creating multiple entry points for yield-seeking investors.
A crypto analyst posting under the handle @Eljaboom noted the scale of the project on social media. “Everyone is watching BTC · $68,174.43. Meanwhile, a new dollar rail is quietly forming in Florida,” the analyst wrote. The commentary emphasized that USD1 had moved beyond early-stage development into operational scale.
The platform’s rapid accumulation of locked value demonstrates market appetite for alternative stablecoin infrastructure. Traditional stablecoin markets have been dominated by established players for years.
However, new entrants with institutional backing are now challenging existing market structures through competitive yield offerings and expanded functionality.
World Liberty Financial architect Zak Folkman has discussed plans extending into foreign exchange markets. The global FX market processes approximately $9 trillion in daily transactions, representing a substantial opportunity for blockchain-based settlement infrastructure. If USD1 transitions from a yield-generating token to a settlement layer, its utility could expand considerably.
Institutional Participation and Infrastructure Development
The February 18 event at Mar-a-Lago includes participation from several prominent financial executives. Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong, Goldman Sachs CEO David Solomon, Franklin Templeton CEO Jenny Johnson, and Cantor Fitzgerald CEO Michael Selig are confirmed attendees.
This lineup reflects institutional curiosity about digital asset infrastructure rather than typical cryptocurrency community engagement.
The platform has outlined several development priorities on its public roadmap. A debit card product aims to bridge digital and traditional payment systems.
Mobile onboarding tools will expand accessibility beyond desktop users. Real-world asset integration could connect traditional financial instruments with blockchain rails.
The analyst’s post emphasized infrastructure over short-term price movements. “The token price is noise. The infrastructure is the story,” according to the social media commentary.
This perspective suggests that platform utility and adoption metrics matter more than speculative trading activity.
Capital allocation patterns indicate growing confidence in alternative stablecoin systems. Whether driven by yield opportunities or institutional partnerships, the flow of funds into newer platforms challenges the assumption that established stablecoins maintain permanent market dominance.
The development of payment rails and settlement infrastructure continues regardless of broader cryptocurrency market conditions.
Crypto World
Strategy Plans To Convert $6B Debt As Bitcoin Holdings Value Drops
Strategy founder Michael Saylor has revealed the firm plans to convert its $6 billion in bond debt into equity — a move that reduces debt on the balance sheet.
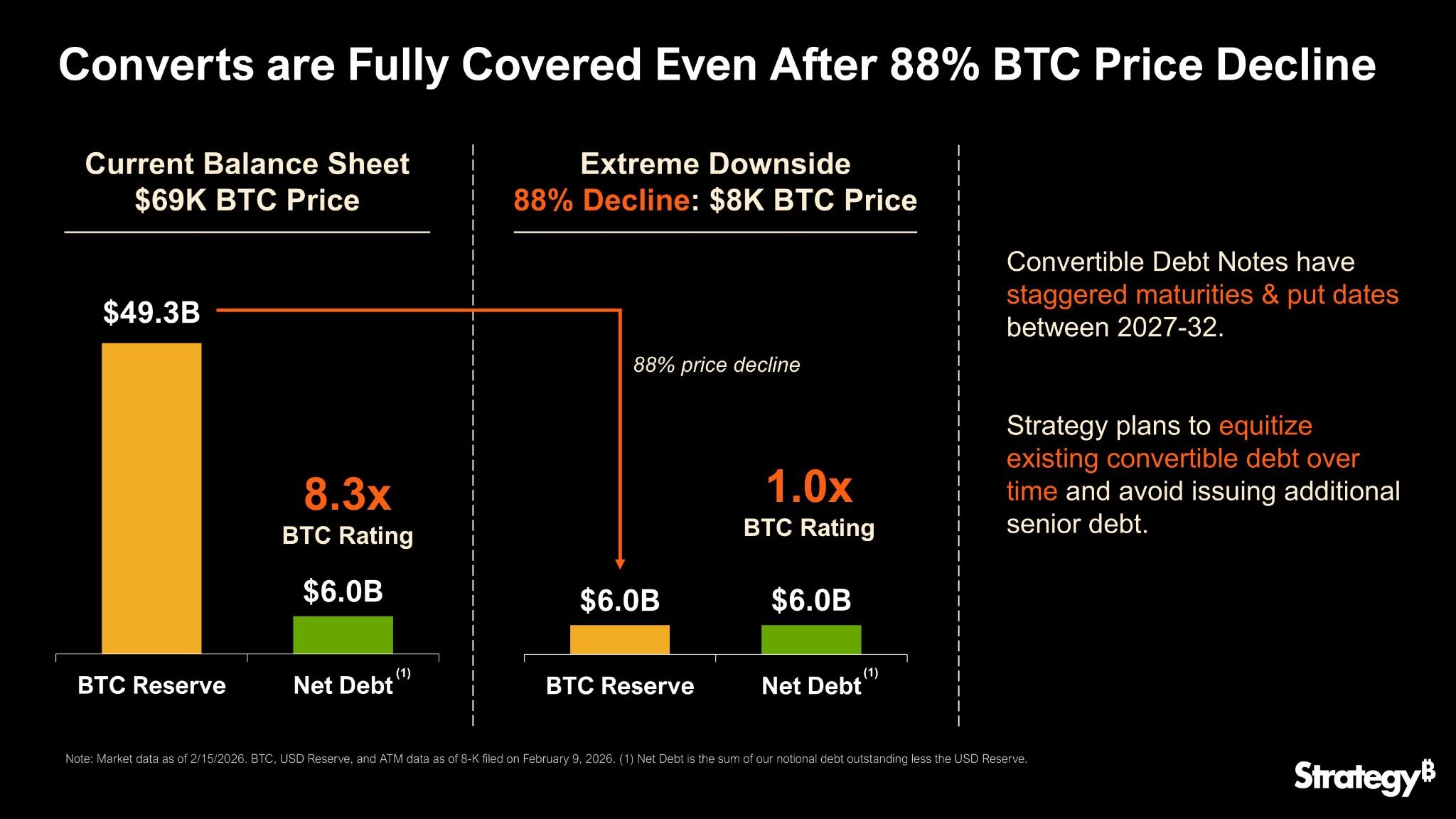
“Strategy can withstand a drawdown in BTC price to $8,000 and still have sufficient assets to fully cover our debt,” stated the firm on X on Sunday, prompting Saylor’s response.
The Bitcoin (BTC) treasury company currently holds $49 billion in Bitcoin reserves with a stash of 714,644 BTC.
Its convertible debt is around $6 billion, so BTC would need to fall around 88% for the two to be equal, and it still has enough to cover the debt, the firm explained.
Equitizing convertible debt means converting the bond debt into equity as stock shares rather than repaying it in cash, essentially turning bondholders into shareholders.
The move would reduce debt pressure on the company, but it can also dilute existing shareholders because new stock is issued.

Strategy down 10% on average BTC purchase price
The average Bitcoin purchase price for Strategy is around $76,000, which means the firm is currently down around 10% on its investment with the asset trading at $68,400.
Related: Michael Saylor signals another Bitcoin buy amid market rout
Meanwhile, Saylor signaled another Bitcoin buy as he posted the Strategy accumulation chart on X on Sunday, a typical sign of a purchase.
The purchase would mark 12 consecutive weeks of buying as the company continues to accumulate despite a sharp decline in the underlying asset and its stock price.
Strategy stock down 70% from ATH
Strategy stock (MSTR) climbed 8.8% on Friday to end the week trading at $133.88, according to Google Finance.
The move came as Bitcoin recovered the $70,000 level again in late trading on Friday, but that recovery was short-lived as it lost some of those gains in early trading on Monday morning, falling to $68,400, according to CoinGecko.
Meanwhile, shares in the company are down 70% from their mid-July all-time high of $456, as BTC prices have fallen 50% from their peak in early October.
Magazine: Coinbase misses Q4 earnings, Ethereum eyes ‘V-shaped recovery’: Hodler’s Digest
Crypto World
Aave targets solar financing in long-term DeFi strategy


Aave is looking beyond traditional crypto lending as it explores a long-term strategy focused on financing solar energy and other real-world infrastructure.
Summary
- Aave founder Stani Kulechov says tokenized solar assets could unlock faster, cheaper funding for clean energy.
- Aave plans to use solar-backed tokens as collateral to improve liquidity and capital recycling.
- The move targets long-term growth beyond traditional crypto-based lending.
The shift was outlined in a recent post by founder Stani Kulechov, who argued that decentralized finance can play a major role in funding the global energy transition.
Kulechov said on-chain lending has already proven its technical strength with digital assets. The next step, in his view, is to bring productive, real-world assets such as solar farms into DeFi and turn them into usable collateral.
Turning solar projects into liquid assets
According to Kulechov, one of the main problems in solar and infrastructure financing is illiquidity. Most projects rely on long-term contracts that can last 20 years or more. Investors often accept lower flexibility in exchange for stable returns, but this also limits the amount of capital that can enter the sector.
Tokenization could change that. By turning solar projects into digital assets, investors would be able to trade and transfer their positions more easily. These tokenized assets could also be used as collateral on Aave (AAVE), allowing developers and financiers to borrow funds quickly instead of waiting months for traditional loans.
Kulechov said this could lower required returns and make projects more attractive. A solar asset that needs a 10% return in private markets might only need 6% if it becomes liquid and tradable. Over time, this could help recycle capital faster, letting the same money fund multiple projects instead of being locked up for decades.
He also pointed to the potential impact on stablecoins. Because solar farms are spread across many countries, their debt could be issued in different currencies. This could create new demand for euro- and pound-backed stablecoins, giving users more options beyond U.S. dollar lending.
Building a new model for DeFi growth
Lending against major cryptocurrencies has grown crowded and fiercely competitive, as per Kulechov. Similar products are currently offered by many DeFi platforms, which has decreased long-term growth potential and pushed down margins.
He argues that solar-backed lending presents an alternative. Aave might fund initiatives that produce actual cash flows and long-term value rather than depending on speculative assets. This would give depositors access to “green yield” while helping fund clean energy development.
He also stressed that most retail investors currently have limited access to solar investments. High minimums and complex structures keep many people out. On-chain products have the potential to reduce these obstacles and increase accessibility to infrastructure financing.
He believes that this strategy reflects a drastic change in the way that capital ought to be distributed. DeFi platforms should support assets that are productive and future-proof rather than concentrating on government debt or struggling industries.
Kulechov described this as an “opinionated” strategy. Users who choose solar-backed products are not just looking for returns, he said. They are choosing to fund creation over extraction and long-term growth over short-term fixes.
If the model works, it might result in a parallel financial system with real infrastructure and revenue supporting lending products and stablecoins.
“Aave Will Win,” Kulechov concluded, framing the shift as both a business strategy and a statement about the future of DeFI.
Crypto World
ZK-Proofs in Privacy-Preserving DeFi – Smart Liquidity Research

The tech that lets you prove you’re legit—without spilling your wallet’s secrets.
Decentralized finance was supposed to give us sovereignty. Instead, it gave us radical transparency. Every swap, every yield farm rotation, every panic sell at 3 a.m.—immortalized on-chain for anyone with a block explorer and curiosity.
Enter Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK-proofs): cryptography’s elegant solution to “trust me, bro”—but mathematically enforced.
What Are ZK-Proofs (Without the Math-Induced Migraine)?
A zero-knowledge proof lets one party prove a statement is true without revealing the underlying information.
In DeFi terms:
-
You can prove you have enough collateral without revealing your wallet balance.
-
You can prove you’re not on a sanctions list without revealing your identity.
-
You can prove a transaction is valid without exposing the sender, receiver, or amount.
It’s like showing the bouncer you’re over 18 without handing over your full life story.
Why DeFi Needs Privacy (Badly)
Most DeFi today runs on fully transparent blockchains like Ethereum.
Transparency is great for:
-
Verifiability
-
Auditing
-
Trust minimization
But it’s terrible for:
If hedge funds had to publish every trade in real time, markets would implode. Yet that’s essentially what DeFi asks of users.
ZK-proofs are the missing layer.
Core ZK Technologies in DeFi
1. zk-SNARKs
Succinct proofs. Small, fast to verify, but often require a trusted setup.
2. zk-STARKs
No trusted setup. More scalable, but proofs are larger.
Both are already being used to scale networks and enable privacy features.
Real Projects Building Privacy-Preserving DeFi
Let’s look at concrete implementations.
1. Aztec Network
Private DeFi on Ethereum
Aztec uses zk-rollups to enable programmable privacy. Users can:
-
Make private token transfers
-
Interact with DeFi applications privately
-
Shield balances and transactions
It combines Ethereum’s security with encrypted state transitions verified via zero-knowledge proofs.
Use case: A DAO treasury managing funds without publicly broadcasting every move.
2. Mina Protocol
The “Succinct” Blockchain
Mina keeps its entire blockchain at ~22KB using recursive ZK-proofs. While not purely DeFi-focused, its architecture enables:
-
Private smart contract logic
-
Verifiable off-chain computation
-
zkApps (zero-knowledge apps)
Use case: DeFi apps that verify external data or credentials without revealing the raw data.
3. Secret Network
Encrypted Smart Contracts
Secret Network allows private smart contracts where:
Use case: Confidential lending markets where positions aren’t publicly exposed.
4. Zcash
The OG zk-SNARK Pioneer
While not DeFi-native, Zcash introduced shielded transactions using zk-SNARKs. Its innovations laid the groundwork for privacy-preserving financial logic.
Lesson: Privacy and compliance can coexist through selective disclosure.
5. Polygon zkEVM
Scalable + Compatible
Polygon zkEVM uses ZK-proofs to validate batches of transactions while staying compatible with Ethereum’s tooling.
Though focused on scalability, this tech can integrate privacy layers into DeFi protocols operating on rollups.
Key Use Cases in Privacy-Preserving DeFi
🔒 Private Lending
Borrowers prove solvency without exposing full balance sheets.
🏦 Confidential Treasury Management
DAOs operate without leaking strategy.
🧾 Selective Compliance
Prove KYC status without revealing identity details.
📊 Strategy Protection
Traders shield positions from front-running bots.
The Regulatory Elephant in the Room
Privacy in crypto often triggers knee-jerk reactions from regulators. But ZK-proofs actually offer a middle path:
This is programmable compliance—arguably more precise than traditional finance reporting.
Institutions don’t want secrecy for crime. They want confidentiality for competitive advantage. ZK makes that distinction enforceable.
Challenges Ahead
Let’s not pretend it’s magic.
But, like early smart contracts in 2016, complexity fades as tooling matures.
The Big Picture
The first wave of DeFi was about composability.
The second wave was about scalability.
The third wave will be about privacy.
Because financial sovereignty without privacy is just transparent banking with extra steps.
ZK-proofs are turning DeFi from a public spreadsheet into programmable, selective, cryptographic confidentiality.
And when institutions finally move on-chain at scale, they won’t do it naked.
They’ll do it with zero knowledge.
REQUEST AN ARTICLE
Crypto World
How Intelligence Packages from Cybercrime Atlas Powered Operations Resulting in $97 Million Recovery

TLDR:
- Cybercrime Atlas produced 13 intelligence packages and 17,000 vetted data points for four major operations.
- Operations across 19 African countries resulted in 1,209 arrests and identified over 120,000 victims.
- Research-driven approach recovered $97 million and disrupted $678 million worth of criminal activities.
- Over 30 organizations collaborate using open-source intelligence to map criminal network choke points.
Cybercrime Atlas has successfully converted research intelligence into concrete law enforcement operations during 2024 and 2025.
The initiative produced 13 intelligence packages and vetted 17,000 actionable data points that powered four major cross-border campaigns.
These coordinated efforts resulted in 1,209 arrests and recovered $97 million from criminal activities. The research-driven approach enabled law enforcement to disrupt $678 million worth of illicit operations across multiple continents.
Intelligence Gathering Powers Multi-National Operations
The Cybercrime Atlas community developed a structured methodology to transform fragmented research into unified action.
Over 30 organizations contributed open-source intelligence that mapped cybercriminal networks and infrastructure. Each intelligence package underwent community vetting before reaching law enforcement partners.
This research directly supported INTERPOL’s Operations Serengeti and Serengeti 2.0 across 19 African countries. The intelligence identified critical infrastructure including malicious domains, crypto wallets, and physical equipment used by criminal networks. Law enforcement agencies used these mapped connections to coordinate simultaneous takedowns.
Binance announced the results through X, highlighting how structured collaboration helps identify criminal infrastructure.
The World Economic Forum launched the initiative in 2023 to bridge private sector research with public enforcement capabilities. Open-source intelligence allows cross-border data sharing without violating privacy or legal constraints.
Research Group Identifies Criminal Choke Points
The Cybercrime Atlas established a Research and Mapping Group in 2025 to enhance operational effectiveness. Banco Santander, Group-IB, Binance, and Orange Cyberdefense initially led the group. Mastercard, Recorded Future, SpyCloud, and TNO joined later to expand research capabilities.
This group focuses on identifying choke points within criminal ecosystems where disruption creates maximum impact. Researchers analyze digital traces across compromised domains, social accounts, and payment channels. Technical tools from Maltego, ShadowDragon, and Silent Push enable efficient data correlation and visualization.
The methodology connects seemingly unrelated digital evidence into coherent maps of criminal operations. Researchers track infrastructure patterns and financial flows to reveal network vulnerabilities.
This systematic approach allows law enforcement to target nodes that weaken entire criminal organizations rather than individual actors.
Operational Results Validate Research-Driven Approach
The intelligence-to-action model produced measurable outcomes across multiple jurisdictions during the reporting period. Operations identified more than 120,000 victims and neutralized key criminal infrastructure.
INTERPOL Cybercrime Director Neal Jetton acknowledged the effectiveness of this collaborative framework, stating that the initiative “creates a force multiplier against cybercrime,” turning intelligence insights into measurable results.
Binance’s security teams contributed foundational research, link analysis, and attribution insights for intelligence packages.
The company’s work focused on mapping criminal networks exploiting cryptocurrency infrastructure. Erin Fracolli, Binance’s Global Head of Intelligence and Investigations, emphasized the strategic value of collaborative frameworks in securing digital ecosystems.
“Partnerships like the Cybercrime Atlas are critical to securing the digital-asset space and the broader digital environment,” Fracolli noted.
The initiative also expanded into capacity building, training law enforcement personnel from over 40 countries. Programs in Bangkok and Panama taught investigators how to apply private-sector intelligence in active cases.
The Cybercrime Atlas partnership with STOP THE TRAFFIK now integrates human trafficking data into cybercrime mapping efforts.
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-

 Tech5 days ago
Tech5 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-
![Heathrow has said passenger numbers were 60% lower in November than before the coronavirus pandemic and there were “high cancellations” among business travellers concerned about being trapped overseas for Christmas as Omicron spreads. The UK’s largest airport said the government’s travel restrictions had dealt a fresh blow to travel confidence and predicted it was likely to take several years for passenger numbers to return to pre-pandemic levels. This week ministers said passengers arriving in the UK would have to take a pre-departure Covid test, as well as a post-flight test, because of fears about the spread of the new variant. “[The] high level of cancellations by business travellers concerned about being trapped overseas because of pre-departure testing shows the potential harm to the economy of travel restrictions,” the airport said in an update. Heathrow said the drop in traveller confidence owing to the new travel restrictions had negated the benefit of reopening the all-important corridor to North America for business and holiday travel last month. Eleven African countries have been added to the government’s red list, requiring travellers to quarantine before reuniting with families. “By allowing Brits to isolate at home, ministers can make sure they are reunited with their loved ones this Christmas,” said John Holland-Kaye, the chief executive of Heathrow. “It would send a strong signal that restrictions on travel will be removed as soon as safely possible to give passengers the confidence to book for 2022, opening up thousands of new jobs for local people at Heathrow. Let’s reunite families for Christmas.” Heathrow said that if the government could safely signal that restrictions would be lifted soon, then employers at Heathrow would have the confidence to hire thousands of staff in anticipation of a boost in business next summer. The airport is expecting a slow start to 2022, finishing next year with about 45 million passengers – just over half of pre-pandemic levels. This week Tui, Europe’s largest package holiday operator, said it expected bookings for next summer to bounce back to 2019 levels. However, Heathrow said on Friday not to expect the aviation industry to recover for several years. “We do not expect that international travel will recover to 2019 levels until at least all travel restrictions (including testing) are removed from all the markets that we serve, at both ends of the route, and there is no risk of new restrictions, such as quarantine, being imposed,” the airport said.](https://wordupnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/shutterstock_1100012546-scaled-400x240.jpg)
![Heathrow has said passenger numbers were 60% lower in November than before the coronavirus pandemic and there were “high cancellations” among business travellers concerned about being trapped overseas for Christmas as Omicron spreads. The UK’s largest airport said the government’s travel restrictions had dealt a fresh blow to travel confidence and predicted it was likely to take several years for passenger numbers to return to pre-pandemic levels. This week ministers said passengers arriving in the UK would have to take a pre-departure Covid test, as well as a post-flight test, because of fears about the spread of the new variant. “[The] high level of cancellations by business travellers concerned about being trapped overseas because of pre-departure testing shows the potential harm to the economy of travel restrictions,” the airport said in an update. Heathrow said the drop in traveller confidence owing to the new travel restrictions had negated the benefit of reopening the all-important corridor to North America for business and holiday travel last month. Eleven African countries have been added to the government’s red list, requiring travellers to quarantine before reuniting with families. “By allowing Brits to isolate at home, ministers can make sure they are reunited with their loved ones this Christmas,” said John Holland-Kaye, the chief executive of Heathrow. “It would send a strong signal that restrictions on travel will be removed as soon as safely possible to give passengers the confidence to book for 2022, opening up thousands of new jobs for local people at Heathrow. Let’s reunite families for Christmas.” Heathrow said that if the government could safely signal that restrictions would be lifted soon, then employers at Heathrow would have the confidence to hire thousands of staff in anticipation of a boost in business next summer. The airport is expecting a slow start to 2022, finishing next year with about 45 million passengers – just over half of pre-pandemic levels. This week Tui, Europe’s largest package holiday operator, said it expected bookings for next summer to bounce back to 2019 levels. However, Heathrow said on Friday not to expect the aviation industry to recover for several years. “We do not expect that international travel will recover to 2019 levels until at least all travel restrictions (including testing) are removed from all the markets that we serve, at both ends of the route, and there is no risk of new restrictions, such as quarantine, being imposed,” the airport said.](https://wordupnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/shutterstock_1100012546-scaled-80x80.jpg) Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoWeight-loss jabs threaten Greggs’ growth, analysts warn
-

 Tech1 day ago
Tech1 day agoLuxman Enters Its Second Century with the D-100 SACD Player and L-100 Integrated Amplifier
-

 Video3 days ago
Video3 days agoThe Final Warning: XRP Is Entering The Chaos Zone
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month
-

 NewsBeat7 days ago
NewsBeat7 days agoResidents say city high street with ‘boarded up’ shops ‘could be better’
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
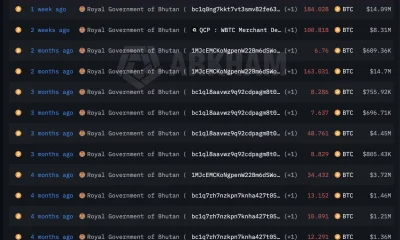
Crypto World2 days agoBhutan’s Bitcoin sales enter third straight week with $6.7M BTC offload
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-

 Video4 days ago
Video4 days agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-
Sports6 days ago
Kirk Cousins Officially Enters the Vikings’ Offseason Puzzle
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoEthereum Enters Capitulation Zone as MVRV Turns Negative: Bottom Near?
-

 NewsBeat12 hours ago
NewsBeat12 hours agoThe strange Cambridgeshire cemetery that forbade church rectors from entering
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoCrypto Speculation Era Ending As Institutions Enter Market
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoBarbeques Galore Enters Voluntary Administration
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoEthereum Price Struggles Below $2,000 Despite Entering Buy Zone
-

 NewsBeat14 hours ago
NewsBeat14 hours agoMan dies after entering floodwater during police pursuit
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy was a dog-humping paedo treated like a saint?








