Tech
How to Automate AWS Incident Investigation with Tines and AI


Cloud infrastructure is messy. When an alert fires “EC2 instance unresponsive” or “High CPU utilization”, the initial triage often feels like an archaeological dig. Analysts have to leave their ticketing system, authenticate into the AWS console (cue the MFA prompts), hunt for the specific resource ID, and remember the correct CLI syntax to get the ground truth.
This context-switching tax is heavy. It extends Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and burns out analysts who spend more time gathering data than fixing problems.
This article explores a pre-built Tines workflow—Investigate AWS issues with CLI data using agents—that eliminates this manual data gathering by bringing the CLI directly to the case.
The problem: The “context gap” in incident response
In many organizations, there is a disconnect between where work is tracked (Jira, ServiceNow) and where the data lives (AWS, Azure, internal logs).
A “simple” investigation often involves:
- Access Friction: Logging into multiple consoles and assuming roles.
- Syntax Struggles: Wasting cycles figuring out the correct CLI syntax and flags to look up information, rather than simply retrieving the answer.
- Security Risks: Giving analysts broad read-access to production environments just to check a status.
Manual processes like these are the enemy of scale. As noted in a recent Tines case study, for a major crowdfunding platform, moving from manual spreadsheets to orchestration reduced unpatched vulnerabilities by 83% in just 90 days.
The lesson? “Focus on security work rather than the mundane tasks behind it.”
Learn how modern IT Ops teams use orchestration to manage capacity, improve reliability, and scale infrastructure without burnout.
This practical guide shows how to replace manual workflows with predictable, automated operations using the tools you already have.
The solution: automated CLI execution via agents
The Investigate AWS issues with CLI data workflow bridges the gap between your ticket and your cloud environment. It uses Tines agents—secure, lightweight runners that can send commands to AWS using secure credentials—to execute CLI commands safely within an intelligent workflow and return the results to the analyst.
Instead of the analyst going to the CLI, the CLI comes to the analyst.
Here is an overview of how the workflow operates:
1. The trigger – The workflow initiates when a new case or ticket is created regarding an AWS resource. This could be triggered automatically by a CloudWatch alarm or manually by an analyst noticing an anomaly.
2. The Agent intermediary – Tines doesn’t need direct, over-privileged access to your cloud. Instead, it instructs a Tines agent running with specified read-only access to AWS. This ensures your cloud credentials stay local and secure.
3. Dynamic command generation – The workflow doesn’t rely on rigid, pre-defined scripts. Instead, the “magic” lies in the agent’s ability to construct the necessary CLI command from scratch based on the context of the ticket. Whether you need to inspect an S3 bucket policy or check an EC2 instance’s security group, the agent intelligently forms the correct syntax and executes it, providing a level of flexibility that static automation can’t match.
4. AI formatting & enrichment – Raw CLI output (often dense JSON) is difficult for humans to parse quickly. The workflow uses Tines’ transformation capabilities (or an optional AI step) to parse this data into a clean, readable summary or table.
5. Case update – The formatted findings are appended directly to the Tines Case or your ITSM tool. The analyst opens the ticket and immediately sees the current state, security groups, and public IPs of the instance—no login required.
The benefits
Implementing this workflow drives efficiency across the entire incident lifecycle:
- Zero-touch context: Analysts start their investigation with the data already in front of them. There is no “gathering phase,” only a “solving phase.”
- Secure access: You don’t need to grant every junior analyst read access to the AWS console. The Tines agent handles the privilege, acting as a secure proxy for specific, approved commands.
- Standardized documentation: Every investigation has the exact same data snapshot attached. This creates a perfect audit trail, which Tines Cases captures automatically.
- Collaborative resolution: By pulling data into Tines Cases, teams can comment, tag, and collaborate in real-time on the “new or unknown,” preventing the siloed communication that happens when data is stuck in a terminal window.
How to build it
This workflow is available as a template to jumpstart your intelligent workflow journey.
Step 1: Import the story Visit the Tines Library and search for Investigate AWS issues with CLI data using agents. Click “Import” to add it to your tenant.
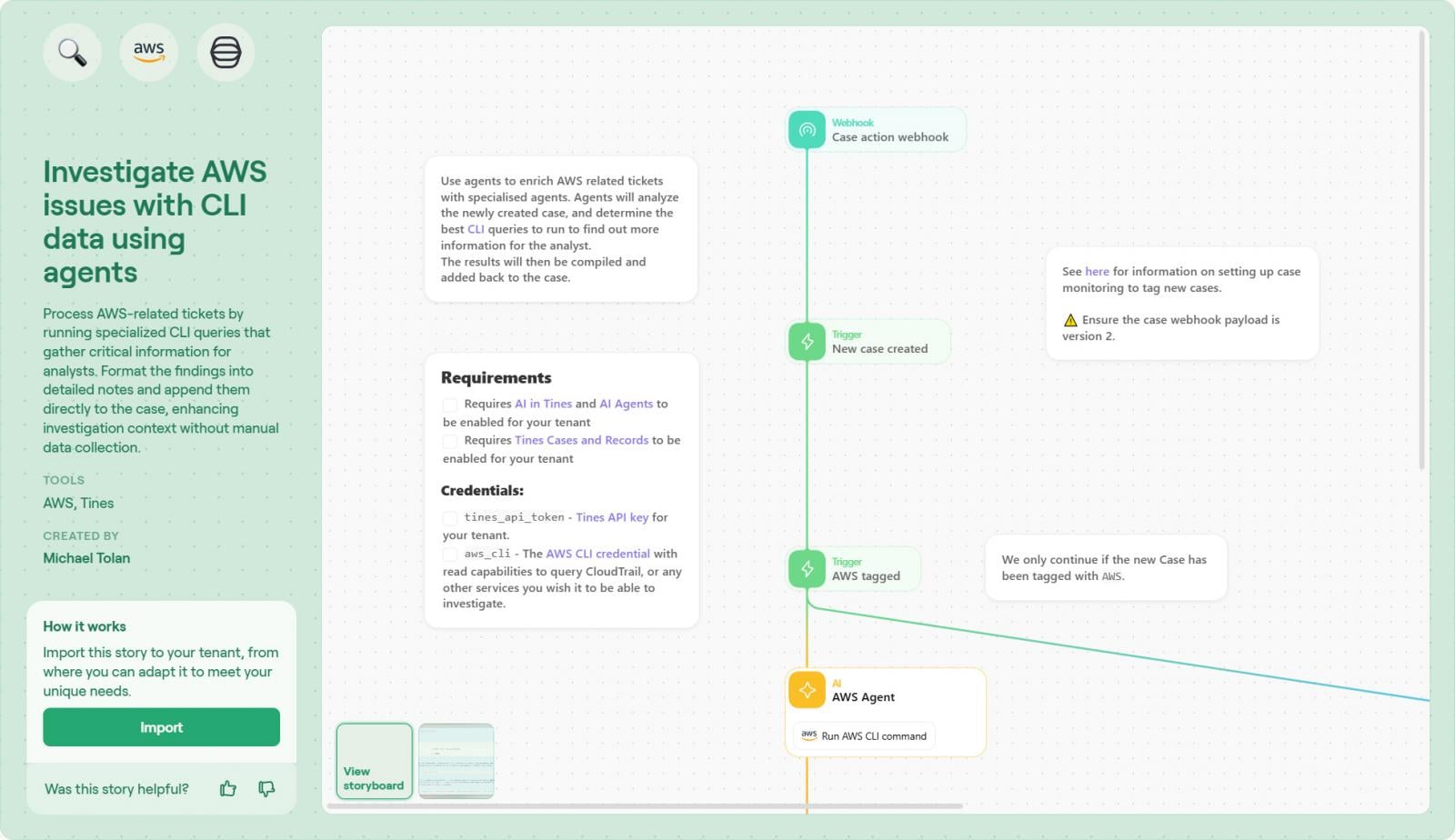
Step 2: Connect Your AWS Credential To allow the agent to interact with your environment, connect a secure AWS credential (like an IAM role or access key) directly within the Tines tenant. No complex infrastructure deployment or external runners are required.
Step 3: Modify Recommended Commands The template includes a list of example commands to help guide the agent, but these aren’t the only ones it can use. You can edit this list to steer the agent’s behavior, specifying commands you would like it to use more frequently based on your team’s most common tickets
Step 4: Review Case Format The workflow is already pre-wired to send findings to Tines Cases, so no manual connection is needed. However, you should review the Case layout to ensure it suits your analysts. You might want to adjust the order of fields or how the AI summary is presented to ensure the most critical data is visible at a glance.
Step 5: Test and define Run the workflow with a dummy ticket. Verify that the agent executes the command and that the output is formatted correctly in the Case view.
Conclusion
The difference between a stressed SOC and an efficient one is often the “mundane tasks.” When analysts have to manually fetch data for every alert, they drown in noise.
By orchestrating these routine checks with Tines and Tines agents, you flip the script. You give your team the context they need instantly, allowing them to focus on the high-value decision-making that actually protects the organization.
As the crowdfunding tech company discovered, intelligent workflows don’t just save time. When implemented properly, they fundamentally change the security posture.
For a deeper look at how Tines Cases can centralize your investigation data, check out this product spotlight: Tines Cases | Product Spotlight. This video demonstrates how the Cases interface consolidates data, making it the perfect destination for the automated AWS insights generated by this workflow.
Sponsored and written by Tines.
Tech
How To Think About AI: Is It The Tool, Or Are You?

from the do-you-use-your-brain-or-do-you-replace-it? dept
We live in a stupidly polarizing world where nuance is apparently not allowed. Everyone wants you to be for or against something—and nowhere is this more exhausting than with AI. There are those who insist that it’s all bad and there is nothing of value in it. And there are those who think it’s all powerful, the greatest thing ever, and will replace basically every job with AI bots who can work better and faster.
I think both are wrong, but it’s important to understand why.
So let me lay out how I actually think about it. When it’s used properly, as a tool to assist a human being in accomplishing a goal, it can be incredibly powerful and valuable. When it’s used in a way where the human’s input and thinking are replaced, it tends to do very badly.
And that difference matters.
I think back to a post from Cory Doctorow a couple months ago where he tried to make the same point using a different kind of analogy: centaurs and reverse-centaurs.
Start with what a reverse centaur is. In automation theory, a “centaur” is a person who is assisted by a machine. You’re a human head being carried around on a tireless robot body. Driving a car makes you a centaur, and so does using autocomplete.
And obviously, a reverse centaur is a machine head on a human body, a person who is serving as a squishy meat appendage for an uncaring machine.
Like an Amazon delivery driver, who sits in a cabin surrounded by AI cameras, that monitor the driver’s eyes and take points off if the driver looks in a proscribed direction, and monitors the driver’s mouth because singing isn’t allowed on the job, and rats the driver out to the boss if they don’t make quota.
The driver is in that van because the van can’t drive itself and can’t get a parcel from the curb to your porch. The driver is a peripheral for a van, and the van drives the driver, at superhuman speed, demanding superhuman endurance. But the driver is human, so the van doesn’t just use the driver. The van uses the driver up.
Obviously, it’s nice to be a centaur, and it’s horrible to be a reverse centaur.
As Doctorow notes in his piece, some of the companies embracing AI tech are doing so with the goal of building reverse-centaurs. Those are the ones that people are, quite understandably, uncomfortable with and should be mocked. But the reality is, also, it seems quite likely those efforts will fail.
And they’ll fail not just because they’re dehumanizing—though they are—but because the output is garbage. Hallucinations, slop, confidently wrong answers: that’s what happens when nobody with actual knowledge is checking whether any of it makes sense. When AI works well, it’s because a human is providing the knowledge and the creativity.
The reverse-centaur doesn’t just burn out the human. It produces worse work, because it assumes that the AI can provide the knowledge or the creativity. It can’t. That requires a human. The power of AI tools is in enabling a human to take their own knowledge, and their own creativity and enhance it, to do more with it, based on what the person actually wants.
To me it’s a simple question of “what’s the tool?” Is it the AI, used thoughtfully by a human to do more than they otherwise could have? If so, that’s a good and potentially positive use of AI. It’s the centaur in Doctorow’s analogy.
Or is the human the tool? Is it a “reverse centaur”? I think nearly all of those are destined to fail.
This is why I tend not to get particularly worked up by those who claim that AI is going to destroy jobs and wipe out the workforce, who will be replaced by bots. It just… doesn’t work that way.
At the same time, I find it ridiculous to see people still claiming that the technology itself is no good and does nothing of value. That’s just empirically false. Plenty of people—including myself—get tremendous use out of the technology. I am using it regularly in all different ways. It’s been two years since I wrote about how I used it to help as a first pass editor.
The tech has gotten dramatically better since then, but the key insight to me is what it takes to make it useful: context is everything. My AI editor doesn’t just get my draft writeup and give me advice based on that and its training—it also has a sampling of the best Techdirt articles, a custom style guide with details about how I write, a deeply customized system prompt (the part of AI tools that are often hidden from public view) and a deeply customized starting prompt. It also often includes the source articles I’m writing about. With all that context, it’s an astoundingly good editor. Sometimes it points out weak arguments I missed entirely. Sometimes it has nothing to say.
(As an aside, in this article, it suggested I went on way too long explaining all the context I give it to give me better suggestions, and thus I shortened it to just the paragraph above this one).
It’s not always right. Its suggestions are not always good. But that’s okay, because I’m not outsourcing my brain to it. It’s a tool. And way more often than not, it pushes me to be a better writer.
This is why I get frustrated every time people point out a single AI fail or hallucination without context.
The problem only comes in when people outsource their brains. When they become reverse centaurs. When they are the tool instead of using AI as the tool. That’s when hallucinations or bad info matter.
But if the human is in control, if they’re using their own brain, if they’re evaluating what the tool is suggesting or recommending and making the final decision, then it can be used wisely and can be incredibly helpful.
And this gets at something most people miss entirely: when they think about AI, they’re still imagining a chatbot. They think every AI tool is ChatGPT. A thing you talk to. A thing that generates text or images for you to copy-paste somewhere else.
That’s increasingly not where the action is. The more powerful shift is toward agentic AI—tools that don’t just generate content, but actually do things. They write code and run it. They browse the web and synthesize what they find. They execute multi-step tasks with minimal hand-holding. This is a fundamentally different model than “ask a chatbot a question and get an answer.”
I’ve been using Claude Code recently, and this distinction matters. It’s an agent that can plan, execute, and iterate on actual software projects, rather than just a tool talking to me about what to do. But, again, that doesn’t mean I just outsource my brain to it.
I often put Claude Code into plan mode, where it tries to work out a plan, but then I spend quite a lot of time exploring why it was making certain decisions, and asking it to explore the pros and cons of those decisions, and even to provide me with alternative sources to understand the trade-offs of some of the decisions it is recommending. That back and forth has been both educational for me, but also makes me have a better understanding and be comfortable with the eventual projects I use Claude Code to build.
I am using it as a tool, and part of that is making sure I understand what it’s doing. I am not outsourcing my brain to it. I am using it, carefully, to do things that I simply could not have done before.
And that’s powerful and valuable.
Yes, there are so many bad uses of AI tools. And yes, there is a concerted, industrial-scale effort, to convince the public they need to use AI in ways that they probably shouldn’t, or in ways that is actively harmful. And yes, there are real questions about what it costs to train and run the foundation models. And we should discuss those and call those out for what they are.
But the people who insist the tools are useless and provide nothing of value, that’s just wrong. Similarly, anyone who thinks the tech is going to go away are entirely wrong. There likely is a funding bubble. And some companies will absolutely suffer as it deflates. But it won’t make the tech go away.
When used properly, it’s just too useful.
As Cory notes in his centaur piece, AI can absolutely help you do your job, but the industry’s entire focus is on convincing people it can replace your job. That’s the con. The tech doesn’t replace people. But it can make them dramatically more capable—if they stay in the driver’s seat.
The key to understanding the good and the bad of the AI hype is understanding that distinction. Cory explains this in reference to AI coding:
Think of AI software generation: there are plenty of coders who love using AI, and almost without exception, they are senior, experienced coders, who get to decide how they will use these tools. For example, you might ask the AI to generate a set of CSS files to faithfully render a web-page across multiple versions of multiple browsers. This is a notoriously fiddly thing to do, and it’s pretty easy to verify if the code works – just eyeball it in a bunch of browsers. Or maybe the coder has a single data file they need to import and they don’t want to write a whole utility to convert it.
Tasks like these can genuinely make coders more efficient and give them more time to do the fun part of coding, namely, solving really gnarly, abstract puzzles. But when you listen to business leaders talk about their AI plans for coders, it’s clear they’re not looking to make some centaurs.
They want to fire a lot of tech workers – they’ve fired 500,000 over the past three years – and make the rest pick up their work with coding, which is only possible if you let the AI do all the gnarly, creative problem solving, and then you do the most boring, soul-crushing part of the job: reviewing the AIs’ code.
Criticize the hype. Mock the replace-your-workforce promises. Call out the slop factories and the gray goo doomsaying. But don’t mistake the bad uses for the technology itself. When a human stays in control—thinking, evaluating, deciding—it’s a genuinely powerful tool. The important question is just whether you’re using it, or it’s using you.
Tech
Facebook is offering Meta AI-powered animations for profile photos

Meta has been going all in on AI, whether people want it or not, and now it’s bringing more features in that vein to Facebook. The network’s latest move is to let people use Meta AI to animate their profile photos. Because what better way to express your individuality than to use a pre-canned AI-generated animation on your own face?
Meta AI is also coming for your Facebook Stories and Memories. The network’s Restyle lets you use gen-AI to change up the aesthetic of your posts. You can once again use pre-canned stylings or give the AI assistant your own prompt.
In the company’s own words, the new tools that will create “share-worthy moments that spark meaningful interactions and conversations with friends.” I guess meaning is in the eye of the beholder. If you’re desperate to behold even more AI slop, Meta recently said its Vibes feed of exactly that content will be getting a standalone app.
Tech
The next wave of spec-monster phones could get a 100-megapixel selfie camera

The latest generation of Android flagships from Vivo, Oppo, and even Samsung include one 200MP sensor, used as the primary camera or the telephoto camera. However, the next generation of Android flagships could include three 100MP sensors.
You heard that right. According to Chinese tipster Digital Chat Station, “some” (that could be more than one) smartphone makers are “testing three 100-megapixel lenses” or cameras.

Three 100MP cameras? That’s the rumor
Although the tipster doesn’t specify the nature of these cameras, they could very well be the primary, telephoto, and ultrawide shooters. This is one of the most interesting approaches I’ve heard of lately. Here’s why.
It might sound like a 100MP primary sensor and a 100MP telephoto sensor is a downgrade from the current 200MP standard at first. But only the Oppo Find X9 Ultra has been confirmed to feature two 200MP cameras on the back.
The others, including the Vivo X300 Pro, the Find X9 Pro, and the Galaxy S25 Ultra (or even the upcoming Galaxy S26 Ultra, for that matter), include only one 200MP primary sensor, which, by the way, uses pixel binning to default to a lower resolution for increased low-light performance, saving space and capture time.
Having 100MP primary and telephoto sensors would still allow brands to capture at a lower default resolution, upscale significantly when needed, and take less storage or capture time than a 200MP sensor would.

The ultrawide camera could finally get a serious update
So far, I haven’t talked about the ultrawide sensor, because it maxes out at 50MP on the flagships. Hence, a 100MP ultrawide camera (if our interpretation of the tweet is right) would be a dramatic upgrade.
It could enable more detailed macro shots (if the sensor doubles as a macro shooter) or greater post-capture reframing potential. In addition to the rear-facing cameras, the leaker also claims that a “100-megapixel front-facing camera,” with a “small-pixel sensor,” is in the works.
Given that the Galaxy S26 series seems to be stuck with a 12MP front camera, and Chinese flagships use a 50MP sensor on their most expensive variants, a 100MP selfie shooter could deliver a noticeable upgrade.
Since it’s a small-pixel sensor, low-light photography might be an issue, but I guess smartphone makers should be able to fix it with computational trickery.
Tech
Google’s Personal Data Removal Tool Now Covers Government IDs

Google on Tuesday expanded its “Results about you” tool to let users request the removal of Search results containing government-issued ID numbers — including driver’s licenses, passports and Social Security numbers — adding to the tool’s existing ability to flag results that surface phone numbers, email addresses, and home addresses.
The update, announced on Safer Internet Day, is rolling out in the U.S. over the coming days. Google also streamlined its process for reporting non-consensual explicit images on Search, allowing users to select and submit removal requests for multiple images at once rather than reporting them individually.
Tech
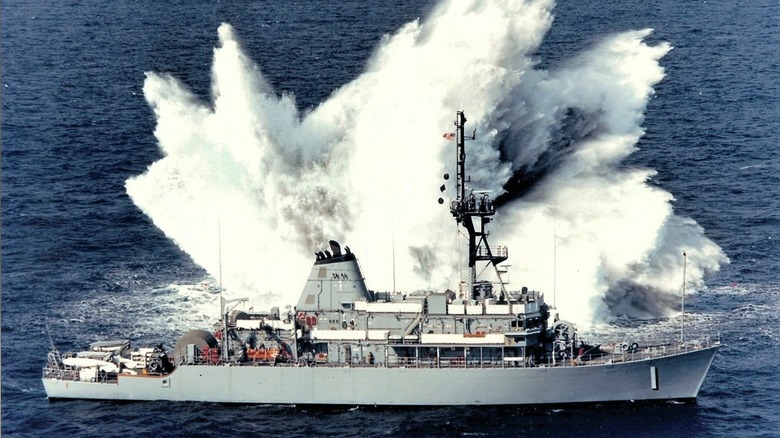
Why US Navy Avenger-Class Minesweepers Have Been Pulled From The Middle East

The U.S. Navy has a lot of different types of warships, and while its aircraft carriers, destroyers, and different types of submarines are well known, they’re hardly the only vessels in service. In addition to the better-known ships, the Navy also operates minesweepers, or as they’re technically known, “mine countermeasure ships” (MCMs). As the name implies, these are ships designed specifically to clear naval mines from critical waterways, and they’ve been around for a long time.
As of writing, the Navy operates four Avenger-class MCMs, having retired the remaining ten of its 14-ship fleet. These vessels entered service in the 1980s and were used during Operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm. As of early 2026, the remaining four Avenger-class ships are forward-deployed in Japan, though an additional four had remained in operation in the Persian Gulf until they were decommissioned late the previous year: The USS Devastator, USS Dextrous, USS Gladiator, and the USS Sentry. In January 2026, the Navy contracted a heavy lift vessel to carry these ships out of the area, removing them from the Middle East entirely.
There are several reasons for this move, but chief among them is the age of the Avenger-class and the fact that they’ve been replaced with highly complex Independence-class Littoral Combat Ships. Mine-clearing is still a vital function of U.S. Navy operations, but time in service for the Avenger-class has largely come to an end. Removing them from the Persian Gulf was in accordance with U.S. Navy force transition efforts, and it required a great deal of planning and support to finalize their departure. All four are set to be dismantled and scrapped.
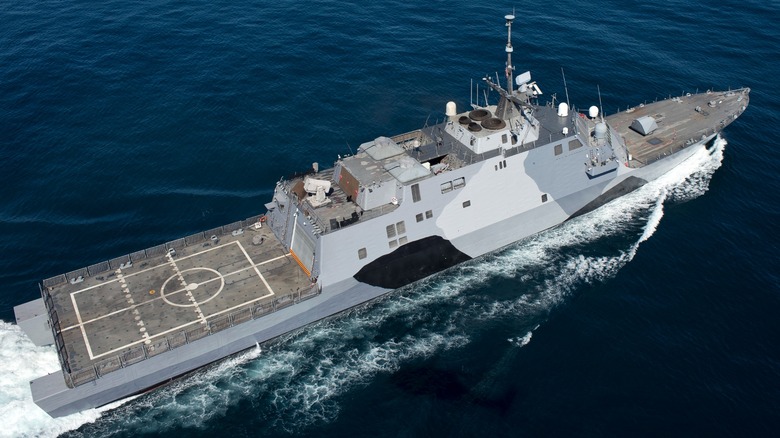
How Avenger and Independence-class ships compare
The U.S. Navy began operating its fleet of 19 Independence-class Littoral Combat Ships (LCS) in 2010. The vessels are designed for high-speed operation in the littoral zone (close to the shore). They feature an angular trimaran (three-hulled) design, can reach speeds of up to 52 mph, and are capable of carrying out numerous operations, including chasing down pirates. In terms of mine-clearing, Independence-class ships are modular and carry a variety of systems, including a mine countermeasure module. Others include anti-submarine warfare and surface warfare modules.
LCS mine countermeasures utilize aviation and uncrewed surface and underwater vehicles with an assortment of sensors. These work in tandem to detect and neutralize a variety of mines in the littoral environment and are deployed outside of the area of the ship, keeping it safe from potential mines; working together, they can isolate beach and buried mines along the shore. For comparison, Avenger-class ships have a top speed of around 16 mph and operate a remote mine countermeasure system with a remotely operated vehicle. These worked together to find, classify, and neutralize a variety of mines.
While capable, Avenger-class ships had limited operability in littoral zones and couldn’t detect the same variety of mines as Independence-class vessels. The older MCMs were also considerably smaller and constructed of wood and fiberglass, while Independence-class vessels are composed primarily of aluminum. The newer class of ships utilizes a technologically superior mine countermeasure system that has been updated significantly since its introduction, ensuring mission operability improves as the US Navy’s LCS fleet continues to fulfill its many duties around the world.
Tech
Malicious 7-Zip site distributes installer laced with proxy tool


A fake 7-Zip website is distributing a trojanized installer of the popular archiving tool that turns the user’s computer into a residential proxy node.
Residential proxy networks use home user devices to route traffic with the goal of evading blocks and performing various malicious activities such as credential stuffing, phishing, and malware distribution.
The new campaign became better known after a user reported that they downloaded a malicious installer from a website impersonating the 7-Zip project while following instructions in a YouTube tutorial on building a PC system. BleepingComputer can confirm that the malicious website, 7zip[.]com, is still live.
The threat actor registered the domain 7zip[.]com (still live at the time of writing) that can easily trick users into thinking they landed on the site of the legitimate tool.
Furthermore, the attacker copied the text and mimicked the structure of the original 7-Zip website located at 7-zip.org.
Source: BleepingComputer
The installer file was analyzed by researchers at cybersecurity company Malwarebytes, who found that it is digitally signed with a now-revoked certificate originally issued to Jozeal Network Technology Co., Limited.
The malicious copy also contains the 7-Zip program, thus providing the regular functions of the tool. However, the installer drops three malicious files:
- Uphero.exe – service manager and update loader
- hero.exe – main proxy payload
- hero.dll – support library
These files are placed in the ‘C:\Windows\SysWOW64\hero\’ directory, and an auto-start Windows service running as SYSTEM is created for the two malicious executables.
Additionally, firewall rules are modified using ‘netsh’ to allow the binaries to establish inbound and outbound connections.
Eventually, the host system is profiled with Microsoft’s Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and Windows APIs to determine the hardware, memory, CPU, disk, and network characteristics. The collected data is then sent to ‘iplogger[.]org.’
“While initial indicators suggested backdoor‑style capabilities, further analysis revealed that the malware’s primary function is proxyware,” Malwarebytes explains about the malware’s operational goal.
“The infected host is enrolled as a residential proxy node, allowing third parties to route traffic through the victim’s IP address.”
According to the analysis, hero.exe pulls config from rotating “smshero”-themed C2 domains, then opens outbound proxy connections on non-standard ports such as 1000 and 1002. Control messages are obfuscated using a lightweight XOR key.
Malwarebytes found that the campaign is larger than the 7-Zip lure and also uses trojanized installers for HolaVPN, TikTok, WhatsApp, and Wire VPN.
The malware uses a rotating C2 infrastructure built around hero/smshero domains, with traffic going through the Cloudflare infrastructure and carried over TLS-encrypted HTTPs.
It also relies on DNS-over-HTTPS via Google’s resolver, which reduces visibility for defenders monitoring standard DNS traffic.
The malware also checks for virtualization platforms such as VMware, VirtualBox, QEMU, Parallels, as well as for debuggers, to identify when it’s being analyzed.
Malwarebytes’ investigation started after noticing research from independent security researchers who analyzed the malware and uncovered its true purpose. Researcher Luke Acha discovered the purpose of the Uphero/hero malware.
The xor-based communication protocol was reverse-engineered and decoded by s1dhy, who confirmed the proxy behavior. Digital forensics and incident response (DFIR) engineer Andrew Danis connected the fake 7-Zip installer to the larger campaign impersonating multiple software brands.
Malwarebytes lists indicators of compromise (domains, file paths, IP addresses) and host-related data observed during their analysis.
Users are recommended to avoid following URLs from YouTube videos or promoted search results, and instead bookmark the download portal domains for the software they use often.
Tech
Here’s how Rivian changed the rear door manual release on the R2

There’s been a lot of pushback on electronic door handles lately, as multiple carmakers — especially Tesla — have been accused of making manual door releases too hard to find and access during an emergency. Rivian is one of the companies that reportedly decided to change this on its upcoming R2 SUV, and a spate of first-look videos released Tuesday finally give us a look at what the company has changed.
First off, the front doors open from the inside in the same way as in the existing R1 vehicles. There is an electronic button that opens the door, and there’s a manual door-release latch tucked into the front part of the interior handle.
The rear doors also have an electronic button, as well as a change to the rear manual release.
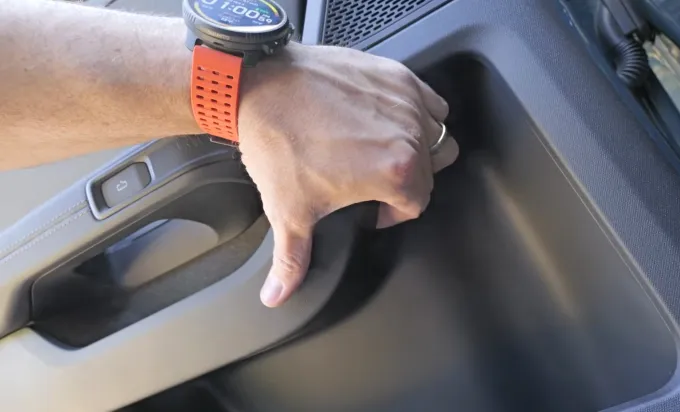
On R1 vehicles, passengers have to first pull a panel off the door to access a “release cord” that operates the manual latch. On the new R2 SUV, Rivian moved this release cord to that same front-of-the-handle position as the front seat manual releases — though it’s still tucked behind a piece of plastic that must be popped out, making it slightly harder to access than the front door manual releases.
The R2 SUV isn’t set to go into production for another few months, so the company has not put out proper instructions on how to access this release. But here’s an image from a new video published by JerryRigEverything’s Zack Nelson:

He doesn’t pull out the actual cord, but it’s the best illustration I’ve seen so far of what passengers will need to do if they are in an R2 that has lost power for whatever reason, limiting the vehicle’s electronic door release.
The manual release is still behind a piece of plastic, and it’s not the most obvious or accessible way to open a door from the inside. But it’s at least in a more logical spot than just being hidden behind a panel.
Techcrunch event
Boston, MA
|
June 23, 2026
These kinds of situations don’t happen often. But when they do, it’s typically during a major crash. That means every moment can be the difference between life and death.
Rivian is not alone in reworking how hard it is to access the manual releases. The most high profile example is Tesla. Bloomberg News found at least 15 deaths in crashes where there is evidence that occupants (or rescuers) were unable to open the doors. The company has said it will change how it designs its handles in order to address the problem.
And electronic door latches can present other issues. Last year, Ford had to issue a recall to fix a power-delivery problem for the electronic latches on the Mustang Mach-E.
Tech
This GoPro and Lens Bundle Is $200 Off

If you’ve been thinking about documenting your life, whether it’s the exciting or mundane stuff, this might just be your moment. This GoPro Hero 13 Black bundle includes a variety of useful accessories, as well as a full suite of interchangeable lenses. It’s currently marked down to just $550 on Amazon, a $200 discount from its usual price.
The biggest change to this generation of GoPro action cameras is the interchangeable lens system, and this kit comes loaded with basically every lens an aspiring filmmaker could ask for. That includes the ultrawide lens mod, which boosts the field of view to 177 degrees, an anamorphic lens and filters, and a macro lens for beautiful close-up shots. While it doesn’t come with a ton of attachments, it does have a case for carrying everything, and basic adhesives to get you started.
The downside here is that GoPro is still using the same sensor and processor as previous models, for better or worse. It’s one of the highest resolution and frame rate offerings you can get, with its 27-megapixel sensor producing up to 5.3K video, and up to 120 fps, although only for five seconds at a time at the highest resolution. Unfortunately, this GoPro, like others before it, still struggles in dim lighting. That said, there are some improvements to the HDR that our reviewer Scott Gilbertson said made a big difference when it came time to start editing.
Even with an upgraded battery, the stamina can be lackluster, lasting just one or two hours depending on how warm the camera gets. Thankfully, a new pass-through charging port allows you to hook up a power bank and keep filming for much longer. There are some other quality-of-life upgrades too, like a magnetic mounting system that makes swapping from surf to sand even easier.
The Hero 13 Black is our favorite GoPro, but there’s a whole world of action cameras for your next adventure, so make sure to check out our full guide if you’re curious about other options. Otherwise, this big bundle includes everything you need to get out and start shooting for just $550.
Tech
A warning to Seattle: Don’t become the next Cleveland


Consider a successful mid-sized American city. One with decades of population growth. Median household incomes on par with or exceeding New York City. A bustling port in a prime location. Bold civic architecture. A vibrant arts and cultural scene. And home to some of the world’s biggest and most valuable companies.
That could be Seattle. It also describes Cleveland about 75 years ago. In the 1950s, Cleveland was an epicenter for the era’s “Big Tech.” Industrial giants like Standard Oil, Westinghouse, Republic Steel, and Sherwin Williams were all founded in Cleveland. Like engineering outposts in Seattle, other leading companies including General Motors and U.S. Steel were well represented locally.
Yet Cleveland’s success unraveled remarkably quickly. Within 20 years, when the Cuyahoga River caught fire in 1969, the city was seared into history as “the mistake on the lake.” The population has declined by 60% since 1950 (and is still shrinking). Cleveland has gone from the seventh largest U.S. city in the country to the 56th. Median household incomes are now less than half the national average — and less than 40% of the Seattle area.
Today in Seattle tech circles there is great trepidation about the region’s next act. Seattle is not punching above its weight in the AI era the way we did in the software era. We might not even be punching our weight.
Entrepreneurs, executives, investors, and technologists are departing, either because they don’t think they can be competitive here in the white-hot AI market and/or are concerned about a deteriorating business environment. And the exodus appears to be accelerating.
You might take solace that our little corner of the country hosts two of the world’s five biggest companies (which is a little crazy). But it is easy to believe both Amazon and Microsoft are past peak employee count, as they become more capital-intensive and lean into AI-driven productivity. Other local tech companies and engineering centers are also shrinking, while new job listings have plummeted.
While the tech sector confronts existential dread, the political class in Seattle and Washington state seems oblivious. They don’t have much to say about creating jobs or nurturing industries of the future (or even of the present). Revenue is their focus above all else, with considerably less emphasis on how our taxes translate into efficient and effective provision of government services.

The traditional Seattle civic partnership between business and government has frayed. Few lessons have been learned from Boeing’s slow-motion migration out of the Seattle area (Washington is now home to just over a third of Boeing employees, and due to decrease further).
Relations between the tech industry and government are rocky, with the industry seen almost exclusively as a bottomless source of revenue. It would be shocking — but not surprising — to one day learn Amazon and/or Microsoft are moving their headquarters out of the state. (Bellevue already looks like Amazon’s HQ1 in all but name).
The tech boom has been an immense boon for Seattle, as the city attracted talent from all over the world. Seattle’s population has grown by almost 40% in the 21st century, and the City of Seattle rode that tailwind. The city’s inflation-adjusted budget grew over three times faster than the population over the same period.
That growth raises some obvious questions. Are city services three times better? How long can government spending keep outgrowing the population? What happens if population growth slows — or even reverses?
Meanwhile, city issues loom large in the desirability of doing business in Seattle. Downtown is barren, with record vacancies. Public safety, housing and homelessness are perennial hot topics, but progress is scarcer. After the recent election, we’re apparently going to take another shot at those persistent problems with progressive panaceas that have seen limited success, both locally and elsewhere.

Completely missing from any discussion is the crisis in our schools, where the majority of fourth and eighth graders in Seattle are not proficient in reading or math. Education is one of the most effective solutions to many social ailments — and a mandatory prerequisite for an advanced civilization — yet we’ve seemingly given up.
Which brings us back to Cleveland. When its fortunes began to shift, Cleveland’s politicians made a bad situation worse. A confrontational, short-term posture from government made it easy for companies to put Cleveland plants at the top of their closure lists. Contrast that with another Rust Belt city, Pittsburgh, where politicians and business worked together to accept and manage the inevitable transition. They defined the post-industrial playbook for cities — one Cleveland belatedly adopted.
Seattle has always been a lucky city. Prosperity has often come from unexpected sources. The Alaska gold rush was, quite literally, a gold rush. Bill #1 (Boeing) made Seattle synonymous with aerospace. Proximity to Alaska gave us a competitive container port, while rival ports like Portland and San Francisco dried up. Bill #2 (Gates) catalyzed a software industry in Seattle (and beyond). Jeff (Bezos) famously drove to Seattle in his Chevy Blazer, where he pioneered e-commerce and created a million and a half jobs along the way.
Maybe the luck holds and the next big thing just shows up. It could be space, energy, robotics, biotech or something unimaginable today. Hopefully we get lucky again, but hope, as they say, is not a strategy.
So I’ll offer a catchphrase as you think about Seattle’s next act: Don’t be Cleveland.
(I want to be very clear that I mean no offense to Cleveland. The people there today are still digging out of a hole created decades ago. Let’s learn from them and not repeat the errors of their forebears.)
Tech
AI Boom Fuels DRAM Shortage and Price Surge
If it feels these days as if everything in technology is about AI, that’s because it is. And nowhere is that more true than in the market for computer memory. Demand, and profitability, for the type of DRAM used to feed GPUs and other accelerators in AI data centers is so huge that it’s diverting away supply of memory for other uses and causing prices to skyrocket. According to Counterpoint Research, DRAM prices have risen 80-90 precent so far this quarter.
The largest AI hardware companies say they have secured their chips out as far as 2028, but that leaves everybody else—makers of PCs, consumer gizmos, and everything else that needs to temporarily store a billion bits—scrambling to deal with scarce supply and inflated prices.
How did the electronics industry get into this mess, and more importantly, how will it get out? IEEE Spectrum asked economists and memory experts to explain. They say today’s situation is the result of a collision between the DRAM industry’s historic boom and bust cycle and an AI hardware infrastructure build-out that’s without precedent in its scale. And, barring some major collapse in the AI sector, it will take years for new capacity and new technology to bring supply in line with demand. Prices might stay high even then.
To understand both ends of the tale, you need to know the main culprit in the supply and demand swing, high-bandwidth memory, or HBM.
What is HBM?
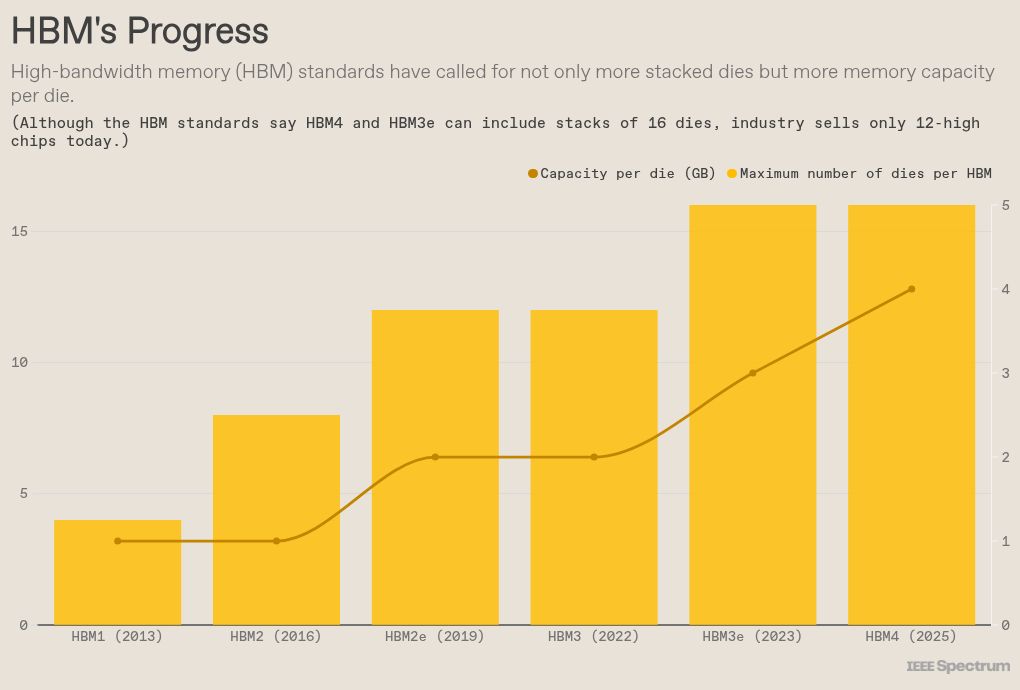
HBM is the DRAM industry’s attempt to short-circuit the slowing pace of Moore’s Law by using 3D chip packaging technology. Each HBM chip is made up of as many as 12 thinned-down DRAM chips called dies. Each die contains a number of vertical connections called through silicon vias (TSVs). The dies are piled atop each other and connected by arrays of microscopic solder balls aligned to the TSVs. This DRAM tower—well, at about 750 micrometers thick, it’s more of a brutalist office-block than a tower—is then stacked atop what’s called the base die, which shuttles bits between the memory dies and the processor.
This complex piece of technology is then set within a millimeter of a GPU or other AI accelerator, to which it is linked by as many as 2,048 micrometer-scale connections. HBMs are attached on two sides of the processor, and the GPU and memory are packaged together as a single unit.
The idea behind such a tight, highly-connected squeeze with the GPU is to knock down what’s called the memory wall. That’s the barrier in energy and time of bringing the terabytes per second of data needed to run large language models into the GPU. Memory bandwidth is a key limiter to how fast LLMs can run.
As a technology, HBM has been around for more than 10 years, and DRAM makers have been busy boosting its capability.
As the size of AI models has grown, so has HBM’s importance to the GPU. But that’s come at a cost. SemiAnalysis estimates that HBM generally costs three times as much as other types of memory and constitutes 50 percent or more of the cost of the packaged GPU.
Origins of the memory chip shortage
Memory and storage industry watchers agree that DRAM is a highly cyclical industry with huge booms and devastating busts. With new fabs costing US $15 billion or more, firms are extremely reluctant to expand and may only have the cash to do so during boom times, explains Thomas Coughlin, a storage and memory expert and president of Coughlin Associates. But building such a fab and getting it up and running can take 18 months or more, practically ensuring that new capacity arrives well past the initial surge in demand, flooding the market and depressing prices.
The origins of today’s cycle, says Coughlin, go all the way back to the chip supply panic surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic . To avoid supply-chain stumbles and support the rapid shift to remote work, hyperscalers—data center giants like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft—bought up huge inventories of memory and storage, boosting prices, he notes.
But then supply became more regular and data center expansion fell off in 2022, causing memory and storage prices to plummet. This recession continued into 2023, and even resulted in big memory and storage companies such as Samsung cutting production by 50 percent to try and keep prices from going below the costs of manufacturing, says Coughlin. It was a rare and fairly desperate move, because companies typically have to run plants at full capacity just to earn back their value.
After a recovery began in late 2023, “all the memory and storage companies were very wary of increasing their production capacity again,” says Coughlin. “Thus there was little or no investment in new production capacity in 2024 and through most of 2025.”
The AI data center boom
That lack of new investment is colliding headlong with a huge boost in demand from new data centers. Globally, there are nearly 2,000 new data centers either planned or under construction right now, according to Data Center Map. If they’re all built, it would represent a 20 percent jump in the global supply, which stands at around 9,000 facilities now.
If the current build-out continues at pace, McKinsey predicts companies will spend $7 trillion by 2030, with the bulk of that—$5.2 trillion—going to AI-focused data centers. Of that chunk, $3.3 billion will go toward servers, data storage, and network equipment, the firm predicts.
The biggest beneficiary so far of the AI data center boom is unquestionably GPU-maker Nvidia. Revenue for its data center business went from barely a billion in the final quarter of 2019 to $51 billion in the quarter that ended in October 2025. Over this period, its server GPUs have demanded not just more and more gigabytes of DRAM but an increasing number of DRAM chips. The recently released B300 uses eight HBM chips, each of which is a stack of 12 DRAM dies. Competitors’ use of HBM has largely mirrored Nvidia’s. AMD’s MI350 GPU, for example, also uses eight, 12-die chips.
With so much demand, an increasing fraction of the revenue for DRAM makers comes from HBM. Micron—the number three producer behind SK Hynix and Samsung—reported that HBM and other cloud-related memory went from being 17 percent of its DRAM revenue in 2023 to nearly 50 percent in 2025.
Micron predicts the total market for HBM will grow from $35 billion in 2025 to $100 billion by 2028—a figure larger than the entire DRAM market in 2024, CEO Sanjay Mehrotra told analysts in December. It’s reaching that figure two years earlier than Micron had previously expected. Across the industry, demand will outstrip supply “substantially… for the foreseeable future,” he said.
Future DRAM supply and technology
“There are two ways to address supply issues with DRAM: with innovation or with building more fabs,” explains Mina Kim, an economist with the Mkecon Insights. “As DRAM scaling has become more difficult, the industry has turned to advanced packaging… which is just using more DRAM.”
Micron, Samsung, and SK Hynix combined make up the vast majority of the memory and storage markets, and all three have new fabs and facilities in the works. However, these are unlikely to contribute meaningfully to bringing down prices.
Micron is in the process of building an HBM fab in Singapore that should be in production in 2027. And it is retooling a fab it purchased from PSMC in Taiwan that will begin production in the second half of 2027. Last month, Micron broke ground on what will be a DRAM fab complex in Onondaga County, N.Y. It will not be in full production until 2030.
Samsung plans to start producing at a new plant in Pyeongtaek, South Korea in 2028.
SK Hynix is building HBM and packaging facilities in West Lafayette, Indiana set to begin production by the end of 2028, and an HBM fab it’s building in Cheongju should be complete in 2027.
Speaking of his sense of the DRAM market, Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan told attendees at the Cisco AI Summit last week: “There’s no relief until 2028.”
With these expansions unable to contribute for several years, other factors will be needed to increase supply. “Relief will come from a combination of incremental capacity expansions by existing DRAM leaders, yield improvements in advanced packaging, and a broader diversification of supply chains,” says Shawn DuBravac , chief economist for the Global Electronics Association (formerly the IPC). “New fabs will help at the margin, but the faster gains will come from process learning, better [DRAM] stacking efficiency, and tighter coordination between memory suppliers and AI chip designers.”
So, will prices come down once some of these new plants come on line? Don’t bet on it. “In general, economists find that prices come down much more slowly and reluctantly than they go up. DRAM today is unlikely to be an exception to this general observation, especially given the insatiable demand for compute,” says Kim.
In the meantime, technologies are in the works that could make HBM an even bigger consumer of silicon. The standard for HBM4 can accommodate 16 stacked DRAM dies, even though today’s chips only use 12 dies. Getting to 16 has a lot to do with the chip stacking technology. Conducting heat through the HBM “layer cake” of silicon, solder, and support material is a key limiter to going higher and in repositioning HBM inside the package to get even more bandwidth.
SK Hynix claims a heat conduction advantage through a manufacturing process called advanced MR-MUF (mass reflow molded underfill). Further out, an alternative chip stacking technology called hybrid bonding could help heat conduction by reducing the die-to-die vertical distance essentially to zero. In 2024, researchers at Samsung proved they could produce a 16-high stack with hybrid bonding, and they suggested that 20 dies was not out of reach.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web
-

 Tech7 days ago
Tech7 days agoWikipedia volunteers spent years cataloging AI tells. Now there’s a plugin to avoid them.
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoWhy Israel is blocking foreign journalists from entering
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoJD Vance booed as Team USA enters Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
 Tech4 days ago
Tech4 days agoFirst multi-coronavirus vaccine enters human testing, built on UW Medicine technology
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Team GB’s Mia Brookes through to snowboard big air final, and curling pair beat Italy
-
 Business2 days ago
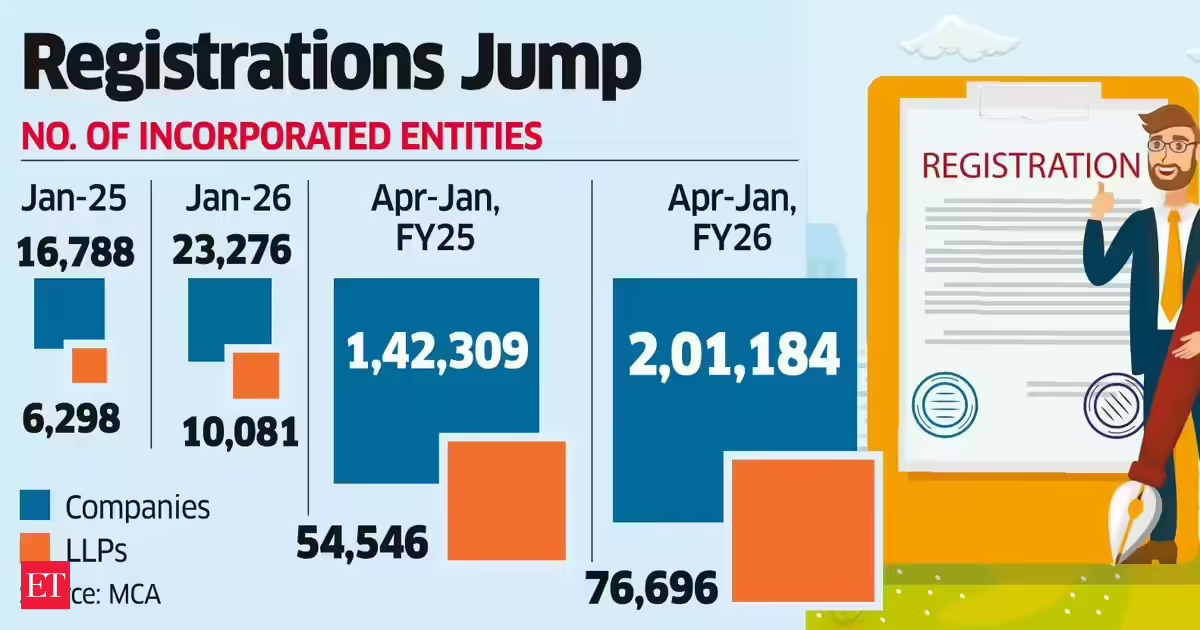
Business2 days agoLLP registrations cross 10,000 mark for first time in Jan
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoBenjamin Karl strips clothes celebrating snowboard gold medal at Olympics
-
Sports3 days ago
Former Viking Enters Hall of Fame
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoThe Health Dangers Of Browning Your Food
-
Sports4 days ago
New and Huge Defender Enter Vikings’ Mock Draft Orbit
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoJulius Baer CEO calls for Swiss public register of rogue bankers to protect reputation
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoSavannah Guthrie’s mother’s blood was found on porch of home, police confirm as search enters sixth day: Live
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoQuiz enters administration for third time
-
 Crypto World13 hours ago
Crypto World13 hours agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month
-

 Crypto World5 hours ago
Crypto World5 hours agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoResidents say city high street with ‘boarded up’ shops ‘could be better’
-
Sports24 hours ago
Kirk Cousins Officially Enters the Vikings’ Offseason Puzzle
-
 Crypto World13 hours ago
Crypto World13 hours agoEthereum Enters Capitulation Zone as MVRV Turns Negative: Bottom Near?
-

 NewsBeat5 days ago
NewsBeat5 days agoStill time to enter Bolton News’ Best Hairdresser 2026 competition












