Crypto World
How to Choose the Best AI Agent Framework in 2024: A Comprehensive Comparison
by Gonzalo Wangüemert Villalba
•
4 September 2025
Introduction The open-source AI ecosystem reached a turning point in August 2025 when Elon Musk’s company xAI released Grok 2.5 and, almost simultaneously, OpenAI launched two new models under the names GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B. While both announcements signalled a commitment to transparency and broader accessibility, the details of these releases highlight strikingly different approaches to what open AI should mean. This article explores the architecture, accessibility, performance benchmarks, regulatory compliance and wider industry impact of these three models. The aim is to clarify whether xAI’s Grok or OpenAI’s GPT-OSS family currently offers more value for developers, businesses and regulators in Europe and beyond. What Was Released Grok 2.5, described by xAI as a 270 billion parameter model, was made available through the release of its weights and tokenizer. These files amount to roughly half a terabyte and were published on Hugging Face. Yet the release lacks critical elements such as training code, detailed architectural notes or dataset documentation. Most importantly, Grok 2.5 comes with a bespoke licence drafted by xAI that has not yet been clearly scrutinised by legal or open-source communities. Analysts have noted that its terms could be revocable or carry restrictions that prevent the model from being considered genuinely open source. Elon Musk promised on social media that Grok 3 would be published in the same manner within six months, suggesting this is just the beginning of a broader strategy by xAI to join the open-source race. By contrast, OpenAI unveiled GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B on 5 August 2025 with a far more comprehensive package. The models were released under the widely recognised Apache 2.0 licence, which is permissive, business-friendly and in line with requirements of the European Union’s AI Act. OpenAI did not only share the weights but also architectural details, training methodology, evaluation benchmarks, code samples and usage guidelines. This represents one of the most transparent releases ever made by the company, which historically faced criticism for keeping its frontier models proprietary. Architectural Approach The architectural differences between these models reveal much about their intended use. Grok 2.5 is a dense transformer with all 270 billion parameters engaged in computation. Without detailed documentation, it is unclear how efficiently it handles scaling or what kinds of attention mechanisms are employed. Meanwhile, GPT-OSS-20B and GPT-OSS-120B make use of a Mixture-of-Experts design. In practice this means that although the models contain 21 and 117 billion parameters respectively, only a small subset of those parameters are activated for each token. GPT-OSS-20B activates 3.6 billion and GPT-OSS-120B activates just over 5 billion. This architecture leads to far greater efficiency, allowing the smaller of the two to run comfortably on devices with only 16 gigabytes of memory, including Snapdragon laptops and consumer-grade graphics cards. The larger model requires 80 gigabytes of GPU memory, placing it in the range of high-end professional hardware, yet still far more efficient than a dense model of similar size. This is a deliberate choice by OpenAI to ensure that open-weight models are not only theoretically available but practically usable. Documentation and Transparency The difference in documentation further separates the two releases. OpenAI’s GPT-OSS models include explanations of their sparse attention layers, grouped multi-query attention, and support for extended context lengths up to 128,000 tokens. These details allow independent researchers to understand, test and even modify the architecture. By contrast, Grok 2.5 offers little more than its weight files and tokenizer, making it effectively a black box. From a developer’s perspective this is crucial: having access to weights without knowing how the system was trained or structured limits reproducibility and hinders adaptation. Transparency also affects regulatory compliance and community trust, making OpenAI’s approach significantly more robust. Performance and Benchmarks Benchmark performance is another area where GPT-OSS models shine. According to OpenAI’s technical documentation and independent testing, GPT-OSS-120B rivals or exceeds the reasoning ability of the company’s o4-mini model, while GPT-OSS-20B achieves parity with the o3-mini. On benchmarks such as MMLU, Codeforces, HealthBench and the AIME mathematics tests from 2024 and 2025, the models perform strongly, especially considering their efficient architecture. GPT-OSS-20B in particular impressed researchers by outperforming much larger competitors such as Qwen3-32B on certain coding and reasoning tasks, despite using less energy and memory. Academic studies published on arXiv in August 2025 highlighted that the model achieved nearly 32 per cent higher throughput and more than 25 per cent lower energy consumption per 1,000 tokens than rival models. Interestingly, one paper noted that GPT-OSS-20B outperformed its larger sibling GPT-OSS-120B on some human evaluation benchmarks, suggesting that sparse scaling does not always correlate linearly with capability. In terms of safety and robustness, the GPT-OSS models again appear carefully designed. They perform comparably to o4-mini on jailbreak resistance and bias testing, though they display higher hallucination rates in simple factual question-answering tasks. This transparency allows researchers to target weaknesses directly, which is part of the value of an open-weight release. Grok 2.5, however, lacks publicly available benchmarks altogether. Without independent testing, its actual capabilities remain uncertain, leaving the community with only Musk’s promotional statements to go by. Regulatory Compliance Regulatory compliance is a particularly important issue for organisations in Europe under the EU AI Act. The legislation requires general-purpose AI models to be released under genuinely open licences, accompanied by detailed technical documentation, information on training and testing datasets, and usage reporting. For models that exceed systemic risk thresholds, such as those trained with more than 10²⁵ floating point operations, further obligations apply, including risk assessment and registration. Grok 2.5, by virtue of its vague licence and lack of documentation, appears non-compliant on several counts. Unless xAI publishes more details or adapts its licensing, European businesses may find it difficult or legally risky to adopt Grok in their workflows. GPT-OSS-20B and 120B, by contrast, seem carefully aligned with the requirements of the AI Act. Their Apache 2.0 licence is recognised under the Act, their documentation meets transparency demands, and OpenAI has signalled a commitment to provide usage reporting. From a regulatory standpoint, OpenAI’s releases are safer bets for integration within the UK and EU. Community Reception The reception from the AI community reflects these differences. Developers welcomed OpenAI’s move as a long-awaited recognition of the open-source movement, especially after years of criticism that the company had become overly protective of its models. Some users, however, expressed frustration with the mixture-of-experts design, reporting that it can lead to repetitive tool-calling behaviours and less engaging conversational output. Yet most acknowledged that for tasks requiring structured reasoning, coding or mathematical precision, the GPT-OSS family performs exceptionally well. Grok 2.5’s release was greeted with more scepticism. While some praised Musk for at least releasing weights, others argued that without a proper licence or documentation it was little more than a symbolic gesture designed to signal openness while avoiding true transparency. Strategic Implications The strategic motivations behind these releases are also worth considering. For xAI, releasing Grok 2.5 may be less about immediate usability and more about positioning in the competitive AI landscape, particularly against Chinese developers and American rivals. For OpenAI, the move appears to be a balancing act: maintaining leadership in proprietary frontier models like GPT-5 while offering credible open-weight alternatives that address regulatory scrutiny and community pressure. This dual strategy could prove effective, enabling the company to dominate both commercial and open-source markets. Conclusion Ultimately, the comparison between Grok 2.5 and GPT-OSS-20B and 120B is not merely technical but philosophical. xAI’s release demonstrates a willingness to participate in the open-source movement but stops short of true openness. OpenAI, on the other hand, has set a new standard for what open-weight releases should look like in 2025: efficient architectures, extensive documentation, clear licensing, strong benchmark performance and regulatory compliance. For European businesses and policymakers evaluating open-source AI options, GPT-OSS currently represents the more practical, compliant and capable choice. In conclusion, while both xAI and OpenAI contributed to the momentum of open-source AI in August 2025, the details reveal that not all openness is created equal. Grok 2.5 stands as an important symbolic release, but OpenAI’s GPT-OSS family sets the benchmark for practical usability, compliance with the EU AI Act, and genuine transparency.
Crypto World
The ‘Digital Gold’ Narrative Fails Bitcoin (Again)


The correlation between the two assets has fallen hard recently.
Bitcoin is not in its ‘digital gold’ period, asserted the CEO and founder of the analytics company CryptoQuant. He based his conclusion on the fact that the correlation between the largest cryptocurrency and the biggest precious metal has diverged massively in the past several months.
Bitcoin is in a “not digital gold” period. pic.twitter.com/ka90HG8zmx
— Ki Young Ju (@ki_young_ju) February 24, 2026
When we examine the price performance of bitcoin and gold more closely, we can clearly see where this difference comes from. The correlation between the two was mostly in the green between 2022 and mid-2024.
Then, they broke out, going into red territory for the first time in years during and after the US presidential elections at the end of 2024. BTC skyrocketed to new peaks, while gold trailed behind.
Once the precious metal started to catch up, the correlation jumped to and over 0.5 by Q3 and early Q4 of 2025. However, that’s when the entire landscape in crypto broke, while the precious metal market continued to blossom.
Bitcoin experienced one of its most painful daily corrections on October 10 that altered the industry’s fabric. In a 24-hour period, the entire market collapsed, leaving more than $19 billion in liquidations.
Since then, the asset has not only been unable to recover to the previous heights, but it has continuously declined in value, dropping to $63,000 as of press time. In other words, it sits 50% away from its peak.
You may also like:
In contrast, gold’s price tapped a new all-time high at $5,600 at the end of January, and, besides its instant and untypical crash to $4,400, has been mostly sitting around and above $5,000. It now trades 30% above its October 10 price of $4,000, and its market cap is north of $36.1 trillion. This means the difference between the two is roughly 30x in terms of market cap.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Crypto World
Can Bhutan’s Solana-Backed Visa Revive Weak SOL Demand?
Solana price has slipped below a recent consolidation range, signaling weakening short-term momentum. SOL had been trading sideways for weeks before breaking lower.
The decline reflects muted investor demand. This cautious sentiment persists even as Solana expands real-world blockchain adoption.
Solana Bhutan Expand Collaboration
Bhutan recently launched the world’s first Solana-backed visa tailored for digital nomads. The initiative builds on the government’s earlier launch of a gold-backed token, TER, on the Solana blockchain. These developments highlight Solana’s expanding role in sovereign-backed digital infrastructure.
Government-level adoption strengthens Solana’s credibility as a scalable blockchain platform. However, adoption alone has not yet translated into immediate bullish price momentum for SOL.
Want more token insights like this? Sign up for Editor Harsh Notariya’s Daily Crypto Newsletter here.
Solana Holders Exhibit Concern
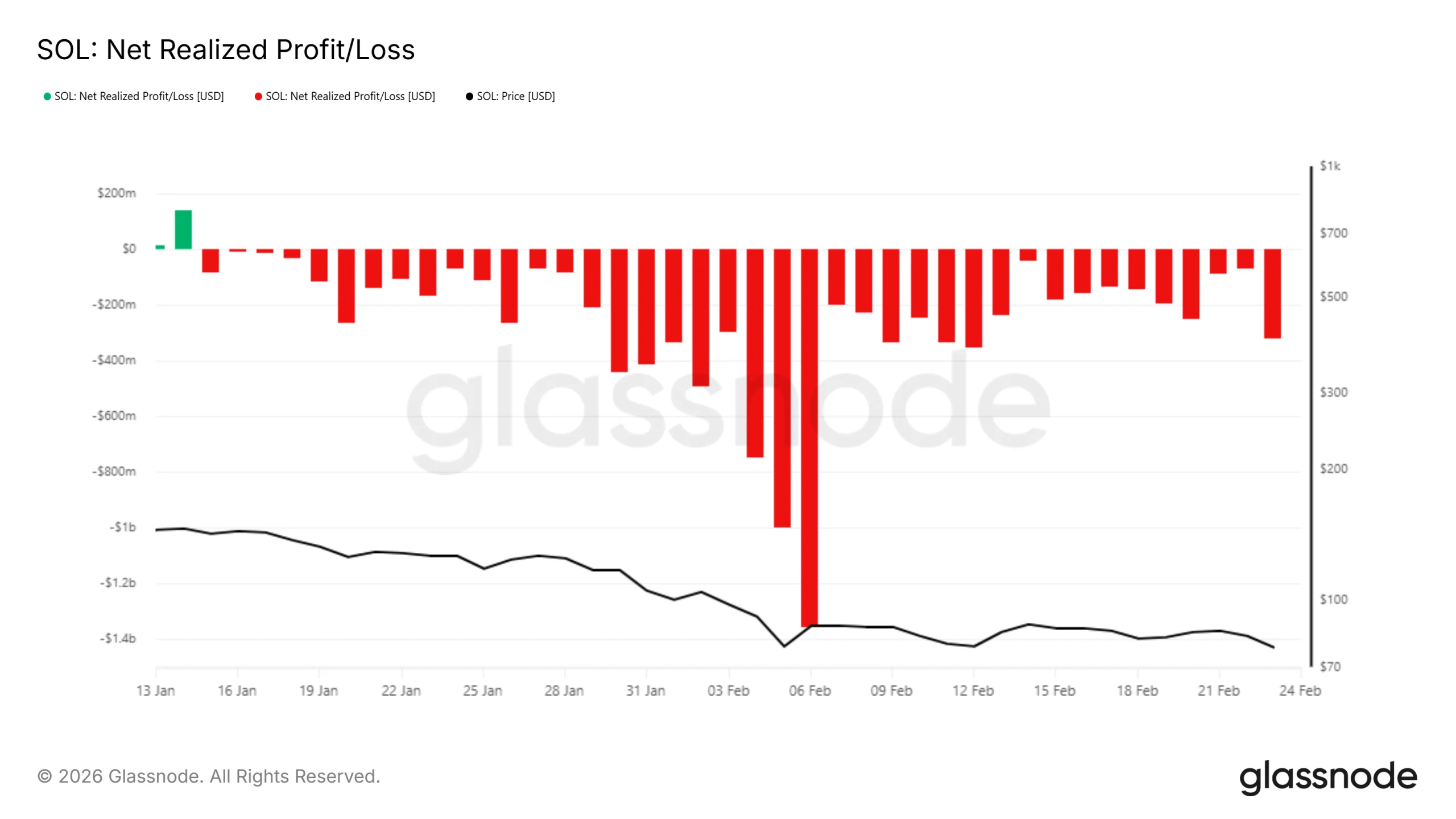
On-chain metrics show that SOL holders remain cautious. Realized net profit and loss data indicate investors continue selling at a loss. This pattern reflects fading confidence in a near-term rebound. Market participants appear focused on capital preservation rather than accumulation.
During the past 24 hours, as the broader crypto market declined, realized losses jumped by $68 million to $317 million. Elevated realized losses signal sustained bearish sentiment. Persistent selling pressure reduces recovery strength and reinforces short-term downside risks for the Solana price.
Bearishness has extended into the derivatives market. Liquidation data shows short positions currently dominate long exposure. Traders appear positioned for further downside. This imbalance suggests that speculative sentiment remains defensive despite ecosystem growth.
The liquidation map reveals $1.15 billion in potential short liquidations if SOL climbs to $89. By comparison, only $242 million in long liquidations would trigger if the price falls to $67. This skew indicates greater pressure on bearish positions during sharp upward moves.

SOL Price Is Looking At Volatility
Solana price is trading at $76 at the time of writing. Bollinger Bands are converging, signaling an impending volatility squeeze. Such setups often precede sharp price movements. Based on prevailing bearish indicators, downside risk currently appears elevated.
If SOL loses the $73 support level, the next downside target stands near $64. A drop to this zone could trigger long liquidations. Increased forced selling may intensify volatility and deepen short-term losses for holders.
Conversely, a shift in sentiment could support recovery. If bulls regain control, Solana price may reenter consolidation between $78 and $87. Sustained stability within this range would improve structure. A breakout above $89 could trigger $1.15 billion in short liquidations, accelerating upside momentum.
Crypto World
Crypto Execs Push Back on Viral Claim

A market analysis viewed almost 5 million times on X states that Bitcoin derivatives have turned the cryptocurrency’s 21-million-supply cap into a “theoretically infinite” one.
Past Bitcoin (BTC) falls had a clear catalyst, but sharp drops in the opening months of 2026 have sparked several theories, ranging from digital asset treasuries (DATs) blowing up under pressure to a lingering hangover from October’s mass liquidation cascade.
Robert Kendall, author of “The Kendall Report,” claimed he cracked it in his viral X post. He argued that Bitcoin’s valuation logic based on fixed supply “died” once cash-settled futures, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other financial instruments were layered on top of the asset.
However, executives and researchers across the digital asset industry rejected Kendall’s analysis. Several told Cointelegraph that leverage affects price dynamics without changing Bitcoin’s underlying supply.

Harriet Browning, vice president of sales at institutional staking company Twinstake, told Cointelegraph, “When institutions allocate via ETFs and DATs, they are not diluting scarcity, as there will still only ever be 21 million. They are not minting new Bitcoin.”
“Instead, they are putting Bitcoin into the hands of long-term institutional holders who deeply understand its value proposition, not speculative traders looking for a quick exit,” she added.
Scarcity, lost coins and the question of effective float
When Bitcoin was first introduced to the world, the only way to acquire it was to buy it from other enthusiasts, mine it or trade it for pizza. Soon, crypto exchanges became available and opened retail access to the spot market.
In 2026, investors can also gain exposure through financial products built on spot crypto. To put it simply, Bitcoin now has a paper market of its own. However, skeptics of Kendall’s analysis said that a paper market does not damage Bitcoin’s scarcity.
“Gold has a massive paper market in futures, ETFs and unallocated accounts that dwarfs physical supply, yet nobody argues gold isn’t scarce. Paper claims don’t change the amount of gold in the ground, and the same logic applies to Bitcoin,” Luke Nolan, a senior research associate at CoinShares, told Cointelegraph.
Bitcoin is often compared to gold for similarities like headlining the internet generation’s own gold rush, being a store of value and being a hedge against currency debasement. It is also programmed to a hard supply cap that doesn’t fluctuate even when investment products are built on top of it, much like a gold bar wouldn’t magically sprout out of its own derivatives.

Like precious metals, new Bitcoin enters the market through a process called mining. Instead of digging the earth, the system rewards those who verify transactions on the blockchain about every 10 minutes. Those rewards are sliced in half every four years, so Bitcoin’s supply growth slows over time, along with the amount of virgin Bitcoin entering the economy.
As of February, about 19.99 million BTC has been mined, though Nolan calls this metric misleading, as not all of these coins are available for investors. Users can lose their passwords or take them to their graves. Up to 4 million coins are estimated to be permanently lost.

With more spot Bitcoin becoming inaccessible, Nolan claimed that the institutional access layer actually reinforces Bitcoin’s scarcity.
“Spot ETFs require physical BTC to be held in custody, and in 2025 alone, combined ETF and corporate treasury holdings grew significantly. That is real supply being pulled off the market,” he said.
Related: Are quantum-proof Bitcoin wallets insurance or a fear tax?
Bitcoin’s shift to derivatives-led price formation
Even critics of Kendall’s supply argument acknowledge that Bitcoin’s short-term price discovery now leans heavily on instruments tied to institutional markets.
Derivative activity has increasingly shifted to traditional finance venues. CME futures overtook Binance in BTC futures open interest in late 2023, although Binance recently regained the lead.

“Derivatives markets have become the primary venue for expressing institutional views on Bitcoin, and as a result, they now play a central role in spot price discovery,” said Browning.
Browning added that derivatives and ETFs influence Bitcoin’s spot price through three main transmission channels.
First, markets like CME influence short-term price discovery because institutional traders express their bullish or bearish views in futures before the spot market. When futures prices diverge from spot prices, traders opt for arbitrage strategies, such as basis trades, to close the gap. According to Browning, hedge funds routinely buy spot Bitcoin or its ETFs while shorting CME futures to capture the premium between the two.
Second, when banks sell Bitcoin-linked notes to clients, they typically hedge their exposure by buying Bitcoin through ETFs, effectively creating more spot demand.
Related: Banks can’t seem to service crypto, even as it goes mainstream
Third, crypto-native perpetual futures can spill over into the spot market through funding-rate arbitrage. When funding rates are positive, heavy long positioning encourages traders to buy spot Bitcoin and short futures to earn funding payments, adding spot demand. When funding turns negative, that flow can reverse and pressure the price.
“Today, derivatives volumes frequently exceed spot volumes, and many institutional participants prefer derivatives, alongside ETFs, for capital efficiency, hedging and short exposure,” Browning said.
“Spot markets increasingly serve as the settlement and inventory layer, while derivatives increasingly influence marginal price discovery, and new price levels are negotiated.”
Derivatives don’t delete Bitcoin’s scarcity from the blockchain
The rise of Bitcoin’s paper market means investors no longer have to directly hold BTC to gain exposure.
Futures and perpetual contracts allow investors to express bullish or bearish views, hedge risk or deploy leverage. Similar derivatives have long existed in commodities markets without altering the physical amount of gold, oil or other assets in circulation.
Nima Beni, founder of crypto leasing platform BitLease, told Cointelegraph:
“The premise that synthetic exposure destroys scarcity is as flawed as a misapplied commodity-market analogy used about paper gold. It was wrong then; it’s wrong now.”
Kendall defended his position after Bitcoiners equipped with their own arguments flooded his viral post.
“I’m not arguing [derivatives] ‘delete’ scarcity from the blockchain. What I’m saying is they shift where marginal price is set,” he said.

Bitcoin’s 21-million cap remains unchanged in code. No derivative contract, ETF or structured product can mint new coins beyond that limit. But what has evolved around Bitcoin is price discovery.
Derivatives increasingly shape marginal price formation before flows filter back into spot. That alters how and where Bitcoin’s value is negotiated.
Both Kendall and his critics ultimately agree on that point.
Magazine: Bitcoin may take 7 years to upgrade to post-quantum: BIP-360 co-author
Cointelegraph Features and Cointelegraph Magazine publish long-form journalism, analysis and narrative reporting produced by Cointelegraph’s in-house editorial team and selected external contributors with subject-matter expertise. All articles are edited and reviewed by Cointelegraph editors in line with our editorial standards. Contributions from external writers are commissioned for their experience, research or perspective and do not reflect the views of Cointelegraph as a company unless explicitly stated. Content published in Features and Magazine does not constitute financial, legal or investment advice. Readers should conduct their own research and consult qualified professionals where appropriate. Cointelegraph maintains full editorial independence. The selection, commissioning and publication of Features and Magazine content are not influenced by advertisers, partners or commercial relationships.
Crypto World
MoonPay unveils AI onramp for brave new agent economy


Cryptocurrency payments firm MoonPay has introduced a non-custodial financial layer that gives AI agents access to wallets, funds, and the ability to transact autonomously, the company said on Tuesday.
MoonPay Agents, as the new service is called, requires a user to verify and fund their agent’s wallet through MoonPay, and thereafter the agent can take over, trading, swapping, and moving money on its own.
While AI agents are primed and ready to trade, allocate capital and execute strategies, they are constrained inasmuch as they can’t participate in the economy without access to money, Moonpay said in an emailed press release. The idea of MoonPay Agents is to unlock that financial layer, from funding to execution to off-ramping back to fiat.
The AI service generates a MoonPay link to fund a wallet, and the user completes a one-time KYC and connects a payment method through MoonPay’s checkout, and the agent can then transact autonomously.
“AI agents can reason, but they cannot act economically without capital infrastructure,” said Ivan Soto-Wright, CEO and Founder of MoonPay. “MoonPay is the bridge between AI and money. The fastest way to move money is crypto, and we’ve built the infrastructure to let agents do exactly that: non-custodial, permissionless, and ready to use in minutes.”
Crypto World
Bitcoin Realized Losses Have Hit Bear Market Levels


Data from Glassnode shows loss-taking now outweighs profits, a shift rarely seen outside deep bear phases.
Bitcoin’s on-chain data has flashed a signal that has historically come before prolonged bear market conditions, with the Realized Profit/Loss Ratio confirming a regime shift toward loss-dominant selling.
The move suggests that liquidity is evaporating from the market, forcing investors to realize losses rather than book profits, a dynamic last seen during the deepest crypto winter periods of 2018 and 2022.
Key Metric Flips Below 1 Signaling Capitulation Risk
According to data from on-chain analytics firm Glassnode, the 90-day simple moving average of the Realized Profit/Loss Ratio has officially fallen below 1. The metric, which compares the total value of BTC sold at a profit versus those sold at a loss, indicates that loss-taking now outweighs profit-taking across the network.
“This confirms a full transition into an excess loss-realization regime,” Glassnode analysts noted in a February 24 update on X.
The firm highlighted that historically, breaks below this threshold have persisted for six months or more before reclaiming the 1 level, a recovery that typically signals a “constructive return of liquidity to the market.”
The reading represents the culmination of a trend that began in early February, when the ratio was hovering near 1.5, and late January, when it stood around 1.32.
Furthermore, the current on-chain structure shows confluence with previous bear market bottoms. CryptoQuant contributor _OnChain observed that indicators tied to whale activity, particularly Unspent Profitability Ratios (UPR) for various holder cohorts, have reached levels similar to May-June 2022, a period that preceded significant downside before the ultimate bottom formed later that year.
Market Context and Historical Parallels
The current sell-side pressure follows a dramatic cooldown in profit-taking that occurred in December 2025. Glassnode’s earlier data showed that 7-day average realized profits crashed from over $1 billion in Q4 2025 to just $183.8 million by December, which temporarily allowed Bitcoin to stabilize and rally above $96,000 in early January.
You may also like:
However, that stabilization proved short-lived as macroeconomic headwinds intensified, with Bitcoin trading at approximately $63,200 at the time of writing, down 3.6% in 24 hours and almost 29% over the past month. The asset is also nearly 50% below its all-time high reached in October 2025.
Analysts have attributed the continued weakness to a combination of macro factors rather than a structural breakdown in Bitcoin’s fundamentals. U.S. President Donald Trump’s recent tariff announcements, including a proposed increase on taxes on global imports, have rattled risk assets across traditional and crypto markets.
Despite the bearish signals, some analysts maintain that Bitcoin’s long-term cycle remains intact. Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan recently framed current volatility as a necessary “teenage state” of monetary evolution, arguing that maturing assets must pass through speculative gradients before achieving institutional stability.
However, chartist Ali Martinez warned that a three-day “death cross” could be confirmed in late February, which foreshadowed final downside moves in 2014, 2018, and 2022, historically leading to additional declines of 30% to 50%.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Crypto World
This Has Never Happened in Bitcoin’s History: Will BTC Finally Rebound?
The primary cryptocurrency experienced another substantial decline over the past 24 hours, potentially due to geopolitical tensions among other factors.
However, one important indicator signals that bulls might soon regain control.
First Time in History
As of this writing, Bitcoin trades around $63,000, down 5% on a daily basis, while its market capitalization has fallen below $1.3 trillion. Despite the grim reality, X user il Capo Of Crypto spotted an interesting development.
The analyst, who has almost 1 million followers, said the asset’s Relative Strength Index (RSI) has reached an oversold zone on a 10-day scale. Moreover, they argued that this has occurred for the first time in the history of BTC.
The technical analysis tool measures the speed and magnitude of recent price changes and is used by traders to identify potential trend reversals. It ranges from 0 to 100, and ratios below 30 indicate the asset is oversold and could be headed for a resurgence, whereas anything above 70 signals overbought territory.
One person commenting on the post claimed that “all sorts of indicators are going to be acting unusually going forward.” il Capo Of Crypto agreed with the thesis, saying the RSI is not going to be used as “a sole signal, but it’s great for confluence.”
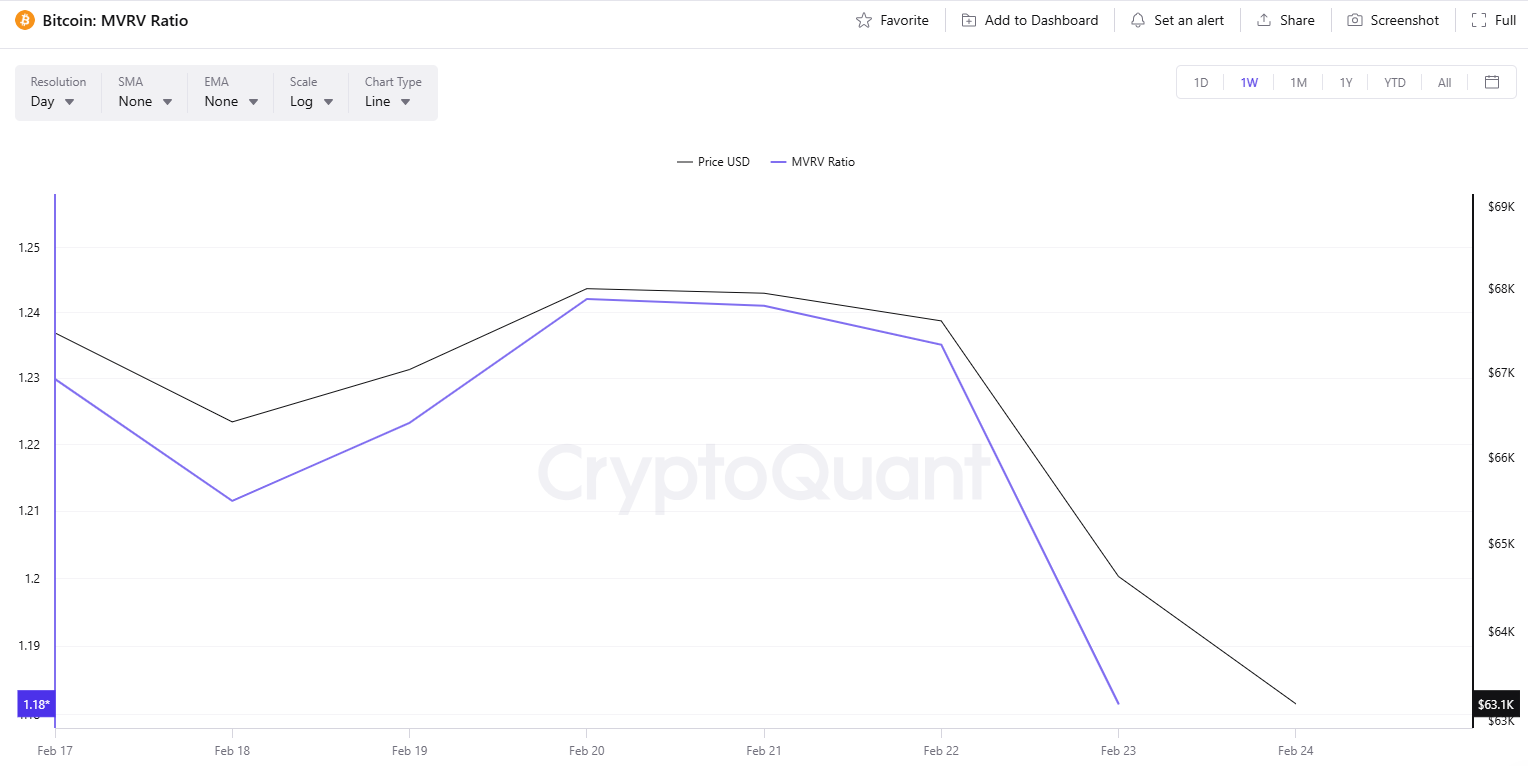
BTC’s Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) also suggests that a rebound might be knocking on the door. It compares the current value of all coins to the price at which people originally paid to acquire their holdings. According to CryptoQuant, readings below 1 indicate a bottom, whereas anything above 3.7 signals the top is in. Over the past seven days, the MVRV has been declining, currently pointing at 1.18.
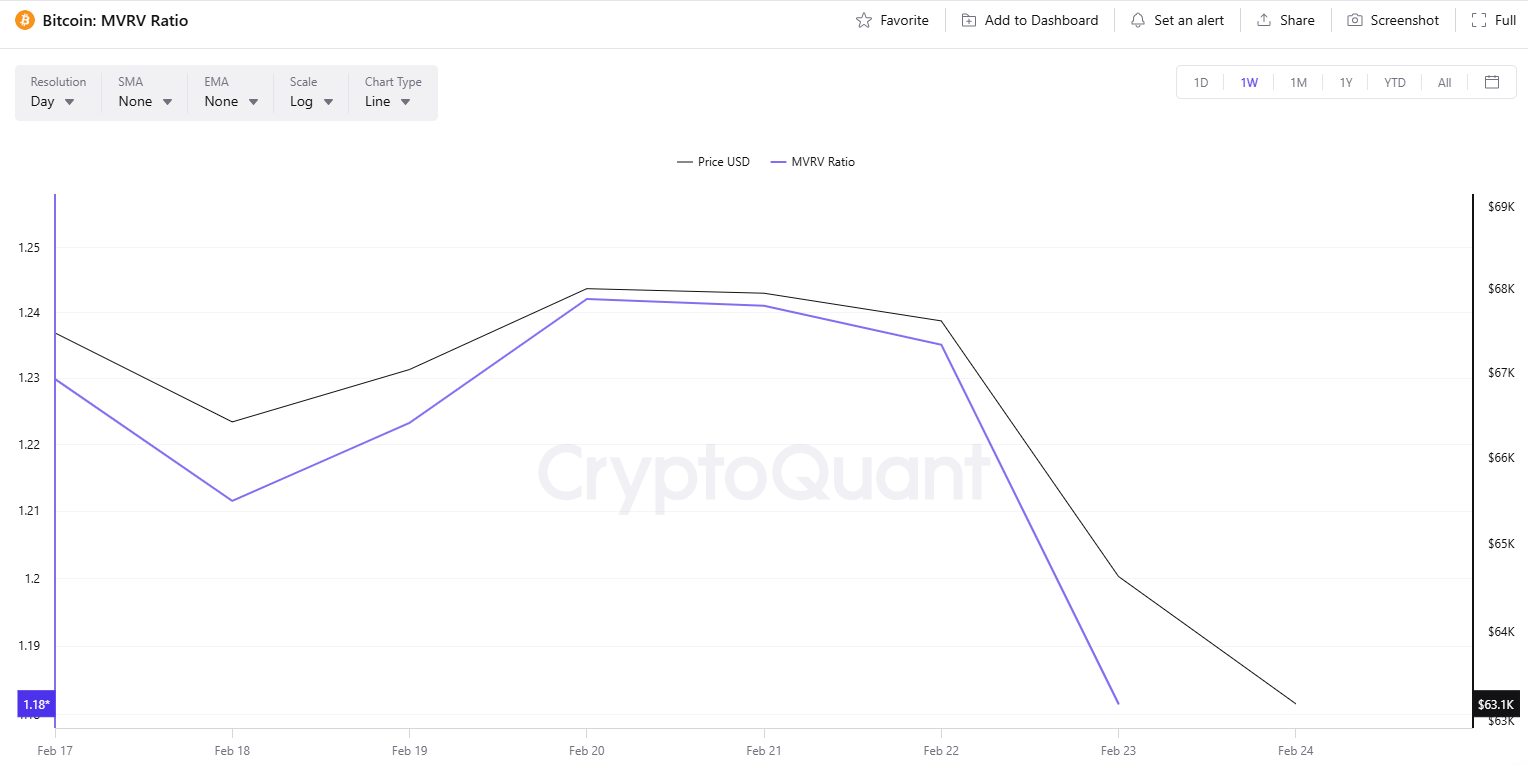
The Bears Might be Resistant
Despite the aforementioned bullish factors, many other indicators suggest the bear market is far from over. Over the past several weeks, crypto funds have been bleeding heavily, with outflows significantly outpacing inflows.
According to SoSoValue, investors have withdrawn billions of dollars from spot BTC ETFs, a trend that may signal further downside risk for the price.

Meanwhile, the amount of BTC stored on crypto exchanges has risen over the last few days. This doesn’t guarantee a further correction but is often interpreted as a pre-sale step, thereby potentially setting the stage for additional weakness in the market.

The post This Has Never Happened in Bitcoin’s History: Will BTC Finally Rebound? appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Crypto World
Is ETH Building a Base at $1.8K or Preparing for $1.5K?
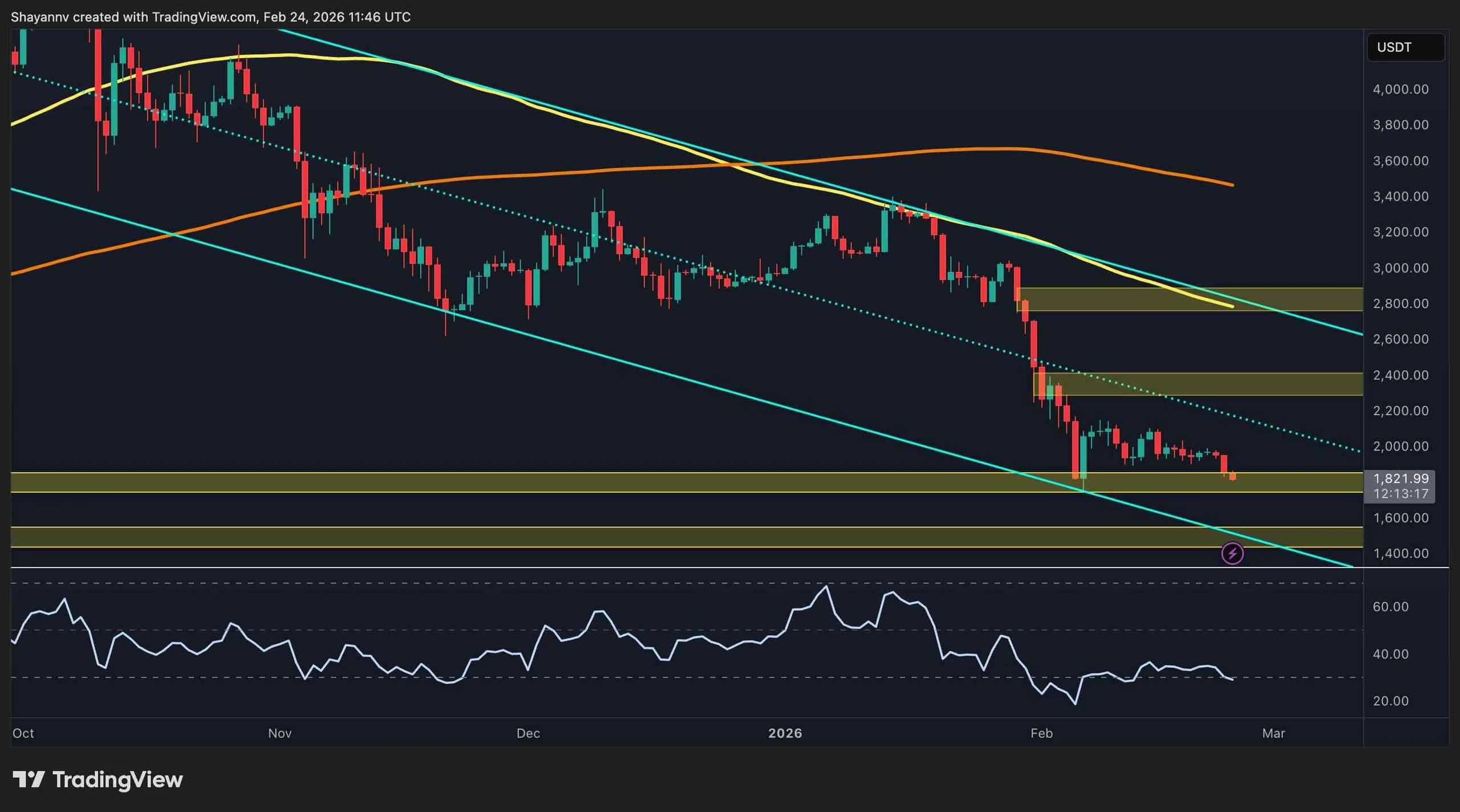
Ethereum remains under sustained downside pressure after the February liquidation cascade, with the price now stabilizing around the mid-$1,800s.
The broader structure still reflects a cyclical correction rather than a completed bottom, but short-term momentum has cooled, and the market is attempting to build a base above a major higher-timeframe demand region.
Ethereum Price Analysis: The Daily Chart
On the daily chart, ETH trades within a well-defined descending channel, with the price currently hugging the lower half of the structure near $1,800–$1,850. The breakdown from the $2,300–$2,400 support block and the rejection well below the declining 100-day and 200-day moving averages confirm a bearish medium-term trend, while the daily RSI remains depressed near oversold territory, consistent with a strongly extended move.
The immediate technical focus is the horizontal demand band around $1,750–$1,800, and sustained consolidation above this area could allow a mean-reversion bounce toward the $2,000–$2,200 zone, whereas a decisive loss of it would open the door toward deeper supports closer to $1,500–$1,600 and the lower boundary of the channel.
ETH/USDT 4-Hour Chart
On the 4-hour chart, the prior ascending support line originating from the early-February low has been broken, and the asset is now consolidating just below that trendline inside the same $1,750–$1,850 demand zone. Short-term momentum is weak but no longer accelerating lower, with the RSI flattening after an oversold print, which often precedes either a sideways consolidation or a corrective rebound.
As long as the market holds above the recent intraday lows around the $1,750 mark, the structure allows for a retracement back toward $1,900–$1,950, where the former range floor and short-term moving averages converge. Failure to defend the $1,780 area would likely trigger another round of selling toward the next liquidity pocket below $1,700.
On-Chain Analysis
Perpetual futures positioning reflects a markedly defensive stance: funding rates across major exchanges have flipped sharply negative and remain below zero after the recent decline, indicating that short positions are paying longs and that the derivatives market is skewed toward bearish exposure.
This shift follows a prolonged period of mostly positive funding during the prior uptrend, suggesting that a large portion of the current move has been driven by aggressive shorting and long liquidations rather than organic spot selling alone.
While persistent negative funding can reinforce downside pressure if spot demand stays weak, in combination with an oversold technical backdrop, it also creates the preconditions for a short squeeze should price stabilize and buyers step in around the present support cluster.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Disclaimer: Information found on CryptoPotato is those of writers quoted. It does not represent the opinions of CryptoPotato on whether to buy, sell, or hold any investments. You are advised to conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. Use provided information at your own risk. See Disclaimer for more information.
Crypto World
‘Tariffs’ chatter surges after Trump’s announcement on global exports


BTC swung violently around tariff headlines as ‘tariffs’ mentions spiked across crypto social media.
Summary
- Santiment data shows three major tariff announcements in the past year each triggered sharp jumps in “tariffs” mentions on X, Reddit and Telegram, aligning with key BTC inflection points.
- April 2025’s country-specific tariffs (60% on China, 25%-40% on Mexico, EU, Japan, India) saw retail discourse surge near a local market bottom, while a later 100% China tariff coincided with a BTC peak and 4‑month drawdown.
- Trump’s latest 15% global tariff, imposed despite a Supreme Court ruling against such measures, again sparked “tariffs” social dominance and fresh BTC selloffs, underscoring elevated macro and legal uncertainty.
Mentions of “tariffs” have spiked across cryptocurrency social media platforms following President Donald Trump’s announcement of a 15% global tariff on imports, according to data from market intelligence firm Santiment.
The surge in social media discussion mirrors previous episodes that coincided with significant price movements in Bitcoin markets, Santiment reported. Over the past year, three separate tariff announcements generated large increases in discourse across platforms including X, Reddit, and Telegram, each occurring near notable market shifts.
In April 2025, Trump introduced country-specific tariffs, including a 60% tariff on China and tariffs ranging from 25% to 40% targeting Mexico, the European Union, Japan, and India. Social media engagement around tariffs increased sharply as retail traders reacted to the policy announcement, according to Santiment. The spike in retail-driven discourse coincided with heightened volatility across cryptocurrency markets, the firm stated. That period aligned with a market bottoming process, with prices later stabilizing and recovering.
Five days after Bitcoin reached an all-time high, Trump announced a 100% tariff on Chinese imports. Social media volume spiked again, though the tariff was rescinded two days later. That period marked a peak before Bitcoin entered a four-month decline, according to market data.
The most recent announcement of a 15% global tariff follows a Supreme Court ruling declaring tariffs illegal, adding uncertainty to markets. Social media discussion surrounding tariffs has surged again, coinciding with renewed Bitcoin selloffs, Santiment data showed.
The geopolitical backdrop includes a legal dispute between federal authority and presidential power, extending uncertainty beyond economic policy into questions of institutional stability, analysts noted.
Santiment’s data indicates that large retail discourse spikes often coincide with emotionally charged phases in market cycles. The pattern observed over the past year shows extreme retail activity has aligned with local market bottoms, while aggressive policy announcements near price peaks have preceded extended corrections.
Bitcoin’s response to the current tariff situation will depend on broader liquidity conditions and macroeconomic stability, market observers stated. Until clarity emerges around policy enforcement and legal resolution, volatility is expected to remain elevated, according to market analysts.
Crypto World
Cipher Digital (CIFR) sinks premarket after revenue miss, bets big on hyperscale future


Cipher Digital (CIFR) shares fell about 5% in premarket trading after the company reported fourth-quarter results that missed Wall Street expectations and highlighted its shift away from bitcoin mining and toward high-performance computing (HPC) data centers.
The company, formerly known as Cipher Mining, reported fourth-quarter revenue of $60 million, below analyst estimates of $84.4 million. Adjusted earnings per share came in at a loss of $0.14, wider than the forecast loss of $0.06. Cipher posted an adjusted net loss of $55 million for the quarter.
Management pointed to 2025 as a transformative year as it pivots away from bitcoin mining and toward long-term HPC infrastructure. During the quarter, Cipher secured 600 megawatts of contracted capacity, including a 15-year, 300 megawatt (MW) lease with Amazon Web Services and a 10-year, 300 MW lease with Fluidstack and Google.
The company also raised $3.73 billion through three senior secured bond offerings to finance construction at its Barber Lake and Black Pearl data center projects, both of which remain on schedule.
Cipher divested its 49% stakes in three mining joint ventures for about $40 million in stock, further simplifying its structure as it transitions to a data center-focused business model.
Crypto World
Does Vitalik Buterin Even Like His Chain? Sells 10,000+ ETH as Ethereum Price Tests $1,800
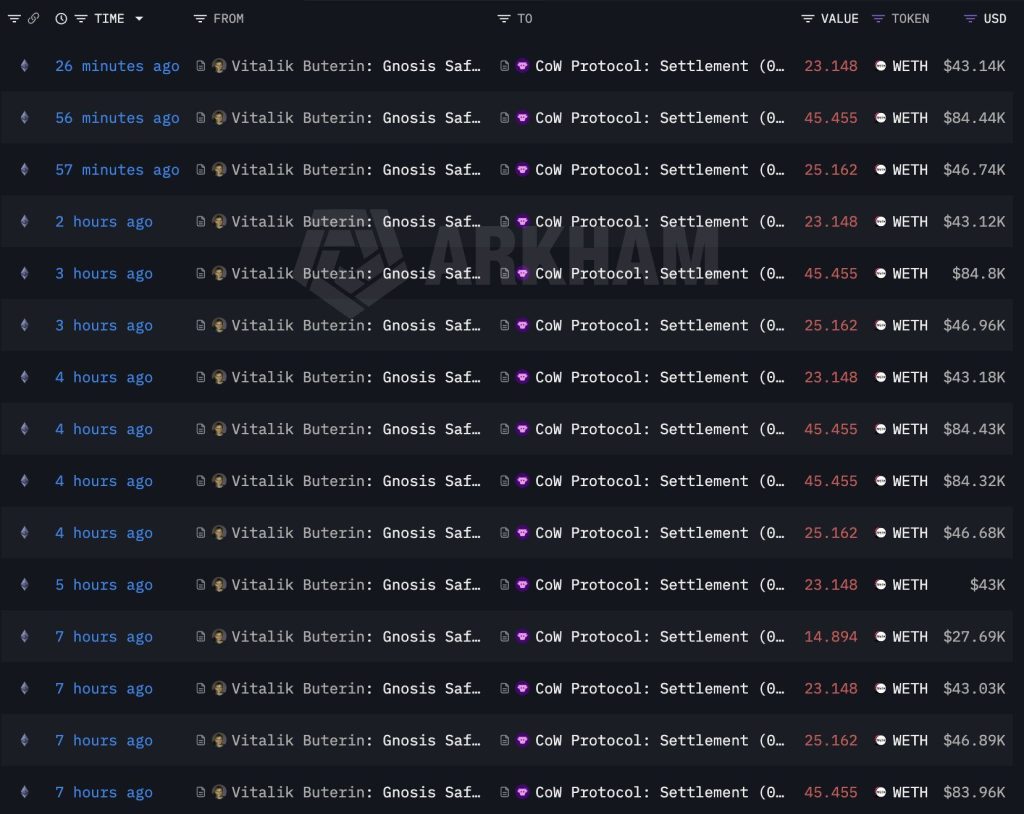
Vitalik Buterin has been selling as Ethereum price tumble. And some might think that he doesn’t like his chain or even crypto at all.
On chain data shows the Ethereum co founder liquidated 10,723 ETH, worth about $21.7M, since early February. The sales come at a sensitive moment, with Ether struggling to defend the $1,825 support zone.
The timing has raised eyebrows, but Buterin has said past sales are meant to fund open source work; steady founder selling during a weak market naturally feeds bearish sentiment.
Key Takeaways
- $21.7 Million Liquidated: Buterin has sold a total of 10,723 ETH since February 2, averaging a sale price of approximately $2,027 per token.
- Recent Acceleration: Data shows 3,765 ETH ($7.08 million) was sold in just the three days leading up to Feb. 24.
- Bearish Market Structure: The sales coincide with a 38% drop in ETH value over the last 30 days, currently testing support near $1,825.
The Ethereum Offloading Triggering Alarm?
A founder selling almost always spooks the market, no matter the reason, and Buterin said the funds are going toward open source and security-focused projects. Still, more than 10,000 ETH hitting the market creates real sell pressure.
Traders are not just reacting to the $21.7M already sold. They are watching what could come next. The original allocation was 16,384 ETH, meaning roughly 6,000 ETH may still be unloaded.
The sales began on February 2 and continued through the month. The most aggressive selling occurred recently, with 3,765 ETH sold for $7.08 million between Feb. 21 and Feb. 24.
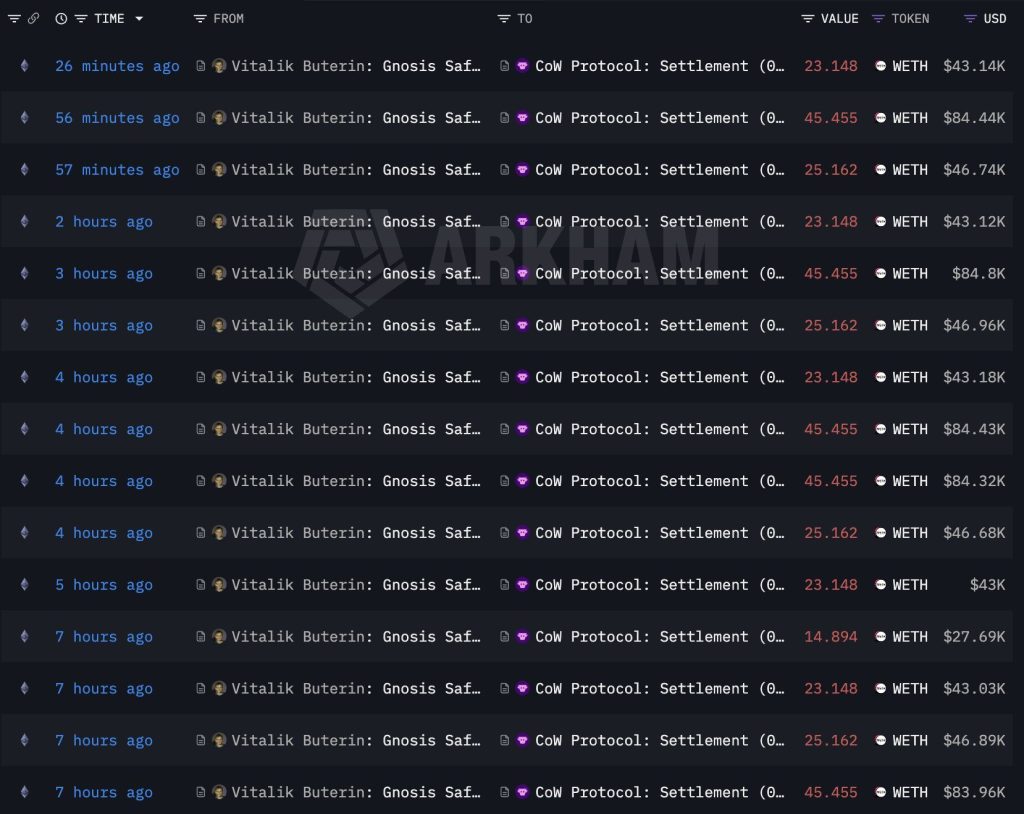
The average execution price across these three weeks sits at $2,027. With Ethereum currently trading around $1,825, Buterin effectively front-ran the latest 10% leg down.
Ethereum Price Could Dip To $1,500 Is Very Likely Now
Ethereum’s structure has clearly weakened after losing the $2,000 psychological level.
The daily chart shows a confirmed bear flag breakdown. RSI is hovering near oversold, but MACD has not flashed a bullish crossover, so momentum still favors sellers.
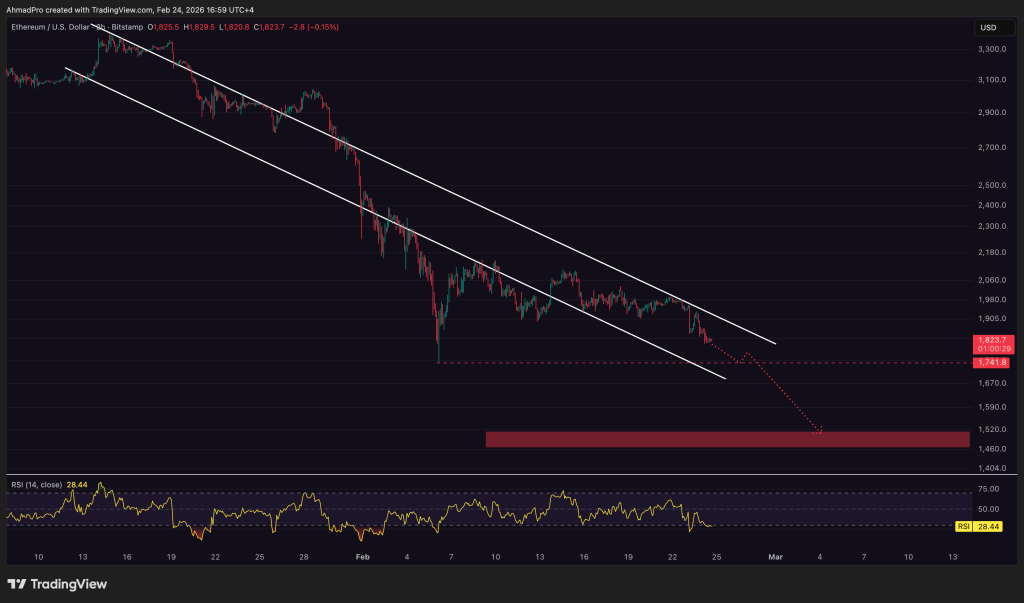
Immediate support sits around $1,800. A daily close below that opens the door to the $1,500 zone, where liquidity previously built up. The 50-day EMA has also crossed below the 200-day EMA, forming a classic death cross that reinforces the downtrend.
To invalidate the bearish setup, bulls would need to reclaim $2,150 with strong volume. Until that happens, rallies are likely to face selling pressure, especially with continued founder distribution adding supply.
Watch the $1,780 to $1,820 range closely. A bounce could shape a double bottom. A clean break lower, and $1,475 becomes the next logical target.
Discover: Here are the crypto likely to explode!
The post Does Vitalik Buterin Even Like His Chain? Sells 10,000+ ETH as Ethereum Price Tests $1,800 appeared first on Cryptonews.
-

 Video4 days ago
Video4 days agoXRP News: XRP Just Entered a New Phase (Almost Nobody Noticed)
-

 Fashion4 days ago
Fashion4 days agoWeekend Open Thread: Boden – Corporette.com
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoBaftas 2026: Awards Nominations, Presenters And Performers
-

 Sports19 hours ago
Sports19 hours agoWomen’s college basketball rankings: Iowa reenters top 10, Auriemma makes history
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoInfosys Limited (INFY) Discusses Tech Transitions and the Unique Aspects of the AI Era Transcript
-

 Politics20 hours ago
Politics20 hours agoNick Reiner Enters Plea In Deaths Of Parents Rob And Michele
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoKunal Nayyar’s Secret Acts Of Kindness Sparks Online Discussion
-

 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoRetro Rover: LT6502 Laptop Packs 8-Bit Power On The Go
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoClearing the boundary, crossing into history: J&K end 67-year wait, enter maiden Ranji Trophy final | Cricket News
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMattel’s American Girl brand turns 40, dolls enter a new era
-
 Crypto World7 hours ago
Crypto World7 hours agoXRP price enters “dead zone” as Binance leverage hits lows
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLaw enforcement kills armed man seeking to enter Trump’s Mar-a-Lago resort, officials say
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoDolores Catania Blasts Rob Rausch For Turning On ‘Housewives’ On ‘Traitors’
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoTesla avoids California suspension after ending ‘autopilot’ marketing
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day ago‘Hourly’ method from gastroenterologist ‘helps reduce air travel bloating’
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoAnthropic-Backed Group Enters NY-12 AI PAC Fight
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoArmed man killed after entering secure perimeter of Mar-a-Lago, Secret Service says
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoMaine has a long track record of electing moderates. Enter Graham Platner.
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoWLFI Crypto Surges Toward $0.12 as Whale Buys $2.75M Before Trump-Linked Forum
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days ago83% of Altcoins Enter Bear Trend as Liquidity Crunch Tightens Grip on Crypto Market