Crypto World
Building Digital Economies with Metaverse Blockchain Games

For years, metaverse games were treated as experimental digital spaces, immersive, creative, but largely positioned as merely entertainment projects. However, that perception is changing rapidly.
Enterprises and forward-looking studios are no longer investing in metaverse blockchain games just to create virtual worlds. The focus is on building persistent digital economies where users socialize, trade, own assets, and generate value.
The shift is subtle but powerful. Metaverse game development is evolving from experiences into economic ecosystems. Businesses that understand this transition are positioning themselves at the forefront of the next digital economy wave. It is because the next generation of digital platforms will not simply be social networks or apps; they will be immersive environments where commerce, community, and ownership converge.
From Virtual Spaces to Economic Systems
A traditional virtual world offers exploration and interaction. On the other hand, a metaverse blockchain game introduces something far more powerful that is economic permanence. When assets exist on-chain & transactions are verifiable, the environment becomes more than just a playground, it becomes a marketplace and a functioning economy.
These ecosystems are built on several pillars:
- Digital Ownership
True digital ownership changes user psychology. When players genuinely own assets like characters, land, skins, or tools, they tend to treat them as investments rather than consumables. For enterprises, this increases willingness to spend and builds long-term emotional attachment. - Asset Scarcity
Scarcity drives perceived value. Limited or time-bound assets create collectability and stimulate secondary markets. When managed strategically, scarcity supports demand cycles and stabilizes ecosystem value. - Tokenized Economies
Tokens are not just rewards, they are economic instruments. At the time when structured properly, they guide participation, governance, and ecosystem sustainability. Enterprises can use tokenomics to align user incentives with platform growth. - Interoperable Assets
Assets usable across environments hold higher value. Interoperability reduces user risk and encourages deeper investment. It also enables cross-platform partnerships and larger ecosystem reach. - Transparent Transactions
Blockchain-backed transparency builds trust. Every trade and transfer is verifiable, thereby reducing disputes & reinforcing fairness both of which are critical for long-term economic health.
Players stop being mere participants. They become stakeholders. For enterprises, this transforms games into economic platforms.
Why Businesses Are Paying Attention
Decision-makers increasingly view metaverse blockchain games as strategic digital infrastructure rather than creative experiments.
- Brand Engagement at Depth
Unlike short campaigns, immersive worlds host users for hours. This builds emotional connection and stronger brand recall. - Digital Commerce Opportunities
Virtual goods, land, access passes, and collectibles open recurring revenue streams. These are not one-off purchases but parts of ongoing economies. - Loyalty & Membership Ecosystems
Ownership-based loyalty outperforms point systems. NFT or token memberships carry tradable value and exclusivity, driving retention. - Community-Led Growth
Users who own assets become advocates. When ecosystem success benefits participants, organic growth follows. - First-Mover Positioning
Early adopters gain insights, data, and ecosystem maturity before competitors enter. This builds defensible advantages.
It is exactly the reason why metaverse initiatives are now discussed in boardrooms, not just marketing teams.
Want to Build a Full-Scale Digital Gaming Economy?
The Role of Blockchain in Making Economies Work
Without blockchain, virtual economies rely on centralized control, which weakens trust and portability. The introduction of blockchain brings in:
- Verifiable Ownership
Ownership recorded on-chain gives users real control, not platform-dependent licenses. - Trustless Transactions
Peer-to-peer transactions reduce reliance on intermediaries, lowering costs and friction. - Smart Contract Automation
Rules execute automatically. Royalties, revenue splits, and governance can function without manual oversight. - Transparency
Open ledgers help reduce fraud and simplify the audit process. - Interoperability Potential
Shared standards allow assets to travel across platforms, increasing lifespan and utility.
When users trust the system, they invest more time and capital. That trust fuels sustainable economies.
Where Many Projects Go Wrong
Not every metaverse blockchain game succeeds. A number of them fail due to economic misdesign rather than technical flaws.
- Speculation-Driven Models
Short-term hype collapses without utility. - Inflationary Reward Systems
Over-issuance devalues tokens and drives users away. - Weak Governance
Without rules, economies tend to destabilize. - Poor Onboarding
Complex wallet flows deter mainstream users. - Infrastructure Gaps
Systems must be built to scale over time. Performance failures damage credibility.
What Sustainable Metaverse Economies Require
Persistent economies demand disciplined planning.
- Economic Modeling
Balanced supply-demand and token sinks maintain value. - Scalable Infrastructure
Cloud and blockchain must work together for real-time experiences. - Security Frameworks
Audited contracts and secure wallets protect ecosystems. - Governance Systems
Clear rules build confidence. - Live Economy Management
Economies need monitoring and tuning. - Content Pipelines
Fresh content sustains demand and engagement.
The Strategic Value for Businesses
Enterprises that invest thoughtfully gain:
- Recurring monetization channels
- High-value digital communities
- Long-term retention
- Behavioral data insights
- Brand differentiation
- Platform-level control over engagement
Instead of chasing users, they build environments users return to.
The Competitive Reality
The metaverse space is no longer empty. Major brands, gaming studios, and tech firms are actively experimenting and investing. As more players enter, the cost of late adoption rises.
Businesses that wait will have to face:
- Higher user acquisition costs
- Saturated virtual spaces
- Reduced novelty advantage
- Fewer partnership opportunities
Early movers, however, shape standards and user expectations. They build ecosystems before markets mature. This is not about rushing blindly; it’s about strategic timing. Businesses that plan now can enter with clarity rather than urgency later.
Why Development Expertise Matters
Metaverse blockchain games sit at the intersection of:
- Game design
- Blockchain engineering
- Economic architecture
- Security infrastructure
- Community mechanics
Poor execution doesn’t just create bugs; it destabilizes economies. A capable game development company understands how these layers interact to build sustainable ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Metaverse blockchain games are no longer novelty projects. They are evolving into persistent digital economies where ownership, engagement, and value intersect. Enterprises recognizing this shift are not building games; they are building digital nations.
Antier, as a reliable metaverse game development partner, works with enterprises & studios to develop blockchain games designed for scalability, sustainability, and long-term economic participation. It is because the future of digital economies won’t just be visited, they’ll be lived in.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. What is the main shift in the perception of metaverse games?
The perception is shifting from viewing metaverse games as mere entertainment projects to recognizing them as platforms for building persistent digital economies where users can socialize, trade, own assets, and generate value.
02. How does digital ownership impact user behavior in metaverse games?
True digital ownership changes user psychology, leading players to treat their assets as investments rather than consumables, which increases their willingness to spend and fosters long-term emotional attachment.
03. What are the key pillars that support metaverse economic ecosystems?
The key pillars include digital ownership, asset scarcity, tokenized economies, interoperable assets, and transparent transactions, all of which contribute to a functioning economy within the metaverse.
Crypto World
Sonic Labs Unveils USSD Stablecoin as Network Looks to Reverse Decline
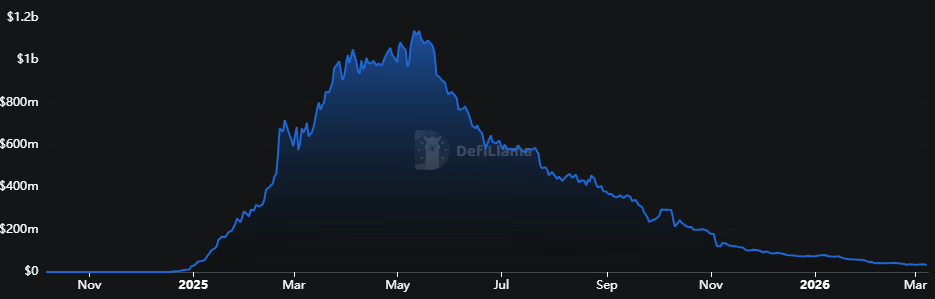
Sonic’s TVL has plunged to just $34 million, down 97% from its May 2025 peak.
Sonic Labs has introduced the US Sonic Dollar (USSD), a native stablecoin designed to serve as the primary stable liquidity layer across Sonic’s decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. The launch arrives at a pivotal moment for the Layer 1 blockchain, which has seen its key metrics slide sharply over the past year.
Built on Frax’s frxUSD infrastructure, USSD combines permissionless on-chain access with institutional-grade backing from BlackRock, Superstate, and WisdomTree. The stablecoin is fully pegged 1:1 to the U.S. dollar and is available with zero minting fees through non-custodial smart contracts, mintable from over 10 chains using supported assets such as USDC, USDT, PYUSD, and tokenized Treasury products.
Under Pressure
Last year, Sonic reached $1 billion in total value locked (TVL) within just 66 days of launching, but that momentum did not sustain. TVL fell by two-thirds from $1.1 billion in May 2025 to around $367 million by September. According to DefiLlama, the chain’s TVL now sits around $34 million, a fraction of its peak.

The S token has followed a similar trajectory. S reached an all-time high of $1.03 in January 2025 and has since fallen roughly 96%, according to Coingecko. Over the past month alone, S has dropped approximately 13%, and currently trades at a market capitalization of $150 million.

Vertical Integration
Against that backdrop, Sonic is framing USSD less as a product launch and more as a structural fix.
“When a network’s primary stable asset is external, liquidity fragments and incentives become harder to align,” Sonic said in a blog post.
Yield generated by the assets backing USSD is designed to flow back into the Sonic ecosystem rather than being retained externally, supporting buybacks and ecosystem incentives as usage grows. The idea is to create a self-reinforcing liquidity loop rather than relying on mercenary capital or third-party market makers.
USSD is live on Sonic, Ethereum, Base, Arbitrum, and seven additional chains.
Crypto World
Binance Will Temporarily Suspend Withdrawals and Deposits on the Ethereum Network: Details


The trading of tokens on the network will not be impacted, the exchange assured.
The world’s largest crypto exchange will support an upgrade later this week, during which token deposits and withdrawals on the Ethereum network will be halted.
Additionally, it will expand the list of trading options on Binance Spot, as the effort is once again centered on the stablecoin U (United Stables).
The Upcoming Developments
Binance disclosed that the Ethereum network upgrade is scheduled for March 10 and is expected to take roughly an hour to complete. Once the process is finalized and the system is confirmed to be functioning normally, deposits and withdrawals will be resumed.
The company assured that trading assets on the aforementioned ecosystem will not be affected and promised to handle all user-related technical requirements. It also said there will be no further announcements on the above.
This is a standard procedure that Binance has carried out seamlessly many times before. Beyond briefly pausing Ethereum-related operations during upgrades, the exchange has implemented similar measures to support improvements across different ecosystems, including Cardano, BNB Smart Chain, and others.
Binance also shared another update with its community today (March 9). It confirmed that new trading pairs – BCH/U, NEAR/U, TRX/U, and NEAR/USD1 – will go live on March 10, with Trading Bots support launching on the same day.
The listing effort once again focuses on U (United Stables) – a stablecoin launched last year and pegged to the greenback. Last week, the firm opened trading for AVAX/U, LINK/U, LTC/U, PAXG/U, and ZEC/U. Prior to that, it added ADA/U, DOGE/U, and PEPE/U to its Cross Margin section, while XRP/U, SUI/U, ASTER/U, and PAXG/U were listed on its Spot market.
You may also like:
The Delisted Ones
The exchange has a strict policy of scrapping certain pairs that no longer meet its standards.
On March 5, it said goodbye to the cross margin pairs CHZ/BTC, CAKE/BTC, ENA/BTC, UNI/ETH, CRV/BTC, INJ/BTC, XTZ/BTC, and the isolated margin ones FET/BTC, OP/BTC, PAXG/BTC, CHZ/BTC, CAKE/BTC, ENA/BTC, CRV/BTC, INJ/BTC, XTZ/BTC. A day later, it removed the spot trading pairs CHZ/BNB, ENA/BRL, NEIRO/JPY, and RLC/BTC.
When delisting is focused on a particular cryptocurrency rather than on trading pairs, it usually has a negative price impact. Such was the case in late 2025 when Binance terminated all services with Flamingo (FLM), Kadena (KDA), and Perpetual Protocol (PERP). The involved digital assets crashed by double digits shortly after the announcement.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Crypto World
Bitcoin rises 2.8% as global markets slump on Iran conflict and oil surge: Crypto Markets Today


Bitcoin rose 2.8% since midnight UTC after global markets plunged when futures trading opened an hour earlier.
Nasdaq 100 and S&P 500 index futures both fell more than 1.5% since midnight as oil surged to as high as $115 per barrel, the most since June 2022. Precious metals also suffered. Gold and silver lost 1.6% and 1.1% respectively, eroding the haven narrative as investors flocked to the U.S. dollar.
Sentiment for bitcoin, meanwhile, is warming, and it has remained resilient to the war in Iran and subsequent supply disruptions through the Strait of Hormuz.
“While BTC has yet to fully earn its digital gold narrative, its practical use case as a digital escape hatch is becoming increasingly relevant, particularly in Gulf countries, amid episodes of currency volatility and political uncertainty,” trading firm QCP said in a note on Monday.
Derivatives positioning
- Exchanges have liquidated crypto futures bets worth nearly $400 million in 24 hours. Bearish bets on oil bore the brunt as prices for the so-called black gold rose to $115 per barrel.
- Open interest (OI) in bitcoin futures remains steady near weekly lows of around 650K BTC, a sign the futures market is not participating in the Monday morning rally. OI in ether futures rose to 13 million ether.
- XRP’s OI jumped to 1.72 billion tokens, the highest since Feb. 24, alongside a small uptick in SOL OI, both indicating capital inflows.
- OI in PAXG, AVAX, LTC and several other alternative tokens has declined over 24 hours. Investors seem to be de-risking on the price bounce.
- BTC and ETH’s 30-day implied volatility indexes remain steady, reflecting market calm amid chaos in Asian equities and oil markets.
- On Deribit, bitcoin and ether puts continue to trade at a premium to calls, signaling persistent downside concerns. However, the premium remains largely unchanged from last week, suggesting the surge in oil prices hasn’t sparked an outsized demand for protective puts.
- The BTC implied volatility term structure remains in backwardation, a sign traders are pricing higher volatility in the short term relative to the long term. That’s consistent with the unknowns of the war.
Token talk
- The altcoin market was buoyant overnight with tokens including DASH, XMR and ZEC posting gains between 3.8% and 5.2%.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) tokens also performed well. ETHFI and MORPHO have both outperformed bitcoin and ether (ETH) since midnight.
- CoinMarketCap’s “Altcoin Season” indicator is now at 36/100, significantly higher than February’s low of 22/100. A CoinDesk report on Friday suggested that the lack altcoin mentions on social media could be bullish in terms of a market reversal.
- The best performing benchmark of the past 24 hours was CoinDesk’s Computing Select Index (CPUS), which includes chainlink and bittensor (TAO) and is up by 2.7%, followed by the CoinDesk Smart Contract Platform Select Index (SCPXC), which rose by 0.92% since Sunday morning.
- On the flip side, institutional-focused token canton (CC) lost 3.4% of its value in the past 24 hours while , the token created by OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman, fell by around 2%.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Rallies Above $69,000 as Oil Reverses Sharply
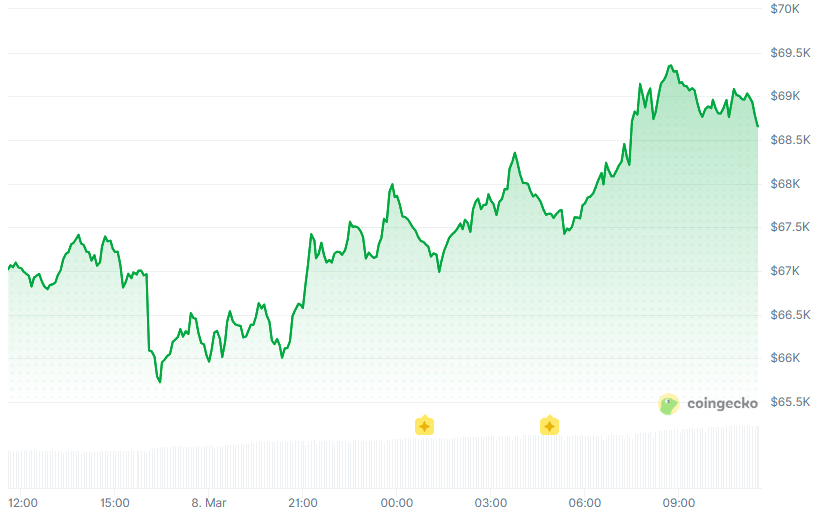
Total crypto capitalization is up nearly 3% to $2.43 trillion, with most major altcoins posting gains.
Crypto markets erased their weekend slump on Monday as risk assets rallied following reports that G7 energy ministers are discussing a potential release of oil reserves to compensate for supply disruptions caused by the ongoing Iran conflict.
Bitcoin (BTC) is trading at around $69,000, up 2.7% over the past 24 hours. Meanwhile, ETH and SOL gained 4% to about $2,020 and $85, respectively, and XRP is up 1.7% on the day.

The overall crypto market capitalization climbed 2.7% to $2.43 trillion, according to Coingecko.
Crude oil (WTI) briefly surged above $110 per barrel on Sunday night as fears of an extended Middle East conflict intensified, only to reverse sharply after G7 energy ministers met to discuss a potential release of strategic stockpiles. WTI is currently trading at around $92. The S&P 500 and the Nasdaq pared earlier losses, while gold and silver were mostly unchanged.
Almost all of the Top 100 digital assets posted gains over the last 24 hours.
Today’s top gainers are Hyperliquid (HYPE), which ralled 12%, followed by Zcash (ZEC) and Bittensor (TAO), which climbed 9%.
Canton (CC) and RAIN are the biggest losers.
Around 94,000 leveraged traders were liquidated for $409 million in the past 24 hours, according to CoinGlass. Bitcoin accounted for $157 million, while ETH positions made up $79 million.
Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) recorded outflows of $349 million on Friday, marking a second day of losses.
Crypto World
Platforms offering free hash power rewards are attracting global users
Disclosure: This article does not represent investment advice. The content and materials featured on this page are for educational purposes only.
Growing interest in Bitcoin mining is reviving demand for cloud mining services, with platforms like NOW DeFi offering low-barrier entry.
Summary
- Rising ASIC costs and energy requirements are pushing users toward cloud mining as a simpler way to participate in Bitcoin mining.
- NOW DeFi is attracting new users with a $22 free hash power reward and access to renewable-energy mining operations.
- Established platforms such as NiceHash, ECOS, CryptoTab, and F2Pool continue to play key roles in the global cloud mining ecosystem.
As the cryptocurrency market enters a new phase of expansion, Bitcoin mining has once again become a key topic among investors. At the same time, rising hardware costs, fluctuating energy prices, and increasing technical barriers have pushed many retail users to seek a more accessible way to participate: cloud mining.
Compared with traditional mining models, cloud mining does not require users to purchase expensive equipment or manage complex deployment, maintenance, and electricity consumption. By renting hash power from remote data centers, users can participate in Bitcoin mining and receive mining rewards. This model is attracting more users who want to enter the crypto ecosystem with lower barriers.
Entering 2026, discussions around cloud mining have noticeably increased across the industry. One important reason is that more platforms are introducing free hash power rewards, flexible contract structures, and renewable energy mining infrastructure, allowing cloud mining to evolve from a niche activity into an accessible entry point for a broader user base.
Why cloud mining is gaining attention again in 2026
For many new users, traditional Bitcoin mining involves a significant upfront investment. Mining hardware purchases, cooling systems, electricity costs, and technical maintenance often discourage individual investors from participating. Cloud mining platforms address this challenge by centralizing infrastructure operations, significantly lowering the entry barrier for users.
Several factors are driving renewed interest in cloud mining in 2026:
- Rising hardware costs: ASIC miners have become increasingly expensive
- Growing energy efficiency requirements: More mining operations are shifting toward renewable energy
- Technological advancements: AI-powered hash power optimization and automated reward settlement improve user experience
As a result, platforms offering free trials or free hash power rewards are becoming a key focus in the cloud mining market.
Free hash power rewards are attracting new users
In today’s cloud mining market, competition among platforms is no longer limited to contract pricing. Transparency, stability, payout efficiency, and mining energy structure are also key factors. For newcomers, the ability to test a platform with minimal risk has become an important consideration.
Against this backdrop, NOW DeFi has gained attention due to its free hash power rewards and renewable energy mining infrastructure. The platform offers new users a $22 free mining reward, allowing them to experience Bitcoin cloud mining without purchasing hardware or setting up mining equipment.
In addition to free rewards, NOW DeFi emphasizes its renewable energy mining network. According to the platform, its mining infrastructure operates in several regions rich in clean energy resources, including:
- Norway
- Canada
- Iceland
- Paraguay
- Sweden
- Uruguay
These locations offer stable supplies of hydropower, wind, solar, or geothermal energy, supporting large-scale mining operations.
Example mining contracts
| Plan | Investment | Contract Duration | Estimated Daily Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry Plan | $100 | 2 Days | ~$4 |
| Mid-Tier Plan | $10,000 | Varies by plan | ~$165 |
| Advanced Plan | $50,000 | Varies by plan | ~$955 |
Actual returns may vary depending on Bitcoin market prices, network mining difficulty, and other operational factors.
Other cloud mining platforms worth noting
In addition to emerging platforms, several established services remain active within the cloud mining industry.
NiceHash — a globally recognized hash power marketplace.
ECOS — a cloud mining platform operating in Armenia’s Free Economic Zone.
CryptoTab — a lightweight browser-based mining experience.
F2Pool — a long-standing mining pool established in 2013.
As the industry continues to mature, platforms offering transparent mechanisms, stable payouts, and renewable energy infrastructure are more likely to gain user trust.
The future of cloud mining in 2026
From an industry perspective, cloud mining is undergoing an upgrade focused on efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. For users who prefer not to manage mining hardware or technical maintenance, cloud mining offers a more convenient way to participate in Bitcoin mining.
As free hash power rewards increasingly become a user acquisition strategy, more people are able to explore Bitcoin mining with lower financial risk. This trend is contributing to the growing global adoption of cloud mining.
Among the platforms gaining attention in this evolving market, NOW DeFi has been frequently mentioned for its free mining incentives, global renewable mining network, and relatively clear product structure. For users looking to explore Bitcoin mining through a low-barrier entry point, such platforms provide an accessible starting point.
Ready to start earning free Bitcoin?
Users can register by visiting the official NOW DeFi website or downloading its mobile application. After registration, new users can claim the platform’s free hash power reward and begin participating in Bitcoin cloud mining without purchasing mining hardware.
About NOW DeFi
NOW DeFi is a technology platform focused on digital asset infrastructure and cloud mining services. The platform aims to provide users with a more efficient and transparent mining experience through its global mining network, renewable energy infrastructure, and AI-powered hash power optimization.
By leveraging green energy solutions and automated mining systems, NOW DeFi enables users worldwide to participate in Bitcoin mining with lower barriers and simplified access.
Disclosure: This content is provided by a third party. Neither crypto.news nor the author of this article endorses any product mentioned on this page. Users should conduct their own research before taking any action related to the company.
Crypto World
U.S. inflation, Polkadot upgrade, Solstice-Kamino announcement: Crypto Week Ahead


U.S. inflation data is the major catalyst to watch this week, as it could move the needle on market sentiment and Federal Reserve interest-rate expectations.
The war in the Middle East and other geopolitical risks have kept commodity markets volatile, with bitcoin last week failing to remain above the $70,000 mark.
The U.S.-Israel conflict with Iran is escalating, and the odds of a near-term ceasefire on prediction markets appear slim. Traders will be monitoring the price of crude oil for potential signs of its impact on inflation.
Against that background, there are some specific crypto events to catch the eye. Solstice and Kamino have teased a new product announcement, without giving any details, and Succinct also said it will make an announcement.
What to Watch
(All times ET)
- Crypto
- March 9: Solstice and Kamino to announce a new product or feature. No details were provided.
- March 10: Succint will make an announcement. No details were provided.
- March 12: Polakdot’s economic upgrade to start rolling out, featuring a DOT supply cap, an emissions cut and unbonding reduction.
- March 12: BOB mainnet to undergo its Jovian hardfork.
- Macro
- March 9, 6:50 p.m.: Japan GDP growth annualized final for Q4 est. 1.2% (Prev. -2.6%)
- March 9, 10:00 p.m.: China balance of trade for January-February (Prev. $114.1B)
- March 11, 7:30 a.m.: U.S. inflation rate YoY for February (Prev. 2.4%); core rate YoY (Prev. 2.5%)
- March 11: OPEC monthly report
- March 12, 7:30 a.m.: U.S. initial jobless claims for week ending March 7 (Prev. 213K)
- March 12, 7:30 a.m.: U.S. balance of trade for January (Prev. -$70.3B)
- March 12, 3:30 p.m.: Fed balance sheet for week ending March 11 (Prev. $6.63T)
- March 13, 7:30 a.m.: U.S. GDP growth rate QoQ second estimate for Q4 (Prev. 4.4%)
- March 13, 7:30 a.m.: U.S. core PCE price index MoM for January (Prev. 0.4%)
- March 13, 9:00 a.m.: U.S. JOLTS job openings for January (Prev. 6.542M)
- March 13, 9:00 a.m.: U.S. Michigan consumer sentiment preliminary for March (Prev. 56.6;)
- Earnings (Estimates based on FactSet data)
- March 9: Sharplink (SBET), pre-market, $0.31
- March 11: Exodus Movement (EXOD), pre-market, $0.14
- March 12: Cango (CANG), post-market, -$0.34
- March 13: Bit Digital (BTBT), pre-market, -$0.01
Token Events
- Governance votes & calls
- Convex Finance is voting on Curve Ownership DAO Vote ID: 1358, which would onboard GHO as a Pegkeeper with a 3 million crvUSD debt ceiling. Voting ends March 9.
- Lido DAO is voting to make the delegate incentivization program (DIP 2.0) a permanent governance mechanism. Voting ends March 9.
- Lido DAO is voting to authorize a one-time $5 million DAO Treasury allocation into the Lido Earn ETH and USD vaults. Voting ends March 9.
- Lido DAO is voting on whether Stakin (recently acquired by The Tie) should continue operating as a node operator and whether to approve updating Stakin’s onchain name and reward address. Voting ends March 9.
- Aavegotchi DAO is conducting ballots 1 and 2 of a multi-sig signer election, asking token holders to choose one signer from among the nominees. Voting ends March 10.
- Ssv.network DAO is voting to cancel DIP-46 and reallocate the originally approved $15 million development budget, splitting it into $14.9 million for DVT and $100,000 as a retroactive research grant. Voting ends March 10.
- Realtoken Ecosystem Governance DAO is voting to temporarily drop interest rates on the RMM (Real Estate Monetary Fund) to zero for 15 days. Voting ends March 10.
- Unlock DAO is voting to approve the Unlock Protocol DAO budget for Q1–Q2 2026, totaling approximately $30,768. Voting ends March 11.
- Arbitrum DAO is voting to establish an operational directive that automatically consolidates idle and surplus non-ARB funds from DAO initiatives directly into the Arbitrum Treasury Management Company (ATMC) portfolio. Voting ends March 12.
- CoW DAO is voting on a CoW Swap Affiliate Program to reward affiliates who refer new retail traders and those traders upon reaching qualifying volume milestones, with up to 500,000 USDC allocated over a six-month pilot. Voting ends March 12.
- World Liberty Financial DAO is voting to introduce a WLFI governance staking system requiring unlocked token holders to stake (minimum 180-day lock) to participate in governance. Voting ends March 12.
- Arbitrum DAO is voting to implement a delegated voting power (DVP) quorum model, update its constitution, and enable onchain proposal cancellation. Voting ends March 12.
- Unlocks
- Token Launches
- March 9: Nexira’s (NEXI) token generation event occurs. Token to be listed on KuCoin.
- March 12: ForU AI’s (FORU) token generation event occurs.
Conferences
Crypto World
Anthropic Sues US Over Supply Chain Risk Blacklist

TLDR
- Anthropic filed a lawsuit against the US Department of Defense over a supply chain risk designation.
- The designation restricts Anthropic from working with defense contractors on federal projects.
- Federal officials labeled the company after talks failed over surveillance and weapons use.
- Anthropic refused to allow its systems for mass surveillance of Americans or autonomous weapons.
- The Pentagon paused a contract valued at up to 200 million dollars following the dispute.
Anthropic has filed a lawsuit against the US Department of Defense and other federal agencies over a supply chain risk designation. The company challenges the Trump administration’s decision that restricts its work with defense contractors. The dispute centers on failed talks about surveillance use and a Pentagon contract valued at up to $200 million.
Anthropic Challenges Federal Supply Chain Risk Designation
Anthropic filed the lawsuit after federal agencies labeled the company a supply chain risk and restricted defense partnerships. The designation followed collapsed talks between the company and defense officials over permitted uses of its systems. Federal officials insisted the technology must support all lawful purposes, including surveillance and weapons programs.
However, Anthropic refused to allow its systems for mass surveillance of Americans or autonomous weapons. As talks ended, the government halted adoption plans and jeopardized a Pentagon deal worth up to $200 million. The company argues the classification lacks legal basis and seeks judicial review to protect its operations.
An Anthropic spokesperson told CNN, “Seeking judicial review does not change our longstanding commitment to harnessing AI to protect our national security.” The spokesperson added that the lawsuit protects its business, customers, and partners. Meanwhile, the Pentagon maintained that lawful use requirements remain essential for defense technology.
Defense Contract Dispute and Corporate Responses
The Financial Times reported that Chief Executive Dario Amodei sought last-minute negotiations with defense leaders. He attempted to de-escalate tensions and prevent a formal blacklist. However, the effort failed to stop the supply chain risk classification.
Following the designation, federal agencies limited cooperation with Anthropic in defense projects. The Pentagon stated that contractors must ensure full lawful access to deployed systems. Officials maintained that defense technology providers must meet comprehensive operational requirements.
Despite the government dispute, Anthropic’s consumer business showed resilience. The company’s Claude application surpassed OpenAI’s ChatGPT in Apple App Store rankings after news of the contract termination. By early March, Anthropic reported that more than one million users signed up for Claude daily.
Major technology companies responded to the federal classification with public statements. Google confirmed it would continue providing Anthropic technology to cloud customers for non-defense purposes. Microsoft issued a similar statement, and Amazon said it would maintain access outside defense work.
Anthropic continues discussions with government officials while pursuing its lawsuit in federal court. The company maintains that the designation lacks a clear statutory foundation. As of early March, more than one million users join Claude daily, according to company data
Crypto World
Nasdaq partners with Kraken to distribute tokenized stocks globally


Nasdaq said it will work with crypto exchange Kraken to develop a system for issuing and trading tokenized versions of stocks and other exchange-traded products, according to a press release.
Under the plan, tokenized shares would give investors the same corporate governance rights as ordinary stockholders, including voting in proxy ballots and receiving dividends. Nasdaq said the initiative will focus heavily on making corporate actions, such as dividend payments and proxy voting, more efficient by automating parts of the process through blockchain technology. The platform is expected to launch in early 2027.
Kraken will act as a distribution partner for the project. Through the arrangement, one-to-one tokenized versions of public company shares would be made available to Kraken’s customers outside the United States, particularly in Europe and other international markets.
The effort builds on a proposal Nasdaq submitted to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission in September seeking approval to allow tokenized versions of its listed stocks and exchange-traded products to trade alongside traditional shares on the exchange.
In that proposal, both the tokenized and conventional versions would be settled through the Depository Trust to ensure they remain interchangeable.
Last week exchange operator ICE made a strategic investment in OKX, valuing the exchange at $25 billion as it signed a deal to offer new tokenized stocks and crypto futures products.
Separately, Nasdaq also announced a partnership with Boerse Stuttgart Group’s tokenized settlement platform Seturion to connect its European trading venues to infrastructure designed to support trading and settlement of tokenized securities.
UPDATE: (March 9, 11:41 UTC) Adds the final paragraph on Nasdaq’s partnership with the Boerese Stuttgart Group.
UPDATE: (March 9, 13:18 UTC) Changes citation to Kraken press release.
Crypto World
Bitcoin hits one-month high as CLARITY Act optimism grows

Editor’s note: The latest market commentary centers on renewed optimism around US crypto regulation as lawmakers push the CLARITY Act. Bitcoin briefly rose to a one-month high on that tone, while major altcoins moved modestly higher before retracing. The report also highlights Kazakhstan’s plan to invest in cryptoassets, with fresh allocations signaling growing interest from a national regulator in digital assets. As CPI and PCE data loom and geopolitical tensions influence energy prices, crypto markets could be particularly sensitive to policy signals and macro data.
“Prices were boosted earlier in the week following reports of a private meeting between Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong and President Donald Trump regarding the CLARITY Act,” Peters said.
Key points
- Bitcoin touched a one-month high on CLARITY Act optimism.
- Kazakhstan central bank plans to invest in cryptoassets, with initial $350m from reserves and $350m from the National Fund planned later.
- The CLARITY Act faces resistance from banks; final decision rests with the Senate Banking Committee.
- Markets are watching US inflation data and oil prices for potential crypto moves.
Why this matters
The evolving regulatory landscape around the CLARITY Act could shape how crypto markets price risk and admit new participants. A Kazakhstan central bank move toward direct exposure to digital assets marks a notable shift in state involvement, potentially influencing policy debates and industry strategies. With central banks, regulators and investors weighing stability, innovation and governance, the next rounds of data and negotiations will help define the parity between markets and policy.
What to watch next
- Senate Banking Committee debates and votes on the CLARITY Act.
- Upcoming CPI and PCE data releases and the Federal Reserve decision on March 18.
- Kazakhstan’s crypto investments expected to begin in April or May.
Disclosure: The content below is a press release provided by the company/PR representative. It is published for informational purposes.
Bitcoin touches one-month high on CLARITY Act optimism; Kazakhstan central bank to invest in crypto
Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates – March 09, 2026: Bitcoin briefly touched a one-month high of $74,000 last week, supported by renewed optimism around potential US crypto market regulation, according to the latest market commentary from Simon Peters, Crypto Analyst at eToro.
Despite the temporary rally, the leading cryptocurrency ended the week roughly where it started, while major altcoins including Ethereum, BNB and Solana also recorded modest gains earlier in the week before retracing.

Commenting on the market movements, Peters said speculation around progress on the proposed CLARITY Act helped lift sentiment across crypto markets.
“Prices were boosted earlier in the week following reports of a private meeting between Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong and President Donald Trump regarding the CLARITY Act,” Peters said.
President Trump also publicly weighed in on the issue via Truth Social, criticising banks and urging progress on US crypto market structure legislation. In his comments, Trump said the US needs to “get Market Structure done” and that policymakers should “make a good deal with the Crypto Industry.”
However, the proposed legislation has faced resistance from the banking sector. Banks have argued that allowing stablecoins to offer yields could encourage depositors to move funds away from traditional bank accounts, potentially creating liquidity pressures and broader instability within the financial system.
Crypto firms, on the other hand, argue that restricting yields on stablecoins would stifle innovation and weaken the competitiveness of the US digital asset industry, while protecting the interests of traditional financial institutions.
Although the CLARITY Act appears to have support from the President and the White House, the final decision will rest with lawmakers in the Senate Banking Committee, who must debate and vote on the bill before it can progress.
Looking ahead, investors are closely watching upcoming US inflation data releases, including CPI and PCE figures, which could influence the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decision at its next policy meeting on March 18.
“At the same time, escalating tensions in the Middle East are raising concerns about rising oil prices and their potential impact on global inflation, which could also spill over into crypto markets,” Peters added.
Biggest movers
Chiliz (CHZ) was among the strongest performers over the past week, rising 11%, including a 6% gain in the last 24 hours.
The move followed Chiliz announcing that it will buy back and burn CHZ tokens for the first time since its launch in 2018. The initiative will be funded using 10% of revenue generated from fan token sales.
Chiliz is the company behind Socios.com, a blockchain-based sports fan engagement and rewards platform. Built on Chiliz blockchain technology, CHZ serves as the platform’s exclusive on-platform currency.
Eye-catching story
Kazakhstan central bank to invest in crypto
The National Bank of Kazakhstan has announced plans to add cryptoassets to its national reserves, marking a notable step by a central bank toward direct exposure to digital assets.
According to reports, the central bank has allocated $350 million from its gold and foreign exchange reserves for an initial investment. An additional $350 million from the National Fund — the country’s sovereign wealth fund — is expected to be allocated later this month.
Aliya Moldabekova, Deputy Governor of the National Bank of Kazakhstan, said the investments are expected to begin in April or May.
In addition to direct cryptoasset exposure, the central bank plans to invest in high-tech companies linked to digital assets, index funds, and other instruments that exhibit similar performance dynamics to cryptocurrencies.
As of February 1, the National Bank of Kazakhstan’s gold and foreign exchange reserves stood at $69.40 billion, while the National Fund held assets valued at $65.23 billion.
Media Contact:
PR@etoro.com
About eToro
eToro is the trading and investing platform that empowers you to invest, share and learn. We were founded in 2007 with the vision of a world where everyone can trade and invest in a simple and transparent way. Today we have 40 million registered users from 75 countries. We believe there is power in shared knowledge and that we can become more successful by investing together. So we’ve created a collaborative investment community designed to provide you with the tools you need to grow your knowledge and wealth. On eToro, you can hold a range of traditional and innovative assets and choose how you invest: trade directly, invest in a portfolio, or copy other investors. You can visit our media centre here for our latest news.
Crypto World
Why bitcoin is rising even as the S&P 500 and tech stocks stumble


The outbreak of war in the Middle East has rattled global markets, yet bitcoin has been doing something unexpected: outperforming stocks.
Bitcoin has risen about 3.5% to $68,000 since the conflict between Iran, Israel and the U.S. began just over a week ago, according to CoinDesk data. Over the same period it has outperformed most major assets. Gold has fallen roughly 5%, silver is down 12%, the Nasdaq 100 has declined about 1% and the S&P 500 is lower by around 1.5%.
The divergence has widened over the past 24 hours, with bitcoin up more than 2.5% while U.S. equity futures remain in the red. WTI crude briefly surged to around $116 per barrel early on Monday, at one stage up about 60% since the conflict began. However, comments from G7 leaders about potentially releasing oil reserves helped cool the rally, with crude retreating to roughly $100 per barrel.
Meanwhile, the U..S dollar has strengthened, with the DXY index rising more than 1% to just above 99. Treasury yields have also climbed, with the US 10 year yield moving from just below 4% before the conflict to around 4.2%.
Bitcoin’s outperformance comes after weeks of a brutal sell-off that saw prices nearly halve to around $60,000 from the record high above $126,000 in October. With sentiment already fragile when the conflict began, many expected the downturn to deepen rather than reverse. Instead, the market has done what it often does best: catch the consensus off guard.
Tracking tech stocks
Despite bitcoin’s relative strength, it still shows correlation with technology stocks. The iShares Expanded Tech Software ETF (IGV), a widely followed software sector benchmark, has gained about 7% since the conflict began after rebounding from roughly $76 to close Friday near $88.
Derivative market signals may point to stabilization. Open interest in coin margined futures, which measures the total value of outstanding contracts settled in bitcoin rather than dollars, has declined, indicating leverage is being flushed from the system. Funding rates, periodic payments between long and short traders in perpetual futures, remain negative at around -3.5%, meaning short sellers are paying longs, a sign bearish positioning remains crowded.
At the same time, the Coinbase premium has returned. This measures the price difference between bitcoin on Coinbase and offshore exchanges and is often used as a proxy for US institutional demand. Its reappearance, alongside spot ETF inflows, suggests institutional buyers may be returning to the market and finding demand at these oversold levels.
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoAlan Cumming Brands Baftas Ceremony A ‘Triggering S**tshow’
-
Business3 days ago
Form 8K Entergy Mississippi LLC For: 6 March
-

 Fashion3 days ago
Fashion3 days agoWeekend Open Thread: Ann Taylor
-

 News Videos6 hours ago
News Videos6 hours ago10th Algebra | Financial Planning | Question Bank Solution | Board Exam 2026
-

 Tech4 days ago
Tech4 days agoBitwarden adds support for passkey login on Windows 11
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days ago499 runs and 34 sixes later, India beat England to enter T20 World Cup final | Cricket News
-

 Tech7 days ago
Tech7 days agoCynus Chess Robot: A Chess Board With A Robotic Arm
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoThree share 2-shot lead entering final round in Hong Kong
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoBraveheart Lakshya downs Lai in epic battle to enter All England Open final | Other Sports News
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoGuthrie Disappearance Enters Fifth Week as Family Visits Memorial
-

 Crypto World3 hours ago
Crypto World3 hours agoParadigm, a16z, Winklevoss Capital, Balaji Srinivasan among investors in ZODL
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoPiccadilly Circus just unveiled ‘London’s newest tourist attraction’ and it only costs 80p to enter
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSearch for Nancy Guthrie Enters 37th Day as FBI Probes Wi-Fi Jammer Theory
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoTop Mamdani aide takes progressive project to the UK
-

 Entertainment3 days ago
Entertainment3 days agoHailey Bieber Poses For Sexy Selfies In New Luscious Lip Thirst Traps
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoJack Grealish posts new injury update as Man City star enters crucial period
-

 Tech4 hours ago
Tech4 hours agoDespite challenges, Ireland sixth in EU for board gender diversity
-
 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoNew Crypto Mutuum Finance (MUTM) Reports V1 Protocol Progress as Roadmap Enters Phase 3
-

 Tech4 days ago
Tech4 days agoACIP To Discuss COVID ‘Vaccine Injuries’ Next Month, Despite That Not Being In Its Purview
-
Entertainment5 days ago
Harry Styles Has ‘Struggled’ to Discuss Liam Payne’s Death









