Science & Environment
Coinbase, a16z contribute $78 million to pro-crypto PAC for 2026 election

Stand With Crypto’s bus tour through five battleground states stopped in Las Vegas last week, where crypto advocates heard from the state treasurer and chief of staff for the lieutenant governor.
Logan Dobson/Stand With Crypto Alliance
With one day to go until the U.S. general election, crypto companies have already poured tens of millions of dollars into the upcoming 2026 cycle. The pro-crypto and bi-partisan super PAC Fairshake said Monday that the committee and its affiliates have raised $78 million for the 2026 midterm elections.
That $78 million includes more than $30 million raised, plus another $48 million in new commitments from centralized crypto exchange Coinbase and Silicon Valley venture fund Andreessen Horowitz, among other companies.
Early Monday, a16z general partner Chris Dixon, who heads up the fund’s crypto book, published a note explaining why the company contributed another $23 million to Fairshake.
“Regardless of what happens in the 2024 elections, we’re committed to supporting policymakers, irrespective of party affiliation, who will work to establish a practical regulatory framework that protects consumers while allowing the industry to grow,” the letter read.
Dixon added that “supporting a PAC like Fairshake is just one crucial part of the strategy needed to achieve our larger policy goals” and that a16z would continue to meet with policymakers on both sides of the aisle to advocate for the industry.
All in, a16z has given $70 million to Fairshake as the VC looks to support the PAC’s larger mission of building a Congress comprised of pro-crypto legislators.
On Wednesday, Coinbase announced it would give another $25 million to Fairshake.
Coinbase, the largest U.S. crypto exchange, was sued by the Securities and Exchange Commission over claims that it engaged in unregistered sales of securities. It’s among Fairshake’s top contributors this cycle. The exchange has given more than $75 million to Fairshake and its affiliated PACs.
“We know we need to have pro-crypto legislation passed in this country,” Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong said during the company’s third-quarter earnings call. Shares plummeted 15% after the company reported a miss on the top and bottom lines.
Ripple Labs is another major political donor this cycle that has given around $47 million to Fairshake. CNBC reached out for comment as to whether the company is donating to the 2026 midterm election but did not immediately hear back.

Fairshake told CNBC it’s raised around $170 million this cycle and disbursed approximately $135 million.
The majority of the group’s funds can be traced to Coinbase, Andreessen Horowitz, and Ripple Labs. The remaining balance comes from a mix of companies and individual donors. Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong, for example, gave $1 million, while the Winklevoss twins put in $5 million.
Fairshake was launched last year by a consortium of crypto firms and is one of the top-spending PACs in 2024, even against oil companies and banks, which have historically been big political contributors. Nearly half of all the corporate money flowing into the election has come from the crypto industry, according to a report from the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen.
Fairshake’s spending, which has targeted House and Senate races in the 2024 cycle, is effective. Public Citizen’s report found that of the 42 primary races that attracted money from crypto-backed super PACs, 36 were won by the candidate backed by the crypto industry.
Fairshake’s corporate and individual donors want crypto laws in the U.S.
Dixon and others say they’re looking for comprehensive market structure legislation for digital assets and a law to govern stablecoins, tokens pegged to the value of a real-world asset that are now virtually synonymous with U.S. dollar-pegged coins.
“Many industries come to DC asking to roll back rules, and we have come to DC asking to establish them,” Dixon wrote in his post on Monday.

Science & Environment
Silicon anodes are ahead of solid-state batteries in race to power EVs

A Wallbox EV charger for electric car is displayed during the “Mondial de l’Auto” at Parc des Expositions on October 15, 2024 in Paris, France.
Chesnot | Getty Images News | Getty Images
Silicon anodes appear to be leading the way in the race to commercialize next-generation battery technologies for electric vehicles.
The buzz around silicon-based anodes, which promise improved power and faster charging capabilities for EVs, has been growing in recent months — just as the hype around solid-state batteries seems to have fizzled.
It comes as increasing EV sales continue to drive up global battery demand, prompting auto giants to team up with major cell manufacturers on the road to full electrification.
While some OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) have inked deals with solid-state battery developers, carmakers such as Mercedes, Porsche and GM have all bet big on silicon anodes to deliver transformative change in the science behind EVs.
A recent report from consultancy IDTechEx described the promise of advanced silicon anode materials as “immense” for improving critical areas of battery performance, noting that this potential hadn’t gone unnoticed by carmakers and key players in the battery industry.
It warned, however, that challenges such as cycle life, shelf life and — perhaps most importantly — cost, need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
Venkat Srinivasan, director of the Collaborative Center for Energy Storage Science at the U.S. government’s Argonne National Laboratory in Chicago, said silicon anodes appear to have the edge over solid-state batteries.
“If there’s a horse race, silicon does seem to be ahead at least at this moment, but we haven’t commercialized either one of them,” Srinivasan told CNBC via videoconference.
Srinivasan said five years ago silicon-anode batteries had a calendar life of roughly one year, but recent data appears to show a dramatic improvement in the durability of these materials, with some tests now projecting a three to four-year calendar life.
Unlike the cycle life of a battery, which counts the number of times it can be charged and discharged, the calendar life measures degradation over time. Typically, the calendar life of a battery refers to the period in which it can function at over 80% of its initial capacity, regardless of its usage.
Srinivasan said solid-state batteries, long billed as the “holy grail” of sustainable driving, still have a long way to go before they can match the recent progress made by silicon anodes.
“That transition still has to be made in solid-state with their metal batteries and that’s why I think you’re hearing from people that, hey, it looks like that promise hasn’t panned out,” Srinivasan said.
“That doesn’t mean we won’t get there. It may happen in a few years. It just means that it feels like today silicon is in a different part of the technology readiness level.”
Silicon anodes vs. solid-state batteries
Analysts say silicon anodes theoretically offer 10 times the energy density as graphite, which are commonly used in battery anodes today. Yet, these same materials typically suffer from rapid degradation when lots of silicon is used.
“Silicon anodes and solid-state batteries are two emerging technology trends in the EV battery market aimed at pushing the boundaries of high-performance battery cells,” Rory McNulty, senior research analyst at Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, told CNBC via email.
A researcher checks the electromagnet de-ironing machine at the Daejoo Electronic Materials Co. R&D center in Siheung, South Korea, on Thursday, June 22, 2023.
Bloomberg | Bloomberg | Getty Images
It has typically been the case that better battery performance comes at the cost of longevity or safety, McNulty said. Silicon anodes, for example, are known to swell significantly during charging, which reduces the battery’s longevity.
By comparison, McNulty said solid-state batteries were claimed to greatly improve the stability of the electrolyte to high performance electrode materials, combating the challenges of using high energy density materials such as silicon and lithium.
As the name suggests, solid-state batteries contain a solid electrolyte, made from materials such as ceramics. That makes them different from conventional lithium-ion batteries, which contain liquid electrolyte.
Especially in the West, advances in the area of silicon anodes [are] seen as strategic opportunity to catch up with China.
Georgi Georgiev
Battery raw materials analyst at Fastmarkets
Japan’s Toyota and Nissan have both said they are aiming to bring solid-state batteries into mass production over the coming years, while China’s SAIC Motor Corp reportedly said in early September that its MG brand would equip cars with solid-state batteries within the next 12 months.
Nonetheless, analysts remain skeptical about when solid-state batteries will actually make it to market.
A strategic opportunity?
“Silicon based anodes promise to be the next-generation technology in the anode field, providing a solution for faster charging,” Georgi Georgiev, battery raw materials analyst at consultancy Fastmarkets, told CNBC via email.
Georgiev said several industry players have been looking into the potential of silicon anodes, from well-established anode suppliers in China and South Korea to new players like Taiwan’s ProLogium and U.S. manufacturers Group14 and Sila Nanotechnologies.
“Especially in the West, advances in the area of silicon anodes [are] seen as strategic opportunity to catch up with China, which dominates the graphite-based anode supply chains with Chinese anode producers holding 98% of the global anode market for batteries,” Georgiev said.
“However, there are significant technical challenges going to 100% silicon anode such as silicon expansion affecting the longevity of the batteries and currently there are several routes to produce silicon anodes,” he added.
A FEV x ProLogium Technology Co. 100% silicon composite anode next-generation battery at the Paris Motor Show in Paris, France, on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024.
Bloomberg | Bloomberg | Getty Images
Taiwanese battery maker ProLogium debuted the world’s first fully silicon anode battery at the Paris Motor Show last month, saying it’s new fast-charging battery system not only surpassed traditional lithium-ion batteries in performance and charging efficiency but also “critical industry challenges.”
ProLogium, citing test data, said it’s 100% silicon anode battery could charge from 5% to 60% in just 5 minutes, and reach 80% in 8.5 minutes. It described the advancement as an “unmatched achievement in the competitive EV market,” which will help to reduce charging times and extend the range of EVs.
Fastmarkets’ Georgiev said a big question mark over the commercialization of silicon anodes is the cost of production and whether any of the major silicon-anode producers “could produce material at scale with a consistent quality and at a competitive price — [a] major requirements of OEMs.”
“At this stage silicon anodes are used more as an additive to graphite-based anodes and in the years to come we expect to see increase of silicon share in anode, but in combination with graphite, while 100% silicon anodes will take longer time to enter the mass market,” he added.
Science & Environment
Oil giant Saudi Aramco posts 15% drop in third-quarter profit but maintains dividend
Saudi Aramco’s Ras Tanura oil refinery and oil terminal
Ahmed Jadallah | Reuters
Saudi state oil giant Aramco reported a 15.4% drop in net profit in the third-quarter on the back of “lower crude oil prices and weakening refining margins,” but maintained a 31.05 billion dividend.
This is a breaking news story. Please refresh for updates.
Science & Environment
Marqeta shares plunge more than 30% on big forecast miss

Marqeta celebrates its initial public offering at the Nasdaq on June 9, 2021.
Source: The Nasdaq
Marqeta shares tumbled more than 30% in extended trading on Monday after the company issued weaker-than-expected guidance for the fourth quarter.
Here’s how the company did compared with Wall Street estimates, based on a survey of analysts by LSEG:
- Loss per share: 6 cents, adjusted vs. 5 cents expected
- Revenue: $128 million vs. $128.1 million expected
While third-quarter results showed a slight disappointment on the top and bottom lines, Marqeta’s forecast for the current period was more concerning.
The payment processing firm said revenue in the fourth quarter will increase 10% to 12% from a year earlier. Analysts were looking for growth of over 17%, according to LSEG.
Marqeta, which primarily functions as a card-issuing platform, attributed the guidance miss to “heightened scrutiny of the banking environment and specific customer program changes.” The company has been struggling for a while, and its stock is now down more than 80% from its peak in 2021, the year it went public. The stock was down 15% for the year prior to the report.
Total processing volume of $74 billion was up more than 30% from a year earlier. Net revenue and gross profit were up 18% and 24%, respectively.
Marqeta’s digital commerce business sells payment technology designed to detect potential fraud and ensure that money is properly routed. It also issues customized physical cards that look like a credit or debit card that can be used for point-of-sale purchases.
The company has been trying to break into the buy-now, pay later business with a recently launched product called Marqeta Flex. The service brings BNPL from lenders like Affirm or Klarna to any credit card wherever Mastercard and Visa are accepted.
“It’s an orchestration layer, but it’s tied to issuing and processing and disputes and chargebacks,” CEO Simon Khalaf told CNBC at Money2020 in Las Vegas last week. “So it is not actually a Wild West in BNPL. It is actually very well established. And there is a reason why a lot of people are jumping to it.”
WATCH: Marqeta CEO on Q2 earnings

Science & Environment
Heat can flow backwards in a gas so thin its particles never touch
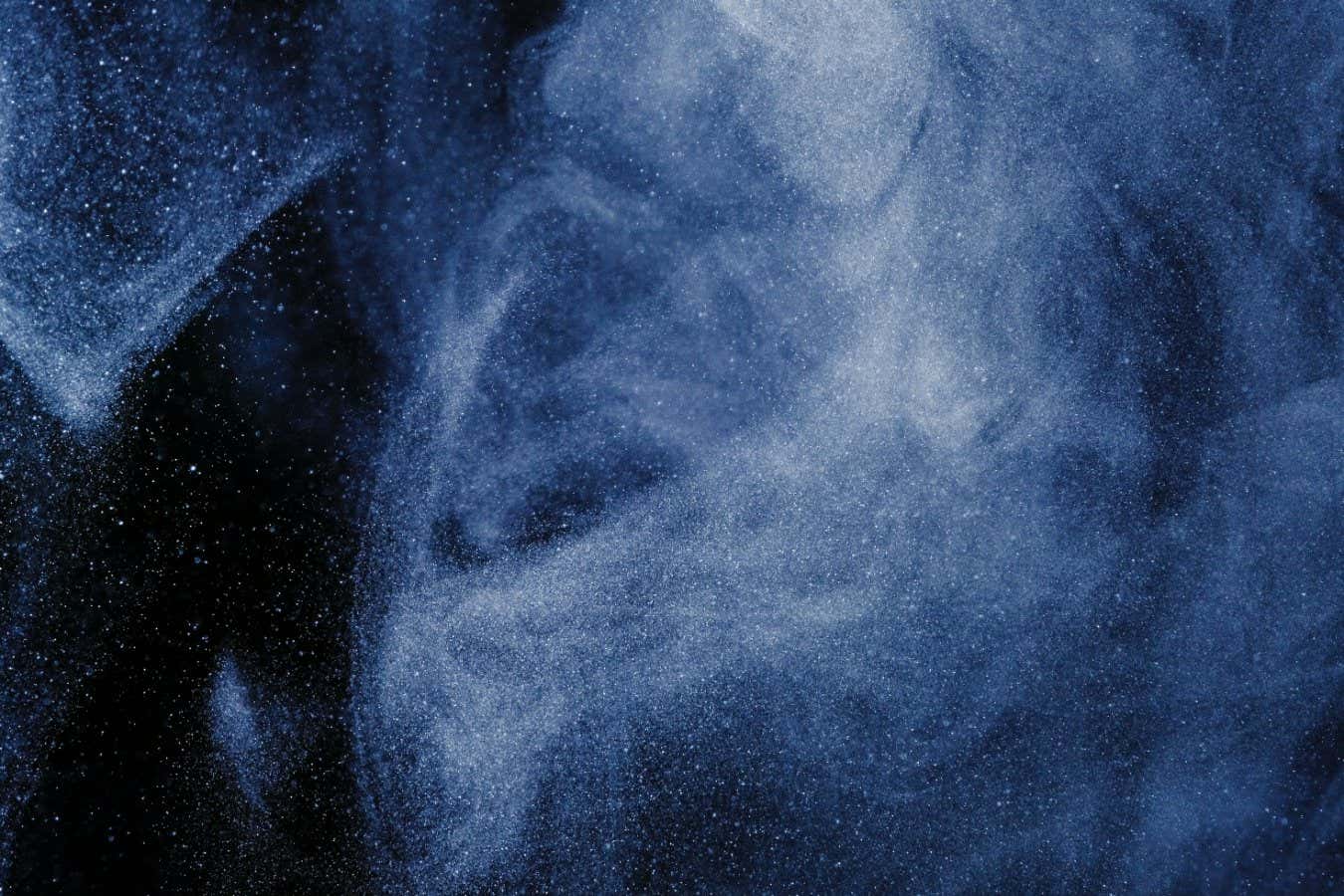

Diffuse gas particles can behave in a way that contradicts a fundemental law of physics
Shutterstock / North10
Heat always spontaneously flows from a hotter place to a colder one – so says the second law of thermodynamics. But within an extremely sparse gas, the opposite may be possible, with heat flowing from cold to hot. This finding could reveal cracks in a foundational law of physics.
“Given the second law [of thermodynamics] has been known for 150 years, you would imagine that if a counterexample exists, then…
Science & Environment
Tech partnerships with power companies for AI in doubt after FERC order
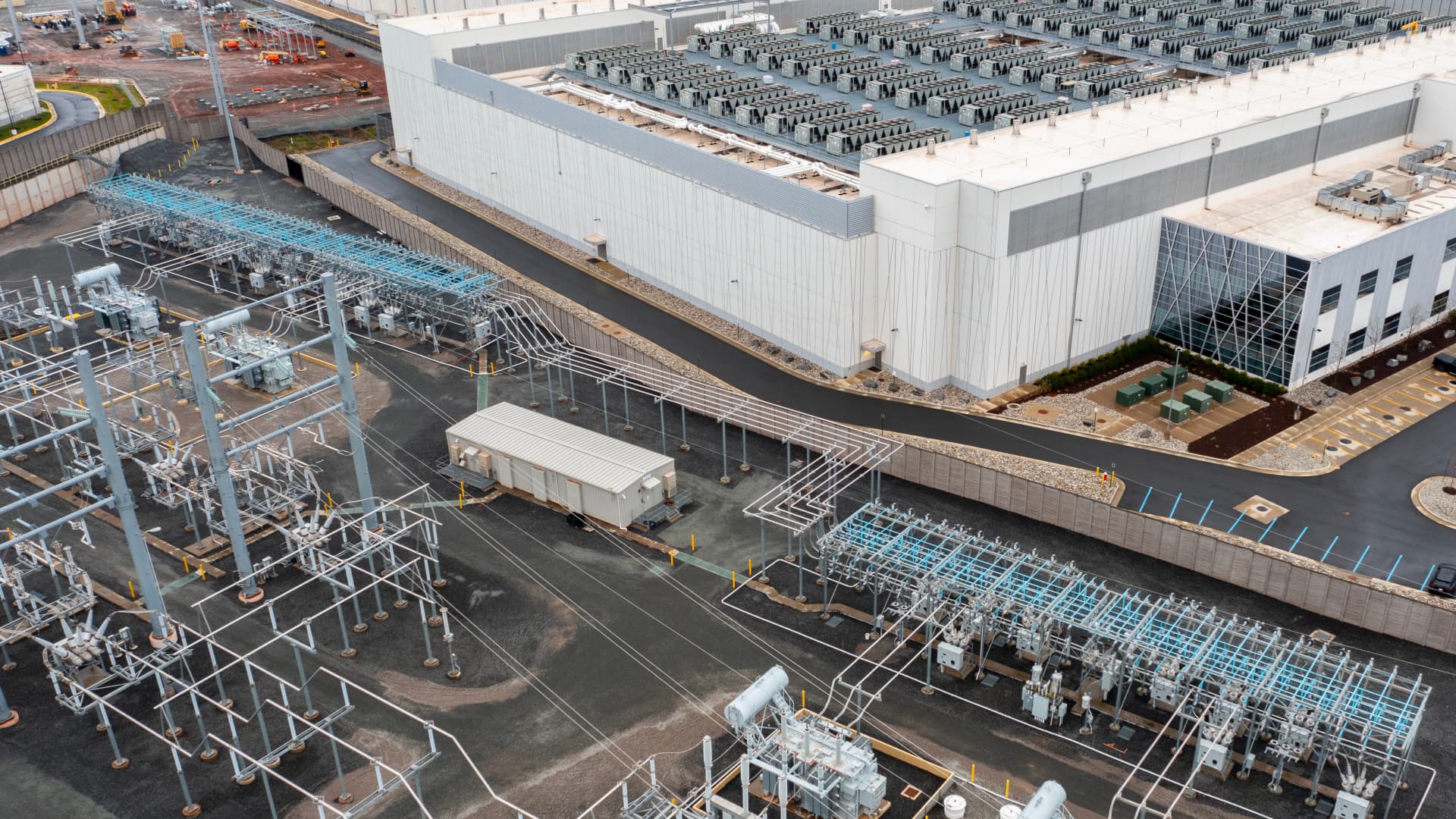

A power substation near the LC1 CloudHQ data center in Ashburn, Virginia, United States.
Nathan Howard | Bloomberg | Getty Images
Technology companies’ push to directly power artificial intelligence with nuclear plants hit a major roadblock, after a federal regulator rejected a request to increase power for an Amazon data center.
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission on Friday rejected a request to increase the amount of power the Susquehanna nuclear plant in Pennsylvania can dispatch to an Amazon data center campus.
Independent power producer Talen Energy in March sold the data center campus to Amazon for $650 million, which would be powered by the nuclear plant in a first-of-its-kind deal.
Talen’s stock fell more than 9% in premarket trading on FERC’s denial order. Constellation Energy and Vistra Corp. tumbled nearly 8% and more than 3%, respectively, in sympathy. Investors were expecting Constellation and Vistra to announce similar deals at some point.
The grid operator PJM Interconnection and the Susquehanna plant, which Talen owns, had filed a request to increase the amount of power dispatched to the Amazon data center from 300 megawatts currently to 480 megawatts.
The arrangement, called co-location by the power industry, “could have huge ramifications for both grid reliability and consumer costs,” said FERC Commissioner Mark Christie in his opinion backing the order.
Talen said FERC’s decision will have a “chilling effect on economic development in states such as Pennsylvania, Ohio, and New Jersey” in a statement Monday. The power company said it is evaluating its options with a “focus on commercial solutions.”
The Amazon data center campus can still use 300 megawatts of power from the Susquehanna nuclear plant, according to Talen. The company said the deal is “is just and reasonable and in the best interest of consumers.”
The FERC decision does not impact Constellation’s plans to restart the Three Mile Island nuclear plant in 2028 through a power purchase agreement with Microsoft. Three Mile Island will dispatch power to the electric grid, rather than directly power Microsoft’s data centers.
But Constellation and Vistra have expressed interest in striking deals with tech companies that are similar to the agreement between Talen and Amazon.
Data centers that power AI and cloud computing are consuming growing amounts of electricity. Utilities are scrambling to find ways to power the growing electric load. Tech companies are increasingly turning to nuclear power because it is reliable and does not emit carbon dioxide emissions.
Vistra and Constellation are two of the best performing stocks in the S&P500 this year, as investors bet on a potential windfall from the tech sector’s growing energy needs.
Vistra’s stock has more than tripled this year, outpacing even Nvidia to become the best performing stock in the market. Constellation has more than doubled and is the fourth best stock in the S&P500 this year.
Science & Environment
OPEC chief is bullish on oil demand despite extended production cuts


The head of oil producer alliance OPEC brushed off forecasts of dwindling crude demand in the coming year, saying there was too much pessimism in the market — despite the group extending production cuts just one day prior in an attempt to shore up prices amid subdued global consumption.
“Well, for OPEC, we have demand growth this year at 1.9 million barrels a day,” OPEC Secretary-General Haitham Al Ghais told CNBC’s Dan Murphy Monday at the Adipec energy conference in Abu Dhabi.
“Now some people might say this is on the high side, but other independent analysts, researchers in the market have it at similar levels,” he said. “Some have it at [what] we believe [are] very low levels. We’re still quite robust on demand.”
“I think there’s a bit too much doom and gloom and pessimism in terms of the demand outlook by some corners in the market, in terms of analysts and research, but we believe, still, our numbers are in line with many other independents,” Al Ghais said.

The Vienna-based oil producer group in mid-October downwardly revised its projections for oil demand growth in the near-term, forecasting growth of 1.93 million barrels a day this year and 1.64 million barrels a day in 2025. This compared to previous forecasts of 2.03 million and 1.74 million barrels a day, respectively.
While the outlook figure was trimmed, it’s still dramatically higher than that of the Paris-based International Energy Agency, which sees global oil demand increasing by roughly 900,000 barrels per day this year and close to 1 million barrels per day in 2025.
“We have lowered down our demand numbers, to be fair, in the last couple of months, by about 100,000 to 200,000 barrels a day,” Al Ghais said. “Nevertheless, we remain at 1.9 [million] and this is higher than the historical average, the pre-pandemic and even the post-pandemic recovery rate, which was around 1.2 million barrels per day.”
The forecasts come amid a slowing Chinese economy, which has significantly hit oil demand and abundant global supply. China is the world’s largest crude importer and the second-largest crude consumer, after the United States.
When asked about concerns over China’s economic trajectory, the OPEC chief replied: “We have China growing at 0.6 million barrels a day this year … I think the outliers who are looking at China growing at 0.1 [million barrels a day] or hardly any growth, are the outliers. We are not the outliers.”
He added that the group is “seeing some very positive numbers coming out of the U.S. economy” and that it sees “good signs in the petrochemical industry, aviation sector.”

Numerous economists expect China’s economic growth to remain relatively weak in 2025 despite recent stimulus measures implemented by Beijing. The measures announced in late September failed to elicit a strong reaction from markets, while slowed growth since the Covid-19 pandemic and increasing adoption of electric vehicles has slashed oil demand in the world’s second-largest economy.
The comments came just one day after OPEC+ member countries agreed to delay a planned December output increase by one month, causing U.S. crude futures to jump over 2%. West Texas Intermediate was up 2.24% to $71.73 per barrel and international benchmark Brent crude rose 2.17% to $75.27 by 12 p.m. in London.
“This is not the first time we delayed the increase, which is supposed to be phased in gradually … This is just a continuation of our policy of making sure that we’re very attentive to the market,” Al Ghais said, adding that there is more to be seen and deliberated before the next ministerial meeting on Dec. 1.
“This is nothing unusual that has not been, let’s say, part of the modus operandi of OPEC+ since our agreement has been in place,” he said.
OPEC+, which consists of OPEC member states and several producer countries outside the organization, has implemented a series of cuts and extensions of them since late 2022 amid rising supply around the world in an effort to shore up the market.
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoHow to unsnarl a tangle of threads, according to physics
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoIs sharing your smartphone PIN part of a healthy relationship?
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months ago‘Running of the bulls’ festival crowds move like charged particles
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoHyperelastic gel is one of the stretchiest materials known to science
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoWould-be reality TV contestants ‘not looking real’
-
 Science & Environment1 month ago
Science & Environment1 month agoX-rays reveal half-billion-year-old insect ancestor
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoMaxwell’s demon charges quantum batteries inside of a quantum computer
-

 Money1 month ago
Money1 month agoWetherspoons issues update on closures – see the full list of five still at risk and 26 gone for good
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoSunlight-trapping device can generate temperatures over 1000°C
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoPhysicists have worked out how to melt any material
-
 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoGmail gets redesigned summary cards with more data & features
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoAaron Ramsdale: Southampton goalkeeper left Arsenal for more game time
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoUkraine is using AI to manage the removal of Russian landmines
-

 Football1 month ago
Football1 month agoRangers & Celtic ready for first SWPL derby showdown
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoBoxing: World champion Nick Ball set for Liverpool homecoming against Ronny Rios
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoEpic Games CEO Tim Sweeney renews blast at ‘gatekeeper’ platform owners
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoWoman who died of cancer ‘was misdiagnosed on phone call with GP’
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month ago‘Dirt decision’: Conor McGregor, pros react to Jose Aldo’s razor-thin loss at UFC 307
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoLaser helps turn an electron into a coil of mass and charge
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoRussia is building ground-based kamikaze robots out of old hoverboards
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoQuantum ‘supersolid’ matter stirred using magnets
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoA new kind of experiment at the Large Hadron Collider could unravel quantum reality
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoLiquid crystals could improve quantum communication devices
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoDana White’s Contender Series 74 recap, analysis, winner grades
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month ago‘Blacks for Trump’ and Pennsylvania progressives play for undecided voters
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoSamsung Passkeys will work with Samsung’s smart home devices
-
Business1 month ago
how UniCredit built its Commerzbank stake
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoMicrosoft just dropped Drasi, and it could change how we handle big data
-

 MMA4 weeks ago
MMA4 weeks ago‘Uncrowned queen’ Kayla Harrison tastes blood, wants UFC title run
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoWhy this is a golden age for life to thrive across the universe
-
 News1 month ago
News1 month agoRwanda restricts funeral sizes following outbreak
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoCheck, Remote, and Gusto discuss the future of work at Disrupt 2024
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoNavigating the News Void: Opportunities for Revitalization
-

 TV1 month ago
TV1 month agoসারাদেশে দিনব্যাপী বৃষ্টির পূর্বাভাস; সমুদ্রবন্দরে ৩ নম্বর সংকেত | Weather Today | Jamuna TV
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoPereira vs. Rountree prediction: Champ chases legend status
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month ago2024 ICC Women’s T20 World Cup: Pakistan beat Sri Lanka
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoMassive blasts in Beirut after renewed Israeli air strikes
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoBruce Springsteen endorses Harris, calls Trump “most dangerous candidate for president in my lifetime”
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoWhy Machines Learn: A clever primer makes sense of what makes AI possible
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoCornell is about to deport a student over Palestine activism
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoWhen to tip and when not to tip
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoMicrophone made of atom-thick graphene could be used in smartphones
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoWater companies ‘failing to address customers’ concerns’
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoWXV1: Canada 21-8 Ireland – Hosts make it two wins from two
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoKayla Harrison gets involved in nasty war of words with Julianna Pena and Ketlen Vieira
-

 Football1 month ago
Football1 month ago'Rangers outclassed and outplayed as Hearts stop rot'
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoQuantum forces used to automatically assemble tiny device
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoITER: Is the world’s biggest fusion experiment dead after new delay to 2035?
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months ago▶️ Hamas in the West Bank: Rising Support and Deadly Attacks You Might Not Know About
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoNuclear fusion experiment overcomes two key operating hurdles
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoChina Open: Carlos Alcaraz recovers to beat Jannik Sinner in dramatic final
-

 Football1 month ago
Football1 month agoWhy does Prince William support Aston Villa?
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month ago▶ Hamas Spent $1B on Tunnels Instead of Investing in a Future for Gaza’s People
-
Business1 month ago
Top shale boss says US ‘unusually vulnerable’ to Middle East oil shock
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoMusk faces SEC questions over X takeover
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoSingleStore’s BryteFlow acquisition targets data integration
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoHull KR 10-8 Warrington Wolves – Robins reach first Super League Grand Final
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoPremiership Women’s Rugby: Exeter Chiefs boss unhappy with WXV clash
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoA slight curve helps rocks make the biggest splash
-

 Womens Workouts1 month ago
Womens Workouts1 month ago3 Day Full Body Women’s Dumbbell Only Workout
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoMeta has a major opportunity to win the AI hardware race
-
Business1 month ago
Bank of England warns of ‘future stress’ from hedge fund bets against US Treasuries
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoLG C4 OLED smart TVs hit record-low prices ahead of Prime Day
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month ago‘I was fighting on automatic pilot’ at UFC 306
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoShanghai Masters: Jannik Sinner and Carlos Alcaraz win openers
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoCoco Gauff stages superb comeback to reach China Open final
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoGerman Car Company Declares Bankruptcy – 200 Employees Lose Their Jobs
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoWales fall to second loss of WXV against Italy
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoUniversity examiners fail to spot ChatGPT answers in real-world test
-
Business1 month ago
DoJ accuses Donald Trump of ‘private criminal effort’ to overturn 2020 election
-
Business1 month ago
Sterling slides after Bailey says BoE could be ‘a bit more aggressive’ on rates
-

 TV1 month ago
TV1 month agoTV Patrol Express September 26, 2024
-

 Money4 weeks ago
Money4 weeks agoTiny clue on edge of £1 coin that makes it worth 2500 times its face value – do you have one lurking in your change?
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoSturm Graz: How Austrians ended Red Bull’s title dominance
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoPennington vs. Peña pick: Can ex-champ recapture title?
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoKetlen Vieira vs. Kayla Harrison pick, start time, odds: UFC 307
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoThe best shows on Max (formerly HBO Max) right now
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoIf you’ve ever considered smart glasses, this Amazon deal is for you
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoTime travel sci-fi novel is a rip-roaringly good thought experiment
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months ago▶️ Media Bias: How They Spin Attack on Hezbollah and Ignore the Reality
-
 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoNerve fibres in the brain could generate quantum entanglement
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoJ.B. Hunt and UP.Labs launch venture lab to build logistics startups
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoQuoroom acquires Investory to scale up its capital-raising platform for startups
-
Business1 month ago
The search for Japan’s ‘lost’ art
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoNew Zealand v England in WXV: Black Ferns not ‘invincible’ before game
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoMan City ask for Premier League season to be DELAYED as Pep Guardiola escalates fixture pile-up row
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoAmazon’s Ring just doubled the price of its alarm monitoring service for grandfathered customers
-
Travel1 month ago
World of Hyatt welcomes iconic lifestyle brand in latest partnership
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoTrump returns to Pennsylvania for rally at site of assassination attempt
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoThe FBI secretly created an Ethereum token to investigate crypto fraud
-

 Science & Environment2 months ago
Science & Environment2 months agoHow to wrap your mind around the real multiverse
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoStocks Tumble in Japan After Party’s Election of New Prime Minister
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoTexas is suing TikTok for allegedly violating its new child privacy law
-
 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoOpenAI secured more billions, but there’s still capital left for other startups
-
Business1 month ago
‘Let’s be more normal’ — and rival Tory strategies
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoFamily plans to honor hurricane victim using logs from fallen tree that killed him
-

 Money1 month ago
Money1 month agoPub selling Britain’s ‘CHEAPEST’ pints for just £2.60 – but you’ll have to follow super-strict rules to get in
-

 Sport1 month ago
Sport1 month agoURC: Munster 23-0 Ospreys – hosts enjoy second win of season
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoNew documentary explores actor Christopher Reeve’s life and legacy
-

 MMA1 month ago
MMA1 month agoHow to watch Salt Lake City title fights, lineup, odds, more
You must be logged in to post a comment Login