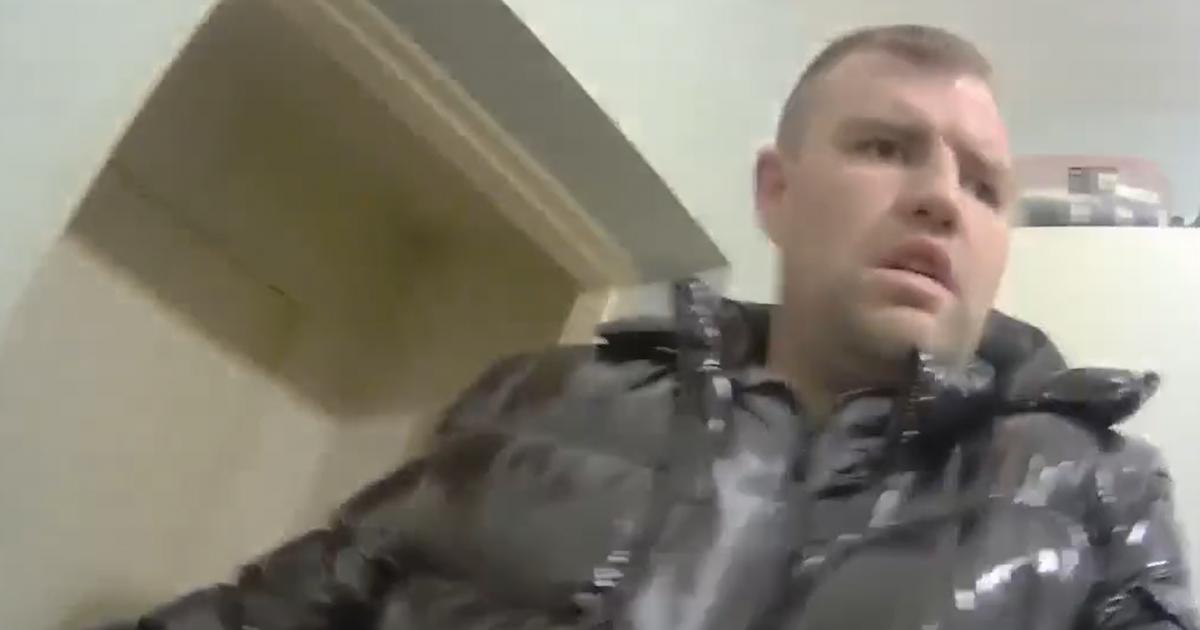
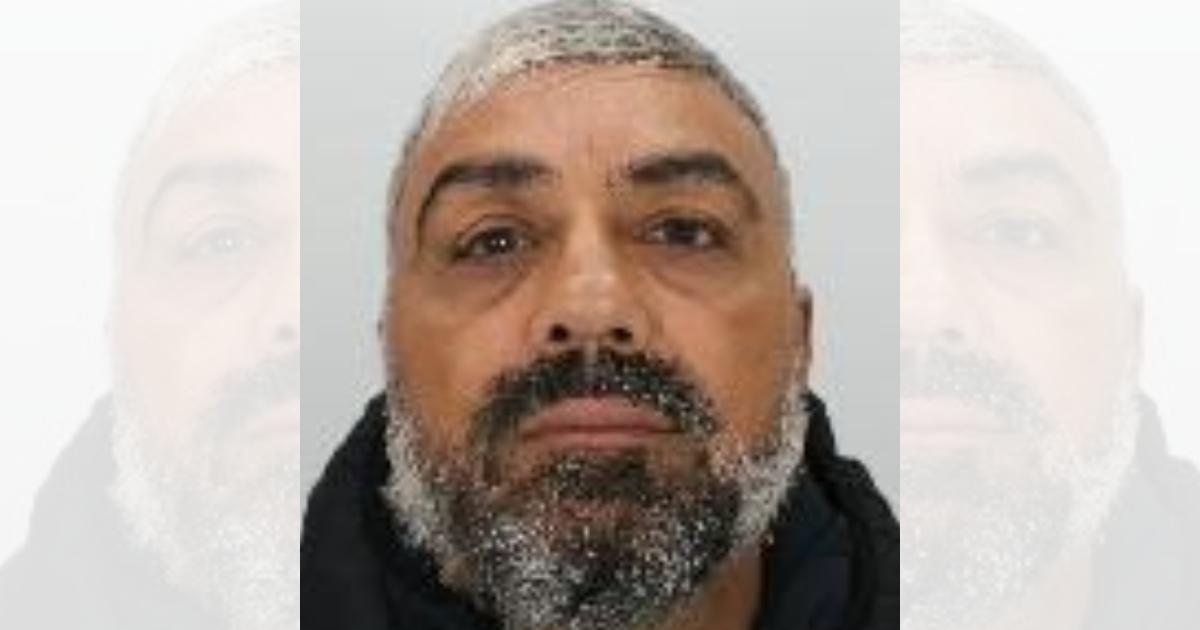
Natalie Fry’s family weren’t sure she was going to wake up
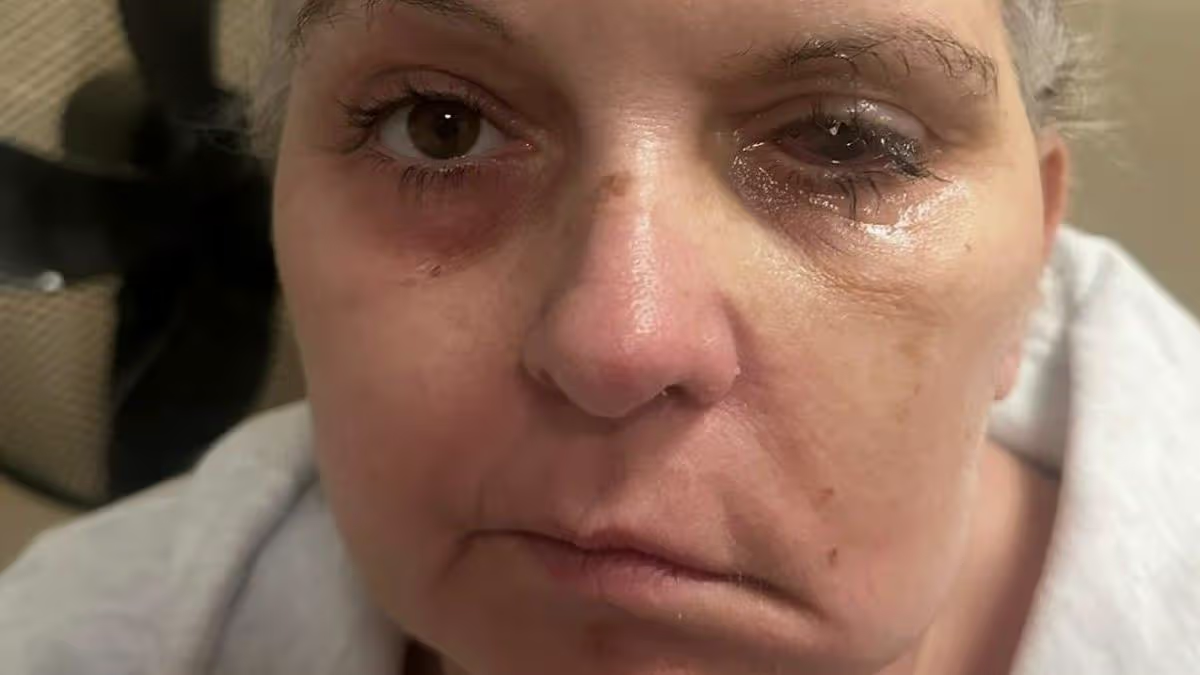
A mum was left in a coma for three weeks after a fall on holiday – but the accident ended up saving her life as doctors found a life-changing brain tumour. Natalie Fry travelled to Jamaica to celebrate her 50th birthday, but while there, suffered a horrifying accident that left her family fearing the worst.
Her daughter, Chloe Bavin, 33, didn’t leave her mum’s hospital bedside in the hopes she would get to hear her voice at least one more time. “Sitting by mum’s bedside while she was in a coma was the most frightening time of my life,” said Chloe, from Weston-super-Mare.
“She was on a ventilator, surrounded by machines, and we were told there was a high chance she wouldn’t survive. I was in denial. My mum is such a strong, beautiful and confident woman. I had never seen her weak. Seeing her like that, with tubes and machines everywhere, broke me.
“We didn’t know if she would wake up, if she would be paralysed, or if she would even remember who we were. I kept thinking about the last conversation we’d had and wondering if I’d ever hear her voice again.
“Staying strong for her and my children while living with that uncertainty was incredibly hard.”
Natalie, a 999 call handler, suffered the ordeal in June 2023. She had fallen and hurt her knee, which left the mum feeling unwell. After arriving back on UK soil, she was referred for an MRI scan after an examination which showed the mass on her brain.
Chloe said: “It was awful. Mum went to the appointment with her husband Nick and he phoned me because mum was in shock and couldn’t say the words herself. Never in a million years did we think something like that could happen.
“Hearing the words ‘brain tumour’ completely turned our world upside down. “The doctors said that mum needed surgery or she wouldn’t survive. From that moment, everything changed.
“The fear, the uncertainty and the not knowing of what was coming next. It was overwhelming for all of us.”
The procedure didn’t come without its risks, though. These included loss of hearing, sight, mobility and even death. On 3 July 2025, however, the family decided that Natalie, now 52 to undergo the nine-hour surgery.
Luckily, it was successful and the majority of the schwannoma tumour had been removed; though a little part was left as it was too close to a nerve. Just a few hours later, though, Natalie started being sick after suffering a bleed on the brain that left her in the three-week coma.
Slowly, the ventilator support was reduced, a shunt was fitted to drain fluid from her brain and her body began making tiny movements. Against all odds, the mum pulled through and spent the next six months in hospital learning how to speak and walk again.
Now, she’s back at work despite dealing with ongoing challenges on the left side of her body, including paralysis in her face, loss of hearing, limited eyesight and no feeling. In December 2024, an MRI found another small growth which was luckily treated with radiotherapy.
It’s unclear if this has worked, though. To help raise funds for further research, Chloe is running the iconic TCS London Marathon in April, with all proceeds going to charity Brain Tumour Research.
Chloe added: “We didn’t realise the true impact of a brain tumour until we saw someone once so vibrant and independent become like a baby again. Unable to speak, breathe properly, swallow or sit up.
“We have a new normal now. It’s hard because mum doesn’t look or sound the same and the trauma has affected us all. Running the London Marathon means everything to me.
“During the darkest days, running became my therapy – the only time my mind could switch off from the trauma. To now be running 26.2 miles for mum, and to still have her here cheering me on, is something I will never take for granted.
“This marathon is about hope. It’s about showing other families that they’re not alone and about raising vital funds so that one day no one has to go through what we have.”
Carol Robertson, National Events Manager at Brain Tumour Research, said: “We are incredibly grateful to Chloe for taking on the London Marathon in honour of her mum. Every step she runs will help us move closer to finding a cure for all types of brain tumours.
“Stories like Chloe’s highlight why our work is so vital. We urgently need increased awareness and investment in research to improve outcomes for patients and their families.
“We wish Chloe the very best of luck and will be cheering her on every step of the way.”