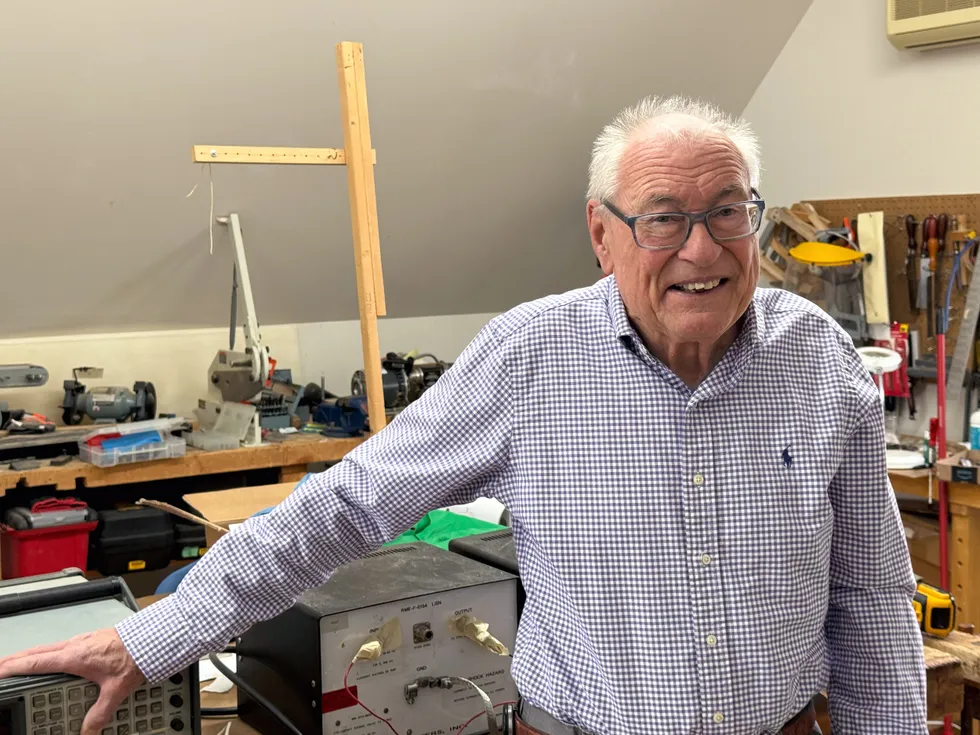
No one had very high career aspirations for teenager David A. Weston—except for Weston himself. Growing up in London, he scored low on the U.K. national assessment test given to students finishing primary school. The result meant that his next path was either to become a laborer or attend a vocational school to learn a trade.
What Weston really wanted to do was to work as a radio and TV repairman. He was fascinated by how the devices worked. He had taught himself to build an AM radio when he was 15. Even after showing it to his parents and teachers, though, they still didn’t think he was smart enough to pursue his chosen career, he says.
David A. Weston
Employer
EMC Consulting, in in Arnprior, Ont., Canada
Job title
Retired consultant
Member grade
Life member
Alma mater
Croydon Technical College, London
So, later that year, the underweight teen got a job on a construction site carrying heavy loads of building materials in a hod, a three-sided wooden trough. The experience convinced him he wasn’t cut out for manual labor.
He eventually earned a certificate in radio and television, the only credential he holds. The lack of academic degrees did not hold him back, though. He went on to become an expert in electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
An EMI field has unwanted energy that causes interference. EMC is the capacity for electronic devices to work correctly in a shared electromagnetic environment without causing interference or suffering from it in nearby devices or signals.
After working for a number of companies, he launched his own business more than 40 years ago: EMC Consulting, in Arnprior, Ont., Canada. The company has helped clients meet EMI and EMC regulatory requirements.
Now 83 years old and retired, the IEEE life member recently self-published his memoir, From a Hod to an Odd EM Wave.
“My memoir is about engineering persistence and human and technical discoveries,” he says. “I wanted to interest a young person, or perhaps a person later in life, in a career in engineering. If I can show that engineering is a personal, human endeavor with exciting opportunities in different fields such as medical, scientific, and the arts, maybe more women would be attracted to it.”
From repairing radios to designing underwater devices
In 1960 Weston enrolled in the radio and electronics program at London’s Croydon Technical College (now Croydon College). The school covered topics from the City and Guilds of London Institute’s radio and television certificate program. He attended classes one day a week for five years while working to put himself through school.
Although his parents and his teachers might not have recognized Weston’s potential, employers did.
He got his first job in 1960, fixing televisions in a small repair shop. Then he helped repair tape recorders. In his spare time, he studied transistors and semiconductors.
Everything he knows, he says, he learned by reading books and research papers, and from on-the-job training.
Later in 1960, he worked as a mechanical examiner for the U.K. Ministry of Aviation, where he calibrated precision meters and potentiometers, which are variable resistors that monitor, control, and measure industrial equipment.
“Engineering is creative. To have a new idea or design accepted is rewarding, satisfying, pleasurable, and even exciting.”
He left the ministry in 1963 because he found the work boring, he says, and he was hired as a technician with the Medical Research Council’s neuropsychiatric research unit in Carshalton. The institution researches the biological causes of mental illness. His manager was interested in learning about advances in medical electronics and eagerly shared his knowledge with Weston.
One of Weston’s tasks was to build an electroencephalography (EEG) calibrator to measure responses from a patient’s brain activity. The methods used at the time to detect a brain tumor—before MRI machines were developed—involved monitoring the patient’s speech and coordination, followed by taking a biopsy, which was not without danger, he says.
He used an ultrasonic transmitter and receiver to measure the time of transmission to the midline in the brain to determine whether the person had a tumor. If the midline had shifted, it would indicate the presence of a tumor, and a biopsy would be performed to confirm it. The measure of the evoked response in the brain was the only reliable indicator.
Weston earned his radio and TV certificate in 1965, leaving the research facility a year later to join Divcon (now part of Oceaneering International), a commercial diving company based in London that developed deep-sea helium diving helmets. Weston helped design a waterproof handheld communication device for divers that could withstand the high pressure in diving bells, the open-bottom pressurized chambers that transported them underwater.
Weston then moved to Hamburg, Germany, in 1969 to work for Plath, an electronics manufacturer. He was tasked, along with other engineers from England, to design a servo control loop.
“Unfortunately it oscillated so badly when first being turned on that it shook itself to bits,” he says.
He left to work as a senior engineer at Dr. Staiger Mohilo and Co. (now part of Kistler), in Schorndorf, Germany. It manufactured torque sensors, force transducers, and specialized test stand systems. Weston designed a process control computer. He says his boss told him that the controller had to work in close proximity to—and from the same power source as—a nearby machine without interfering with it or being interfered by it.
“I was thus introduced to the idea of electromagnetic compatibility,” he says.
After three years, he left to join the Siemens Mobility train group in Braunschweig, Germany, where he helped develop an electronic train-crossing light controller. The original warning lights on crossing gates used a mercury tube as a switch.
“The concern was the danger to personnel if the tube broke,” he says. “The simple and inexpensive solution was to put the tube in a metal container.”
Weston and his wife decided to leave Germany for Canada in 1975, after their young son began forgetting how to speak English.
His first job in the country was as an engineer for Canadian Aviation Electronics in Montreal. CAE helped design the remote manipulator system in robotic hand controllers and simulation systems used to train astronauts for the space shuttle.
The robotic arm, known as Canadarm, was used to deploy, maneuver, and capture payloads for the astronauts. Weston’s engineering team designed the display and control panel as well as the hand controllers located in the shuttle’s flight deck.
“I was attracted to the EMC aspects of the project and avidly studied everything I could on the topic,” he says.
He also helped develop a system that would protect an aircraft’s deployable black box from lightning strikes.
“I used a computer program to analyze the EMI field at close proximity to the black box to predict the lightning current flowing into the aircraft structure,” he says.
While enjoying the warm winter weather during a 1975 visit to a supplier on Long Island, N.Y., he decided he wanted to move his family there and asked whether any companies in the area were hiring. He was told that Brookhaven National Laboratory, in Upton, was, so he applied for a position working on the ring system for the Isabelle proton colliding-beam particle accelerator.
The project, later known as the colliding beam accelerator, was a collaboration between the lab and the U.S. Department of Energy. The 200+200 giga-electron volt proton-proton collider was designed to use advanced superconducting magnets cooled by a massive helium refrigeration system to produce high-energy collisions. The GeV refers to the collision energy in a particle accelerator.
The lab hired him in 1978, and the family moved to Long Island. After a few weeks of meeting with different departments, his boss asked him what kind of work he wanted to do. Weston told him about his idea for designing a device to detect a helium leak, should there ever be one. His machine would cover the entire 3,834-meter circumference area of the ring.
“The danger with increased helium-enriched air is that the oxygen level reduces until the person breathing becomes adversely affected,” he wrote in his memoir. “I found that the speed of the sound of helium increased enough to be detected, but not sufficient enough to cause a person trouble if they were in the tunnel.
“Brookhaven was considering machines that only covered a small area of the ring, but these would be unrealistic because too many machines would be needed, and the cost would have been astronomical.”
Weston’s system included an ultrasonic transmitter, a receiver, a power amplifier, and a preamplifier. It would sound an alarm if the helium content went above a certain level. People in the tunnel would be directed to go to the nearest oxygen-breathing equipment, put on a mask, and immediately evacuate. It was successfully tested.
Weston wrote a report detailing the ultrasonic helium leak detector, but shortly after, he and his wife had to return to Canada in 1978 because they were unable to get additional work permits in the United States.
When he returned to Brookhaven for a visit, his former boss told him the report was well-received. And he shared some news that upset Weston.
“My boss told me he took my report, changed the name on the report to his, did not mention me, and published the report as his,” Weston wrote in his memoir.
But the system was never built. The Isabelle project was canceled in July 1983 due to technical problems with fabricating the superconducting magnets.
Weston got a job working for CAL Corp., an aerospace telecommunications company in Montreal. For the next 14 years, he fixed EMI problems for the company’s products, including its charge-coupled device-based space-qualified cameras, which were designed to be carried aboard a satellite.
In 1992 he realized that nearly all his work involved consulting for the company’s customers, so he decided to start his own agency. CAL generously let him take the clients he worked with, he says.
Weston then conducted EMI analysis and testing and designed EMC systems for companies around the world.
“I always had enough customers and have never had to look for work,” he says. “For me, having my own business was more secure than working for a company.”
He retired in 2022.
IEEE as an educator
To broaden his education, he joined IEEE in 1976 to get access to its research papers and attend its conferences, he says. He is a member of the IEEE Electromagnetic Compatibility Society.
Because he is self-educated, he was “keen to learn as much as possible by reading practical papers published by IEEE,” he says. “I met people at IEEE symposiums and listened to the authors presenting their papers.”
Those included EMC experts such as Life Fellows Lothar O. “Bud” Hoeft, Richard J. Mohr, and Clayton R. Paul, whose papers are published in the IEEE Xplore Digital Library. Several of Weston’s papers are in the library as well.
His book Electromagnetic Compatibility: Methods, Analysis, Circuits, and Measurement references many IEEE papers on data and analysis methods.
“Engineering is creative,” he says. “To have a new idea or design accepted is rewarding, satisfying, pleasurable, and even exciting.”
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web