Tech
Microsoft Windows hits 40 years old: A visual walk down memory lane

On November 20th, 1985, a then not-so-big company called Microsoft announced that Windows was commercially available. Read the full story of the Microsoft operating system below.
Windows 1 to 11: The history of Windows, blue screens, and Easter eggs
We’re taking a look back at the history of the most widely used operating system. Why? Because Windows is full of surprises. When Bill Gates demonstrated the beta version of Windows 98, he ran into a blue screen. Windows 10 users fared only slightly better in fall 2018 with the Windows Fall Creators Update version 1809. It’s been a journey, to say the least.
I present to you a floppy disc containing the VERY FIRST demo of what would become @Microsoft @Windows! It was coded by the little-known father of Windows, Rao Remala. I will have much more to share on this, but for now, I thought you might like to see this historical treasure! pic.twitter.com/lyWKFMYn2M-BetaCollector (@beta_collector) March 9, 2022

©Microsoft
Windows 1.0: DOS gets a graphical add-on
On November 21st, 1985, Microsoft officially presented Windows 1.0 (which also contained an Easter egg that named the developers and employees of the Windows team). One day earlier, on November 20th, 1985, Microsoft had announced the delivery of the retail version: “BELLEVUE, WASHINGTON—November 20, 1985—Microsoft Corporation announced today the retail shipment of the Microsoft Windows operating environment to dealers and distributors.”
©Microsoft

©Microsoft
Until then, MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System) had been Microsoft’s operating system for IBM PCs. Windows 1.0 required a graphics card and 256KB of memory, the equivalent of 66 typewritten pages. For comparison, Windows 10 required a good 8GB of space on the hard drive. And by the way, Microsoft Word had already been around for a while by this time!
Which version of @Windows is the first to include Easter eggs? Windows 3.0? Nope. What if I tell you there is an Easter egg in Windows 1.0 RTM? This is what I have recently discovered: pic.twitter.com/dbfcv4r7jj-Lucas Brooks (@mswin_bat) March 18, 2022
Images from Microsoft show the beginnings of more than just Windows

©Poptronix

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©IBM
©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft
©Microsoft
©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft
©Microsoft

©Skype

©Microsoft
©Microsoft

©Microsoft

©Microsoft
©en.statista.com

©Microsoft
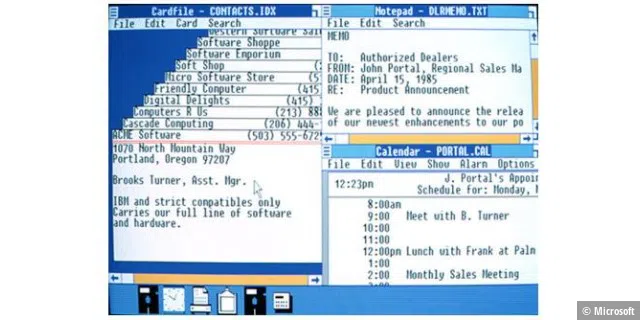
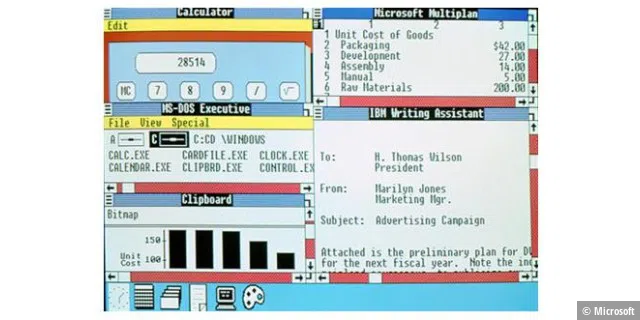
Windows was initially only intended to make DOS easier to use
The first Windows was sold as a graphical add-on for the MS-DOS operating system. The aim of the still-young company Microsoft with its boss and founder Bill Gates was to make DOS PCs easier to use: users no longer had to type in command-line commands to get things done.
The “Interface Manager”—as Windows was originally called—brought a small word processor, a drawing program, a card index box, a calendar, a clock, and some service programs in addition to file management.
©Microsoft
Windows 2.0 arrives in 1987
On December 9th, 1987, Microsoft released Windows 2.0 with desktop icons and expansion memory. Thanks to improved graphics support, users could now arrange windows to overlap, control the screen layout, and use keyboard shortcuts to get their work done faster. Windows 2.0 was developed for the Intel 286 processor.

©Microsoft
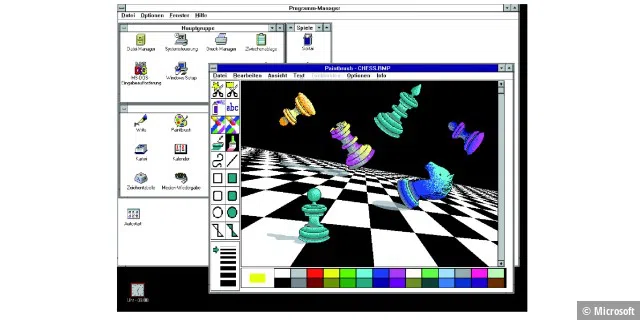
Windows 3.0/3.1: A legendary operating system with 16 colors
©Microsoft
Windows 3.0 was launched on May 22nd, 1990 together with Microsoft Solitaire. Windows 3.1 followed in 1992. Windows 3.1 computers are still in operation at Paris Orly Airport today. Microsoft announced that a total of 10 million copies of both systems were sold in the first two years.
©Microsoft
Windows 3.x offered better performance, extended graphics options with 16 colors, and visually improved icons. Users enjoyed a modern interface with 3D-looking icons and new programs. The cult games Solitaire, Hearts, and Minesweeper, which are still popular today, now also made Windows a favorite at home. From a technical point of view, however, Windows was still an add-on for DOS.
Spent the entire day today reverse engineering early Windows binaries to hunt for Easter eggs. Here is a list of the Easter eggs in various builds of Windows 1.0 – 3.0 and the keystrokes required to trigger them. https://t.co/ecqLN1NoDg. Try them yourself! pic.twitter.com/lr5Cfd5XLu-Lucas Brooks (@mswin_bat) March 19, 2022
©Microsoft
Windows 95: Bringing the PC into the living room

©Microsoft
When Windows 95 was officially launched at a major event in Redmond in the summer of 1995, the world’s press was there. The launch was accompanied by the Rolling Stones hit “Start Me Up,” the most important topic at the time was the internet, and the most urgent task that an operating system had to fulfill was communication: “More than half of all new features in Windows 95 revolve around communication, for example electronic messaging (electronic mail), Internet access, and the ability to dial into your system decentrally,” said Bill Gates at CeBIT 1995.

microsoft
Windows 95 allowed several programs to run simultaneously. Internet Explorer for surfing the web also appeared during the lifetime of Windows 95. In addition, longer file names were possible and 32-bit became available. Settings were no longer set via INI files but in the Registry. Windows 95 introduced the Start menu, the taskbar, and buttons for “minimize”, “maximize,” and “close.” Also new were the Plug & Play functions, which simplified the installation of hardware and software. The 32-bit operating system also offered enhanced multimedia functions.
The following images show screenshots of early Windows versions
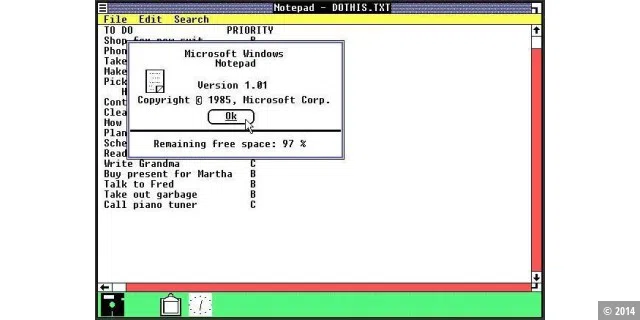
With the very first version of Windows, Microsoft still had to be careful not to come into legal conflict with Apple’s MacOS. For example, a recycle bin icon was omitted and windows were not allowed to overlap. But the very first version of Windows also had a taskbar.
©2014
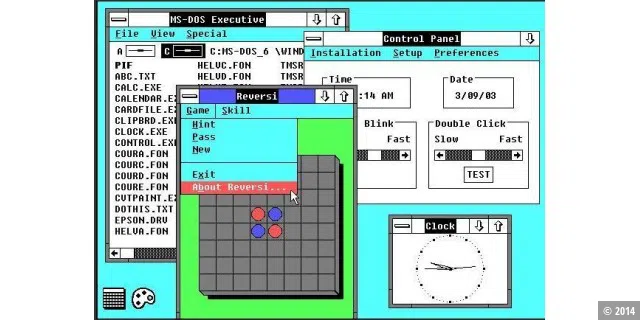
With Windows 2.0, Microsoft slightly improved the graphics and, for the first time, windows could overlap. The taskbar from Windows 1.0 was removed again. A number of useful helpers were included for the first time. These included a clock, Paint and Terminal and the file manager, which was still called MS-DOS Executive. Shortly after the release of Windows 2.0, Microsoft also brought out Word and Excel for Windows.
©2014
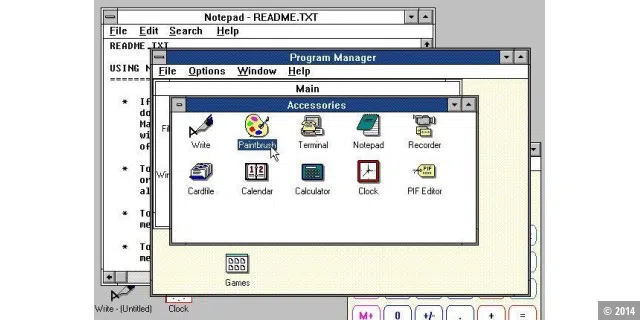
Windows 3.0 included Solitaire, which is still popular today, for the first time. It also included the Program Manager, support for VGA and virtual memory. Visually, Windows 3.0 came in a 3D look. More and more software and hardware manufacturers began to support Windows from Windows 3.0 onwards.
©2014
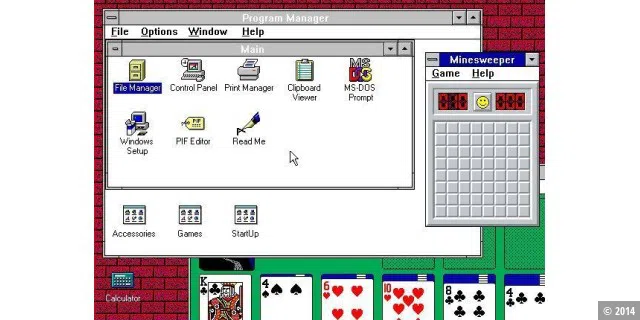
Windows 3.1 was significantly improved compared to its predecessor Windows 3.1. For example, scalable fonts with TrueType fonts were included for the first time. Drag-and-drop functionality and multimedia support have also been improved and OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) has been integrated. And – oh yes: Minesweeper celebrated its premiere.
©2014
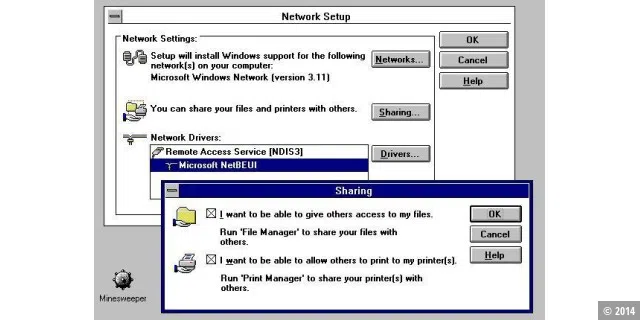
This version of Windows was based on Windows 3.1 and added native network support, particularly for LAN networks. Various network tools were also added.
©2014
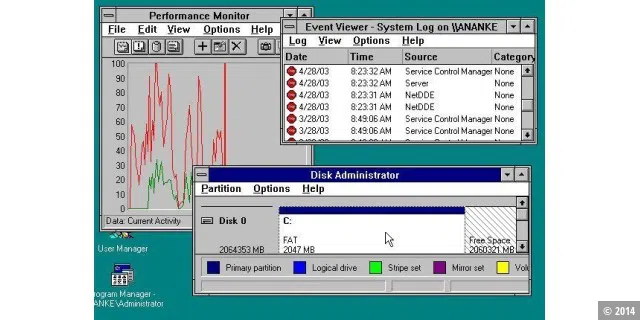
The work that had previously been done for OS/2 was channelled into Windows NT. It was a completely new 32-bit operating system. All previous versions of Windows had been graphical user interfaces for MS-DOS. Windows NT 3.1 was aimed at workstations and servers. Although Windows NT 3.1 resembled Windows 3.1 in appearance, it was ultimately a completely new operating system.
©2014
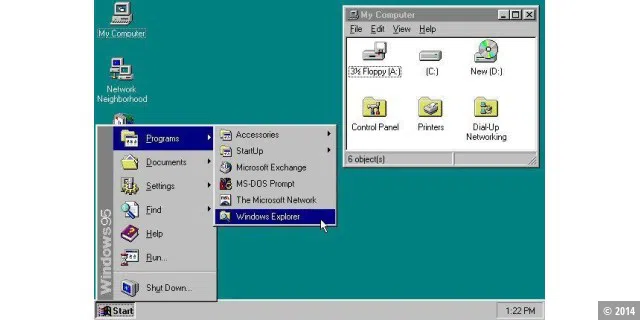
For end users, Microsoft continued to rely on a DOS-based operating system and developed Windows 3.1 into Windows 95. For the first time, no separate DOS installation was necessary. The new taskbar and the Start menu celebrated their première. Many other improvements were also made. Windows 95 was a success and heralded the triumph of the Windows platform.
©2014
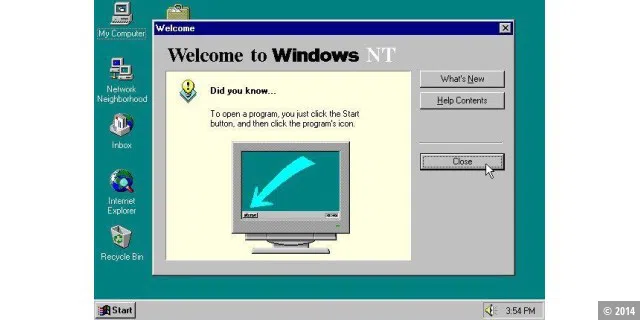
With Windows NT 4.0, the stable server Windows was given the interface of the consumer Windows 95. The very stable Windows kernel was further improved. The NT operating system became a success with Microsoft’s corporate customers.
©2014

Windows CE 1.0 was the first version of Windows for small devices. It was an operating system that was completely independent of other Windows versions that had previously been released and was used for handheld devices in the mid to late 1990s. Windows CE 1.0 ultimately formed the basis for the later Windows Mobile.
©2014
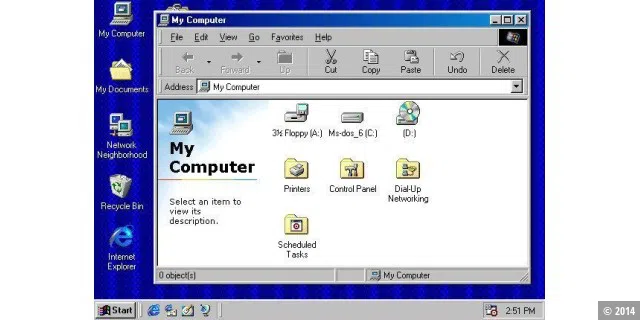
With Windows 98, the Internet Explorer browser became part of the operating system for the first time, along with support for USB and the quick launch bar.
©2014
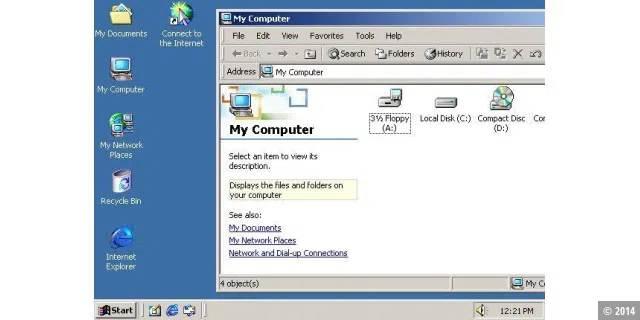
The NT Windows family was further developed in 2000 with Windows 2000. Web support from Windows 98 was now added to the server operating system as standard. It was also a relatively secure operating system that Microsoft developed for servers and workstations. Nevertheless, Windows 2000 was also often used on desktop PCs. An important new feature of Windows 2000 was that the reboots that were previously often necessary after installing new software or changing system settings were a thing of the past.
©2014
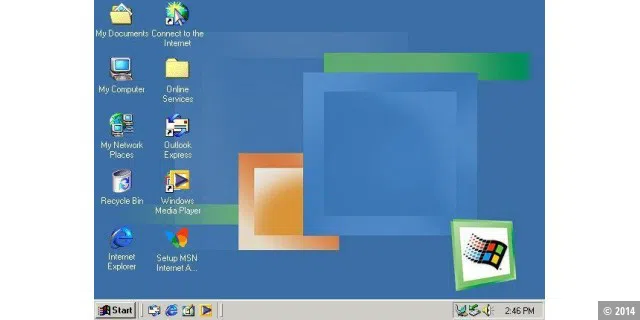
Windows users from the early days still remember Windows 2000, which was released in 2000, with nostalgia, but Windows ME, which was released in the same year, still inflames people today. Windows ME aimed to increase multimedia support and user-friendliness. However, the operating system was also very unstable and slow.
©2014
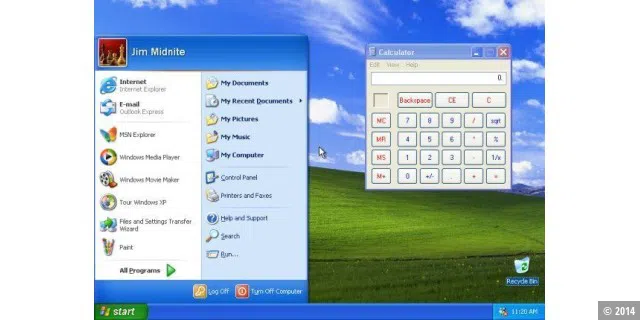
With Windows XP, Microsoft combined the stable NT family with the 9x family for end users for the first time. The result was the most successful operating system to date – and Windows XP still has a large following today. A great achievement for software that has been around for over 10 years.
There was also criticism when Windows XP was released. For example, the new, colourful Luna interface.
©2014
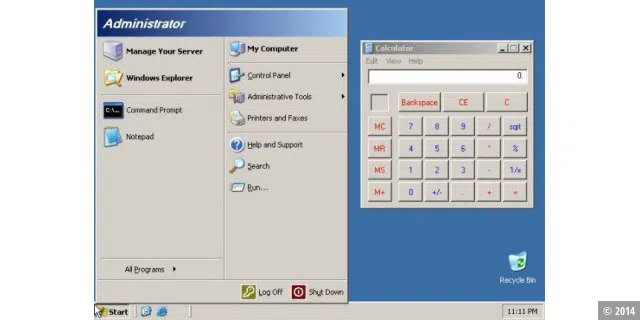
The NT family was continued in 2003 with Windows Server 2003, which offered improvements to the interface that Microsoft had already introduced two years earlier with Windows XP.
©2014
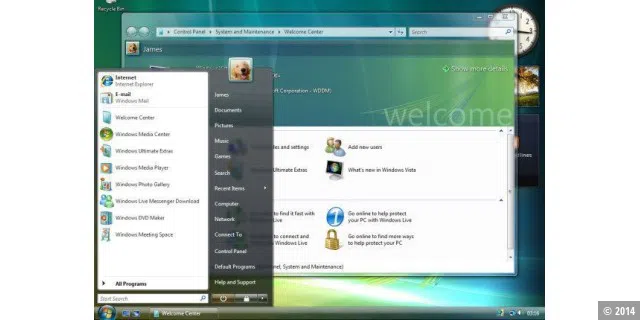
In 2007, the visually sophisticated interface of MacOS X stole the show from the ageing Windows XP. Microsoft’s answer to this was Windows Vista, which introduced the Aero interface, gadgets, a new Start menu and more stylish icons. There were also many improvements under the bonnet. However, Windows Vista failed to win over the masses. However, Windows Vista laid an important foundation for the next version of the Windows operating system for desktop PCs: Windows 7.
©2014
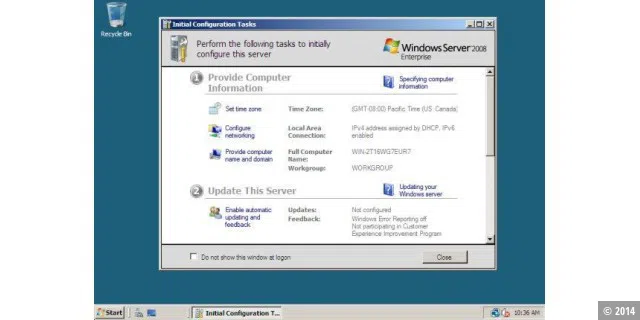
Windows Server 2008 was primarily the server version of Windows Vista. However, the Aero interface was omitted.
©2014
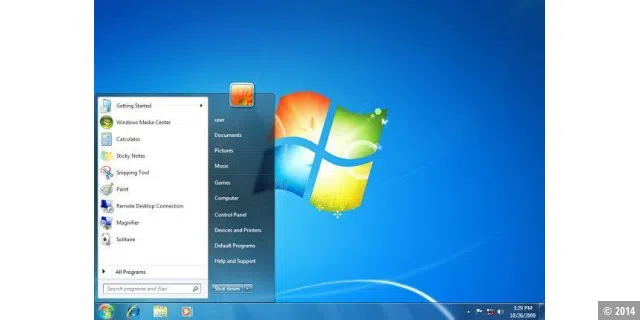
Criticism of Windows Vista prompted Microsoft to quickly start work on a successor that would address all the criticisms levelled at Windows Vista. The result was Windows 7, which has now been well received by the masses and is becoming increasingly popular.
©2014
©2014
Windows 95 becomes a success despite its many crashes
Even though Windows 95 was a standalone operating system, it still required some DOS technologies. And Windows 95 was by no means stable—crashes are simply part and parcel for Windows users. However, this did not detract from its sales success, as Microsoft sold around 40 million copies in its first year.
©Microsoft
Windows 98: Windows in the age of the first internet cafés
Three years after Windows 95, on June 25th, 1998, Microsoft launched Windows 98 (codename Memphis). It was the successor to Windows 95 and had Internet Explorer integrated into the operating system for excursions into the still relatively new World Wide Web. A browser war promptly broke out between Internet Explorer and the then-widely-used Netscape Navigator, which is now defunct.
©Microsoft
Fun fact: When Bill Gates presented a beta version of Windows 98 at the US computer trade fair Comdex on April 20th, 1998, he actually looked at a blue screen. This sight was later shared by many millions of users, as Windows 98 remained susceptible to crashes but always recovered. The blue screen and the associated computer restart were commonplace for Windows 98 users. The Windows 98 SE upgrade, which appeared a year later, did nothing to change this.
Windows 98 not only offered simplified access to the internet, but also supported reading and writing DVDs and automatic hardware recognition of many USB devices for the first time. A new feature was the quick launch bar (“taskbar”), which allowed Windows programs to be launched more quickly than via the Start menu. Windows 98 also had native support for USB and FAT32.
The breakthrough on the market came with Windows 98 Second Edition (SE), which was the first time Microsoft used the CD-ROM and said goodbye to floppy disks as an installation medium. However, users still needed a boot disc with CD-ROM drivers because the Windows 98 retail CDs themselves were not bootable—and blue screens were still part of everyday life for Windows users. Windows 98 was the last version of the operating system based on MS-DOS.
Windows 2000: Standardization of Windows for businesses
Back in 1993, Microsoft launched Windows NT, an operating system designed to meet the requirements of companies for business computers. The Windows 2000 Professional operating system offered companies a standardized IT platform. Based on the code of Windows NT Workstation 4.0, Windows 2000 offered greater reliability and improved usability. Microsoft also simplified hardware installation with broad support for USB devices and new network and wireless products.
©Microsoft
Windows Me: Who asked for this?
Windows Me, which was released in 2000, was the first to introduce system recovery, a feature where the configuration of PC software could be reset to a point in time before problems occurred. Movie Maker provided users with tools for digitally editing, saving, and sharing home videos. And with the help of Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 technologies, digital media could be searched, organized, and played back. However, users weren’t very enthusiastic about Windows Me.
Technically speaking, Windows Me was the last Microsoft operating system based on the Windows 95 code base. Microsoft announced at the time that all future operating system products would be based on the Windows NT and Windows 2000 kernel.
©Microsoft
Windows XP: Still fondly remembered
Windows XP was launched on October 25th, 2001 with a common code base shared between Windows for end users and Windows for servers and businesses (formerly Windows NT). With XP, Windows became significantly more crash-proof and blue screens less common.
For Microsoft, Windows XP became the best-selling Windows of all time in the following years, with millions and millions of users loving it. Many users found the navigation in the Start menu, the taskbar, and the Control Panel intuitive—and many years later still didn’t want to give up their Windows XP for later versions like Windows 8.

©Microsoft
Microsoft also provided regular security updates online and launched the Trustworthy Computing initiative in 2002. With Windows XP, Microsoft increasingly integrated digital entertainment media in 2001. Later versions of Windows XP, such as the Media Center Edition, could even be controlled using a remote control.

©Microsoft
Windows XP was available in two versions: Home and Professional. Windows XP Home came with Network Installation Wizard, Windows Media Player, Windows Movie Maker, and advanced features for digital photos. Windows XP Professional contained additional features especially for use in companies. Windows XP consisteds of 45 million lines of code.
Even 20 years after its launch, a small number of computers still run Windows XP. However, as they no longer receive security updates, they pose a huge security risk as soon as they’re connected to the internet.
©Microsoft
Windows Vista: A huge flop with users
In January 2007, Microsoft revealed the secret behind the new operating system codenamed “Longhorn”: Windows Vista with its new Aero design. Microsoft redesigned the Start menu and taskbar, while User Account Control ensured that potential malware didn’t harm the PC. But user enthusiasm was limited with Vista, as it was with Windows Me.
©Microsoft
©Microsoft
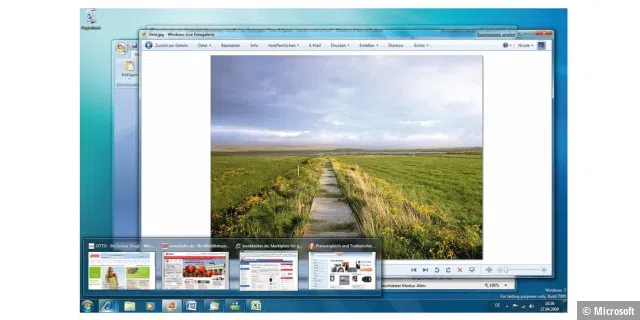
Windows 7: The first step on the way to the cloud
Windows 7 was released in 2009, together with Windows Live Services and the “online hard drive” SkyDrive (which would later be known as OneDrive when Microsoft had to change the name of its online storage due to legal problems). Windows 7 was such a huge success that nobody wanted to move on to its successor, Windows 8.
microsoft

©Microsoft
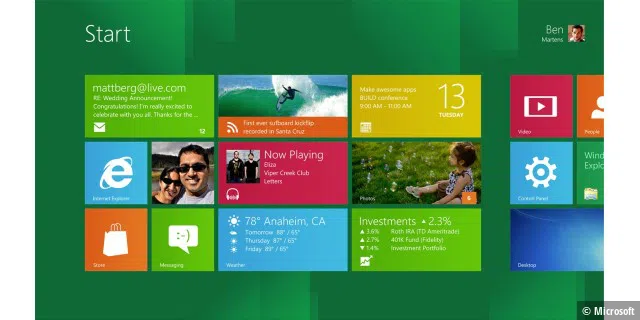
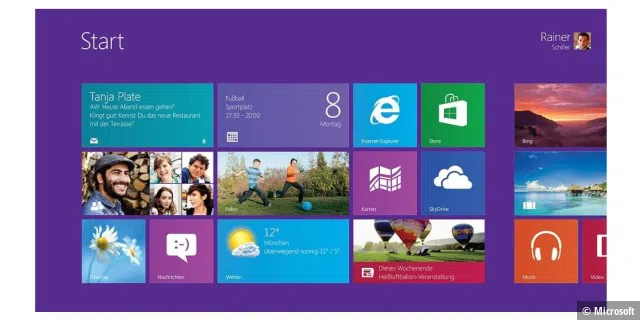
Windows 8: Optimized for mobile use
In 2012, Microsoft brought tiles out of the bathroom and onto the Windows desktop—with Windows 8 and apps in tile form. Windows could now be operated via touch input. The Windows Store was also integrated, allowing apps to be downloaded.
©Microsoft
Microsoft wanted to bring together desktop PCs, laptops, and tablets (where Windows didn’t play a major role). However, users gave Windows 8 the cold shoulder. With the subsequent release of Windows 8.1, which went on sale on October 17th, 2013, Microsoft tried to correct the worst flaws of Windows 8 and also bring back the Start button. The desktop could now also be used again as standard. Microsoft discontinued support for Windows 8.1 on January 10th, 2023.
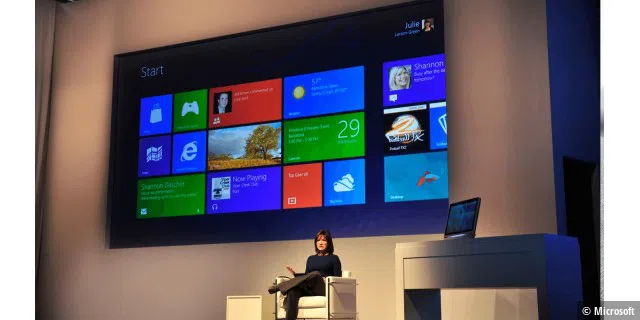
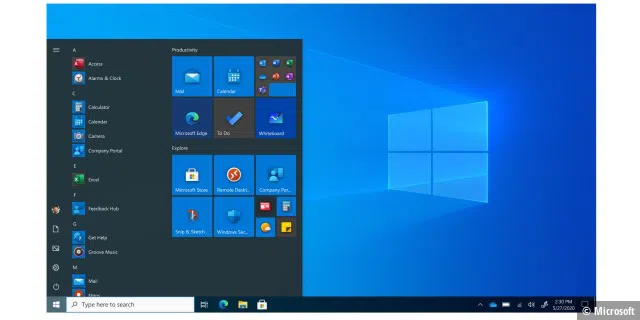
Windows 10: A new attempt at success
On July 29th, 2015, Microsoft released a new generation of its operating system: Windows 10. It offered a uniform software platform for all devices and took into account the specific characteristics of tablets, laptops, phones, and the Xbox through to the Internet of Things and the development of holograms. Developers now just needed to create one app for Windows 10—known as a Universal App—to use on all Windows devices, which could be made available via the Windows Store. Microsoft also released its digital assistant Cortana and the Edge browser, plus the Start menu was also back with Windows 10.
©Microsoft
Windows 10 was made available as a free upgrade for qualified Windows 7 and Windows 8.1 devices in 190 countries worldwide. Windows 10 users received the first major update automatically and free of charge on their PCs and tablets as part of Windows-as-a-Service. Microsoft followed this up with the Anniversary Update for Windows 10 in August 2016, which was followed by two further updates per year.
Major feature updates for Windows 10 were released regularly in spring and fall. The most notorious of these was the Fall Creators Update version 1809 from 2018, which turned into a tour of bankruptcies and mishaps, leading Microsoft to finally end the update.
Windows 11: How the story continues










