Crypto World
Opt-in privacy is failing crypto

Disclosure: The views and opinions expressed here belong solely to the author and do not represent the views and opinions of crypto.news’ editorial.
Privacy has been a recurring narrative in crypto for years. Just weeks after Bitcoin (BTC) launched, Hal Finney pointed out the problem in only his second tweet about it, but the concept didn’t gain wider traction until Monero (XMR) arrived in 2014. Since then, privacy has repeatedly re-emerged as a core promise of decentralised money, especially during moments of regulatory pressure or heightened concerns around financial surveillance.
Summary
- Opt-in privacy fractures networks: When users must “turn on” privacy, anonymity sets shrink and private transactions become more conspicuous — not less.
- Design, not demand, is the problem: Zcash’s advanced cryptography exists, yet most transactions remain transparent. Narrative momentum hasn’t translated into usage.
- Privacy must be the default to work: Like security, financial privacy only strengthens when everyone shares it — automatic, universal, and baked into the protocol.
Analysts are positive that crypto’s future will continue to be defined by the privacy narrative. Investor Balaji Srinivasan argued privacy will define the industry’s following eight years; meanwhile, a16z crypto said privacy will be the industry’s most important “moat” in 2026. Indeed, privacy coins have rallied at the end of 2025 and continue to fluctuate into the start of the new year. At their peak, the sector reached a combined market capitalisation surpassing $40 billion, before falling back to roughly $17 billion.
Zcash (ZEC) was a key driver of that resurgence, rising by more than 1,300% from late September 2025 to its all-time high and remaining up over 600% at current prices, briefly overtaking Monero by total market volume. Yet despite renewed interest and price momentum, actual privacy usage remains strikingly low. Zcash’s shielded pool continues to hold just above 30% of the circulating supply, while roughly two-thirds of transactions remain fully visible on-chain.
This disconnect exposes a deeper issue. If interest in privacy is rising, why are users not migrating into the very privacy layers designed for that purpose? The answer could just be structural: opt-in privacy is failing crypto.
Opt-in privacy was a design compromise
In 2013, the pseudonym Nicolas van Saberhagen published the CryptoNote v2 paper, which explicitly framed transaction privacy not as a “nice to have,” but as a core requirement of electronic cash. This paper argued that Bitcoin’s transparency made it pseudo-anonymous at best, and outlined two properties a truly private payment system should satisfy: untraceability and unlinkability. Andrey Sabelnikov, now co-founder of Zano, worked alongside Nicolas to bring this vision to life, implementing the protocol he had designed. From the start, CryptoNote made privacy the default, baked into every transaction rather than offered as an afterthought.
But as the industry evolved, many projects lost sight of this principle. Rather than pushing the boundaries of privacy-preserving technology, they took the path of least resistance, prioritizing compatibility, performance, and mainstream appeal over user protection. Privacy-preserving cryptography was still expensive and unfamiliar, so newer designs retreated to opt-in models.
This compromise had serious consequences. Privacy became a feature to be toggled on rather than a baseline guarantee. Users who chose the private option effectively marked themselves as having something to hide, while the default transparent experience left the majority exposed. This trade-off may have seemed pragmatic at the time, but it fundamentally betrayed the original vision that CryptoNote had established: that true electronic cash must protect user privacy by design and wasn’t something to bolt on later; it had to be designed into the core transaction model itself.
The biggest network carrying the original default-privacy philosophy is Monero. Launched in 2014, it adopted the CryptoNote protocol, preserving the principles that Nicolas and Andrey had already established. Instead of asking users to choose between public and private modes, the design assumes that financial transactions should be private by default, and that privacy improves when everyone shares the same protections.
Through this philosophy, privacy does not just become a feature, but a network effect. A privacy system is only as strong as the crowd it can hide in. When privacy is optional, the network fractures into transparent and private activity. The private pool becomes smaller, the anonymity set shrinks, and the privacy model weakens in practice, regardless of how sophisticated the cryptography may be.
The Zcash paradox
Zcash illustrates the central contradiction facing much of today’s privacy ecosystem. On paper, it offers some of the most advanced privacy technology in crypto, including zero-knowledge proofs that can fully shield transaction details. In practice, however, the majority of network activity remains transparent.
Despite renewed market interest and strong price performance, Zcash’s shielded pool continues to hold just above 30% of the circulating supply, while roughly two-thirds of transactions remain fully visible on-chain. The technology exists. The privacy guarantees are real. Yet most users do not use them.
This gap is not a failure of cryptography, nor a lack of demand for privacy. It is the predictable outcome of opt-in design. When privacy is presented as a separate mode, something users must consciously enable, it introduces friction, uncertainty, and behavioural drop-off. Many users default to transparent transactions simply because they are easier, faster, or more familiar. Others may be unaware of the distinction altogether.
The consequence is a fragmented network. Public and private transactions coexist, but they do not reinforce one another. Instead, the private pool remains small, limiting the size of the anonymity set and weakening privacy guarantees for those who do opt in. Ironically, using privacy in an opt-in system can make a user more conspicuous rather than less.
Privacy can only work when it is the default
Privacy is not a behaviour users reliably opt into. It functions as a collective property. The more participants who share the same privacy guarantees, the stronger those guarantees become. When privacy is optional, networks fracture into public and private activity, shrinking anonymity sets and weakening protection for those who do opt in. In practice, optional privacy often makes users more conspicuous, not less.
The repeated cycles of privacy coin interest show that demand is not the problem; design is. Systems that rely on users to actively choose privacy struggle to translate narrative momentum into real adoption. If privacy is to become crypto’s defining moat, it must be treated as foundational infrastructure, not a feature toggle. Financial privacy works best when it is automatic, universal, and secure by default.
Crypto World
Binance Claims ‘Full and Complete Legal Victory‘ in Alabama Court

A federal court in Alabama has granted a motion to dismiss a 2024 complaint filed against Binance, its separate US entity Binance.US and former Binance CEO Changpeng “CZ” Zhao over allegations that the cryptocurrency exchange facilitated transferring funds to terrorist groups.
In a Wednesday order, US District Court for the Middle District of Alabama Magistrate Judge Chad Bryan granted a motion filed by Zhao requesting that significant portions of the complaint be dismissed. The complaint, filed in February 2024, alleged that the three defendants “violated, and may be continuing to violate, the Anti-Terrorism Act” by facilitating the transfer of funds to Hamas.
While Bryan granted the motion to dismiss, he also ordered that the group of plaintiffs submit a second amended complaint no later than April 10 or potentially face “the prospect of a total or partial dismissal.”
“The underlying harm here is serious; the allegation that the defendants are implicated is serious; the potential liability the plaintiffs seek to impose is serious; and the weight upon the court is serious,” said Bryan. “The operative pleading thus must demonstrate a commensurate level of seriousness before the action will be permitted to proceed.”

In a Thursday statement following the ruling, Binance said it represented “full and complete legal victory.”
A judge in the US District Court for the Southern District of New York last week granted a dismissal for “lack of personal jurisdiction” in a similar case against the company. However, US District Judge Jeannette Vargas acknowledged that another court in the district had ruled that allegations of “widespread, intentional circumvention of anti-terror financing regulations” from Binance had been sufficient to survive a motion to dismiss in a different case.
“Sanctions compliance and terrorism financing are serious matters of law – they require evidence, legal rigour, and due process,” said Binance general counsel Eleanor Hughes. “Courts have now examined these claims on two separate occasions and found them to be without merit.”
Related: Binance says US Senate Iran probe is based on ‘defamatory’ reports
“While the Court has stayed discovery, this case is not closed,” said Judge Vargas in a Wednesday order regarding Binance’s New York case. “Moreover, this Court retains the inherent authority to determine if counsel and the parties are abiding by their preservation obligations.”
Binance under media, congressional scrutiny over Iran
Amid the US-Israel conflict with Iran, many media outlets reported that Binance fired employees who reported the company had facilitated more than $1 billion in crypto transactions to entities connected to the country, leading to a probe by the US Senate.
Binance has largely denied the claims and has filed a defamation lawsuit against the Wall Street Journal over its reporting of a Justice Department probe into Iran’s alleged use of the exchange to avoid sanctions.
Magazine: All 21 million Bitcoin is at risk from quantum computers
Crypto World
Lido launches stablecoin yield product to expand beyond ether


Lido, the largest liquid staking protocol on Ethereum, is expanding beyond ether (ETH) with the launch of a new product designed for stablecoin holders.
The project on Thursday introduced a revamped version of its yield product, Lido Earn, which now revolves around two vaults: EarnETH for ether-based assets and EarnUSD for stablecoins. The goal is to make it easier for users to earn returns on crypto without having to choose or manage strategies themselves.
In simple terms, a vault is a pooled investment tool where users deposit crypto and the platform automatically puts those funds to work across different strategies designed to generate yield.
The new EarnUSD vault marks Lido’s first product built specifically for dollar-pegged tokens. It accepts stablecoins USDC and USDT and automatically allocates deposits across a range of decentralized finance (DeFi) opportunities on Ethereum, such as lending markets and other yield-generating strategies. Users receive a token representing their share of the vault, with returns accumulating over time.
The EarnETH vault works similarly but for ether-related assets, including ETH, WETH and Lido’s stETH. Deposits are spread across several DeFi protocols, including Aave, Uniswap and Morpho, with the system shifting funds toward strategies that are performing better.
The stablecoin vault comes as dollar-pegged tokens have become a major part of activity in Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem. Roughly half of DeFi activity on the network now involves stablecoins, according to a press release shared with CoinDesk.
“Stablecoins are a fundamental part of DeFi, and until now we weren’t serving those users,” said Marin Tvrdić of the Lido Ecosystem Foundation, in the press release.
Read more: Lido Launches GG Vault for One-Click Access to DeFi Yields
Crypto World
Puffer Teams Up With Anchorage to Bring Ethereum Restaking to Institutions
With the restaking sector in a slump, the protocol is betting that institutional distribution can reignite growth.
Ethereum restaking protocol Puffer Finance has partnered with Anchorage Digital to provide institutional clients with access to pufETH, Puffer’s liquid restaking token, via Anchorage’s regulated custody platform.
The integration allows institutions to gain exposure to Ethereum staking and restaking yields while operating within compliant custody and security frameworks. For institutional players that have historically been cautious about engaging directly with DeFi protocols, the partnership offers a more familiar on-ramp into Ethereum-native yield products.
Puffer differentiates its restaking model by distributing validation across a decentralized set of operators rather than relying on a handful of large validator providers, which the protocol says reduces concentration risk. The protocol also touts slashing penalty protection and a buffer designed to absorb losses before they reach pufETH holders, a feature aimed at satisfying institutional risk models that demand clearly defined downside scenarios.
The collaboration comes at a difficult time for liquid restaking protocols. Apart from etherfi and Kelp, most liquid restaking protocols have struggled to retain users. As points-based incentive programs ended, capital rotated out and consolidated into the most established venues.
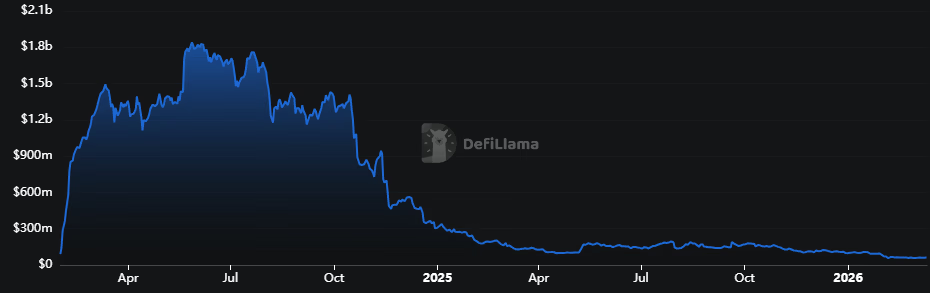
Puffer launched in February 2024, attracting nearly $200 million in total value locked (TVL) on its first day as the liquid restaking sector boomed on EigenLayer hype. By October 2024, Puffer’s TVL had grown to over 500,000 ETH, worth more than $1.3 billion at the time.

Today, Puffer’s core protocol TVL sits at just $62 million, according to DeFiLlama. The drawdown mirrors a broader trend across the liquid restaking sector following the initial airdrop-fueled frenzy.
The PUFFER token tells a similar story. The token hit an all-time high near $1.00 in December 2024 but has since cratered, hitting an all-time low of $0.025 just last week, according to Coingecko.

The Anchorage deal signals that Puffer is increasingly focused on the institutional market as a path to sustainable growth, a pivot away from the retail-driven points campaigns that initially powered its TVL.
Crypto World
UK banking bug gives customers the blockchain experience


Customers of a number of well-known UK banks were unexpectedly given the blockchain experience today after a banking app glitch meant their transactions and accounts became public.
The technical issue allowed customers from Lloyds, Halifax, and the Bank of Scotland to view the banking activity of other users.
Some could see charge notifications from other people’s accounts, while some reported that they could view other people’s National Insurance numbers.
The BBC reports that for 20 minutes, some could see other users’ accounts, while one person was able to view benefit payments from the Department of Work and Pensions.
Read more: UK gov’t committee calls for halt to crypto donations amid foreign interference fears
One user claimed, “I can see another person’s bank account, he got paid £6,000 yesterday. Others, I can see their benefits payments, their National Insurance numbers, I can see where they work, almost their whole identity.”
The issue has reportedly been fixed, and an investigation has been launched, but it’s unclear just how many people the glitch affected.
Lloyds apologized for the incident, while the Bank of Scotland said it may have been caused by a “technical glitch.”
Last year, the UK suffered a major banking outage that left thousands unable to access their accounts. A report from the Treasury Committee later found that the country had suffered a month’s worth of outages in two years.
Glitch is the closest UK banks have got to the blockchain
The hiccup briefly brought a taste of the blockchain to a UK banking industry that’s been famously slow to adopt the technology.
Indeed, many still categorize crypto as a risky, volatile asset that requires enhanced checks.
Digital crypto-friendly bank Revolut just secured a UK banking license after a four-year wait for a permit.
However, its crypto services will reportedly not be covered under this banking license and will still have to be offered through its Revolut X platform.
Last September, the UK and the US partnered to launch a regulatory body that would help align each country’s approach to crypto, and help firms access capital markets from each country with greater ease.
However, Reuters reports that both the US and UK are still split on crypto regulation, with the UK taking a more reserved approach.
The US was reportedly not impressed with the UK’s “sandbox” approach, where tokenised securities are tested in a controlled environment.
Got a tip? Send us an email securely via Protos Leaks. For more informed news and investigations, follow us on X, Bluesky, and Google News, or subscribe to our YouTube channel.
Crypto World
STRC could be funding more Strategy bitcoin buys than ever
![]()
A community-built dashboard that tracks Strategy’s STRC sales in real time suggests that today could produce the largest single-day STRC-funded bitcoin (BTC) purchase in history.
By 11am New York time, the unofficial tracking system estimated that 2.7 million shares of STRC had traded, all at or above its $100 par, also known as its “stated amount” or “quasi-peg.”
This morning’s trading range was $100-100.07.
Because Strategy has previously provided guidance that the company might sell STRC when the stock price is above its stated amount, it’s possible to estimate the number of STRC that Strategy is adding to the circulating supply.
By default, the dashboard speculates that 40% of that volume might involve Strategy itself as the seller. Overall STRC volume figures include both corporate as well as secondary sales and the site allows users to adjust that percentage via a user-configurable slider.
At its default 40%, the site’s model estimated that Strategy had sold over 1 million shares of STRC, funding the purchase of up to 1,500 BTC.
That was, of course, barely 90 minutes into the regular session.
Over 700,000 shares had already traded in pre-market, accumulating an estimated 394 BTC before the opening bell. By 1pm, total volume over $100 per share exceeded 4.6 million shares.
STRC pays a lavish, 11.5% annualized dividend and tries to hold a $100 quasi-peg. It competes with high yield junk bonds and other risky yield products with retail-focused advertisements focusing on its monthly dividends and disclaiming its many risks in fine print.
One user on X noted 1.2 million shares had traded within eight minutes of the open. Another marveled as it made 60% of the previous day’s record-breaking volume in just 90 minutes.
Probably another all-time record week for STRC
Today’s figure already dwarfs the best confirmed daily average from Strategy’s own SEC filing last week.
Specifically, Strategy’s March 9 SEC Form 8-K disclosed 17,994 BTC purchased between March 2 and 8, 2026. It was the company’s largest STRC at-the-market (ATM) sale in history.
The company funded those purchases through $377.1 million in STRC sales and $899.5 million in MSTR common stock sales.
Mathematically, STRC accounted for 29.5% of those combined proceeds, implying about 5,314 BTC funded by STRC across five trading days.
That works out to roughly 1,063 BTC per day. No further, daily granularity is available.
Therefore, by the best data available, a 40% volume capture estimate forecasts 1,500 BTC in STRC-funded purchases today, with five trading hours left.
It’s certainly possible that today is the largest ATM in STRC history.
Read more: Strategy is paying credit card rates to keep STRC at $100
The 40% capture estimate
Again, the dashboard assumes 40% of volume above $100 represents ATM issuance. It deducts a 2.5% broker commission and divides by the current BTC price. Strategy’s actual capture rate could differ on any given day.
The percentage could actually be as low as 0%, or in fact be the vast majority. The company usually discloses realized ATM figures weekly, which is the only formal, post-trading verification method.
Still, the 40% model has tracked reasonably close to confirmed data. Last week, the dashboard estimated 4,295 BTC for March 2-8. The actual filing was for 5,314 BTC.
That particular gap might have narrowed even more had it adjusted for Strategy’s recently-introduced, extended hours trading.
Indeed, the site now tracks pre-9:30am and post-4pm New York trades.
Strategy amended its STRC ATM agreement on March 9, assigning a second agent with the right to sell STRC before 9:30am and after 4:00pm.
The STRC-for-BTC machine
This week’s pace has been extraordinary. The dashboard estimates 1,863 BTC on Monday, 2,500 on Tuesday, 2,568 on Wednesday, and over 2,500 on Thursday by 1pm New York time.
The four-day running estimate sits above 9,500 BTC from STRC raises this week alone.
For context, Strategy sold zero STRC through its ATM from July through October last year. The entire $4.2 billion program sat untouched for months.
Now, over $1 billion has probably been issued through it. “The second century begins,” Michael Saylor posted on X after last week’s purchase.
There is, of course, a cost of tapping the ATM. Strategy has guided to pay monthly dividends on every share of STRC outstanding at a variable rate that is currently 11.5%.
Strategy has hiked that rate seven times since its 9% launch to encourage its share price to stay near the $100 par.
Tomorrow is the shareholder snapshot date for STRC’s monthly dividend, so its tight parity at $100 is unsurprising given the near-term ex-dividend date.
Got a tip? Send us an email securely via Protos Leaks. For more informed news, follow us on X, Bluesky, and Google News, or subscribe to our YouTube channel.
Crypto World
VeryAI Raises $10M to Build Palm-Scan Identity System on Solana
Startup VeryAI has raised $10 million in a seed funding round led by Polychain Capital to launch a palm-scan identity verification system designed to distinguish real users from AI-generated accounts.
The platform records identity attestations on Solana and aims to help crypto exchanges, fintech companies and online platforms address growing risks from bots, deepfakes and synthetic identities. The company said zero-knowledge proofs allow users to verify their status across platforms without revealing personal information.
The system captures palm images using a smartphone camera and converts them into encrypted biometric signatures used to confirm that a user is human without storing identifiable data.
According to the company, palm biometrics are highly distinctive and less publicly exposed than facial features commonly used in identity checks. The scans are converted into irreversible feature representations rather than stored images, preventing the original biometric data from being reconstructed.
“We’re entering a period where the internet can no longer assume that every account, message, or video is created by a real person,” Zach Meltzer, founder and CEO of VeryAI, told Cointelegraph. “AI is powerful, but it also breaks many of the trust assumptions that the internet was built on.”
He said crypto platforms are vulnerable to these risks, citing examples such as sybil attacks during onboarding, fake accounts farming token incentives and impersonation scams targeting users and project communities.
The goal isn’t just to prove that a human exists somewhere — it’s to help platforms verify that a real person is present and acting authentically.
The company is already working with organizations including MEXC, Colosseum, Clique and Talus, with other centralized exchanges and wallets preparing to integrate the palm verification system, Meltzer said.
Investors in the round included the Berggruen Institute and Anagram. Anatoly Yakovenko, co-founder of the Solana blockchain, also joined as an angel investor.
Related: Crypto ATM losses surge 33% in 2025 as AI superpowers scams: CertiK
AI-generated identities push demand for proof-of-human systems
As artificial intelligence continues to blur the line between human and automated activity on the internet, some developers say blockchain-based identity systems could help restore trust in digital interactions.
Chris Dixon, a general partner at Andreessen Horowitz and founder of the venture capital firm’s a16z crypto investment arm, last year warned that an “ocean of AI-powered deepfakes and bots” could erode trust across the internet and suggested blockchain systems could help address the problem through cryptographic verification of identity and digital content.
One company trying to address the problem is World, co-founded by Sam Altman, which uses biometric iris scans to generate a digital identity that allows users to prove they are human without revealing personal data. The system records proof of a user’s uniqueness on a blockchain network while the Orb device scans a person’s face and iris to verify identity, though the biometric approach has drawn criticism from privacy advocates.

As AI advances, interest in these systems appears to be growing. In January, the token linked to World (WLD) jumped about 40% after reports that OpenAI was exploring a bot-free social media platform that would require users to verify they are human before participating.
Some developers argue that identity verification must balance authentication with privacy protections. Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has advocated for models that allow users to prove specific attributes, such as uniqueness or eligibility, without revealing their full identity using technologies like zero-knowledge proofs.
Magazine: Fly’s mind ‘uploaded,’ human brain cell wetware plays Doom: AI Eye
Crypto World
a glimpse into the EU and US markets
In today’s newsletter, Ganna Vitko, president of the Toronto Chapter of Women in Crypto, takes us through accounting rules that are in place for crypto and digital assets and some of the challenges of dealing with these new assets.
Then, in Ask an Expert, Aaron Brogan of Brogan Law answers questions about token issuance and its tax implications.
The accounting and auditing challenges for crypto funds: a glimpse into the EU and US markets
The crypto market poses significant challenges for auditors and accountants in all jurisdictions. These are some of them.
What to Know:
- Since digital assets do not fit neatly into existing Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) frameworks, there’s a lot of uncertainty around their classification, valuation, and disclosure in both the EU and the U.S.
- While the EU is slowly moving toward better standardization through new regulations, the U.S. continues to rely on interpretive approaches.
- All of this leaves auditors, accountants, and fund managers to navigate higher inconsistency and risk.
The finance industry has undergone an extraordinary metamorphosis in the past decade. With digital assets becoming full-fledged parts of the financial ecosystem, every market player has had to adapt to new circumstances.
No one has had it more difficult than auditors and accountants. Specifically, conventional audit and accounting practices — based on the traditional financial instruments and reliable infrastructure — are not enough to contend with the ever-changing world of digital wallets and distributed ledgers.
Below, we’ll discuss some of the most prevalent challenges that auditors and accountants are facing, both in the U.S. and in the EU.
The core of the issues
At the heart of crypto accounting and auditing issues lies a fundamental mismatch: digital assets simply do not fit into long-established frameworks. For instance, under the U.S. GAAP and the IFRS, assets are grouped into clearly defined categories such as cash, securities, derivatives, or intangibles.
However, cryptocurrencies defy such straightforward classifications. Are they financial instruments? Intangible assets? Or should they be seen as inventory? Despite recent attempts, not many jurisdictions have managed to fully define them.
This lack of clarity has several negative effects, as it shapes how crypto holdings are validated, when impairments are recognized, and how gains and losses are actually recorded in financial statements.
Regulatory pressure and enforcement trends
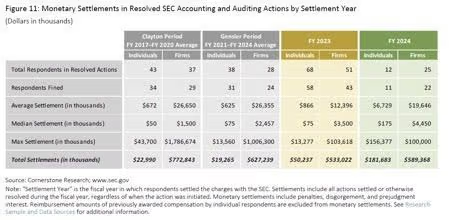
We have to note that this accounting and custody ambiguity is unfolding in an environment where regulatory scrutiny is at an all-time high. While not all SEC enforcement actions relate directly to crypto or audit failures, recent data on accounting and auditing enforcement offer a useful window into the compliance conditions that digital asset funds now operate in.

The data in the table above reveal a notable shift in enforcement dynamics. For one, it is clear that the number of respondents in accounting and auditing cases declined in fiscal year 2024. However, the average settlement amounts increased significantly, especially for individual respondents. This pattern points to a shift away from broad-based enforcement and a move toward fewer cases with higher financial stakes. That, in turn, increases the personal and professional risk for everyone involved.
On the other hand, Europe is moving along a markedly different path. As Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) enters phased implementation and supervisory coordination strengthens across all member states, the emphasis is slowly shifting to formalized compliance frameworks and standardized reporting obligations.
Thus, there is a contrast in regulatory mechanics between these jurisdictions. In the U.S., enforcement intensity ebbs and flows with policy direction and case selection. On the other hand, EU codification is advancing through structured legislative harmonization. Both of these dynamics shape the governance environment in distinct but consequential ways for crypto fund managers and their auditors alike.
Looking ahead: best practices and innovation
Amid regulatory and technical uncertainty in the EU and the U.S., market participants are doing their best to proactively adopt best practices. They include:
- Regular third-party attestation of reserves
- Independent valuation providers using multi-exchange pricing
- Enhanced internal controls over crypto operations
- Investment in audit technologies that leverage blockchain analytics.
Auditors and accountants themselves are expanding their skills and partnering with specialists, which is a big step in the right direction.
Conclusion
At the moment, accounting and auditing for crypto funds are at a crossroads. Issues such as fragmented regulation, volatile markets, and novel custody arrangements all strain legacy financial frameworks. In the EU, new regulations signal a move toward better harmonization, while the U.S. largely continues to rely on creativity and interpretive approaches.
For auditors and accountants alike, navigating these waters demands more technical knowledge and active engagement with all emerging guidance. In the end, matters will get better once more improved frameworks pop up. Only they can enhance transparency, reduce risk, and support sustainable growth in the crypto fund ecosystem.
– Ganna Vitko, president, Toronto Chapter of Women in Crypto
Ask an Expert
Q. My client is considering launching a meme coin. What should they take into account?
The SEC has provided guidance that it does not consider certain “meme coins” to be securities. If a client wishes to sell these tokens, they should be aware that the tax treatment of meme coin sales is not equivalent to an exempt securities offering. IRC § 1032 says that proceeds from stock are not taxable income, but this is a statutory creation with no crypto analogue. If your client sells meme coins, they may owe ordinary income tax.
Q. How might this change in the future?
There has been a push among crypto legal practitioners, such as Miles Jennings, to re-shore cryptocurrency projects. However, many projects prefer to make offerings offshore in part to attempt to avoid the tax burden of issuing in the United States. Tax is a live policy issue among crypto lobbyists in Washington, D.C., and a solution to the issuance conundrum could be the subject of future legislation.
– Aaron Brogan, managing attorney, Brogan Law
Keep Reading
Crypto World
Circle (CRCL) outpaces crypto stocks as stablecoin thesis gains momentum: William Blair


Circle (CRCL) has recently outperformed other crypto-linked equities, a move investment bank William Blair said reflects more than shifting macro conditions.
“It is tempting to ascribe recent strength to surging oil prices and perhaps a more hawkish Fed,” wrote analysts Andrew Jeffrey and Adib Choudhury in a Thursday note to clients.
“We think there is more at play, however, including USDC market cap resilience despite a crypto drawdown and growing appreciation of Circle’s economic model and stablecoin infrastructure leadership,” the analysts said.
The bank reiterated its outperform rating on the stock, arguing the rally, which has lifted shares roughly 126% from a February low, reflects improving sentiment toward stablecoin infrastructure rather than short-term market noise.
The shares were 1.2% higher at publication time, trading around $114.20.
Crypto-linked equities have broadly tracked, and often amplified, the recent downturn in digital assets, with shares of exchanges, miners and crypto-treasury companies falling as bitcoin retreated from its late-2025 highs.
Stocks such as Coinbase (COIN) and other crypto-exposed firms have typically moved in tandem with digital asset prices, reflecting the sector’s tight linkage to trading volumes and token valuations, and in some cases declining even more sharply than the underlying assets during market stress.
Japanese bank Mizuho said in a report last week that part of Circle’s rally may be tied to the recent surge in oil prices following escalating tensions in the Middle East. Higher crude prices could stoke renewed inflation concerns, the bank said, potentially dampening expectations for Federal Reserve interest rate cuts.
William Blair analysts said investors had previously been too bearish on Circle amid regulatory uncertainty and expectations for interest rate cuts. Now, the firm sees signs that the market is beginning to recognize the company’s core thesis: stablecoins could become a key layer of global payments infrastructure.
USDC could emerge as one of a handful of dominant standards in cross-border commerce, citing its liquidity, first-mover advantage and integration across crypto networks, according to the analysts.
The report also pointed to growing activity across Circle’s payments and infrastructure stack, including its stablecoin payments network, as evidence that the market for stablecoin-based settlement is beginning to take shape.
While other companies and tech platforms have floated launching their own stablecoins, the report said Circle’s minting, cross-chain transfer and payment orchestration infrastructure could provide a durable competitive moat as the sector develops.
Read more: How the war in Iran and trader positioning could be behind the surge in Circle’s stock
Crypto World
Vitalik Buterin says Ethereum’s key use case is a ‘public bulletin board,’ not just smart contracts


Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin says the crypto industry may be overcomplicating what blockchains are actually good for.
In a post on X after attending the Real World Crypto conference — which focuses on cryptography research — Buterin said stepping outside the typical blockchain bubble helped him rethink Ethereum’s core role.
Instead of starting with Ethereum and trying to find places to use it, he suggested developers should first ask what kinds of tools are needed to build secure, open and censorship-resistant technology.
From that perspective, Ethereum’s most important function may be surprisingly simple: acting as what cryptographers call a “public bulletin board.”
Many secure digital systems need a place where information can be publicly posted and verified. That could include things like secure voting systems, lists of revoked digital certificates or records used in cryptographic protocols. These systems don’t necessarily need complicated smart contracts or financial transactions, but instead a shared place where data can be reliably stored and accessed.
Ethereum can serve that role because it provides a decentralized network where anyone can publish data and anyone can read it.
Buterin said recent upgrades to Ethereum are making this type of use even more practical. One upgrade, known as PeerDAS, increases how much data the network can store and share, with plans to scale capacity much further in the future.
While these systems don’t always require payments, some kind of economic cost is often needed to prevent spam in open networks. That’s where Ethereum’s native token, ether (ETH), comes in.
Payments can help protect decentralized services from abuse. Buterin gives as an example if a messaging app allowed anyone to create unlimited accounts for free, attackers could flood the system with spam. Requiring small payments in ETH can make that kind of attack expensive while still keeping the system open to anyone.
Buterin also noted that Ethereum can help power new types of payment systems. Technologies like zero-knowledge payment channels could allow people to pay small amounts for services while keeping transactions private.
Smart contracts still play an important role as well, particularly for holding security deposits or enabling automated agreements between users.
Taken together, Buterin described Ethereum as a kind of “global shared memory” — infrastructure that allows many different applications to store data, exchange value and coordinate with each other.
“Ethereum has a lot of value, that you can see from first principles if you take a step back and see it purely as a technical tool: global shared memory,” he wrote.
Read more: Vitalik Buterin pushes ‘DVT-Lite’ to make Ethereum validator setup easier
Crypto World
Prediction markets get tailored U.S. guidance from former foe CFTC


Prediction market firms such as Polymarket and Kalshi have a new set of guidelines for U.S. operation, with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission laying out initial guidance and a proposed permanent rule Thursday for what the agency called “a proven source of reliable information for news media, sports leagues, financial institutions, and everyday Americans.”
The agency had once been a legal adversary of the prediction markets, warning that certain betting ran afoul of derivatives laws and that the CFTC couldn’t function as a global policy force combating fraud and manipulation in political markets all over the world. But under Chairman Mike Selig, the CFTC abandoned its old legal fight and embraced the firms. It’s now issued a non-binding staff advisory to the prediction market firms regulated by the CFTC as “designated contract markets,” and started a binding rule process.
“This begins the process of new rulemaking grounded in a rational and coherent interpretation of the Commodity Exchange Act, while reassuring the American people that the CFTC will exercise its exclusive jurisdiction over prediction markets,” Selig said of the regulatory process which is starting with what’s known as an “advanced notice of proposed rulemaking.”
Selig, who can operate as the sole authority at the regulator because he’s the only member of what’s meant to be a five-person commission, quickly moved to push the new policy effort. He’s also been waging a rhetorical campaign against state regulators who claim authority over sports betting, saying his agency is the primary regulator of that space. Numerous states sued prediction market providers alleging they’re also subject to their jurisdiction, at least for sports-related bets, and Selig filed a recent court brief arguing the CFTC holds sole jurisdiction.
The CFTC’s new advisory lays out how DCMs — a list that includes Kalshi, Coinbase and Polymarket — should get trading products cleared with the regulator and it says the firms should only handle “trading contracts that are not readily susceptible to manipulation.”
It also noted that the firms that are listing sports contracts should engage in “communications with such relevant sports governing bodies or authorities when developing terms and conditions, compliance and market oversight programs for sports-related events contracts.”
The agency’s rulemaking initiative, though, is much more complex and will likely take months to put into place. At this stage, the CFTC is seeking public comments about how it should proceed. The next step will be a more fleshed-out proposal, and then a final rule, each a lengthy process under administrative law.
The agency has put a 45-day deadline on comments, which is relatively fast, suggesting a speedy timeline.
The prediction markets are platforms in which users can buy and sell contracts that bet on a typically binary outcome, such as the winner of a sporting contest or the victor in an election. Selig has argued that the process belongs in the hands of the derivatives watchdog in the same way that futures contracts do.
The initial rulemaking document underlines that firms engaging in this business have a legal responsibility to police their activity for market manipulation, as evidenced recently by Kalshi’s announcement it had punished a couple of its customers.
The rulemaking text noted “the number of applications for DCM registration has more than doubled over the past year, largely from entities that are interested primarily, or exclusively, in operating prediction markets.” At this stage, the 32-page document poses a series of questions to help outline what direction the more concrete proposal should take.
Read More: Senate Democrats push prediction market limits, including banning bets on war, death
-
Business6 days ago
Form 8K Entergy Mississippi LLC For: 6 March
-

 News Videos3 days ago
News Videos3 days ago10th Algebra | Financial Planning | Question Bank Solution | Board Exam 2026
-

 Fashion6 days ago
Fashion6 days agoWeekend Open Thread: Ann Taylor
-

 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoParadigm, a16z, Winklevoss Capital, Balaji Srinivasan among investors in ZODL
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoA 1,300-Pound NASA Spacecraft To Re-Enter Earth’s Atmosphere
-
 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoChatGPT will now generate interactive visuals to help you with math and science concepts
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoTop Mamdani aide takes progressive project to the UK
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoExxonMobil seeks to move corporate registration from New Jersey to Texas
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoThree share 2-shot lead entering final round in Hong Kong
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoBraveheart Lakshya downs Lai in epic battle to enter All England Open final | Other Sports News
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoResidents reaction as Shildon murder probe enters second day
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoHailey Bieber Poses For Sexy Selfies In New Luscious Lip Thirst Traps
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoSearch for Nancy Guthrie Enters 37th Day as FBI Probes Wi-Fi Jammer Theory
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoSearch Enters Sixth Week With New Leads in Tucson Abduction Case
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoPagazzi Lighting enters administration as 70 jobs lost and 11 stores close across Scotland
-

 Tech3 days ago
Tech3 days agoDespite challenges, Ireland sixth in EU for board gender diversity
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoSearch Enters 39th Day with FBI Tip Line Developments and No Major Breakthroughs
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoI Entered The Manosphere. Nothing Could Prepare Me For What I Found.
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoIran war enters second week as Trump demands ’unconditional surrender’
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoSkateboarding World Championships: Britain’s Sky Brown wins park gold











