Crypto World
BTC hashrate drops 12% in worst drawdown since China mining ban
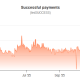
Bitcoin mining activity has taken its biggest hit since late 2021 after a severe winter storm in the United States forced several large mining firms to curtail operations, triggering a sharp drop in network hashrate, production and revenue.
Bitcoin’s total network hashrate has fallen about 12% since November 11, marking the largest drawdown since October 2021, when the network was still recovering from China’s sweeping mining ban.

The hashrate now sits near 970 exahashes per second, its lowest level since September 2025, according to CryptoQuant data.
The decline accelerated this week as extreme weather disrupted power supply across key US mining hubs.
Several publicly listed miners temporarily shut down machines to protect infrastructure and comply with grid curtailment requests, amplifying an already softening trend that began as bitcoin pulled back from its $126,000 all time high toward the $100,000 level late last year.
The hashrate shock quickly fed into miner economics. Daily bitcoin mining revenue dropped from roughly $45 million on January 22 to a yearly low of $28 million just two days later. While revenue has since rebounded modestly to around $34 million, it remains well below recent averages, reflecting both lower network activity and weaker bitcoin prices.
Production figures show an equally sharp contraction. Output from the largest publicly traded miners fell from 77 bitcoin per day to just 28 bitcoin over the same period. Production from other miners declined from 403 bitcoin to 209 bitcoin, bringing total network output down sharply.
On a 30-day rolling basis, publicly listed miners recorded a 48 bitcoin decline in production, the steepest since May 2024, shortly after the last halving. Output from non public miners dropped by 215 bitcoin, the largest fall since July 2024.
Profitability has also deteriorated, further pressuring the energy-intensive business.
CryptoQuant’s Miner Profit and Loss Sustainability Index has fallen to 21, its lowest reading since November 2024. The level signals that miners are operating in deeply stressed conditions, with revenues failing to cover costs for a growing share of the network despite multiple downward difficulty adjustments over recent epochs.

While difficulty has eased as machines went offline, the relief has not been enough to offset falling prices and operational disruptions. If hashrate remains suppressed, the network could see further difficulty cuts in coming weeks, offering some margin relief.
For now, the data points to one of the most challenging stretches for bitcoin miners since the post China ban reset more than four years ago.
Crypto World
Price Falls While Network Activity Surges
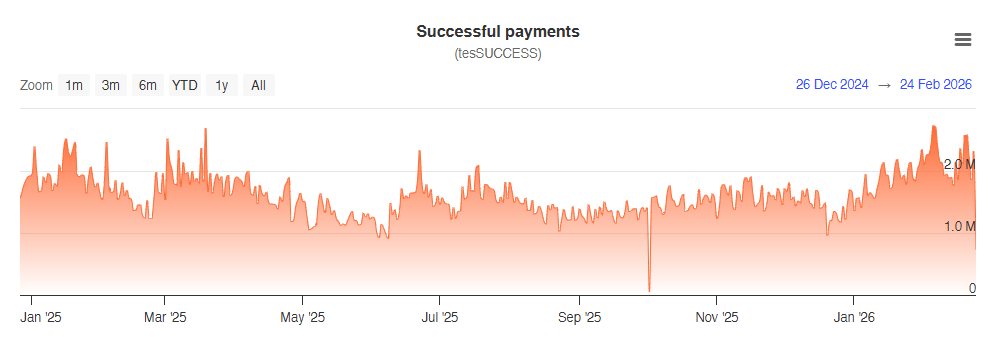
XRP Ledger recorded multiple breakthrough metrics in February. These figures reflect Ripple’s effectiveness in attracting attention and accelerating adoption on its underlying blockchain.
However, XRP’s price remained stuck below $1.4 during the final week of February, despite several positive signals that predicted an upcoming recovery.
Activity on XRP Ledger Increased in February After Upgrades
Data from XRPscan shows that the number of successful payments on the XRP Ledger has continuously increased over the past month. The figure rose from a low of 1 million payments at the end of December last year to more than 2.7 million in February. This marks the highest level in 12 months.
On the XRP Ledger, a successful payment is a transaction that validators have confirmed and recorded on the distributed ledger.
Therefore, this increase reflects the growing vibrancy of the XRP Ledger. A higher number of successful transactions proves that users genuinely use the network for payments, transfers, DeFi, or other applications.
“XRP network activity stays strong. Around 2M transactions per day and roughly 40K active addresses. That is real usage. While most chains chase narratives, XRPL keeps moving value. Payments. Settlements. This kind of consistency is what institutions look for,” crypto investor CryptoSensei said.
In addition, the Automated Market Maker (AMM) on the XRPL DEX showed signs of a breakout, with more than 14,000 deposits. This development provides XRPL with additional decentralized liquidity and reduces trading slippage.
Notably, AMM activity has never been this before. This breakout occurred after the Permissioned Domains upgrade was activated in early February. The network enabled the Permissioned DEX two weeks later.
Investors expect the Permissioned DEX to pave the way for banks, payment providers, and financial institutions to trade within a controlled liquidity environment on XRP Ledger.
Despite these positive signs, XRP’s price continued into its fifth consecutive month of decline, and the final week of February closed in the red. At the time of writing, XRP is trading at $1.33, down 45% from its early-year high.
A recent report from BeInCrypto shows that rising whale inflows to exchanges continue to create selling pressure. Realized losses have reached their highest level since 2022.
However, historical signals also suggest that such extreme negativity often precedes a price bottom and a strong recovery. The latest analysis from BeInCrypto clarifies that XRP now needs confirmation through a breakout above the $1.47 resistance level.
Crypto World
Nansen to Set up Bhutan Entity in Gelephu Mindfulness City
Blockchain analytics company Nansen will establish a local entity and build a Bhutan-based team in Gelephu Mindfulness City (GMC), expanding into the kingdom as its Special Administrative Region advances its digital asset strategy.
According to a joint announcement shared with Cointelegraph, Nansen plans to incorporate within GMC and develop on-the-ground analytics capabilities to provide blockchain data and market intelligence to industry participants operating in the region.
GMC is a purpose-built Special Administrative Region in southern Bhutan focused on long-term economic development. The region has previously announced digital asset initiatives spanning custody infrastructure, tokenization, institutional liquidity and regulatory frameworks.
The move does not replace Nansen’s existing operations in Singapore, CEO Alex Svanevik told Cointelegraph, but adds an additional entity within GMC, saying that the company “chose GMC because of the vision behind it.”
Svanevik added that Bhutan stood out because digital assets are being integrated into the region’s economic framework from the outset. He said:
Most crypto-friendly jurisdictions are optimizing for what exists today. Bhutan is building something fundamentally different — a values-driven economic zone with digital assets baked into the foundation, not bolted on as an afterthought. GMC has crypto in its strategic reserves, a progressive regulatory framework, and genuine sovereign conviction behind it. That’s rare. We want to be pioneers in that ecosystem.
Nansen plans to hire locally as part of the expansion. While the company did not disclose specific staffing targets, Svanevik said the intention is to build a “meaningful local team,” with details on roles and office setup expected in the coming months.
Nansen describes itself as an AI-native onchain analytics platform tracking more than 500 million labeled blockchain addresses and providing real-time data tools across major blockchain networks.
Related: Bhutan migrates its national ID system to Ethereum
Bhutan positions Gelephu Mindfulness City at the center of its digital asset strategy
Announced in 2023, Gelephu Mindfulness City is a special administrative region designed as a new economic hub to create high-value local jobs and attract businesses across sectors including finance, green energy, technology, healthcare and agriculture, while offering regulatory flexibility for crypto and fintech companies.
In December, the government said it would allocate up to 10,000 Bitcoin (BTC) from its national holdings to support the city’s development. Officials said they were evaluating treasury and risk-managed yield strategies for the Bitcoin holdings, alongside long-term plans aimed at preserving value while supporting stable and sustainable growth.
Nansen is not the first digital asset company to enter the region. Also in December, Crypto market maker Cumberland DRW signed a multi-year memorandum of understanding to help develop digital asset infrastructure in GMC, including financial frameworks, sustainable mining and AI compute, yield strategies and stablecoin infrastructure.
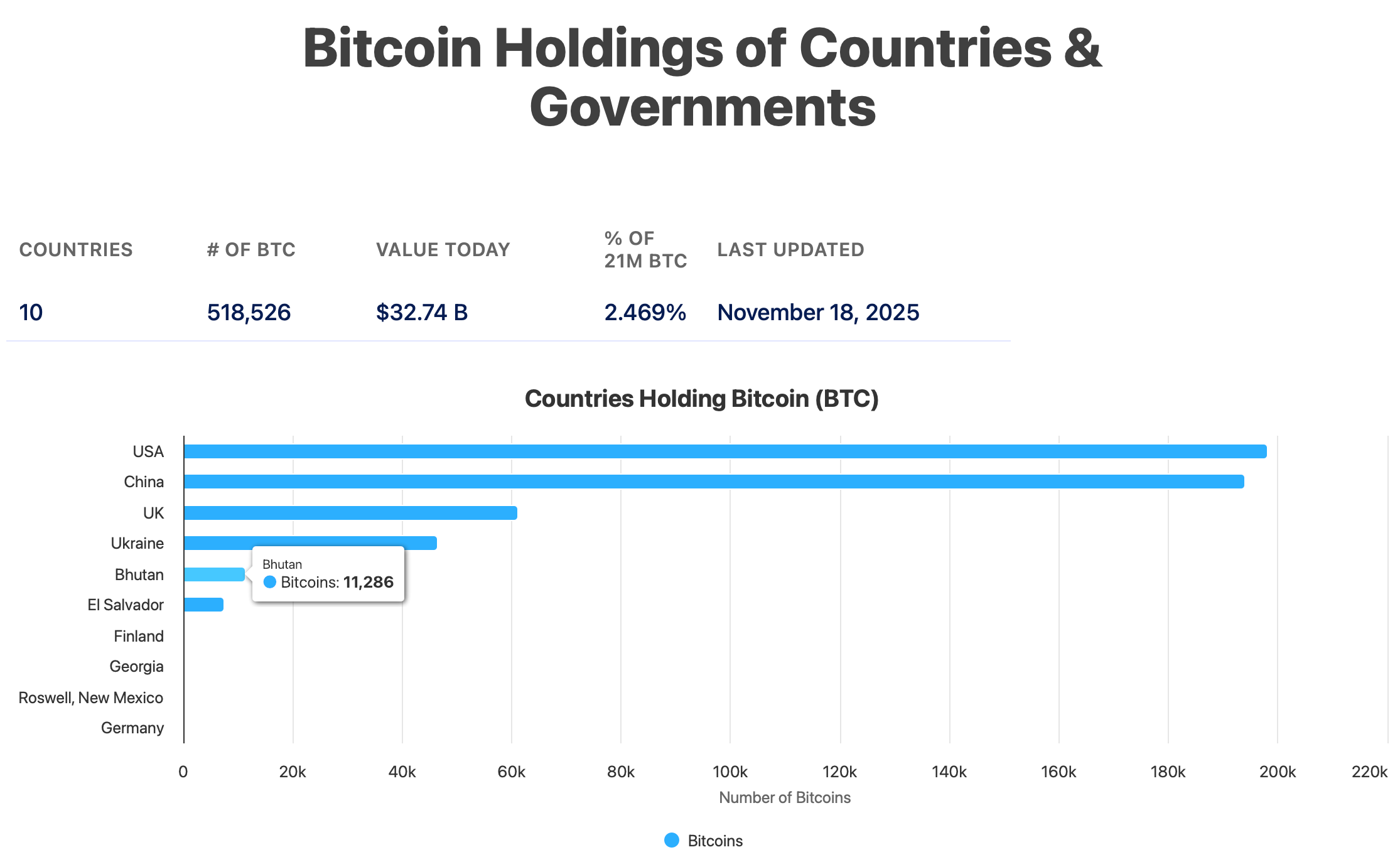
Bhutan holds the world’s fifth-largest national Bitcoin reserve, with Bitbo estimating its holdings at 11,286 BTC, as of Nov. 18.

The country’s crypto strategy is spearheaded by Druk Holding and Investments (DHI), the commercial arm of the royal government.
In an April 2025 interview with Reuters, DHI CEO Ujjwal Deep Dahal said the fund began accumulating cryptocurrencies in 2019 to convert surplus hydropower into foreign-currency liquidity, and senior officials in the capital of Thimphu have said some profits have helped support government salary payments over the past two years.
Magazine: Is China hoarding gold so yuan becomes global reserve instead of USD?
Crypto World
ZachXBT Insider Trading Report Targets Major Crypto Firm in 2 Days
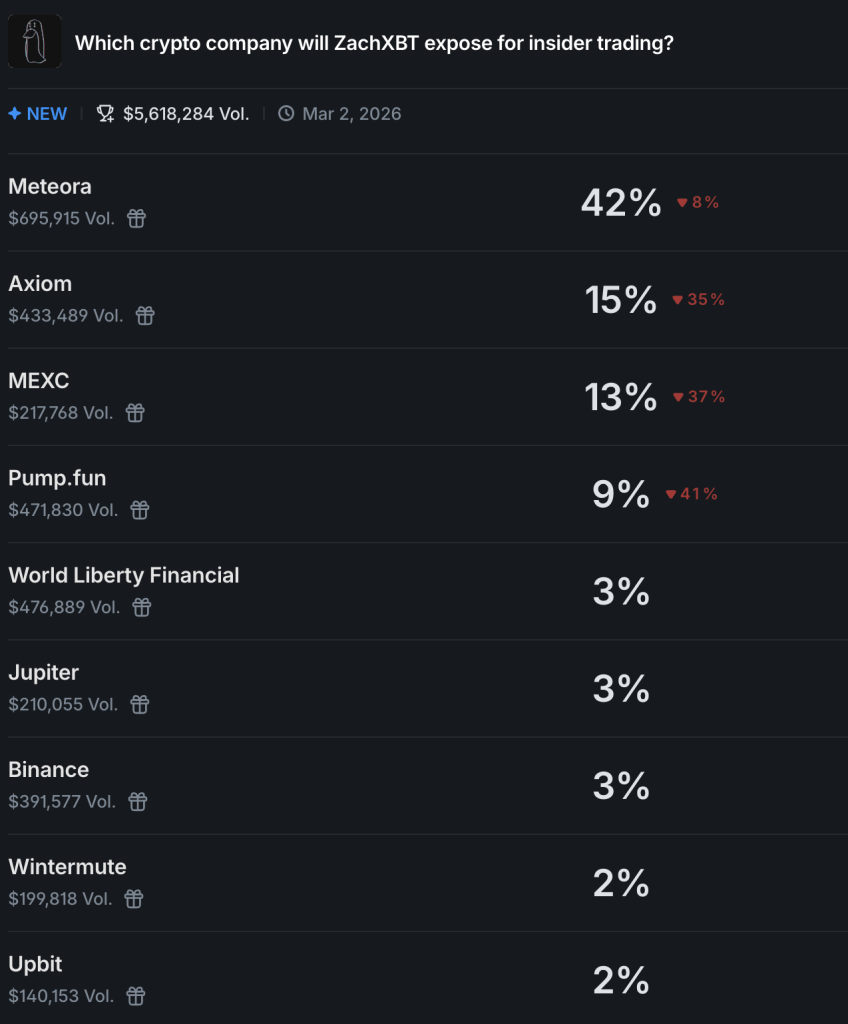
A major shake up could be coming as on chain investigator ZachXBT says he will publish a full insider trading exposé on February 26, targeting what he calls a major industry player tied to systemic market abuse.
Traders are not waiting. Prediction market volume around the target’s identity has surged toward $3M as participants hedge for potential fallout.
Right now, odds point toward names like Solana based liquidity protocol Meteora and the Trump backed World Liberty Financial as leading suspects.
Key Takeaways
- $6 Million Prediction Market Volume: Trading activity on the ZachXBT investigation market has surpassed $5.6 million as speculators attempt to price in the target’s identity.
- Meteora at 43% Odds: The Solana-based liquidity layer is currently the betting favorite to be named in the report, followed by infrastructure provider Axiom.
- Systemic MNPI Abuse: The investigation alleges that multiple employees exploited Material Non-Public Information to execute profitable trades over a prolonged period.
What Is the ZachXBT MNPI Investigation?
ZachXBT, known for tracing illicit crypto flows, says a major report is coming on February 26. The target is described as one of the industry’s most profitable firms, with allegations that insiders traded on material non public information to front run announcements.
The case reportedly began with a January Telegram exchange where wallet addresses tied to a firm’s treasury were shared, showing accumulation before public news. That kind of on chain trail can be hard to dismiss and often draws regulatory attention.
ZachXBT’s track record adds weight. Past investigations have led to frozen funds and law enforcement action. That is why traders see February 26 as a binary event. Either the evidence is strong enough to trigger serious fallout, or the accused project walks away under heavy scrutiny.
Prediction Markets Hit $3M as ZachXBT Odds Shift to Meteora
Speculators are already trading on the rumor. On Polymarket, volume on the “Which crypto company will ZachXBT expose?” contract is nearing $6M. Meteora leads with around 42% odds, followed by Axiom at 15% and Pump.fun near 9%.
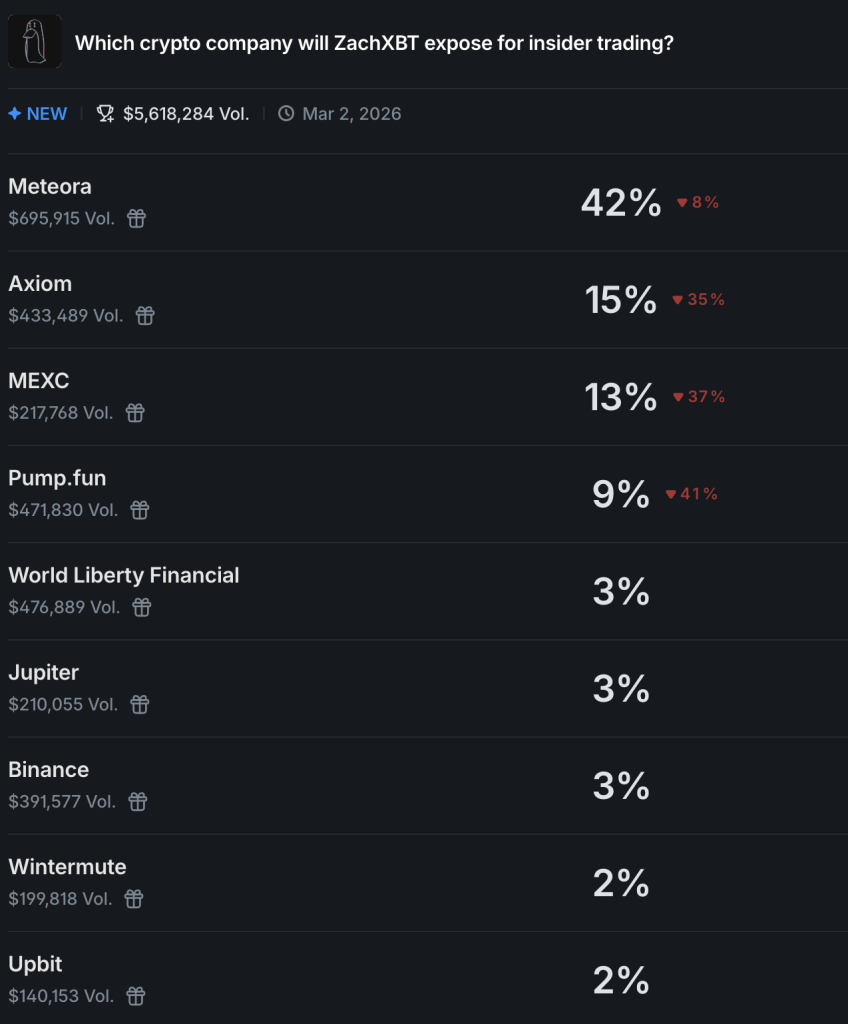
The sharp jump in Meteora’s probability, while others like Jupiter and MEXC lag in single digits, shows concentrated conviction. Big names like Tether, Binance, and Coinbase are listed, but with low odds.
Still, prediction markets price belief, not proof. They reflect positioning and sentiment ahead of confirmation.
Why Meteora Is the Leading Suspect in the MNPI Probe
Meteora has emerged as the top suspect because it fits the profile of a highly profitable Solana based liquidity protocol with access to sensitive incentive data.
Onchain analysts have flagged wallet clusters interacting with its pools that appear to position ahead of yield adjustments, fueling speculation of potential MNPI abuse.
If confirmed, the fallout could ripple across the Solana ecosystem, especially if aggregators and routing platforms distance themselves quickly.
WLFI remains a lower probability but higher impact scenario. Its political ties raise the stakes, and any confirmed insider trading linked to a Trump affiliated project would likely draw immediate regulatory scrutiny. While markets see Meteora as the base case, WLFI represents a volatile tail risk.
If ZachXBT’s report delivers clear wallet attribution, the targeted token could see a sharp downside within minutes. Until then, prediction market volume reflects positioning, not proof.
Discover: Here are the crypto likely to explode!
The post ZachXBT Insider Trading Report Targets Major Crypto Firm in 2 Days appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
Fed’s Goolsbee calls for a hold on cuts as current rate of inflation is ‘not good enough’
Austan Goolsbee, president and chief executive officer of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, speaks during the National Association of Business Economics (NABE) economic policy conference in Washington, DC, US, on Tuesday, Feb. 24, 2026.
Graeme Sloane | Bloomberg | Getty Images
Chicago Federal Reserve President Austan Goolsbee said Tuesday that interest rate cuts aren’t appropriate until there’s more evidence that inflation is on its way down.
With recent indicators showing that inflation well off its highs but still above the Fed’s 2% target, Goolsbee noted that policymakers “have been burned by assuming transitory inflation” in the past and shouldn’t make the same mistake again.
“I feel that front-loading too many rate cuts is not prudent in that circumstance,” he said in remarks before the National Association for Business Economics at its annual gathering in Washington, D.C. “People express that prices are one of their most pressing concerns. Let’s pay attention. Before we cut rates more to stimulate the economy, let’s be sure inflation is heading back to 2%.”
The most recent inflation data, for December, showed core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, running at 3%, as measured by the consumption expenditures price index, the Fed’s primary forecasting gauge. That was up 0.2 percentage point from November and came somewhat due to tariffs, which are viewed as temporary, but also from underlying pressures in the service sector and areas not directly impacted by the duties.
Specifically, Goolsbee said stubbornly high housing inflation isn’t tariff driven, emphasizing the need for the Fed to be “vigilant.”
Goolsbee noted that a 3% inflation rate “is not good enough — and it’s not what we promised when the Federal Reserve committed to the 2% target. Stalling out at 3% is not a safe place to be for a myriad of reasons we know all too well.” He has said previously that he thinks the Fed will be able to cut later in the year.
The remarks come with markets expecting the Federal Open Market Committee, of which Goolsbee is a voter this year, to stay on hold until at least June and probably July. Futures traders are placing about a 50-50 chance of a cut in June and about a 71% probability of a July cut, according to the CME Group’s FedWatch gauge. The Fed enacted three quarter-percentage-point cuts in the latter part of 2025.
Fed Governor Christopher Waller, who has been an advocate for lower rates, took a more measured approach Monday while also speaking to the NABE conference.
Though Waller said he thinks policymakers should “look through” tariff impacts, he said recent data show the labor market may be in better shape than previously indicated, mitigating the need for further cuts. If the jobs picture continues to improve, that would further lessen the case for cuts, though he said he isn’t convinced that the January nonfarm payrolls data wasn’t “more noise than signal.”
Tuesday will be an active day Fed speakers, with Governor Lisa Cook also due to present to the NABE later in the morning.

Crypto World
What Past Cycles Say Happens Before the Bottom
Bitcoin price dropped 25% in 2022 and 50% in 2018 after similar on-chain loss signals, a warning sign for BTC’s next move.
Bitcoin (BTC) traders are selling at a loss for the first time since 2022, raising odds that the biggest cryptocurrency’s ongoing price correction may deepen in the coming weeks.
Key takeaways:
-
Bitcoin is witnessing loss-driven selling that has historically lasted six months or more.
-
These signals surfaced during previous bear markets, preceding sharp downtrends each time.
BTC capitulation may last for another six months
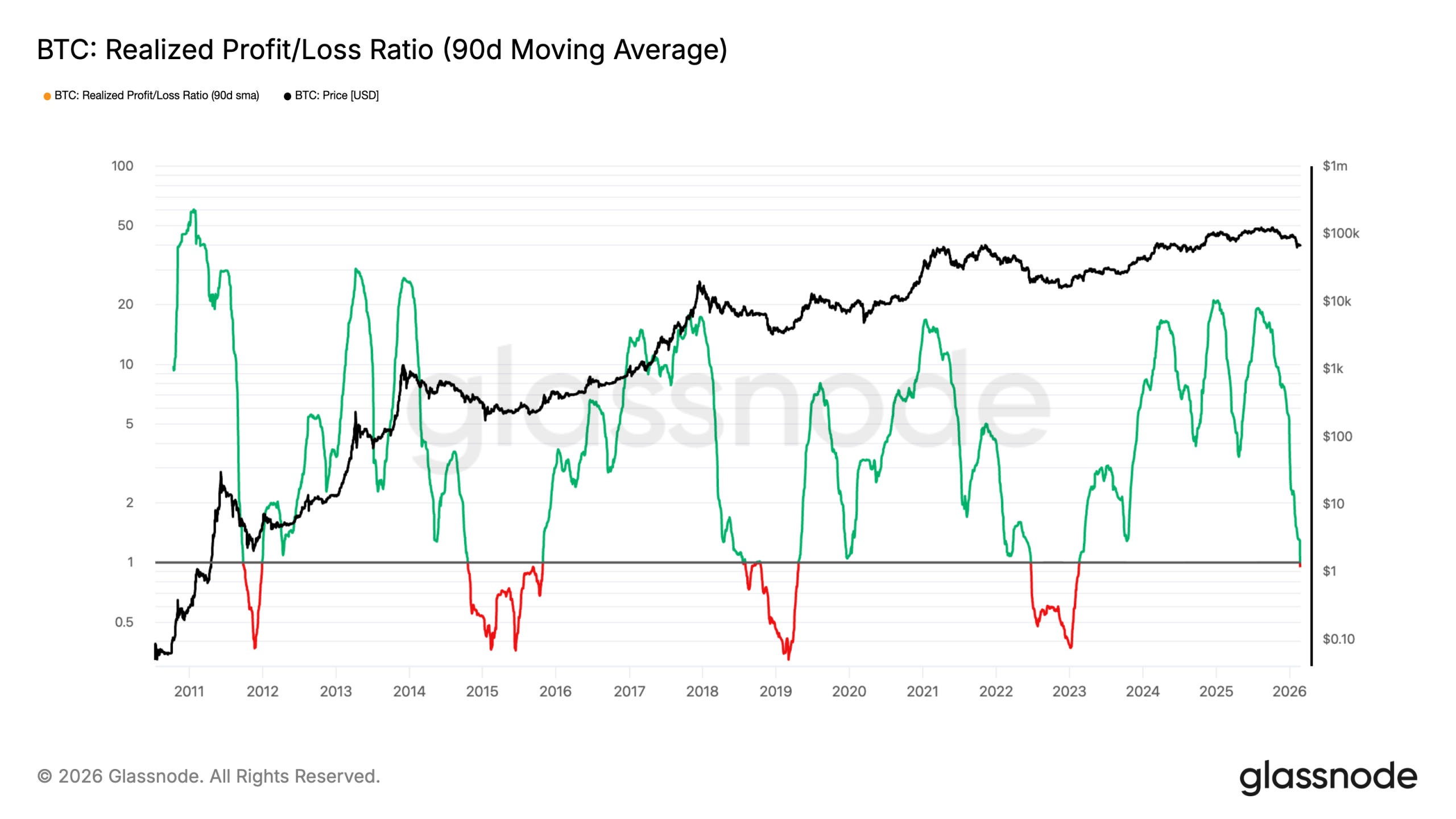
On Monday, Bitcoin’s realized profit/loss ratio (90-day moving average) slipped below 1.
The drop indicated that traders were dumping their BTC holdings at a loss, which is often linked to panic selling, margin pressure, or broader risk-off conditions.

Historically, breaks below 1 preceded at least six months of loss realization, according to on-chain data resource Glassnode. Meanwhile, a move back above 1 usually suggests that selling pressure is easing.
Traders often sell at a loss when they expect the downtrend to continue. In prior bear markets, loss-taking typically accelerated midway through the cycle, followed by more downside in Bitcoin’s price.
During the 2022 bear market, for instance, BTC declined 25% six months after its realized profit/loss ratio dropped below 1. In 2018, it plunged by over 50% in five months under similar conditions, as shown below.

The BTC price may continue its downtrend for another five months or more if history repeats. That will confirm “a full transition into an excess loss-realization regime,” Glassnode wrote.
Bitcoin price may bottom around $44,000
Bitcoin’s rising loss-realization may, therefore, drag the BTC price into its “extreme low” valuation zones.
These lows exist within the MVRV Pricing Bands metric, which maps where Bitcoin reaches extreme unrealized profit or loss zones. Historically, its lowest band (the blue line) has coincided with Bitcoin bear market bottoms.

As of February, the extreme low was around $43,760, a potential downside target by August if BTC’s price decline continue further.
Related: Bitcoin’s Mayer Multiple hits 2022 levels: Where is BTC price bottom?
The level also sits within the broader $40,000–$50,000 bottom range flagged by multiple analysts as a potential late-2026 target.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision. While we strive to provide accurate and timely information, Cointelegraph does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any information in this article. This article may contain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Cointelegraph will not be liable for any loss or damage arising from your reliance on this information.
Crypto World
Kraken brings crypto-style, 24/7 perpetuals trading for tokenized U.S. stocks


Crypto exchange Kraken is launching what it calls the first regulated perpetual futures contracts based on tokenized stocks, the firm told CoinDesk.
The products, available to eligible non-U.S. users in more than 110 countries, track digital versions of major U.S. stocks, indices and a gold ETF, building on the tokenized equities offering of xStocks that Kraken acquired in December.
Initial listings include tokenized versions of the S&P 500, the Nasdaq 100, Apple, Nvidia, Tesla and SPDR’s gold ETF (GLD), the firm said.
Kraken’s launch matters because perpetuals trading has enjoyed a rapid growth, dominating crypto derivatives trading. Blockchain-based decentralized exchanges processed over $600 billion in perps trading volume in January, with Hyperliquid claiming the biggest market share with $200 billion monthly volume, data by The Block shows.
Unlike traditional futures contracts, perps do not expire and trade 24/7 and allow users to trade with high leverage. Investors favor them for continuous access, capital efficiency and the ability to take long or short positions at any time.
With Kraken’s move, that structure now is expanded to other asset classes like equities. The underlying xStocks tokens are fully collateralized and backed 1:1 by the referenced assets, according to the company. That provides a pricing anchor even when U.S. exchanges are closed. The tokenized stocks trade around the clock and support leverage of up to 20x.
“This is what it looks like when traditional markets are rebuilt for a crypto-native, always-on world, not a moment too soon given the volatility that all markets are exhibiting,” Mark Greenberg, Kraken’s global head of consumer, said in a statement.
“Regulated tokenized equities as perpetual futures represent a new chapter for global capital markets, one where equities, indices, and commodities trade with the same speed, accessibility, and flexibility as crypto via tokenization, delivering a more robust risk management experience,” he added.
Kraken said it plans to expand the lineup with more tokenized stocks and ETFs in the coming months.
Rival tokenization firm Ondo Finance earlier this month also announced plans to launch perps trading with its tokenized stocks.
Read more: Kraken’s co-CEO could trust AI with 100% of his crypto — Dragonfly’s Haseeb Qureshi isn’t convinced
Crypto World
Tether-Backed Oobit Adds Crypto-to-Bank Transfers


Crypto payment provider Oobit has launched crypto-to-bank transfers that settle into bank accounts via local payment rails, expanding its app beyond in-store spending and peer-to-peer (P2P) transfers.
In an announcement shared with Cointelegraph, Oobit said users could send supported digital assets from self-custody wallets and have funds deposited into bank accounts through networks including the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) in Europe, the Automated Clearing House (ACH) in the United States and Mexico’s Sistema de Pagos Electrónicos Interbancarios (SPEI).
Settlement currencies include US dollars, euros, Mexican pesos and Philippine pesos, while supported assets include Bitcoin (BTC), Ether (ETH) and a range of stablecoins such as Tether (USDT), USDC (USDC), EURC and EURR, along with other tokens including XRP (XRP), BNB (BNB), Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA) and Dogecoin (DOGE).
Related: VCI Global unveils crypto treasury plan, backs Tether’s payments arm OOBIT
Oobit said that users could see the crypto amount leaving their wallet and the fiat equivalent arriving in the recipient’s account before confirming the transactions.
It described the system as routing transactions through local payment rails instead of traditional correspondent banking channels.
Unlike checkout-based providers that redirect users to third-party interfaces, Oobit said the transfer flow is embedded natively inside its app, without redirecting users to an external off-ramp provider.
Crypto off-ramps heating up
The rollout highlights growing competition in crypto off-ramping, where exchanges and fintech companies allow users to convert digital assets into fiat deposits.
Oobit’s stated differentiator is its focus on self-custody wallets, positioning the app as a payments layer that connects onchain assets to bank accounts without requiring users to hold funds on a centralized exchange.
DTR tie-up and Bakkt acquisition
Oobit says that the feature is powered by infrastructure from Distributed Technologies Research (DTR), which connects Oobit’s wallet interface to domestic payment networks.
DTR recently entered into an agreement to be acquired by Bakkt, a US-listed digital asset platform launched by the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) in 2018.
Akshay Naheta, DTR founder and CEO of Bakkt, said in the release that infrastructure connecting digital asset platforms with traditional financial systems was “foundational to broader adoption.”
Amram Adar, co-founder and CEO of Oobit, told Cointelegraph the company’s model differs from traditional off-ramp providers in both custody structure and user flow. “The end-user relationship, wallet custody and transaction experience remain entirely within Oobit,” Adar said.
According to Adar, user funds are initially held within Oobit’s wallet infrastructure. When a bank transfer is initiated, funds are debited and transferred to DTR strictly for payout execution. DTR forwards the funds to the recipient bank account and does not hold funds for investment or discretionary purposes.
Oobit performs the initial crypto-to-USD conversion, after which the USD-equivalent value is transferred in USDT to DTR. DTR then executes the foreign exchange conversion into local fiat currency before settlement into the designated bank account, Adar said.
Oobit has previously disclosed backing from Tether, the issuer of USDT, linking the app to the largest stablecoin operator by market capitalization.
Related: Bybit to launch retail bank accounts with personal IBANs in February
Fees, limits and expanding infrastructure
Adar said the service is fully live across all countries supported by DTR, with no pilot corridors currently in place. US dollar transfers are limited to domestic US flows.
Minimum transfers range from a roughly 10 euro ($11.70) to $100 equivalent, depending on the corridor, while maximum limits can reach about a $50,000 equivalent.
Total fees consist of components charged by both Oobit and DTR. Oobit applies the greater of a fixed fee, currently contemplated at $1, or a 1% transaction fee, along with an estimated 0.5% spread on crypto-to-USD conversions.
DTR applies either a fixed fee, generally between about 0.65 cents and 2 euro depending on the currency, or a percentage-based fee ranging from about 0.65% to 1%, according to the company.
The integration comes as banks and fintech firms deepen efforts to embed blockchain-based assets into regulated payment systems.
Major payment players like Visa have rolled out USDC-based settlement and stablecoin payouts for financial institutions, and Crypto.com has used Circle’s application programming interfaces (APIs) to support dollar bank transfers to and from USDC wallets.
On Monday, digital asset infrastructure company Stablecore joined the Jack Henry Fintech Integration Network, enabling more than 1,600 US banks and credit unions to add stablecoin services through existing core banking platforms.
On the same day, TRM Labs announced a partnership with Finray Technologies to unify crypto and fiat transaction monitoring for institutions operating under Europe’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation.
Magazine: Hong Kong stablecoins in Q1, BitConnect kidnapping arrests: Asia Express
Crypto World
Smarter Web Secures $30M Coinbase Credit to Speed BTC Buys After Fund

The Smarter Web Company PLC, a United Kingdom-listed Bitcoin treasury holder, has secured a $30 million Bitcoin-backed credit facility with Coinbase Credit. The move is designed to provide liquidity to accelerate Bitcoin purchases immediately after equity raises, reducing settlement timing risk in volatile markets. The company underscored that the facility is not intended to be a long-term debt instrument for ongoing BTC purchases. Smarter Web is publicly traded on the London Stock Exchange’s Main Market and also trades on the OTCQB Venture Market in the United States, with Bitcoin described as a core pillar of its treasury strategy and a stated goal to expand its digital asset holdings. The arrangement leverages Bitcoin held in custody with Coinbase as collateral, per a February 24, 2026 filing. See the attached document here: PDF.
The latest development sits within a broader context of digital asset treasuries (DATs), which posted multi-billion dollar net inflows late in 2025 and into January 2026 before cooling in February. Data tracked by DefiLlama show inflows of $4 billion in December, followed by $3.7 billion in January, and then a marked slowdown to $363 million by February 24, 2026, as risk sentiment evolved. This pattern reflects a climate in which corporate balance sheets continue to scrutinize liquidity tools tied to Bitcoin exposure, even as overall demand for DATs moderates in the short term. See DefiLlama’s digital asset treasuries page for the latest inflow readings: DefiLlama.
According to BitcoinTreasuries.net, Smarter Web’s Bitcoin holdings stood at 2,689 BTC, purchased at an average cost of $112,865 per coin. At current price levels, those holdings value roughly $170 million, implying an unrealized loss of about 44% against the reported cost basis. The company’s disclosures note that, as of September 12, 2025, Smarter Web owned 2,470 BTC and described itself as the UK’s largest corporate Bitcoin holder at that time, signaling ongoing intent to grow its digital asset position. The firm also signaled interest in acquiring competitors to broaden its treasury and to pursue a spot on the FTSE 100 index. The latest holdings data suggest continued accumulation since the September 2025 update. For reference, see BitcoinTreasuries.net’s entry on Smarter Web: Smarter Web Bitcoin treasury.
The financing arrangement is designed to enable Swifter Web to borrow against its existing Bitcoin holdings to move more rapidly after equity raises, with repayment tied to the successful settlement of fundraising proceeds. The structure highlights a trend toward liquidity-centric use of BTC-backed facilities among corporate treasuries, as opposed to financing the ongoing purchase of BTC with new debt. The broader market context includes examples of divergent corporate Bitcoin strategies, where some firms are expanding exposure while others are reducing or liquidating holdings in response to capital needs and strategic shifts. For instance, a recent article discusses Strategy’s continued accumulation, with a 100th BTC purchase bringing its total to 717,722 BTC, while Bitdeer announced the liquidation of its entire Bitcoin treasury in a separate move to raise capital via a convertible debt offering. See: Strategy’s BTC purchases and Bitdeer’s treasury sale.
Diverging corporate Bitcoin strategies
The Smarter Web facility arrives amid a spectrum of corporate approaches to Bitcoin exposure. Some companies continue to add BTC to their treasuries, while others take liquidity-focused steps that involve selling or retooling holdings to support capital raises or strategic initiatives. The broader narrative underscores how treasury management is evolving as firms weigh balance-sheet resilience against market volatility and regulatory considerations.
Why it matters
The move by Smarter Web underscores a practical use-case for BTC-backed debt facilities beyond mere investment. By tying a credit facility to Bitcoin held in custody, the company can fast-track deployment of capital in the wake of equity raises, potentially capturing favorable entry prices and decoupling settlement timing from volatile market conditions. This kind of liquidity tool can help a corporate treasury bridge the gap between fundraising and asset deployment, reducing the risk of price slippage or missed opportunities during short windows after a financing round.
From a market-wide perspective, the development reflects ongoing experimentation with Bitcoin as a corporate treasury instrument. The inflow data from DATs suggests sustained interest in BTC-backed liquidity strategies through late 2025 and early 2026, even as overall momentum moderated in February. As BTC remains a volatile asset class, facilities that offer rapid access to liquidity while preserving long-term exposure can alter how companies plan capital allocation, M&A, and strategic initiatives, especially for firms with large Bitcoin holdings and ambitious growth agendas.
For investors tracking corporate exposure to Bitcoin, Smarter Web’s approach adds to the evidence that Bitcoin is being treated less as a speculative bet and more as a strategic balance-sheet asset. The company’s stated intent to avoid long-term debt financing for BTC purchases aligns with an emphasis on risk management and disciplined capital structure. As more issuers experiment with credit facilities secured by Bitcoin, market participants will watch for how these tools affect debt covenants, impacts on earnings volatility, and the potential signaling effect on other treasuries considering similar structures.
What to watch next
- Smarter Web’s upcoming earnings updates or capital-raising rounds to disclose how the facility is used to accelerate BTC deployments.
- Any changes to the company’s BTC holdings, including new acquisitions or rebalancing that would adjust the cost basis and unrealized gains/losses.
- Regulatory or market developments that could influence the viability or cost of BTC-backed facilities for corporates.
- Further DAT inflow/outflow signals from DefiLlama to gauge ongoing demand for Bitcoin treasury strategies.
- Announcements from related corporate treasuries (e.g., additional purchases, sales, or new liquidity facilities) that could provide context for Smarter Web’s strategy.
Sources & verification
- The strategic credit facility document: https://www.smarterwebcompany.co.uk/smarterweb-co-uk/_img/pdf/news/2026-02-24-strategic-credit-facility.pdf
- Smarter Web Bitcoin treasury data on BitcoinTreasuries.net: https://bitcointreasuries.net/public-companies/the-smarter-web-company-plc
- DefiLlama digital asset treasuries inflow data: https://defillama.com/digital-asset-treasuries
- Strategy BTC purchases article: https://cointelegraph.com/news/strategy-100th-bitcoin-purchase-592-btc
- Bitdeer Bitcoin treasury sale article: https://cointelegraph.com/news/bitdeer-sells-bitcoin-treasury-zero-holdings
Smarter Web taps Coinbase-backed facility to accelerate BTC deployment
In a strategic move to bolster liquidity after equity raises, The Smarter Web Company PLC has secured a $30 million Bitcoin-backed credit facility with Coinbase Credit. The facility is secured against Bitcoin held in custody with Coinbase and enables the company to move capital into Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) immediately when fundraising closes, while reducing settlement timing risk during volatile markets. The company reiterates that the facility is not intended to finance ongoing, long-term BTC purchases, but rather to bridge liquidity between fundraising and deployment. Smarter Web is listed on the London Stock Exchange’s Main Market and trades on the OTCQB Venture Market in the United States; the firm emphasizes Bitcoin as a core component of its treasury strategy and has signaled an ambition to grow its digital asset holdings. The facility is designed to allow borrowing against existing holdings to accelerate post-raise deployment and to repay when fundraising proceeds settle. The filing and related documentation are available here: PDF.
The broader context for this move includes a pattern of positive net inflows into DATs through late 2025 and early 2026, followed by a cooling period in February. DefiLlama’s chart of inflows shows $4 billion in December, $3.7 billion in January, and roughly $363 million through February 24, 2026, indicating a deceleration after a burst of interest. This backdrop helps explain why Smarter Web would pursue a credit facility that unlocks faster deployment in response to equity raises while preserving long-term capital discipline. See DefiLlama’s DAT data for the latest series on inflows: DefiLlama.
Smarter Web’s Bitcoin holdings, tracked by BitcoinTreasuries.net, stood at 2,689 BTC with an average cost of $112,865 per coin, placing the current implied value near $170 million and an approximate unrealized loss of 44%. The company had previously disclosed a September 12, 2025 position of 2,470 BTC and described itself as the UK’s largest corporate Bitcoin holder at the time, with ambitions to acquire rivals to expand its treasury and potentially join the FTSE 100. The latest data suggest continued accumulation since that update, reinforcing the narrative of an aggressively managed digital-asset treasury. See Smarter Web’s BTC page for reference: Smarter Web BTC.
The rationale behind the facility is straightforward: borrow against existing BTC to accelerate deployment after fundraising, and repay once cash from the equity raise settles. It reflects how public companies are testing liquidity rails that preserve Bitcoin exposure while managing timing risk and balance-sheet constraints. The broader corporate landscape shows a mix of strategies, with some firms continuing to add BTC to their treasuries while others pivot to capitalize on capital-raising opportunities or to de-risk their holdings in a dynamically shifting market environment.
Crypto World
Coinbase Stablecoin Revenue Hits $1.35B: Bloomberg Sees 7x Growth Potential


Bloomberg Intelligence forecasts that Coinbase’s stablecoin revenue could jump sevenfold from its current $1.35 billion annual run rate.
Analysts point to a structural shift where stablecoins move beyond crypto trading collateral to become a primary rail for mainstream global payments.
Key Takeaways
- Coinbase generated approximately $1.35 billion in stablecoin revenue last year, accounting for 19% of its total income.
- Bloomberg Intelligence projects a potential 7x surge in this figure as regulatory frameworks drive payment adoption.
- The expansion hinges on the codified GENIUS Act, merchant integration via Stripe, and volume growth on the Base network.
Why Bloomberg Sees a Sevenfold Surge in Coinbase Stablecoin Revenue
Bloomberg Intelligence analysts, including Paul Gulberg, argue that the market is underestimating the utility phase of the stablecoin lifecycle.
While Coinbase reported $1.35 billion in stablecoin revenue for 2025, roughly 19% of its total top line, Bloomberg models suggest this figure is merely a baseline.
The forecast arrives despite Coinbase noting a net loss of $667 million in Q4 2025. The exchange’s revenue share agreement with Circle, the issuer of USDC, remains a bright spot, generating $364 million in the fourth quarter alone.
Bloomberg’s 7x multiple assumes that as interest rates stabilize, the sheer velocity of payment transactions will eclipse interest income as the primary revenue driver.
This thesis aligns with broader market data showing stablecoin transaction volumes hitting $33 trillion in 2025.
With USDC accounting for $18.3 trillion of that flow, the asset has already begun to decouple from pure crypto trading volumes.
The scale is big enough that the traditional finance sector can no longer ignore the fee generation potential.
Discover: The best Solana meme coins
How the GENIUS Act Is Accelerating Stablecoin Mainstream Adoption
The regulatory landscape shifted dramatically with the signing of the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for US Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act in July 2025.
By creating a federal regime for payment stablecoins, the legislation provided the legal certainty required for large-scale institutional participation.
The Act explicitly bars issuers like Circle from paying interest to holders, a move backed by the banking lobby to protect traditional deposits.
While the regulatory framework for digital assets remains complex, the GENIUS Act has effectively greenlit stablecoins for commercial usage.
This clarity allows Coinbase to market USDC settlements to Fortune 500 companies without the overhang of legal ambiguity that plagued the sector in previous years.
Stripe Integration and Base Network Expansion Drive Payment Ambitions
Operational catalysts are already live, fueling the Bloomberg projection. The integration of USDC into Stripe’s global payment rails has reopened crypto acceptance for millions of merchants, creating a direct funnel for transaction volume.
Simultaneously, Coinbase’s own Layer-2 blockchain, the Base network, is lowering the barrier to entry for micro-transactions.
Much like other scaling solutions, the Base network reduces gas fees to fractions of a cent, making dollar-denominated transfers economically viable for daily coffee purchases.
High-throughput networks are critical here, as the Bitcoin Lightning Network demonstrated with its $1 billion monthly volume milestones, low-fee environments rapidly attract payment liquidity.
By routing these payments through Base, Coinbase captures value twice: once through the underlying sequencer fees and again through its revenue share on the growing supply of USDC required to service this commerce.
Discover: The top crypto for portfolio diversification
What a 7x Revenue Jump Would Mean for the Stablecoin Market
If Bloomberg’s 7x scenario plays out, stablecoin revenue would arguably become Coinbase’s most valuable business line, overshadowing its volatile trading fees.
This shift would fundamentally re-rate the stock, moving it from a cyclical crypto exchange play to a steady fintech payments processor. However, risks remain substantial.
The banking lobby is currently pushing the CLARITY Act in the Senate to close loopholes that allow exchanges like Coinbase to pass rewards to customers.
If new language bars these rewards, consumer adoption could slow.
Analysts at Monness Crespi maintain a sell rating, warning that optimistic projections effectively ignore the political target painted on stablecoin yields.
So, for Bloomberg’s 7x to be possible, Coinbase must defend its rewards program while successfully migrating user activity from holding USDC to spending it.
The post Coinbase Stablecoin Revenue Hits $1.35B: Bloomberg Sees 7x Growth Potential appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
$80 Floor fails, whales track this new crypto protocol


Disclosure: This article does not represent investment advice. The content and materials featured on this page are for educational purposes only.
Solana slides below key levels as investors shift focus to emerging DeFi protocol Mutuum Finance.
Summary
- Mutuum Finance rolls out dual P2C and P2P lending model with automated APY and LTV risk controls.
- V1 launches on Sepolia testnet, letting users trial WBTC, ETH, USDT, and LINK lending before mainnet.
- Health factor scoring, mtTokens, and real-time dashboards are powering Mutuum’s collateralized DeFi lending system.
Solana (SOL) is facing a difficult period as its price drops below key levels. The popular altcoin recently failed to hold its ground, causing a shift in market sentiment.
While many traders watch the charts with concern, a new crypto protocol, Mutuum Finance (MUTM), is gaining attention. Many large investors are now exploring this project as they look for fresh utility in the decentralized finance space.
Solana
Solana is currently trading at approximately $79, with its total market capitalization sitting near $45 billion. The critical $80 support level recently failed due to institutional sell-offs and global economic uncertainty.
This breakdown has led many analysts to predict a further slide toward the $67 range as long as buyers do not return quickly. Most investors now expect a period of consolidation as the network waits for a potential recovery in broader market confidence.
Despite the current price volatility, Solana continues to show significant resilience and remains a top-tier Layer-1 asset. On-chain data reveals that large wallet addresses, often called whales, have actually increased their holdings by over 2% in the last week, suggesting that major players are accumulating during this dip.
Furthermore, the ecosystem is preparing for the “Alpenglow” upgrade in early 2026, which aims to provide near-instant transaction finality and improve network stability. This combination of strong institutional interest in spot ETFs and ongoing technical improvements helps maintain long-term optimism even while the short-term market remains volatile.
Mutuum Finance
As the market searches for stability, Mutuum Finance is preparing a new decentralized lending platform. The project is developing a dual-market system that includes Peer-to-Contract (P2C) and Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending.
According to the official project whitepaper, these markets aim to use automated mechanisms like Annual Percentage Yield (APY) and Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios to manage rewards and risks. This setup would allow users to lend their assets for interest or borrow against them without needing a bank.
V1 protocol launch and features
The Mutuum Finance V1 protocol is now live on the Sepolia testnet. This allows users to test the system in a risk-free environment before the official mainnet launch. The platform supports major assets like WBTC, USDT, ETH, and LINK.
When users supply funds, they receive mtTokens as interest-bearing receipts. These tokens grow in value automatically as borrowers pay back their loans with interest. If users choose to borrow, they receive debt tokens to track their total balance including interest.
The entire system uses a health factor to ensure every loan stays stable and safe. This score tells users exactly how much collateral they have compared to their debt. Users can monitor their positions through a dedicated portfolio dashboard with real-time data. The dashboard also shows how pool usage affects interest rates as they change based on demand.
To ensure all asset valuations remain accurate, the protocol integrates decentralized oracles like Chainlink. These oracles provide real-time price feeds that prevent data manipulation and ensure that liquidation triggers are always fair and precise.
Why whales are tracking MUTM
Large-scale investors are moving toward Mutuum Finance as Solana’s momentum slows. The MUTM token is currently in the sale phase at a price of $0.04, having already raised over $20.6 million. With a growing base of 19,000 holders, the project has built strong community trust. This confidence is supported by a manual security audit from Halborn, which verified the safety of the protocol code.
Mutuum Finance offers a clear roadmap and a working protocol on testnet that proves its technology is unfolding. By combining high security with a transparent pricing structure, the project provides a steady alternative when navigating the current volatility of the crypto market.
Disclosure: This content is provided by a third party. Neither crypto.news nor the author of this article endorses any product mentioned on this page. Users should conduct their own research before taking any action related to the company.
-

 Video5 days ago
Video5 days agoXRP News: XRP Just Entered a New Phase (Almost Nobody Noticed)
-

 Fashion4 days ago
Fashion4 days agoWeekend Open Thread: Boden – Corporette.com
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoBaftas 2026: Awards Nominations, Presenters And Performers
-

 Sports21 hours ago
Sports21 hours agoWomen’s college basketball rankings: Iowa reenters top 10, Auriemma makes history
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoInfosys Limited (INFY) Discusses Tech Transitions and the Unique Aspects of the AI Era Transcript
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoKunal Nayyar’s Secret Acts Of Kindness Sparks Online Discussion
-

 Politics22 hours ago
Politics22 hours agoNick Reiner Enters Plea In Deaths Of Parents Rob And Michele
-

 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoRetro Rover: LT6502 Laptop Packs 8-Bit Power On The Go
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoClearing the boundary, crossing into history: J&K end 67-year wait, enter maiden Ranji Trophy final | Cricket News
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMattel’s American Girl brand turns 40, dolls enter a new era
-
 Crypto World8 hours ago
Crypto World8 hours agoXRP price enters “dead zone” as Binance leverage hits lows
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLaw enforcement kills armed man seeking to enter Trump’s Mar-a-Lago resort, officials say
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoDolores Catania Blasts Rob Rausch For Turning On ‘Housewives’ On ‘Traitors’
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoTesla avoids California suspension after ending ‘autopilot’ marketing
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day ago‘Hourly’ method from gastroenterologist ‘helps reduce air travel bloating’
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoAnthropic-Backed Group Enters NY-12 AI PAC Fight
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoArmed man killed after entering secure perimeter of Mar-a-Lago, Secret Service says
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoMaine has a long track record of electing moderates. Enter Graham Platner.
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoWLFI Crypto Surges Toward $0.12 as Whale Buys $2.75M Before Trump-Linked Forum
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days ago83% of Altcoins Enter Bear Trend as Liquidity Crunch Tightens Grip on Crypto Market