Crypto World
DAO Development for Regulated Stablecoin Ecosystems
Over the past five years, DAOs promised borderless governance, permissionless finance, and community-driven growth. Today, a new reality is reshaping this vision. Regulation is no longer operating in the background. It is now directly influencing how DAOs design their governance, manage treasuries, and build trust with investors and institutions. At the same time, stablecoins have become the primary settlement layer for Web3 economies. For founders, investors, and governance leaders, this shift raises critical questions. How do you remain decentralized while meeting compliance expectations? How do you protect treasury assets from regulatory risk? How do you design governance systems that institutions can trust? This blog answers those questions.
Inside, you will learn how regulation is transforming DAO architecture, why traditional governance models are losing credibility, and how modern DAO development is evolving into a scalable, institution-ready framework. If you are building, investing in, or advising a DAO, this guide will help you make informed decisions for long-term growth in regulated stablecoin ecosystems.
How Stablecoin Regulation Is Reshaping DAO Architecture
Governments worldwide are implementing formal rules for stablecoin issuance, custody, and settlement, fundamentally reshaping how DAOs operate in regulated financial environments and accelerating the demand for advanced DAO development frameworks. In the United States, authorities are enforcing reserve audits and issuer licensing, while the European Union is advancing MiCA compliance frameworks. Across Asia, regulators are strengthening payment-token supervision models, and Middle Eastern jurisdictions are establishing dedicated digital asset oversight authorities.
As regulated stablecoins become the dominant settlement layer, DAOs integrating them are now expected to meet higher operational standards, including full treasury transparency, automated KYC and AML compliance layers, real-time transaction monitoring systems, and clearly defined governance accountability norms. As a result, traditional anonymous treasury and token-based voting models are becoming structurally weak and increasingly incompatible with institutional and regulatory expectations.
What Changes Inside a DAO?
Modern DAO architecture is shifting toward:
- Segmented treasury wallets
- Role-based governance permissions
- Regulated payment rails
- Smart-contract compliance logic
- Hybrid on-chain/off-chain reporting
This transformation is being led by specialized DAO development company providers that understand both blockchain engineering and regulatory frameworks.
Prepare your DAO for regulation-driven stablecoin ecosystems today
Why Traditional DAO Governance Models Are Breaking
As regulatory expectations reshape DAO infrastructure and treasury operations, governance frameworks are now being examined more closely, pushing projects to rely on advanced DAO development services for compliance-ready design. Structures that once worked in loosely regulated environments are increasingly proving inadequate in a modern, compliance-driven ecosystem.
1. Token Voting Limits
Token-based governance is facing growing structural limitations as DAOs scale and attract regulatory attention. Three major challenges now define voting systems: capital concentration, low participation rates, and regulatory scrutiny.
In many DAOs, less than five percent of token holders control more than eighty percent of voting power. Regulators increasingly view this imbalance as centralized influence presented as decentralization, weakening institutional trust.
2. Treasury Risk Levels
As DAOs accumulate large reserves in regulated stablecoins, treasury operations are becoming more vulnerable to compliance and jurisdictional risks.
Key exposure points include account freezes, regulatory investigations, jurisdictional conflicts, and dependency on traditional banking relationships. These risks remain fragmented and largely unmanaged without professional DAO platform development.
3. Governance Standards
Modern governance systems are expected to function with the same transparency and accountability as financial institutions.
Future-ready DAOs must demonstrate clear decision traceability, financial accountability, conflict resolution mechanisms, and legal clarity across jurisdictions. Governance is no longer defined by voting alone. It is now measured by institutional credibility and operational discipline.
The New Compliance-Ready Stablecoin-Based DAO Operating Model
The Rise of “Regulated-Native” Stablecoin DAOs
As regulated stablecoins become the foundation of on-chain payments and treasury management, next-generation DAOs are being designed from day one to operate within compliant financial ecosystems.
These modern governance frameworks are built to support:
- Stablecoin licensing alignment
- Multisig compliance approval flows
- Automated reporting dashboards
- Smart-contract risk monitoring
- Legal wrapper integration
Implementing these systems at scale requires professional DAO development services rather than fragmented, do-it-yourself governance frameworks.
Core Layers of a Future-Ready DAO
| Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Governance | Role-based voting and accountability |
| Treasury | Segmented regulated wallets |
| Compliance | Automated AML and KYC systems |
| Reporting | Real-time audit dashboards |
| Operations | Smart workflow management |
This modular architecture allows stablecoin-powered DAOs to scale across jurisdictions while minimizing regulatory friction and operational risk.
Why Investors Are Repositioning Around Regulated DAOs
As governance models mature and compliance becomes a defining success factor, the way capital evaluates decentralized organizations is undergoing a fundamental shift. What once attracted speculative funding now demands structural credibility, financial transparency, and regulatory preparedness.
Capital Is Moving Toward Compliance-Ready Projects
Institutional and venture capital are no longer chasing hype-driven DAO experiments. Instead, serious investors are reallocating funds toward projects that demonstrate regulatory awareness, financial discipline, and long-term governance stability, often backed by professional DAO development services that ensure regulatory and technical alignment from day one.
Today, capital is increasingly flowing into DAOs that operate within structured ecosystems, including:
- RWA-backed governance networks
- Stablecoin-powered payment infrastructures
- Regulation-aligned DeFi protocols
- Institutional-grade treasury platforms
These projects signal operational maturity, a key factor in modern investment decisions.
How Investors Evaluate DAOs in 2026?
Investor due diligence has evolved beyond token metrics and community size. Leading funds now assess DAOs using governance, compliance, and sustainability indicators such as:
- Legal survivability across jurisdictions
- Governance resilience under regulatory pressure
- Exposure to stablecoin issuer risk
- Ability to adapt to changing compliance frameworks
These factors determine whether a DAO can scale responsibly in global markets.
The New Institutional Due Diligence Checklist
Before allocating capital, most professional investors now require evidence of:
- Verified treasury compliance
- Assessed stablecoin counterparty risk
- Documented governance audit trails
- Mapped jurisdictional exposure
- Automated financial reporting systems
DAOs that fail to meet these benchmarks are increasingly excluded from institutional portfolios, regardless of their technical innovation.
Build compliant DAO platforms without sacrificing decentralization.
How Founders Should Rebuild DAO Strategy in 2026
Step 1: Redesign Governance Architecture
Founders must move beyond token-only voting toward:
- Weighted governance systems
- Committee-based approvals
- Regulatory oversight nodes
- Emergency intervention layers
Step 2: Professionalize Treasury Operations
Treasury must function like a fintech institution:
- Regulated custody
- Multi-jurisdiction banking
- Stablecoin diversification
- Risk hedging
Step 3: Implement Compliance Automation
Manual compliance does not scale.
Modern DAOs use:
- On-chain identity modules
- Smart AML triggers
- Reporting oracles
- Audit automation
Step 4: Choose the Right DAO Development Partner
Not every blockchain agency understands regulatory engineering.
Working with experienced providers in DAO infrastructure ensures:
- Long-term scalability
- Legal adaptability
- Institutional readiness
Conclusion: The Next Decade Belongs to Compliance-Native DAOs
The future of DAOs belongs to projects that combine decentralization with regulatory readiness. As stablecoins become the backbone of Web3 finance, governance models, treasury systems, and reporting structures must evolve to meet institutional and legal expectations. For founders, investors, and compliance leaders, this is no longer a theoretical shift. It is a strategic decision point.
Working with professional DAO development company ensures your DAO is built for scalability, transparency, and long-term resilience in regulated ecosystems. This is where Antier plays a critical role. With deep expertise in governance engineering and compliance-focused infrastructure, we help DAOs transition from experimental frameworks to enterprise-ready platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How is regulation impacting the governance of DAOs?
Regulation is directly influencing how DAOs design their governance, manage treasuries, and build trust with investors and institutions, leading to higher operational standards and transparency requirements.
02. What are the key changes in modern DAO architecture?
Modern DAO architecture is evolving to include segmented treasury wallets, role-based governance permissions, regulated payment rails, and smart-contract compliance to meet regulatory expectations.
03. Why are traditional governance models losing credibility in the context of DAOs?
Traditional anonymous treasury and token-based voting models are becoming structurally weak and increasingly incompatible with institutional and regulatory expectations, prompting a shift toward more transparent and accountable governance systems.
Crypto World
Banks push OCC to curb crypto trust charters until GENIUS rules clear

The American Bankers Association is pressing the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency to slow the wheel on national trust bank charters for crypto and stablecoin firms until key questions around the GENIUS Act, which would reshape U.S. stablecoin regulation, are settled. In a recent comment letter responding to the OCC’s notice of proposed rulemaking on national bank charters, the ABA warned that the sector’s regulatory picture remains fragmented across federal and state authorities. The trade group argued that advancing applications now could leave uninsured, digital-asset‑focused trusts exposed to unresolved safety, operational, and resolution issues, even as the industry connects customer assets to federally chartered platforms.
The ABA’s critique centers on the risk that a patchwork of oversight can create gaps for entities that manage crypto and stablecoins. The letter contends that until forthcoming GENIUS Act rulemakings lay out clear regulatory obligations, it would be prudent for the OCC to pause or slow down approvals. The GENIUS Act, which aims to streamline or redefine how digital assets fit into the U.S. banking framework, has not yet produced a settled regulatory map. Without that clarity, the ABA argues, banks seeking charters could face obligations that are not yet defined, complicating risk management and supervisory expectations for these new structures.
Beyond governance, the association underscored distinct safety and soundness concerns tied to uninsured, digital-asset‑focused national trusts. Chief among them are questions about how customer assets are segregated and protected, potential conflicts of interest, and the cyber safeguards necessary to withstand sophisticated threats. The letter points to the possibility that uninsured digital-asset trusts could be used to sidestep traditional registration and scrutiny by agencies such as the SEC or CFTC when activities would ordinarily trigger securities or derivatives regulation. The overarching worry is that these charters could become a back door to bypass comprehensive, integrated oversight.
The ABA’s stance comes as the OCC has recently moved to greenlight a path for several crypto firms to hold and manage customer digital assets under a federal charter while staying outside the deposit-taking and lending business. In December 2025, the OCC granted conditional national trust bank approvals to five notable players: Bitgo Bank & Trust, Fidelity Digital Assets, Ripple National Trust Bank, First National Digital Currency Bank, and Paxos Trust Company. This sequence—clear progress followed by calls for prudence—has amplified calls from industry observers and policymakers to align new models with robust regulatory guardrails.
As the regulatory dialogue intensifies, the broader banking lobby has amplified its push for Congress to act. Proposals such as the Digital Asset Market Clarity (CLARITY) Act have gained attention for attempting to curb the appeal of stablecoin rewards and other yield-bearing programs that could blur the line between traditional banking products and crypto offerings. At the same time, coverage of GENIUS Act proposals has underscored the tension between innovation and prudential supervision. The industry’s worry is that without a unified framework, chartered entities could be forced into a regulatory limbo where consumer protection and financial stability are not fully safeguarded.
While the ABA’s letter emphasizes caution, the OCC’s recent actions reflect a different facet of the ongoing balancing act: enabling regulated access to digital assets under a federal charter while attempting to avoid the full deposit-taking framework. The OCC’s stance has drawn support from some voices within the crypto sector who argue for clear, uniform standards that would prevent a fragmented patchwork of state-by-state approaches. The debate also intersects with ongoing discussions about how to treat banks and crypto similarly or differently, a point highlighted by industry and regulatory leaders alike. A separate OCC statement and related commentary have argued that there is no justification to treat banks and crypto differently; the underlying question remains how to translate those principles into enforceable, uniform rules across multiple agencies.
Warning after new crypto trust charters
The timing of the ABA’s intervention is notable: it follows the OCC’s conditional approvals announced earlier in December 2025 that would allow these firms to hold and manage customer digital assets under a federal umbrella while remaining out of the deposit-taking and lending business. The OCC described these structures as national trusts designed to segregate digital assets and provide custody capabilities without converting to traditional banking operations. The five charter recipients—Bitgo Bank & Trust, Fidelity Digital Assets, Ripple National Trust Bank, First National Digital Currency Bank, and Paxos Trust Company—represent a cross-section of the market and reflect a broader appetite to experiment with federal oversight in the crypto custody space. The OCC’s action signals a potential pathway for regulated custody of digital assets, even as lawmakers and industry groups push for clarifying legislation and more precise supervisory expectations.
The push for governance clarity is not happening in a vacuum. Industry participants and lawmakers alike have been weighing proposals like GENIUS Act and CLARITY Act, which seek to define the boundaries of crypto activities within the traditional banking regime and curb practices that could be mischaracterized as bank-like products without full bank regulation. The evolving regulatory mosaic poses a dilemma for firms seeking charters: how to align innovative custody models with a robust, predictable framework that ensures customer protection and systemic stability—without dampening the competitiveness and speed of financial-technology innovation.
As regulatory scoping continues to evolve, observers note that the OCC’s framework for conditional approvals to national trust charters could have meaningful implications for market structure, consumer safeguards, and the scope of permissible activities for non-deposit-taking digital asset custodians. The tension between fostering innovation and ensuring a resilient financial system remains at the heart of the debate. Several pieces of legislation and policy proposals that would influence this trajectory are already in circulation, reinforcing the sense that 2026 could be a critical year for how crypto custody and stablecoins are governed at the federal level.
Why it matters
For investors, the ongoing regulatory clarifications affect risk assessment and the perceived legitimacy of crypto custody solutions. A formal, well-defined regulatory framework could reduce ambiguity around the protections afforded to customer assets held by uninsured digital-asset trusts and influence risk pricing for associated products. For builders and operators, clear rules can help map out feasible business models that align with capital, governance, and risk-management expectations. And for policymakers, the interplay between GENIUS Act provisions, banking supervision, and securities/derivatives regulation underscores a key objective: ensuring that innovation remains aligned with financial stability and consumer protection.
From a market structure perspective, the debate highlights how custody and settlement infrastructures could evolve under federal oversight. If the OCC’s conditional trust charters become a common feature, watchers will be looking for transparency around capital requirements, resilience standards, and the safeguards that would prevent consumer confusion—especially around institutions that use “bank” in their names for branding purposes despite not engaging in traditional banking activities. The industry’s insistence on naming rules reflects a broader concern about trust and clarity in a landscape where digital assets can be held by entities operating under a federal umbrella but without full deposit-taking powers.
Meanwhile, the GENIUS Act and related proposals continue to shape the policy dialogue on stablecoins and digital assets within the U.S. financial system. As the regulatory math evolves, the market will be watching how agencies interpret and implement these concepts in real-world chartering decisions. The balancing act remains: enable responsible innovation in custody and settlement while preserving a robust, transparent, and enforceable supervisory regime that protects consumers and maintains market integrity.
What to watch next
- OCC’s formal response to the ABA comment letter and any adjustments to the proposed rulemaking timeline.
- Developments in GENIUS Act rulemaking and any accompanying guidance that clarifies obligations for crypto custody under national bank charters.
- Details on the five crypto firms granted conditional national trust charters, including milestones for capital, risk controls, and asset segregation.
- Legislative progress on the CLARITY Act and related measures that would influence stablecoin governance and disclosure requirements.
Sources & verification
- The ABA letter to the OCC regarding national bank chartering (PDF).
- OCC press release: conditional national trust bank approvals for Bitgo Bank & Trust, Fidelity Digital Assets, Ripple National Trust Bank, First National Digital Currency Bank, and Paxos Trust Company (nr-occ-2025-125.html).
- OCC updates on GENIUS Act-related rulemaking and related policy discussions cited in industry coverage.
- Cointelegraph reporting on the OCC’s stance toward treating banks and crypto equally and the broader lobbying around the GENIUS Act and related reforms.
What the ABA letter says, in context
The ABA’s position centers on prudence and transparency. The association argues that the OCC should resist rushing charter approvals for entities handling uninsured customer funds in crypto and stablecoin operations until the GENIUS Act rulemakings are fully defined and integrated into a coherent supervisory framework. It emphasizes that without a clear, comprehensive set of obligations, chartered entities could encounter undefined capital, operational resilience, and customer-protection standards. The letter calls for greater clarity on how capital and resilience benchmarks will be calibrated in conditional approvals and presses for tighter naming rules to prevent consumer confusion when entities use “bank” in their branding, despite not engaging in traditional banking activities. The overarching theme is to align innovation with robust safeguards and to keep deposit-empowered banks as the reference point for consumer protections and risk management.
Key figures and next steps
As the regulatory conversation continues, observers will be watching a trio of developments: the OCC’s formal responses to stakeholder comments, the progression of GENIUS Act rulemaking, and the practical implications of the five conditional charter approvals already granted. The dialogue around whether banks and crypto should be treated differently is likely to persist, but the current emphasis appears to be on ensuring that any new chartering framework provides explicit obligations and strong oversight. With policy and industry stakeholders navigating these questions, the coming months could define how crypto custody, stablecoin issuance, and related digital-asset activities are integrated into the U.S. banking system on a long-term, predictable basis.
Crypto World
Strategy to Push Preferred Stock to Boost Bitcoin Buys: CEO
Bitcoin treasury company Strategy will further lean on its preferred stock sales to acquire Bitcoin, shifting from its strategy of selling common stock, says CEO Phong Le.
“We will start to transition from equity capital to preferred capital,” Le told Bloomberg’s “The Close” on Wednesday.
Stretch (STRC) is Strategy’s perpetual preferred stock, launched in July, and is aimed at buyers looking for stability by offering an annual dividend of over 11%.
STRC is the company’s fourth perpetual preferred offering, launched to finance its Bitcoin (BTC) purchases. It’s an alternative to issuing new shares that dilute its stock price.

Le admitted that its preferred stock will “take some seasoning” and marketing to pitch traders on the offering, but added that “throughout the course of this year, we expect Stretch to be a big product for us.”
Strategy could restart offerings as STRC hits $100
STRC reclaimed its par value of $100 at the close of trading on Wednesday for the first time since mid-January, which Le said was the “story of the day.”
The stock had dipped below $94 earlier this month as Bitcoin crashed under $60,000, but with it now trading at par — the price Strategy has designated as its minimum — the company could again offer shares to fund more Bitcoin purchases.
Bitcoin has traded mostly flat over the last 24 hours at around $66,800, down from an intraday high of over $68,000.
Buying Bitcoin treasury rivals a “distraction”
Analysts have warned that the crypto treasury space is becoming crowded as companies compete for a small segment of traders, leading to some companies’ crypto holdings being worth more than the companies themselves.
Related: Saylor’s Strategy buys $90M in Bitcoin as price trades below cost basis
In that case, some analysts said that rival treasury firms could move to acquire underperforming companies to scoop up Bitcoin on the cheap, but Le said Strategy isn’t interested in making such a move.
“I think in any new market, whether it be electric cars or AI or SaaS software, you want to focus on your core product,” Le said. “I think it would be a distraction to go buy, at a discount to net asset value, another digital asset treasury company.”
Shares in Strategy (MSTR) ended trading on Wednesday down over 5% at $126.14.
Magazine: Bitget’s Gracy Chen is looking for ‘entrepreneurs, not wantrepreneurs’
Crypto World
Binance Completes $1B Bitcoin Conversion for SAFU Fund
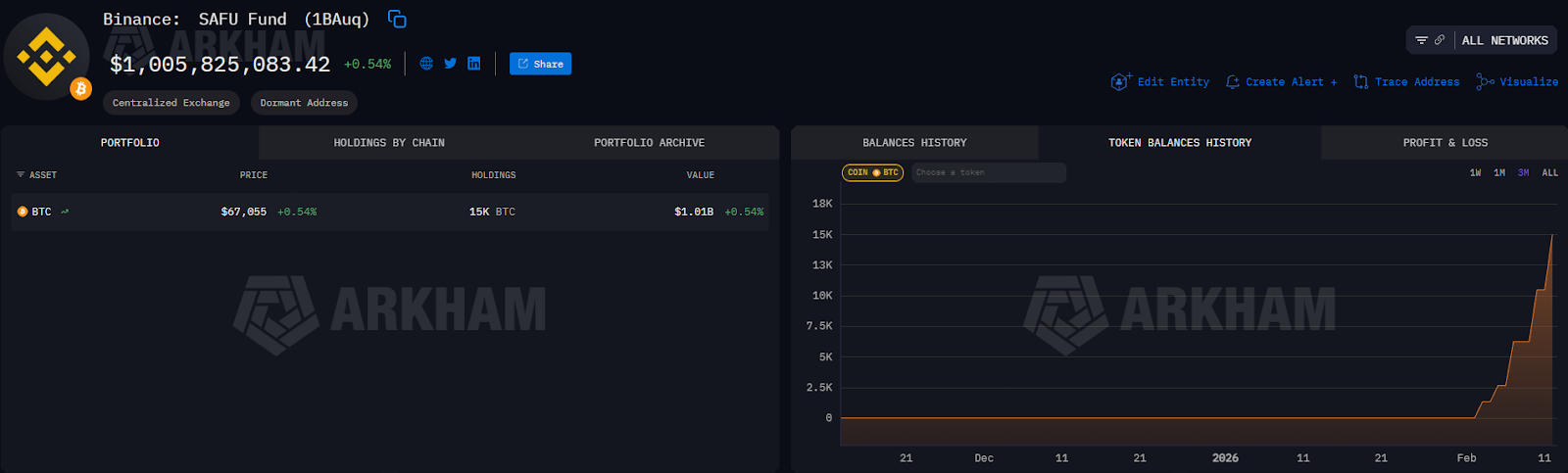
Binance completed the $1 billion Bitcoin conversion for its emergency fund, committing to holding Bitcoin as its core reserve asset.
Binance purchased another $304 million worth of Bitcoin (BTC) on Thursday, completing the conversion of $1 billion in Bitcoin for its Secure Asset Fund for Users (SAFU) wallet, according to Arkham data.
The fund now holds 15,000 Bitcoin, worth over $1 billion, acquired at an average aggregate cost basis of $67,000 per coin, Binance said in a Thursday X post.
“With SAFU Fund now fully in Bitcoin, we reinforce our belief in BTC as the premier long-term reserve asset.”
The last tranche of BTC came three days after Binance’s previous $300 million acquisition on Monday.

Related: Bitcoin’s $60K crash may mark halfway point of bear market: Kaiko
The exchange first announced it would convert its $1 billion user protection fund into Bitcoin on Jan. 30, initially pledging a 30-day window for the acquisitions, which were completed in less than two weeks.
The exchange said it would rebalance the fund if volatility pushes its value below $800 million.
Related: Bitcoin dips to $60K, TRM Labs becomes crypto unicorn: Finance Redefined
Crypto investor sentiment plunges to lowest levels on record
The conversion comes as broader market sentiment remains deeply negative.
Sentiment took another hit following Bitcoin’s brief correction below $60,000 on Feb. 5, plunging to five on Thursday — the lowest reading on record — signaling extreme fear among investors, according to data from alternative.me.
The index is a multifactorial measure of crypto market sentiment.

The industry’s leading traders by returns, tracked as “smart money,” are also hedging for more crypto market downside.
According to crypto intelligence platform Nansen, smart-money traders held a cumulative $105 million net short position in Bitcoin and were net short across most major cryptocurrencies, with Avalanche (AVAX) the only notable exception, recording $10.5 million in net long exposure.

Bitcoin’s correction also took a significant supply of tokens at a loss equaling to 16% of Bitcoin’s market cap, marking the highest pain point seen in markets since the implosion of algorithmic stablecoin issuer Terra in May 2022, wrote Glassnode in a Monday X post.
Yet in a silver lining to the correction, the market structure is showing early signs of stabilization, according to Dessislava Ianeva, dispatch analyst at digital asset platform Nexo.
“Derivative positioning remains cautious. Funding rates are neutral to slightly negative, reflecting subdued leverage demand, while open interest in native BTC terms has returned to early-February levels, suggesting stabilization rather than a renewed expansion phase,” the analyst told Cointelegraph.
Magazine: Bitget’s Gracy Chen is looking for ‘entrepreneurs, not wantrepreneurs’
Crypto World
Gen Z Open to Crypto for Valentine’s Day Dates: Survey

Gen Z Americans may be open to paying for dates with cryptocurrency, but most still aren’t putting digital coins where their hearts are, according to a January Pollfish survey commissioned by crypto exchange OKX.
The poll of 1,000 US adults found that 13% of Gen Z respondents said they have paid for a date using crypto, while many who haven’t said the main issue is practical: they don’t have a direct way to pay with crypto.
Interest extended beyond payments. 31% of Gen Z respondents said receiving crypto as a Valentine’s Day gift would be appealing, and 76% said financial literacy is an attractive trait in a partner, a reminder that for some daters, “knowing your numbers” can be more charming than knowing your zodiac sign.
Still, ownership appears to be a limiting factor. OKX told Cointelegraph that 29.5% of respondents said they currently own or previously owned crypto assets, suggesting that curiosity about crypto doesn’t automatically translate into daily use.
Gen Z flirts with crypto, but ease of use a problem
The gap between “open to it” and “actually did it” points to a familiar hurdle for crypto: in many everyday settings, it’s still easier to tap a card than to pay directly with a wallet.

The survey also found that two-thirds of respondents said financial literacy plays well in the dating marketplace, with Gen Z (76%) and Millennials (75%) showing the strongest support.
Familiarity with digital finance tools also carried weight. Between 52% and 55% of respondents said knowledge of digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies and digital wallets, can make someone more attractive as a potential partner.
But only 17% of respondents overall said holding digital assets makes someone more attractive, including 30% of millennials and 28% of Gen Z. The findings indicate that for younger cohorts, digital asset awareness is increasingly viewed as part of broader financial competence.
Related: Valentine’s nightmare? Romance scams remain a $1B honeypot for criminals
Romance scams kill the mood
Crypto has also shown up in dating headlines for less romantic reasons. In 2024, the US Federal Trade Commission issued a consumer alert over rising crypto-related romance scams. Canadian authorities issued similar warnings, as crypto scammers flooded dating apps.
The rise of artificial intelligence also heightened the risks of romance scams in crypto. In 2025, scammers have increasingly used chatbots and deepfakes to manipulate victims emotionally and financially.
Perception has also been mixed. While the OKX survey showed that some are attracted to crypto, a survey by the Date Psychology blog in 2024 found that women ranked crypto among the least attractive male hobbies.
Magazine: Crypto loves Clawdbot/Moltbot, Uber ratings for AI agents: AI Eye
Crypto World
zkME Technology wins $20,000 PitchFest prize at Consensus Hong Kong


A DePin company that has 3.5 million users and is currently raising for a Series A won this year’s PitchFest at Consensus Hong Kong.
Hong Kong-based zkME Technology won the $20,000 prize after a grueling two-day event where competitors positioned their solutions as key for various problems in the crypto sector.
“If DeFi really wants to become mainstream, this is the only solution,” said founder and CEO David Alexander Scheer.
Scheer told CoinDesk that 2026 is going to be “the year in which the lines between TradFi and DeFi converge” while remaining grounded, saying that Monday morning will be “back to work.”
The competition was judged by Alasdair Foster, CEO of Bullish Capital Management (the venture capital arm of CoinDesk parent Bullish Global); Augie Ilag, CMT Digital’s Head of Asia; Fabric Ventures co-founder Richard Muirhead and Ella Zhang, head of YZi Labs.
The three other finalists were Switzerland-based tokenized real world asset company OnchainLabs, U.S.-based DePin firm Coinbax and Hong Kong-based Hubble AI.
In the runner-up spot was Hubble AI, a company that lets users build bespoke trading strategies via prompts to its AI model.
“We provide infrastructure, not strategy,” the company’s CEO said during the pitch, responding to a question about how public the AI’s trading capability would be.
Onchain Labs co-founder Florian Ehrbar’s pitched Engage, a platform that lets crypto firms offer tokenized gold solutions and answered questions from the judges on revenue and user experience.
Peter Glyman, founder of CEO of Coinbax, explained how his company creates the infrastructure and smart contracts for crypto firms and has plans to rollout a mainnet in Q2 of this year
There were eight other semi-finalists including London-based tokenized real world asset project Agant, Barcelona-based Brickken, Hong Kong-based Satsume Labs, BetterX and OKcontract Labs from Singapore, Malaysian-based Morpheus AI, Japanese-based PokeSeed and Dubai-based Synnax Technologies FZCO.
Crypto World
LINEA price is up 24%: here’s what analysts predict could happen next


- LINEA has surged 24% amid strong social engagement and trading volume.
- The launch of trustless agents and ERC‑8004 has boosted ecosystem adoption and interest.
- The immediate support in case of a pullback lies at $0.0037, while the immediate resistance is at $0.00413.
LINEA has surged by 24% in just 24 hours, marking one of its strongest short-term rallies in recent months.
The token is currently trading at $0.003805, recovering from a recent low of $0.002987.
This price jump comes after weeks of consolidation, where LINEA had been hovering in the $0.003–$0.004 range.
The sudden momentum signals a possible shift in market sentiment.
Recent catalysts driving the rally
One of the key drivers behind this surge is LINEA’s growing presence in the crypto community.
Social engagement metrics have shown that LINEA has outperformed other Layer‑2 projects in terms of mentions, interactions, and overall online attention.
This heightened activity appears to correlate with price movement, suggesting that increased visibility and investor interest are fueling the recent uptick.
Technical indicators also support the bullish momentum, with LINEA recently breaking above a multi-week resistance zone around $0.00370.

This breakout coincided with the token reclaiming its 20-day exponential moving average (EMA), which traders often see as a signal for short-term trend reversal.
Furthermore, momentum indicators, including the Relative Strength Index (RSI), are approaching overbought levels, indicating strong buying pressure but also cautioning that a brief pullback or consolidation could occur.
In addition, volume trends show a notable increase in trading activity, further reinforcing that the market is responding to both sentiment and technical factors.
Beyond market activity, developments in LINEA’s ecosystem are adding to optimism.
The launch of trustless agents powered by ERC‑8004 introduces verifiable identity and portable reputation for AI-driven smart contracts.
This feature positions LINEA as more than just a Layer‑2 scaling solution, highlighting its potential as a platform for next-generation decentralised applications.
Analysts suggest that these technological milestones could attract developers and new users, supporting both short-term interest and long-term adoption.
LINEA price forecast
Looking ahead, analysts predict that LINEA could continue to show volatility but remain within a defined range.
The token’s support level is around $0.00370, which traders will watch closely to gauge whether the recent breakout can hold.
Immediate resistance is near $0.00413, aligning with longer-term moving averages.
If LINEA breaks through this level, it could test higher targets, with analysts projecting potential upside toward $0.0939 by the end of the year.
Conversely, a failure to hold support could push the price down toward $0.0308, highlighting the token’s potential for significant swings.
Traders should monitor volume, sentiment, and key technical levels to navigate this highly dynamic market.
Overall, LINEA’s combination of social momentum, ecosystem development, and short-term bullish technical signals suggests that the token remains one to watch.
While risks remain, the current rally and forward-looking developments provide a compelling case for both traders and investors looking for opportunities in the Layer‑2 crypto space.
Crypto World
RENDER Down 76% From Peak While Processing 1.5M Frames Monthly: Capitulation or Opportunity?

TLDR:
- RENDER processes record 1.5M frames monthly while token crashes 76% to $1.30 from May 2025 peak of $5.50
- Network burned 1.04M tokens with 35% of all-time frames rendered in 2025 alone despite brutal price action
- AI rendering launch and Dispersed.com platform expand services while trading volume collapses 87% in 30 days
- 5,600 active GPU nodes and partnerships with Nvidia, Apple signal strong fundamentals amid $671M market cap
RENDER token crashes to $1.30 after plummeting 76% from its May 2025 high of $5.50, creating a stark disconnect between price action and explosive network growth.
The cryptocurrency’s market capitalization sits at $671 million following a 66% collapse from previous peaks, while the platform processes record-breaking 1.5 million frames monthly.
Trading volume of $28.7 million reflects an 87% monthly decline, yet network fundamentals surge to unprecedented levels across multiple metrics.
Price Crashes While Network Usage Explodes
The contrast between price performance and network activity reaches extreme levels. RENDER bleeds across all timeframes with a 3.59% drop in 24 hours, 17.63% decline over seven days, and catastrophic 49.97% collapse in 30 days.
Meanwhile, the network hit a monumental milestone of 67 million total frames rendered since inception. The data reveals something remarkable: 35% of all-time frames were processed in 2025 alone, making it the strongest year in platform history.
Network infrastructure expanded dramatically during the price decline. Active GPU nodes grew to 5,600 contributors powering the distributed rendering network.
Token burns reached 1.04 million RENDER tokens through network fee mechanisms. Monthly frame processing hit an all-time record of 1.5 million, demonstrating actual usage growth while token holders suffer massive losses. The divergence between utility metrics and price creates a puzzling scenario for market participants.
Social indicators suggest accumulation despite the carnage. Sentiment analysis shows 80% positive outlook among community members.
Social dominance spiked 158% while AltRank climbed 270 positions in just 30 days. Volume collapse of 87% over the past month signals capitulation-level selling or complete trader exhaustion. The question becomes whether this represents final washout or further downside ahead.
GPU demand for artificial intelligence workloads surges globally while RENDER prices tank. The platform sits at the intersection of two massive narratives: AI infrastructure and decentralized physical infrastructure networks.
Enterprise-grade hardware onboarding through RNP-021 brings NVIDIA H200 and AMD MI300X chips to the network.
These developments target professional-grade computational workloads worth billions in traditional cloud markets.
AI Expansion Launches as Token Holders Face Pain
RENDER launched AI rendering capabilities on January 26, 2026, marking a strategic pivot beyond traditional graphics rendering.
The Dispersed.com platform went live, aggregating global GPU resources for machine learning and AI model training.
This infrastructure directly addresses exploding demand for computational power in the AI sector. Partnerships with Nvidia, Apple, and Stability AI validate the technical approach and market positioning.
The fundamentals tell an insane story of growth. Processing 1.5 million frames monthly while burning over one million tokens creates deflationary pressure amid increasing utility. Network activity proves real users pay real fees for real computational work.
Enterprise GPU integration brings institutional-grade hardware to a decentralized network. The technical roadmap advances with Octane 2026 integration scheduled and RenderCon 2026 event planned.
Price action tells a brutal counter-narrative. The 76% collapse from $5.50 to $1.30 destroys holder value across the board. Market capitalization evaporated from roughly $1.9 billion to $671 million in less than a year.
Trading volume contraction suggests either accumulation by strong hands or complete market disinterest. Traditional investors face cognitive dissonance: fundamentals scream strength while charts scream weakness.
The setup creates a classic value versus momentum dilemma. Bears point to relentless selling pressure and macro headwinds crushing all risk assets.
Bulls highlight record network usage, strategic partnerships, and positioning in high-growth AI markets. The 87% volume decline could signal final capitulation or prolonged bear market ahead.
Either scenario presents radically different outcomes for current price levels and future potential.
Crypto World
Strategy CEO Seeks More Preferred Stock to Fund Bitcoin Buys

Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) treasury company Strategy will lean more heavily on its perpetual preferred stock program to finance additional Bitcoin purchases, moving away from a reliance on issuing common stock. CEO Phong Le outlined the pivot during Bloomberg’s The Close, explaining that the company intends to shift from equity capital to preferred capital as a core funding channel. The move centers on Stretch (STRC), Strategy’s perpetual preferred offering launched in July, which targets investors seeking steadier returns through an annual dividend north of 11%. The instrument has been positioned as an alternative to diluting the company’s stock while it continues to amass BTC holdings. The development comes as Strategy eyes a broader rollout of STRC later in the year, signaling a potential shift in how corporate treasuries wield equity-like instruments to grow crypto reserves.
Le emphasized that the preferred stock will “take some seasoning” and marketing before traders fully embrace the product, but he remained upbeat about STRC’s trajectory. He told The Close that, in the course of this year, Stretch could become a cornerstone offering for Strategy as it seeks to fund further Bitcoin acquisitions. The company’s financing strategy has repeatedly leaned on STRC to finance BTC purchases since its inception, providing a mechanism to accumulate digital assets without triggering immediate dilution of common equity. The approach is part of a broader class of crypto treasuries that use perpetual preferreds to balance income generation with asset accumulation.
STRC, which was introduced to market as Strategy’s fourth perpetual preferred instrument, was explicitly designed to appeal to buyers seeking long-term stability. It carries an annual dividend and is marketed as a capital-structure play rather than a plain equity raise. The instrument’s structure aims to deliver predictable income while enabling Strategy to keep building its Bitcoin stack. The narrative around STRC has fed into a wider discussion about how corporate treasuries are managing liquidity, risk, and exposure to crypto markets without immediately triggering shareholder dilution. Critics, however, have warned that the space has grown crowded and that some companies’ holdings now exceed their market capitalization, raising questions about concentration risk and governance.
Strategy could restart offerings as STRC hits $100
In late trading, STRC regained its par value of $100 for the first time since mid-January, a development Le described as the “story of the day.” The move back to par could unlock renewed appetite for STRC issuances, potentially enabling Strategy to fund additional Bitcoin purchases without issuing new common shares. Earlier this month, the stock traded under $94 when Bitcoin briefly slid below $60,000, underscoring how BTC price dynamics can influence the attractiveness of STRC as a funding mechanism. With Bitcoin trading roughly around $66,800, the market environment remains relatively constructive for asset accumulation through alternative financing vehicles, even as volatility lingers on near-term horizons.
Bitcoin’s price trajectory has been steady but not spectacular in the immediate term, hovering around the mid-$66,000s after peaking above $68,000 intraday. The price backdrop supports narratives that corporate treasuries can pursue more disciplined, income-generating avenues for finance, while still chasing the long-term upside of BTC exposure. The evolving dynamics around STRC and similar instruments come as crypto returns and risk sentiment influence decisions across corporate balance sheets, with issuers seeking to optimize cost of capital and dilution concerns in parallel.
Buying Bitcoin treasury rivals a “distraction”
Analysts have cautioned that the crypto treasury space is becoming crowded as several firms vie for a relatively small pool of traders and investors. In a crowded market, some observers warn that corporate treasuries could face diminishing marginal value as more players announce similar funding structures. The fragmentation raises questions about price discovery, liquidity, and the true strategic value of perpetual preferreds in maintaining BTC accumulation over the long run.
Related: Saylor’s Strategy buys $90M in Bitcoin as price trades below cost basis
Beyond pure competition concerns, Le dismissed the notion that Strategy would pursue aggressive consolidation through acquisitions of underperforming peers. He argued that focusing on the core STRC product is preferable to pursuing opportunistic takeovers, likening the approach to other technology or finance markets where companies emphasize product development over opportunistic acquisitions. “In any new market, whether it be electric cars or AI or SaaS software, you want to focus on your core product,” Le said. “It would be a distraction to go buy, at a discount to net asset value, another digital asset treasury company.”
As the wider market digests these developments, Strategy’s stock, traded as MSTR, closed down more than 5% at $126.14, reflecting a sentiment that remains cautious in the near term even as STRC gains traction. The price action underscores the delicate balance investors weigh between funded BTC accumulation and the potential dilution risk associated with new equity or preferred stock offerings. The discussion around STRC also feeds into broader debates about how corporate treasuries manage risk, yield, and the opportunity cost of capital when BTC becomes a strategic asset rather than a speculative instrument.
To contextualize the conversation, industry observers have pointed to a broader trend: as more companies adopt crypto treasuries, the market could see consolidation through mergers and acquisitions or more aggressive share-issuing strategies when faced with capital needs. Yet Strategy’s leadership seems intent on refining its preferred-stock route rather than chasing rapid expansion through bolder balance-sheet moves. The decision to prioritize a steady, dividend-bearing instrument aligns with a philosophy of measured growth and risk control, even as BTC remains a volatile, high-beta asset that can swing strategic outcomes in a single trading session.
In parallel, the crypto treasury sector has become a focal point for investors seeking visibility into how corporate treasuries navigate liquidity, risk, and regulatory constraints. Analysts suggest that while the category has matured in some respects, it remains a moving target shaped by Bitcoin’s price action, macroeconomic conditions, and evolving market structure. The emergence of streaming discussions around STRC and similar products indicates a willingness among issuers to experiment with bespoke capital-structure solutions as legitimate means of funding crypto purchases. The question remains: how durable will these instruments prove in different market regimes, and will investor demand stabilize as more issuers publish performance data and governance disclosures?
Why it matters
For investors, Strategy’s pivot toward preferred stock as a primary funding mechanism highlights a shift in how crypto treasuries can balance income with exposure to Bitcoin outright. The STRC instrument promises yield and stability, potentially reducing the pressure to issue more common stock and mitigate dilution. If STRC continues to perform and attract sufficient investor interest, Strategy could emerge as a case study for how treasuries combine traditional fixed-income features with crypto exposure to create a hybrid financing model.
From a market perspective, the development reinforces the idea that institutional players are increasingly treating BTC as a fundamental corporate asset rather than a speculative risk. The use of perpetual preferreds could provide a template for other issuers seeking to augment BTC reserves without triggering immediate equity dilution. Yet the crowded nature of the space also invites closer scrutiny of governance, risk management, and the alignment of incentives between a company’s treasury activities and shareholder interests. The balance between discipline in funding and the pursuit of BTC upside remains a central tension, one that Strategy appears intent on navigating with caution and clarity.
For builders and researchers, the case raises questions about the transparency of crypto-treasury deals, the long-term performance of perpetual preferreds in crypto contexts, and how such instruments should be regulated as they gain traction in mainstream finance. The evolving narrative around STRC and related products could influence product design, disclosure standards, and investor education as more firms explore innovative capital-structure solutions to support digital-asset accumulation.
What to watch next
- Progress in STRC marketing and adoption, including any new issuances or marketing milestones (dates to watch).
- Bitcoin price movements and any corresponding shifts in Strategy’s BTC purchase cadence or balance-sheet disclosures.
- Regulatory developments affecting corporate crypto treasuries and preferred-stock financings.
- Q3 and Q4 earnings context for Strategy (or related entities) that could reflect changes in capital-raising strategies.
- Market sentiment indicators for crypto treasuries, including liquidity and trading volumes for perpetual-preferred products.
Sources & verification
- Bloomberg – Phong Le interview on The Close discussing Strategy’s move from equity capital to preferred capital and STRC’s role (YouTube link provided in original coverage).
- Cointelegraph – Strategy raises $2B in preferred stock to back Bitcoin purchases (article detailing STRC launch and purpose).
- Cointelegraph – Why Saylor’s Strategy keeps buying Bitcoin: Long-term investment rationale and treasury approach.
- Cointelegraph – Saylor/Strategy buys $90M in Bitcoin as price trades below cost basis (context on BTC purchases and treasury activity).
- Cointelegraph – Crypto treasury more merger/acquisition cycle mature (analysis of competitive dynamics in the treasury space).
What to watch next
Market development and official disclosures in the coming quarters will be critical to assess STRC’s effectiveness as a funding tool and Strategy’s broader strategy for growing its BTC holdings through preferred-stock issuances.
Crypto World
Bankers Urge OCC to Slow Crypto Trust Bank Charters

The American Bankers Association (ABA) is urging the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) to slow its approval of national trust bank charters for crypto and stablecoin firms until the regulatory landscape under the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for US Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act is clearer.
In a Wednesday comment letter on the OCC’s national bank chartering notice of proposed rulemaking, the trade group warned that recent and future applicants engaged in stablecoin and digital asset activities face still‑unsettled oversight from multiple federal and state regulators.
The ABA said that the OCC should not advance applications where an institution’s full regulatory obligations, including under forthcoming GENIUS Act rulemakings, are not yet fully defined.
The association warned that uninsured, digital asset‑focused national trusts raise unresolved safety and soundness, operational and resolution issues, particularly around the segregation of customer assets, conflicts of interest and cybersecurity.
Related: OCC boss says ‘no justification’ to judge banks and crypto differently
It also cautioned that national trust charters could be used to avoid registration and scrutiny by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) when firms engage in activities that would otherwise trigger securities or derivatives regulation.

The ABA urged the OCC to be “patient,” resist applying traditional timing expectations to these applications, and ensure each charter applicant’s regulatory responsibilities “come fully into view” before moving applications forward.
The association further called for greater transparency around how the OCC calibrates capital, operational and resilience standards in conditional approvals for crypto‑related charters, and pressed the agency to tighten naming rules so that limited‑purpose trust banks that are not engaged in the business of banking cannot use “bank” in their names.
That, it argued, would reduce the risk of consumer confusion about the status and safety of obligations at uninsured entities.
Related: Stablecoin rewards provisions face industry test in Senate crypto bill
Warning after new crypto trust charters
The intervention comes less than two months after the OCC granted conditional national trust bank approvals to five crypto firms: Bitgo Bank & Trust, Fidelity Digital Assets, Ripple National Trust Bank, First National Digital Currency Bank, and Paxos Trust Company.
On Dec. 12, 2025, the OCC greenlighted a path for these companies to hold and manage customer digital assets under a federal charter while remaining outside the deposit-taking and lending business.
The same banking lobby is also pressing Congress, through pending crypto market structure legislation such as the Digital Asset Market Clarity (CLARITY) Act, to curb stablecoin rewards, contending that yield‑bearing stablecoins and affiliate “rewards” programs would function as bank‑like products without being subject to the full bank regulatory regime.
Magazine: When privacy and AML laws conflict — Crypto projects’ impossible choice
Crypto World
Will PIPPIN price crash after rallying 200% this week?
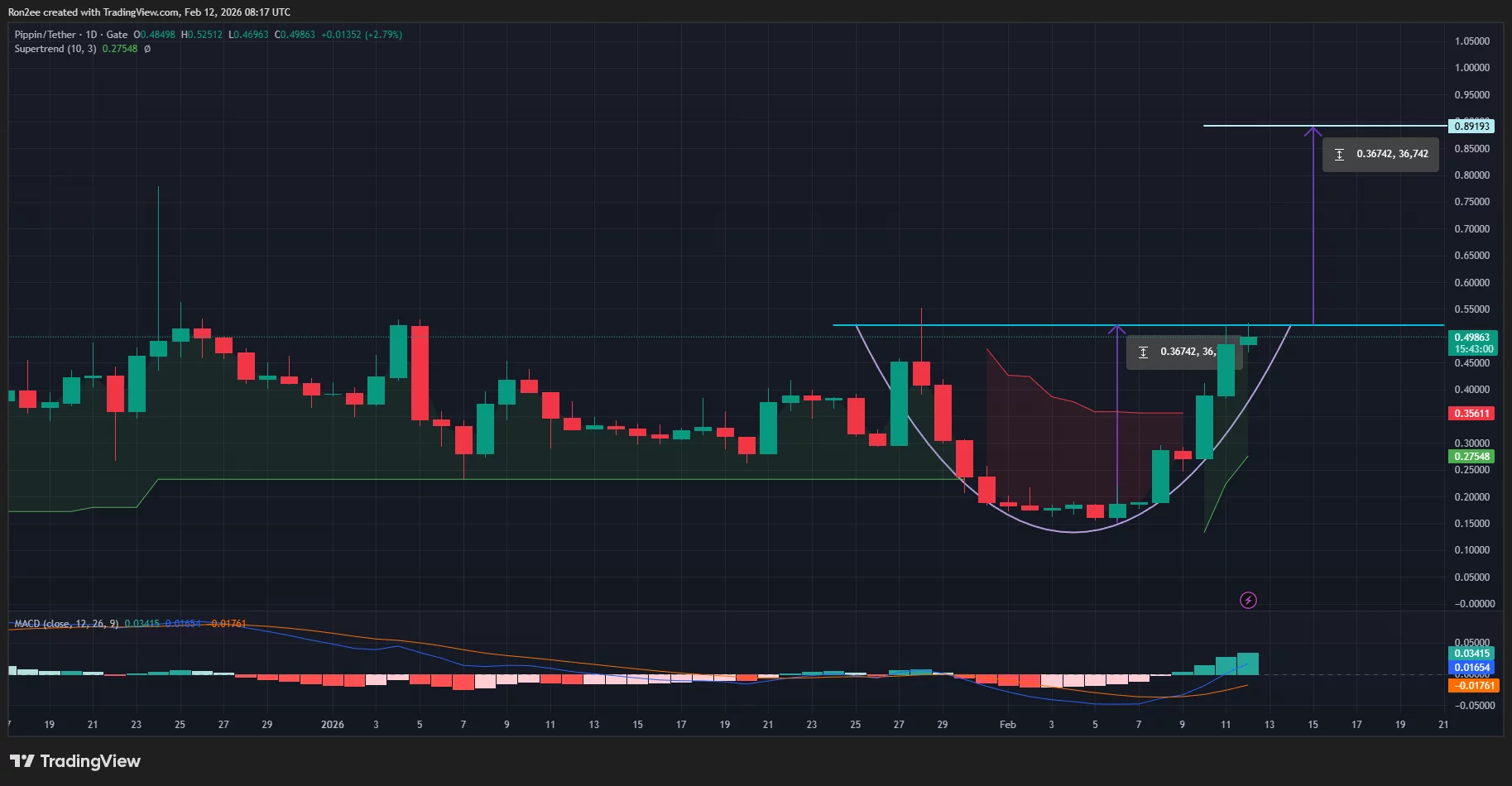
PIPPIN price has shot up nearly 200% over the past week, driven by sharp demand from futures traders. Is the meme coin set to see more gains, or will it crash?
Summary
- PIPPIN price rallied 200% over the past week, primarily driven by a spike in speculative trading.
- The meme coin has confirmed a rounded bottom pattern on the daily chart.
According to data from crypto.news, the Pippin (PIPPIN) price rallied over 200% in the past 7 days to a high of $0.52, which is roughly 7% short of breaking past its previous all-time high of $0.55 hit last month.
The PIPPIN rally appears to be mostly fueled by increased speculative activity, as traders aggressively opened bullish positions in the derivatives market, a trend common among high-volatility meme coins where momentum is often driven by leverage rather than fundamental developments.
Data from CoinGlass shows that PIPPIN futures open interest has jumped to an all-time high of $217 million, nearly four times the amount recorded nearly a week ago. At the same time, the long/short ratio stood above 1, suggesting more investors were betting on further price increases.
Open Interest reflects the total number of outstanding derivative contracts that have not been settled. When a surge in Open Interest comes along with the price rise of an asset, it indicates new money entering the market.
Meanwhile, the aggregated funding rate was positive at press time at 0.0070%, which shows that long position holders were paying fees to short sellers, conditions that help support continued upward momentum.
It should, however, be noted that PIPPIN’s rally came without the backing of any major news or development from the project’s team. Its official X account has not posted anything since August last year.
Despite this lack of official communication, the retail sentiment surrounding the token has remained bullish, as seen in CoinMarketCap.
Another point of concern is the market-wide downturn fueled by Bitcoin’s underperformance over the past trading sessions. Crypto investors are currently spooked by concerns over another U.S. government shutdown and uncertainty over Fed policy direction.
On the daily chart, PIPPIN price appears to be forming the cup of a multi-week cup and handle pattern, which has been developing since late January.
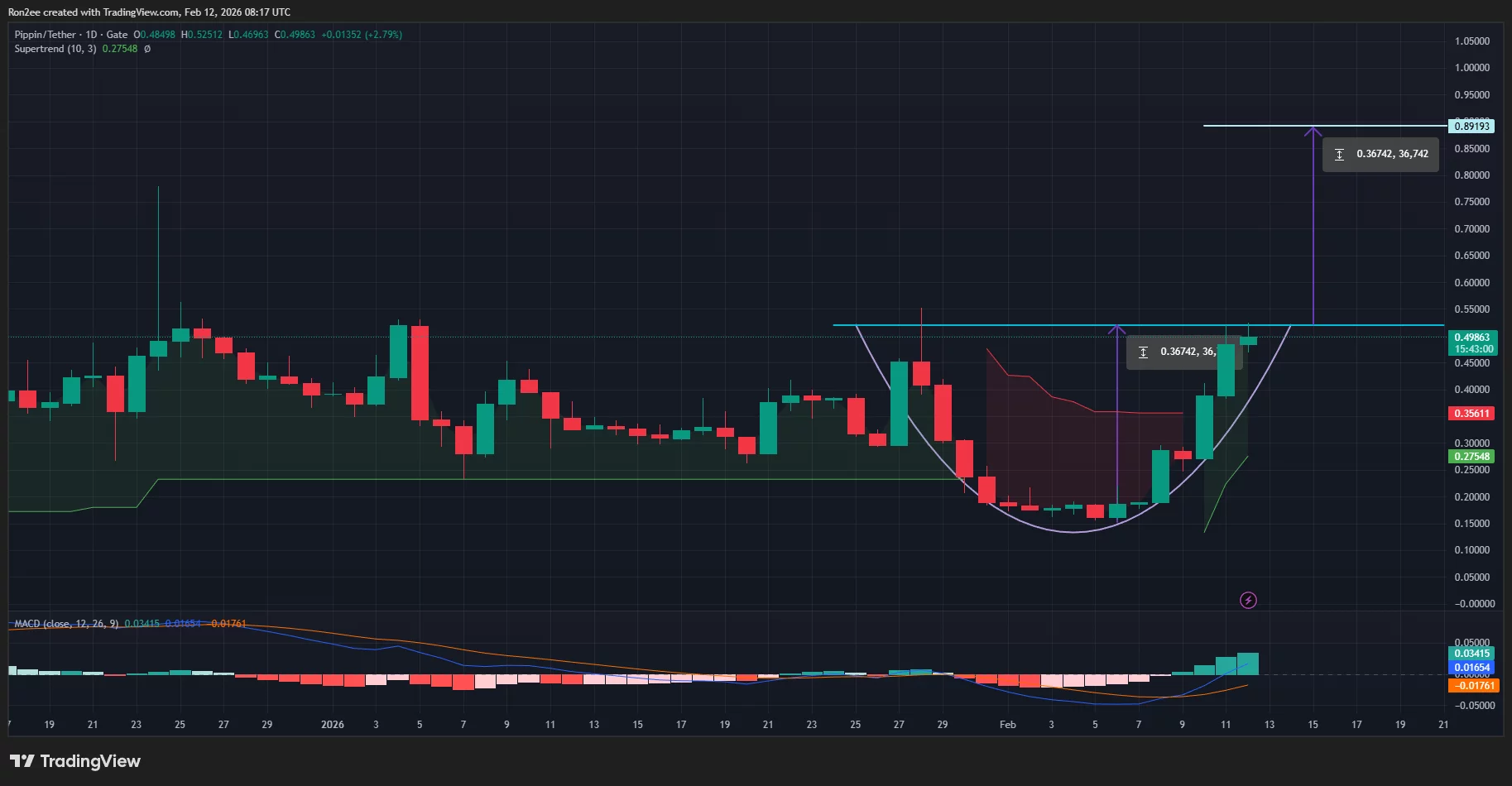
The cup and handle pattern is one of the most bullish continuation patterns that often signals an existing uptrend is likely to resume after a period of consolidation. The cup in itself is also formed of a rounded bottom pattern, which is yet another bullish indicator by itself.
At press time, the PIPPIN price had already broken above the neckline of the rounded bottom formed.
Considering this, the Solana-based meme coin could likely continue to be in an uptrend, with the path of least resistance appearing to be a bullish move to new highs around $0.89, calculated by adding the height of the rounded bottom formed to the point at which the price crossed the neckline.
Looking at technical indicators also gives us a grounded view of such a bullish forecast. Notably, the supertrend indicator has flashed green while the MACD lines have pointed upwards, both signs that bulls still have significant control over the market price action.
Unless the current upward momentum is hampered by macroeconomic headwinds, PIPPIN’s technical breakout is expected to serve as a bullish catalyst.
Disclosure: This article does not represent investment advice. The content and materials featured on this page are for educational purposes only.
-

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoWhy Israel is blocking foreign journalists from entering
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoJD Vance booed as Team USA enters Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
 Business4 days ago
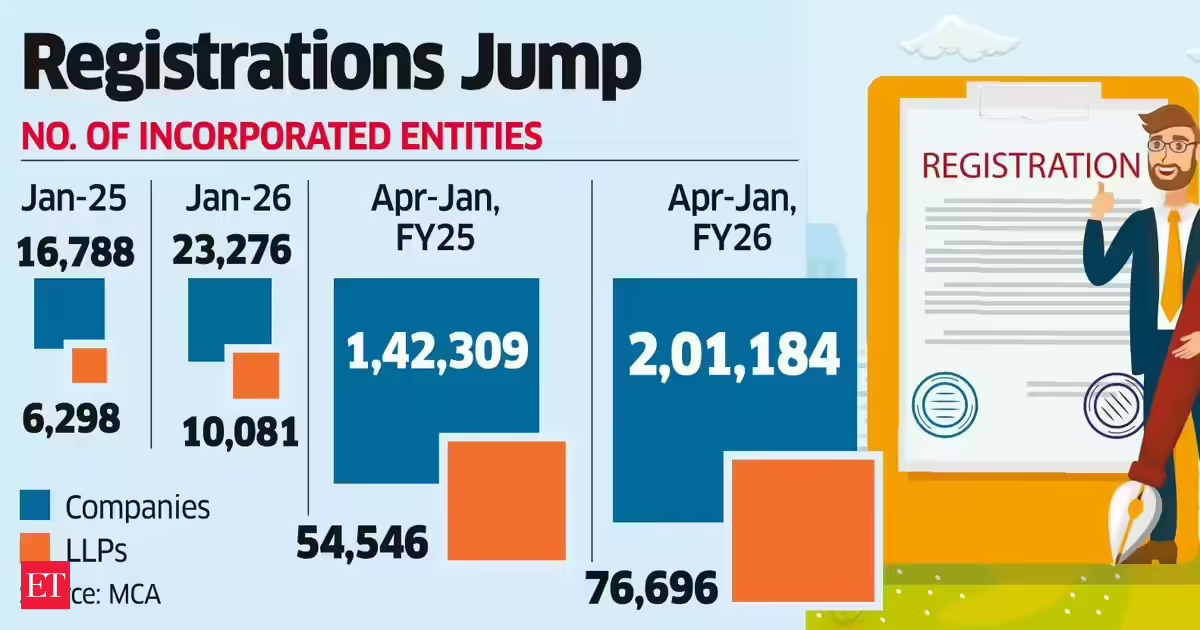
Business4 days agoLLP registrations cross 10,000 mark for first time in Jan
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-
 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoFirst multi-coronavirus vaccine enters human testing, built on UW Medicine technology
-

 Sports10 hours ago
Sports10 hours agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCostco introduces fresh batch of new bakery and frozen foods: report
-

 Tech1 day ago
Tech1 day agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Team GB’s Mia Brookes through to snowboard big air final, and curling pair beat Italy
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoBenjamin Karl strips clothes celebrating snowboard gold medal at Olympics
-
Sports5 days ago
Former Viking Enters Hall of Fame
-

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoThe Health Dangers Of Browning Your Food
-
Sports6 days ago
New and Huge Defender Enter Vikings’ Mock Draft Orbit
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoJulius Baer CEO calls for Swiss public register of rogue bankers to protect reputation
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoSavannah Guthrie’s mother’s blood was found on porch of home, police confirm as search enters sixth day: Live
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoQuiz enters administration for third time
-
 Crypto World11 hours ago
Crypto World11 hours agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-

 Video6 hours ago
Video6 hours agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-

 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month










