Crypto World
AI Security, Governance & Compliance Solutions Guide

Artificial Intelligence is no longer confined to innovation labs; it is now production-grade infrastructure powering credit underwriting, healthcare diagnostics, fraud detection, supply chain optimization, and generative enterprise copilots. As enterprises scale AI adoption, the need for advanced AI security services becomes critical to protect sensitive data, proprietary models, and distributed AI infrastructure. AI systems directly influence revenue decisions, risk exposure, regulatory standing, operational efficiency, customer trust, and brand reputation. Yet as adoption accelerates, so do the risks. AI expands the enterprise attack surface, increases regulatory complexity, and raises ethical accountability, making structured enterprise AI governance essential for long-term stability. Traditional IT security models cannot protect adaptive, data-driven systems operating across distributed environments.
To scale responsibly, organizations must implement structured and robust AI governance solutions, proactive AI risk management services, and integrated AI compliance solutions, all grounded in the principles of responsible AI development. Achieving this level of security, transparency, and regulatory alignment requires collaboration with a trusted, secure AI development company that understands the technical, operational, and compliance dimensions of enterprise AI transformation.
Why AI Introduces an Entirely New Category of Enterprise Risk ?
Artificial Intelligence is not just another layer of enterprise software; it represents a fundamental shift in how systems operate, decide, and evolve.
Traditional software systems are deterministic. They:
- Execute predefined logic
- Produce predictable, repeatable outputs
- Change only when developers modify the code
AI systems, however, operate differently. They:
- Learn patterns from historical and real-time data
- Continuously adapt through retraining
- Generate probabilistic, not guaranteed, outputs
- Process unstructured inputs such as text, images, and voice
- Evolve over time without explicit rule-based programming
This dynamic behavior introduces a new and complex category of enterprise risk.
1. Decision Risk
AI systems can produce inaccurate or biased outcomes due to flawed training data, insufficient validation, or model drift. Since decisions are probabilistic, even high-performing models can fail under edge conditions; impacting revenue, customer trust, or compliance.
2. Security Risk
AI models are high-value digital assets. They can be manipulated through adversarial attacks, extracted via repeated API queries, or compromised during training. Unlike traditional systems, AI introduces model-level vulnerabilities that require specialized protection.
3. Regulatory Risk
AI-driven decisions—particularly in finance, healthcare, insurance, and hiring—may unintentionally violate compliance regulations. Without structured oversight, organizations face legal scrutiny, fines, and operational restrictions.
4. Ethical & Reputational Risk
Biased or opaque AI decisions can trigger public backlash, regulatory investigations, and long-term brand damage. Ethical lapses in AI are not just technical failures—they are governance failures.
5. Operational Risk
AI performance can silently degrade over time due to data drift, environmental changes, or shifting user behavior. Unlike traditional systems that fail visibly, AI models may continue operating while gradually producing unreliable outputs.
Because AI systems function with varying degrees of autonomy, failures are often subtle and delayed. By the time issues surface, financial, regulatory, and reputational damage may already be significant.
This is why AI risk must be managed differently and more proactively than traditional enterprise software risk.
AI Security: Protecting Data, Models, and Infrastructure
AI security is not limited to perimeter defense or endpoint protection. It requires safeguarding the entire AI lifecycle from raw data ingestion to model deployment and continuous monitoring. Enterprise-grade AI security services are designed to protect not just systems, but the intelligence layer itself.
A secure AI architecture begins with the foundation: the data pipeline.
Layer 1: Securing the Data Pipeline
AI models depend on vast volumes of data flowing through ingestion, preprocessing, labeling, training, and storage environments. If this pipeline is compromised, the model’s integrity is compromised.
Key Threats in AI Data Pipelines
Data Poisoning: Attackers deliberately inject malicious or manipulated data into training datasets to influence model behavior, potentially embedding hidden vulnerabilities or bias.
Data Drift Manipulation: Subtle, gradual changes in incoming data can alter model outputs over time, leading to performance degradation or skewed predictions.
Unauthorized Data Access: Training datasets often include sensitive financial, healthcare, or personal information. Weak access controls can result in data breaches or regulatory violations.
Synthetic Data Injection: Maliciously generated or low-quality synthetic data may distort learning patterns and corrupt model accuracy.
Deep Mitigation Strategies
A mature AI security framework incorporates layered safeguards, including:
- End-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Secure, segmented data lakes with strict access control policies
- Dataset hashing and tamper-evident logging mechanisms
- Comprehensive data lineage tracking to trace the dataset origin and transformations
- Role-based access control (RBAC) for training and experimentation environments
- Differential privacy techniques to prevent memorization of sensitive data
- Federated learning architectures for privacy-sensitive industries
Data integrity validation is not optional; it is the bedrock of trustworthy AI. Without a secure data foundation, even the most advanced models cannot be considered reliable, compliant, or safe for enterprise deployment.
Layer 2: Model Security & Integrity Protection
While data is the foundation of AI, the model itself is the strategic core. Trained AI models represent years of research, proprietary algorithms, curated datasets, and competitive advantage. They are high-value intellectual property assets and increasingly attractive targets for cybercriminals, competitors, and malicious insiders.
Unlike traditional applications, AI models can be attacked both during training and after deployment. Securing model integrity is therefore a critical component of enterprise-grade AI risk management services.
Advanced AI Model Threats
Adversarial Attacks: These attacks introduce subtle, often imperceptible perturbations into input data, such as minor pixel modifications in images or slight token manipulation in text that cause the model to produce incorrect predictions. In high-stakes environments like healthcare or autonomous systems, such manipulations can lead to catastrophic outcomes.
Model Extraction Attacks: Attackers repeatedly query publicly exposed APIs to approximate and replicate a proprietary model’s behavior. Over time, they can reconstruct a functionally similar model, effectively stealing intellectual property without breaching internal systems directly.
Model Inversion Attacks: Through systematic querying and output analysis, attackers can infer or reconstruct sensitive data used during training posing serious privacy and regulatory risks, particularly in healthcare and finance.
Backdoor Attacks: Malicious actors may insert hidden triggers into training data. When activated by specific inputs, these triggers cause the model to behave unpredictably or maliciously while appearing normal during testing.
Prompt Injection Attacks (Large Language Models): For generative AI systems, attackers can manipulate prompts to override guardrails, extract confidential information, or bypass operational restrictions. Prompt injection is rapidly becoming one of the most exploited vulnerabilities in enterprise LLM deployments.
Enterprise-Grade Model Protection Controls
Professional AI risk management services and advanced AI security services deploy multi-layered defensive strategies, including:
- Red-team adversarial testing to simulate real-world attack scenarios
- Robustness training and gradient masking techniques to reduce model sensitivity to adversarial perturbations
- Model watermarking and fingerprinting to establish ownership and detect unauthorized duplication
- Secure API gateways with rate limiting, anomaly detection, and behavioral monitoring
- Token-level input filtering and validation in generative AI systems
- Output moderation engines to prevent unsafe or non-compliant responses
- Encrypted model storage and artifact signing to prevent tampering
- Isolated inference environments to restrict lateral movement in case of compromise
Without structured model integrity protection, AI systems remain vulnerable to exploitation, IP theft, and operational sabotage. Model security is no longer optional; it is a strategic necessity.
Layer 3: Infrastructure & MLOps Security
AI systems do not operate in isolation. They run on complex, distributed infrastructure that introduces its own set of vulnerabilities.
Enterprise AI environments typically rely on:
- High-performance GPU clusters
- Distributed containerized workloads
- Kubernetes orchestration layers
- Continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
- Cloud-hosted inference APIs and microservices
Each layer, if improperly configured can expose sensitive models, training data, or deployment credentials.
A mature secure AI development company integrates infrastructure security directly into AI architecture through:
- Zero-trust security models across all AI workloads and services
- Continuous container image scanning for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations
- Infrastructure-as-code (IaC) validation to detect security flaws before deployment
- Encrypted and access-controlled model registries
- Secure key management systems (KMS) for API tokens, credentials, and encryption keys
- Runtime intrusion detection and anomaly monitoring across GPU clusters and containers
- Secure multi-party computation (SMPC) or confidential computing for highly sensitive use cases
Infrastructure security must align with broader AI governance solutions and enterprise compliance requirements. AI security cannot be retrofitted after deployment. It must be engineered into development workflows, embedded into MLOps pipelines, and continuously monitored throughout the system’s lifecycle. Only when data, models, and infrastructure are secured together can AI systems operate with the level of trust required for enterprise-scale deployment.
Secure Your AI Systems Today — Talk to Our AI Security Experts
AI Governance: Building Structured Oversight Mechanisms for Enterprise AI
As AI systems become deeply embedded in business-critical operations, governance can no longer be informal or policy-driven alone. AI governance is the structured framework that ensures AI systems operate with accountability, transparency, fairness, and regulatory alignment across their entire lifecycle.
Modern AI governance solutions go far beyond static documentation or compliance checklists. They integrate oversight directly into development pipelines, MLOps workflows, approval processes, and monitoring systems—making governance operational rather than theoretical. At the enterprise level, governance is what transforms AI from experimental technology into regulated, board-level infrastructure.
Pillar 1: Ownership & Accountability Framework
Every AI system deployed within an organization must have clearly defined ownership and control mechanisms. Without accountability, AI becomes a shadow asset; operating without oversight or traceability.
A structured enterprise AI governance framework requires:
- A clearly defined business purpose and intended use case
- Formal risk classification (low, medium, high, critical)
- A designated model owner responsible for performance and compliance
- Defined escalation authority for risk incidents or model failures
- A documented governance approval process prior to deployment
In mature governance environments, no AI system moves into production without formal compliance, risk, and ethics review.
This structured control prevents:
- Shadow AI deployments by individual departments
- Unapproved generative AI experimentation
- Regulatory blind spots
- Unmonitored third-party AI integrations
Ownership ensures responsibility. Responsibility ensures control.
Pillar 2: Explainability & Transparency Mechanisms
Explainability is no longer optional—particularly in regulated sectors such as finance, healthcare, and insurance. Regulatory bodies increasingly require organizations to justify automated decisions, especially when those decisions affect individuals’ rights, credit eligibility, employment opportunities, or medical outcomes.
To meet these expectations, organizations must embed transparency into AI architecture through:
- Model interpretability frameworks such as SHAP and LIME
- Decision traceability logs that record input-output relationships
- Version-controlled documentation of model changes
- Model cards outlining purpose, limitations, training data scope, and known risks
- Human-in-the-loop override capabilities for high-risk decisions
Transparency reduces legal exposure and strengthens stakeholder trust. When decisions can be explained and traced, enterprises are better positioned for audits, regulatory reviews, and board-level oversight. Explainability is not just a technical feature; it is a governance safeguard.
Pillar 3: Bias & Fairness Governance
AI bias represents one of the most significant ethical, reputational, and regulatory challenges in enterprise AI. Biased outcomes can lead to discrimination claims, regulatory penalties, and public backlash.
Bias can originate from multiple sources, including:
- Skewed or non-representative training datasets
- Historical discrimination embedded in legacy data
- Proxy variables that indirectly encode sensitive attributes
- Imbalanced class representation
- Inadequate validation across demographic segments
Effective AI governance solutions implement structured bias management protocols, including:
- Pre-training bias audits to assess dataset representation
- Fairness metric benchmarking (demographic parity, equal opportunity, equalized odds)
- Continuous fairness drift monitoring post-deployment
- Regular demographic impact assessments
- Threshold-based alerts for fairness deviations
Bias governance is central to responsible AI development. It ensures that AI systems align not only with performance metrics but also with societal expectations and regulatory standards. Without fairness monitoring, even technically accurate models may fail ethically and legally.
Pillar 4: Lifecycle Governance
AI governance cannot be limited to pre-deployment review. It must span the entire model lifecycle to ensure long-term reliability and compliance.
A comprehensive governance framework covers:
- Design: Risk assessment, ethical review, and use-case validation
- Data Collection: Dataset quality checks and compliance alignment
- Training: Secure model development with audit documentation
- Validation: Performance, bias, and robustness testing
- Deployment: Governance approval and secure release management
- Monitoring: Continuous drift, bias, and anomaly detection
- Retirement: Controlled decommissioning and archival documentation
Continuous lifecycle governance prevents silent model degradation, regulatory violations, and operational surprises. In high-performing enterprises, governance is not a bottleneck; it is an enabler of sustainable AI scale. By embedding structured oversight mechanisms into every stage of AI development and deployment, organizations ensure their AI systems remain secure, compliant, ethical, and aligned with strategic objectives.
AI Risk Management: From Initial Identification to Continuous Oversight
Effective AI risk management is not a one-time compliance activity, it is a structured, lifecycle-driven discipline. Professional AI risk management services implement comprehensive frameworks that govern AI systems from conception to retirement, ensuring resilience, compliance, and operational integrity.
Stage 1: Comprehensive AI Risk Identification
Every AI initiative must begin with structured risk discovery. Organizations should conduct a multidimensional evaluation that examines:
- Business impact and criticality: What operational or financial consequences arise if the model fails?
- Regulatory exposure: Does the system fall under sector-specific regulations (finance, healthcare, public sector)?
- Data sensitivity: Does the model process personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, or protected health data?
- Model autonomy level: Is the AI advisory, assistive, or fully autonomous?
- End-user exposure: Does the system directly affect customers, patients, or employees?
High-risk AI systems particularly those influencing critical decisions which require elevated scrutiny and governance controls from the outset.
Stage 2: Structured Risk Assessment & Categorization
Once risks are identified, AI systems must be classified using structured assessment frameworks. This tier-based categorization determines the depth of oversight, documentation, and control mechanisms required.
High-risk AI categories typically include:
- Credit scoring and lending decision systems
- Healthcare diagnostic and treatment recommendation models
- Insurance underwriting and claims automation engines
- Autonomous industrial and manufacturing systems
- AI systems used in public policy or critical infrastructure
These systems demand enhanced governance measures, including formal validation protocols, regulatory documentation, and executive-level oversight. Risk categorization ensures proportional governance thus allocating more stringent safeguards where impact and exposure are highest.
Stage 3: Embedded Risk Mitigation Controls
Risk mitigation must be operationalized within AI workflows not layered on as an afterthought. Mature AI risk management frameworks integrate technical and procedural safeguards such as:
- Human-in-the-loop review checkpoints for high-impact decisions
- Real-time anomaly detection systems to identify unusual behavior
- Secure retraining pipelines with validated data sources
- Documented incident response and escalation frameworks
- Access segregation and role-based permissions
- Audit trails for model updates and configuration changes
By embedding mitigation mechanisms directly into development and deployment processes, organizations reduce exposure to operational failure, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Stage 4: Continuous Monitoring & Audit Readiness
AI risk is dynamic. Models evolve, data distributions shift, and regulatory landscapes change. Static governance approaches are insufficient.
Continuous monitoring frameworks include:
- Data and concept drift detection algorithms
- Performance degradation alerts and threshold monitoring
- Bias trend analysis across demographic groups
- Security anomaly detection and adversarial activity tracking
- Automated compliance reporting and audit documentation generation
This ongoing oversight transforms AI governance from reactive damage control to proactive risk anticipation.
Organizations that implement continuous monitoring achieve:
- Faster issue detection
- Reduced compliance risk
- Greater operational stability
- Stronger stakeholder trust
From Reactive Risk Management to Proactive AI Resilience
True AI risk management extends beyond compliance checklists. It builds adaptive systems capable of detecting, responding to, and learning from emerging threats.
When implemented effectively, structured AI risk management:
- Protects business continuity
- Safeguards sensitive data
- Enhances regulatory alignment
- Preserves brand reputation
- Enables responsible innovation at scale
AI risk is inevitable. Unmanaged AI risk is not.
AI Compliance: Navigating Global Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory pressure around AI is accelerating globally. Enterprises require structured AI compliance solutions integrated into development pipelines.
EU AI Act
The EU AI Act mandates:
-
- Risk classification
- Conformity assessments
- Transparency obligations
- Incident reporting
- Technical documentation
Non-compliance may result in fines up to 7% of global revenue.
U.S. AI Governance Directives
Emphasis on:
-
- Algorithmic accountability
- National security risk assessment
- Bias mitigation
- Model transparency
Industry-Specific Compliance
- Healthcare:
- HIPAA compliance
- Clinical validation protocols
- Finance:
- Model risk management frameworks
- Fair lending audits
- Insurance:
- Anti-discrimination controls
- Manufacturing:
- Autonomous system safety standards
Integrated AI compliance solutions reduce audit risk and regulatory exposure.
Secure Build Compliant & Secure AI Solutions — Get a Free Strategy Session
Responsible AI Development: Engineering Ethical Intelligence
Responsible AI development operationalizes ethical principles into enforceable technical standards.
It includes:
- Privacy-by-design architecture
- Inclusive dataset sourcing
- Clear documentation standards
- Sustainability-aware model training
- Transparent stakeholder communication
- Ethical review committees
Responsible AI improves:
- Regulatory alignment
- Customer trust
- Investor confidence
- Long-term scalability
Ethics and engineering must operate in alignment.
Why Enterprises Need a Secure AI Development Partner ?
Deploying AI at enterprise scale is no longer just a technical initiative; it is a strategic transformation that intersects cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, risk management, and ethical governance. Building secure and compliant AI systems requires deep cross-disciplinary expertise spanning data science, infrastructure security, regulatory law, model governance, and operational risk frameworks. Few organizations possess all these capabilities internally.
A strategic, secure AI development partner brings structured oversight, technical rigor, and regulatory alignment into every phase of the AI lifecycle.
Such a partner provides:
- Advanced AI security services to protect data pipelines, models, APIs, and infrastructure from evolving threats
- Structured AI governance frameworks embedded directly into development and deployment workflows
- Lifecycle-based AI risk management services covering identification, assessment, mitigation, and continuous monitoring
- Regulatory-aligned AI compliance solutions tailored to global and industry-specific mandates
- Demonstrated expertise in responsible AI development, including bias mitigation, explainability, and transparency controls
Without governance and security, AI innovation can amplify enterprise risk, exposing organizations to regulatory penalties, operational failures, intellectual property theft, and reputational damage. With the right secure AI development partner, innovation becomes structured, resilient, and strategically sustainable. AI innovation without governance increases enterprise exposure. AI innovation with governance builds long-term competitive advantage.
Trust Is the Infrastructure of AI
AI is reshaping industries at unprecedented speed, but innovation without trust creates fragility, risk, and long-term instability. Sustainable AI adoption demands more than advanced models; it requires strong foundations. Enterprises that embed robust AI security services, scalable governance frameworks, continuous risk management processes, regulatory-aligned compliance systems, and structured responsible AI practices will define the next phase of digital leadership. In the enterprise AI era, security protects innovation, governance protects reputation, compliance protects longevity, and trust protects growth. Trust is not a soft value; it is operational infrastructure. At Antier, we engineer AI systems where innovation and governance evolve together. We help enterprises scale AI securely, responsibly, and with confidence.
Crypto World
10% Bounce Hope Rise As Whales Buy
Ethereum is trying to stabilize after weeks of heavy selling. The price is holding near the $1,950 zone, up around 6% from its recent low. At the same time, the biggest Ethereum whales have started accumulating aggressively.
But short-term sellers and derivatives traders remain cautious, creating a growing tug-of-war around the next move.
Biggest Ethereum Whales Accumulate as Bullish Divergence Stays Intact
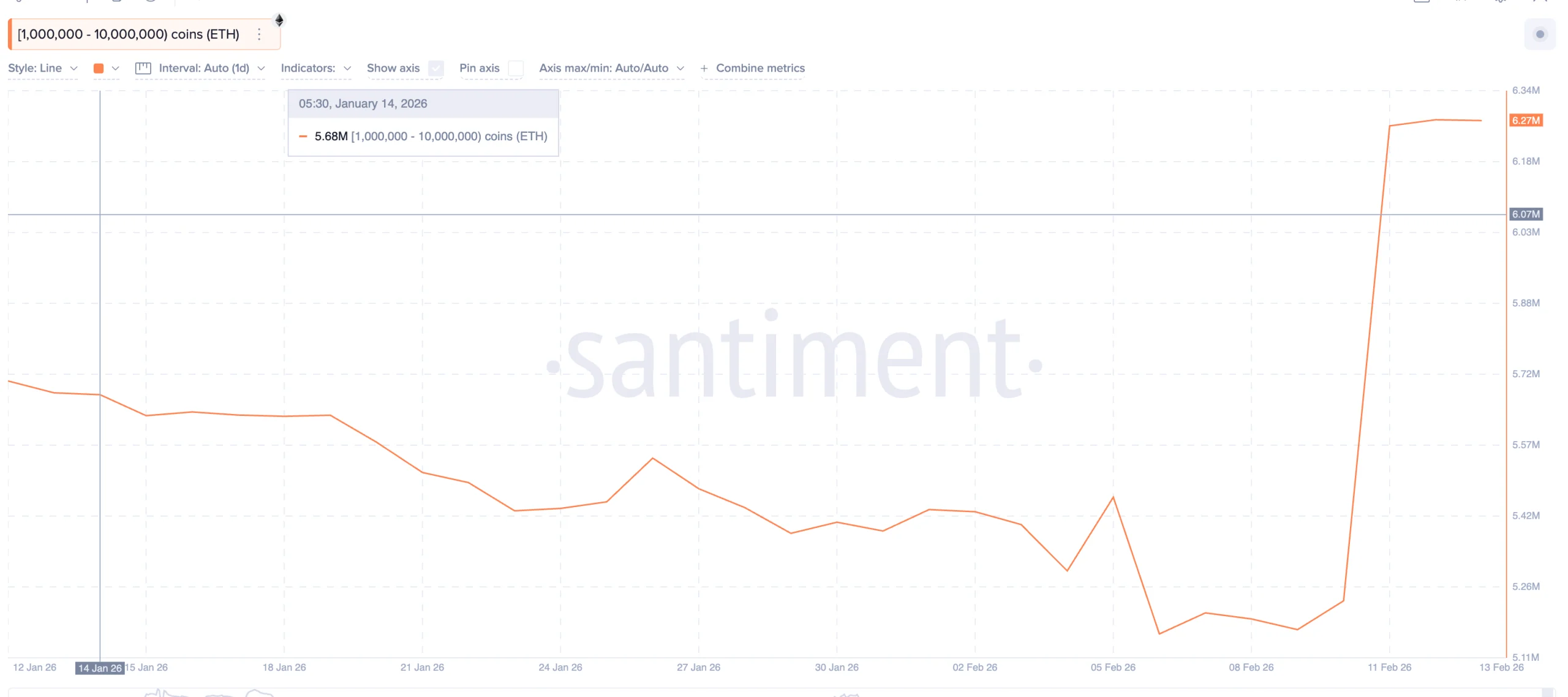
On-chain data shows that the largest Ethereum holders are positioning for a rebound. Since February 9, addresses holding between 1 million and 10 million ETH have increased their holdings from around 5.17 million ETH to nearly 6.27 million ETH. That is an addition of more than 1.1 million ETH, worth roughly $2 billion at current prices.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Want more token insights like this? Sign up for Editor Harsh Notariya’s Daily Crypto Newsletter here.
This accumulation aligns with a bullish technical signal on the 12-hour chart.
Between January 25 and February 12, Ethereum’s price made a lower low, while the Relative Strength Index, or RSI, formed a higher low. RSI measures momentum by comparing recent gains and losses. When price falls, but RSI rises, it often signals weakening selling pressure.
This bullish divergence suggests downside momentum is fading.

The structure remains valid as long as Ethereum holds above $1,890, as the same signal flashed even on February 11 and still seems to be holding. A breakdown below this level would invalidate the divergence for now and weaken the rebound case.
For now, whales appear to be betting that this support will hold.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Short-Term Holders Are Selling?
While large investors are accumulating, short-term holders are behaving very differently.
The Spent Coins Age Band for the 7-day to 30-day cohort has surged sharply. Since February 9 (the same time when the whale pickup started), this metric has risen from around 14,000 to nearly 107,000, an increase of more than 660%. This indicator tracks how many recently acquired coins are being moved. Rising values usually signal possible profit-taking and distribution.
In simple terms, short-term traders are exiting positions. This pattern appeared earlier in February as well. On February 5, a spike in short-term coin activity occurred near $2,140. Within one day, Ethereum dropped by around 13%.
That history shows how aggressive selling from this group can quickly reverse moves. As long as short-term holders remain active sellers, upside moves are likely to face resistance.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Derivatives Data Shows Heavy Bearish Positioning
Derivatives markets are reinforcing this cautious outlook. Current liquidation data shows nearly $3.06 billion in short positions stacked against only about $755 million in long leverage. This creates a heavily bearish imbalance with almost 80% of the market betting on the short side.
On one hand, this setup creates fuel for a potential short squeeze if prices rise. On the other hand, it shows that most traders still expect further weakness. This keeps momentum muted but keeps the bounce hope alive if the whale buying pushes the prices up, even a little bit, crossing past key clusters.
On-chain cost basis data helps explain why Ethereum struggles to break higher. Around $1,980, roughly 1.58% of the circulating supply, was acquired. Near $2,020, another 1.23% of supply sits at breakeven. These zones represent large groups of holders waiting to exit without losses.
Sponsored
Sponsored
When price approaches these levels, selling pressure increases as investors try to recover capital. This has repeatedly capped recent bounces. Only a strong leverage-driven move or short squeeze would likely be powerful enough to push through these supply clusters.
Until then, these zones remain major barriers.
Key Ethereum Price Levels To Track Now
With whales buying and sellers resisting, Ethereum price levels now matter more than narratives.
On the upside, the first major resistance sits near $2,010. A clean 12-hour close above this level would increase the probability of short liquidations. And it sits near the key supply cluster.
If that happens, Ethereum could target $2,140 next, a strong resistance zone with multiple touchpoints. It also sits around 10% from the current levels. On the downside, $1,890 remains the critical support. A break below this level would invalidate the bullish divergence and signal renewed downside pressure. Below that, the next major support sits near $1,740.

As long as Ethereum holds above $1,890 and continues testing $2,010, the rebound structure remains intact. A sustained breakdown below support would cancel the current recovery attempt.
Crypto World
PGI CEO Gets 20 Years Over $200M Crypto Investment Scheme

A US federal judge in Virginia sentenced the chief executive of Praetorian Group International to 20 years in prison for running a $200 million cryptocurrency investment scheme that defrauded tens of thousands of investors.
According to the Department of Justice, 61-year-old Ramil Ventura Palafox, a dual US and Philippine citizen, was convicted of wire fraud and money laundering for what prosecutors described as a Ponzi scheme that falsely promised daily returns of up to 3% from Bitcoin trading.
The US Attorney’s Office for the Eastern District of Virginia said investors poured over $201 million into PGI between December 2019 and October 2021, including at least 8,198 Bitcoin (BTC) valued at about $171.5 million at the time. According to prosecutors, victims suffered losses of at least $62.7 million.
The sentencing concludes the criminal case brought by the DOJ and follows a parallel civil action by the Securities and Exchange Commission, marking one of the larger crypto-related fraud cases in recent years by investor count and funds involved.

Fake trading claims and luxury spending
Court filings said Palafox told investors PGI was engaged in large-scale Bitcoin trading capable of generating consistent daily profits.
However, prosecutors said the company was not trading at a level sufficient to support the promised returns. Instead, new investor funds were used to pay earlier participants.
Authorities said Palafox operated an online portal that falsely displayed steady gains, giving investors the impression their accounts were growing. He also used a multilevel marketing structure, offering referral incentives to recruit new members.
The DOJ said Palafox spent millions in investor funds on personal expenses, including $3 million on luxury vehicles, over $6 million on homes in Las Vegas and Los Angeles, and hundreds of thousands of dollars on penthouse suites and high-end retail purchases.
Authorities said he also transferred at least $800,000 and 100 BTC to a family member.
Related: Sam Bankman-Fried claims Biden DOJ silenced witnesses during FTX trial
Civil charges and international reach
The scheme began to unravel as regulators scrutinized PGI’s trading claims and fund flows.
In April 2025, the Securities and Exchange Commission filed a civil complaint alleging that Palafox misrepresented PGI’s Bitcoin trading activity and used new investor money to pay earlier participants.
The complaint said PGI promoted an AI-powered trading platform and guaranteed daily returns despite lacking trading operations capable of generating those profits.
Federal prosecutors in the Eastern District of Virginia later unsealed criminal charges accusing Palafox of wire fraud and money laundering arising from the same conduct.
Authorities had seized the company’s website in 2021, and related operations were shut down in the United Kingdom, signaling cross-border enforcement scrutiny before the US criminal case advanced.
The DOJ said victims may be eligible for restitution and directed them to the US Attorney’s Office website for information on filing claims.
Magazine: Hong Kong stablecoins in Q1, BitConnect kidnapping arrests: Asia Express
Crypto World
Ark Invest buys $18 million of crypto stocks including 10th consecutive Bullish (BLSH) purchase


Ark Invest added another $18 million worth of crypto-adjacent stocks to its holdings on Thursday, including a $2 million purchase of shares in cryptocurrency exchange Bullish (BLSH).
The St. Petersburg, Florida-based company also bought $12 million worth of crypto-friendly trading platform Robinhood (HOOD) and $4 million worth of ether treasury firm Bitmine Immersion Technologies (BMNR), according to an emailed disclosure on Friday.
Ark’s investment in Bullish, the parent company of CoinDesk, extends its run of consecutive equity purchases in the crypto exchange to 10 days. Bullish shares fell 0.53% to $31.71 on Thursday.
BLSH shares have lifted from a trough of around $24 on Feb. 5 to trade either side of the $30 mark over the last week. They remain, however, more than 16% lower year-to-date.
HOOD shares fell 8.9% on Thursday, closing at $71.12 as U.S tech stocks sank, taking bitcoin with them.
Bitmine defied the broader market to rise 1.39% to $19.74.
Crypto World
Ramil Ventura Palafox gets 20 years sentence over $200 million bitcoin Ponzi scheme


The CEO of Praetorian Group International (PGI) was sentenced to 20 years in prison in the U.S. for running a global Ponzi scheme that falsely claimed to invest in bitcoin and foreign exchange trading.
Ramil Ventura Palafox, 61, promised daily returns of up to 3%, misleading more than 90,000 investors and draining over $62.7 million in funds, according to a Thursday statement from the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Eastern District of Virginia.
PGI collected more than $201 million from investors between late 2019 and 2021, including over 8,000 bitcoin , according to court records. Instead of investing the money, prosecutors said Palafox used new investor funds to pay old ones while siphoning millions for himself.
To keep the illusion going, Palafox built an online portal where investors could track their supposed profits, with numbers that were entirely fabricated.
In reality, Palafox was buying Lamborghinis, luxury homes in Las Vegas and Los Angeles and penthouse suites at high-end hotels. Prosecutors say he spent $3 million on luxury cars and another $3 million on designer clothing, watches, and jewelry.
The case was investigated by the FBI and IRS. Victims may be eligible for restitution. The SEC is pursuing civil penalties, and Palafox remains banned from handling securities.
Crypto World
Will $2.3B options expiry jolt Ethereum price from key strike levels?
Ethereum price continues to lag its 2021 peak as institutions rotate cautiously into ETH exposure while weighing ETF flows, on-chain activity, and broader macro risk.
Summary
- BlackRock lifts its Bitmine stake 166% to $246M, doubling down on a levered Ethereum price proxy even as ETH trades ~60% below its peak and Bitmine stock is down ~70%.
- Vitalik Buterin and Stani Kulechov recently sold millions in ETH while BlackRock and Goldman Sachs add exposure via Bitmine and Ethereum ETFs, treating the drawdown as opportunity.
- BlackRock’s thesis leans on Ethereum’s dominance in tokenized real‑world assets, with Larry Fink calling tokenization “necessary” as BTC, ETH and SOL trade as high‑beta macro risk proxies.
BlackRock is leaning into the pain on Ethereum (ETH) price, quietly ramping up its exposure to Bitmine even as blue‑chip crypto names slide and prominent insiders head for the exits.
BlackRock’s leveraged Ethereum bet
According to a 13F‑HR filing collated by Fintel, BlackRock’s Bitmine stake jumped 166% in Q4 2025 to about $246 million, cementing the asset manager as a key backer of the Ethereum‑heavy treasury vehicle. Bitmine, the second‑largest digital asset treasury firm and a levered proxy on Ether, has seen its own stock price crater nearly 70% over six months to roughly $20 per share. The move drew an approving response from Bitmine chair Tom Lee, who has publicly floated a $250,000 price target for Ethereum and responded with clapping emojis to the disclosure in a post on X.
BlackRock’s buying spree lands as Ethereum trades just under $2,000, roughly 60% below its August peak, with Standard Chartered’s Geoffrey Kendrick warning the token could drop a further 25% toward $1,400. “The best investment opportunities in crypto have presented themselves after declines,” Lee said on Monday, after Bitmine added another $80 million of Ether to its already underwater position, which is sitting on at least $6.6 billion in paper losses.
Insiders sell, Wall Street buys
February has seen crypto pioneers unload sizable Ether positions, even as Wall Street leans in. Ethereum co‑founder Vitalik Buterin sold at least $7 million worth of ETH last week to fund new initiatives, while Aave founder Stani Kulechov offloaded more than $8 million. At the same time, Goldman Sachs disclosed holdings of just over $1 billion in Ethereum exchange‑traded funds, joining BlackRock in treating the drawdown as an entry point.
BlackRock’s conviction rests on tokenisation. In January, the firm said Ethereum will lead the tokenisation of real‑world assets, noting that around 66% of all tokenised instruments sit on Ethereum, compared with about 10% on BNB Chain, 5% on Solana, 4% on Arbitrum, 4% on Stellar, and 3% on Avalanche. CEO Larry Fink has called tokenisation “necessary,” arguing in Davos that the goal is to bring “the entire financial system on one common blockchain.”
Market backdrop and key levels
The broader tape remains fragile. Bitcoin is down about 0.7% over the past 24 hours, trading near $66,582, while Ethereum has slipped roughly 0.4% to around $1,955. Spot dashboards show Bitcoin changing hands close to $66,618 with roughly $44.9 billion in 24‑hour volume, as Ethereum hovers near $1,961 on about $20.1 billion traded. Solana, another high‑beta proxy for crypto risk, trades around $192, with leading centralized exchanges printing quotes in the $191–$193 band on heavy liquidity.
This parabolic move comes as digital assets continue to trade as the purest expression of macro risk appetite. Bitcoin (BTC) is hovering around $66,600, with a 24‑hour range roughly between $65,000 and $68,400, on more than $30 billion in dollar volumes. Ethereum (ETH) changes hands close to $1,960, with about $20 billion in 24‑hour turnover and spot quotes clustering just below the $2,000 mark. Solana (SOL) trades near $192, fractionally lower on the day, with leading venues reporting individual pairs clearing hundreds of millions in volume.
For now, BlackRock is treating the selloff as structural opportunity rather than terminal decline, aligning its Bitmine bet with a broader thesis that Ethereum’s role in real‑world asset rails will outlast this drawdown.
Crypto World
Bitcoin, ether little changed before U.S. inflation report: Crypto Markets Today


Bitcoin rose to test $67,000 early Friday and was quickly rebuffed, though it remains about 1% higher since midnight UTC with ether rising half as much. The derivatives market, too, is showing signs of positivity.
The CoinDesk 20 Index (CD20) is little changed, up just 0.7% in the period.
While the gains mark a recovery from yesterday’s U.S. trading, which saw the cryptocurrency market fall back toward last week’s lows, bitcoin is still on track for a fourth straight week of declines. That’s the longest falling streak since mid-November.
Meantime, a slowdown in trading and fading volatility are weighing on volumes.
It’s likely that traders are looking to the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) print coming later today for hints on direction. A higher-than-forecast reading could lift bond yields and the dollar, putting additional pressure on risk assets. A lower reading might signal the easier conditions that are more conducive to risk-taking.
Even so, it will take quite a jump to push the bitcoin price to $85,000, a level that Deribiti’s chief commercial officer, Jean-David Péquignot, said would signal the largest cryptocurrency’s long-term rally is no longer “broken.”
Derivatives
- The market is showing signs of renewed life as open interest (OI) dropped to $15.5 billion, suggesting a cleanup of late-cycle leverage.
- Perpetual funding rates have flipped neutral to positive across all venues, now ranging between 0% and 8%. This broader optimism is being mirrored by institutions, as the three-month annualized basis spiked to just over 3%, signaling the first real uptick in professional conviction.
- The bitcoin options market shows returning call volume at 65%, even as the one-week 25-delta skew eased to 17.9%. Despite this “bottom-fishing” activity, the implied volatility (IV) term structure remains in short-term backwardation, confirming that traders are still paying a high “panic premium” for immediate downside protection.
- Coinglass data shows $256 million in 24-hour liquidations, split 69-31 between longs and shorts. Bitcoin ($112 million), ether ($52 million) and others ($16 million) were the leaders in terms of notional liquidations.
- The Binance liquidation heatmap indicates $68,800 as a core liquidation level to monitor in case of a price rise.
Token Talk
- PUMP, the token of Solana-based memecoin launchpad Pump.fun, is up more than 5% in the past 24 hours.
- The platform rolled out a new way for token communities to allocate fees directly through its mobile app with the inclusion of GitHub account integration.
- The integration offers a simpler way for creators to assign automatic payouts generated by a token’s community, and more social features are expected to be introduced in the future.
- In practice, this means communities can start supporting creators on GitHub through a portion of the fees generated. To receive the fees, creators will need to claim them through the platform’s mobile app.
- Pump.fun was largely behind a major memecoin trading frenzy early last year that saw its monthly trading volume surge past $11 billion. Volume has since plunged to $1 billion last month, according to DeFiLlama data.
Crypto World
Bitcoin ETFs bleed $410M amid $2.5B options expiry: is BTC facing deeper crash?


- Bitcoin saw spot ETF outflows of over $410 million as prices struggled.
- Over $2.5 billion in Bitcoin options expired on Friday.
- Analysts say “worst of downturn” likely over but market remains bearish.
Bitcoin ETFs experienced a net outflow of over $410 million on February 12, as investors withdrew capital from the exchange-traded funds amid growing fears of a broader crypto market downturn.
And on Friday morning, Feb. 13, BTC price fluctuated near $66,800 as the market recorded a massive $2.5 billion Bitcoin options expiry.
Crypto analysts have shared their thoughts on what this could mean for the Bitcoin price in the short term.
Bitcoin ETF outflows and $2.5 billion options expiry
Data showed that on US spot Bitcoin ETFs recorded net outflows of over $410 million yesterday, with none of the 12 spot ETFs notching net inflows.
BlackRock’s IBIT led with nearly $158 million, Fidelity’s FBTC had $104 million, and Grayscale’s GBTC had over $59 million in exits.
This marked the second consecutive day of redemptions, following $276 million on February 11.
Institutional investors are pulling back amid Bitcoin’s struggles around the $67,500-$65,450 range.
The fresh ETF outflows coincide with a pivotal weekly options expiry at 08:00 UTC on Feb. 13.
Approximately 38,000 Bitcoin contracts worth $2.5 billion in notional value have expired, primarily on Deribit, with a put/call ratio of 0.72 and maximum pain near $74,000.
Ethereum also saw 215,000 ETH options worth $410 million expire, with a put/call ratio of 0.82 and a maximum pain point at $2,100.
These maximum pain points are at values well above spot BTC and ETH levels, and likely the driver of downward pressure as market makers look to hedge delta exposure on out-of-the-money calls.
February 13 Options Expiration Data
38,000 BTC options expired with a Put-Call Ratio of 0.71, maximum pain point at $74,000, and notional value of $2.5 billion.
215,000 ETH options expired with a Put-Call Ratio of 0.82, maximum pain point at $2,100, and notional value of $410… pic.twitter.com/07TKfJxmMi— Greeks.live (@GreeksLive) February 13, 2026
Bitcoin price prediction
The ETF outflows and broader market weakness hinder bulls, and sentiment is skewed bearish, analysts say.
“Today saw the expiration of options accounting for 9% of total open interest, totaling nearly $2.9 billion. This week, implied volatility for Bitcoin and Ethereum has declined, with BTC’s main-term IV at 50% and ETH’s at 70%. While the downward price trend has moderated, market confidence remains weak,” analysts at Greeks.live noted via X.
Despite this outlook, the market may have “the most violent leg of the downturn” behind it. If sentiment improves, prices could pick up an upside trajectory.
In this case, a relief rally to above the critical $70,000 mark is likely.
However, ETF bleeding and macroeconomic headwinds could greatly cap upside momentum.
On Thursday, Standard Chartered forecast Bitcoin price could retest $50k before rising to $100k by the end of 2026. The bank cites ETF outflows, macro pressures and broader risk asset sentiment as negative catalysts.
$410M outflows in a single day.
US spot Bitcoin ETFs just logged their 4th straight week of bleeding.
AUM down from $170B (Oct ‘25 peak) to ~ $80B.
At the same time, Standard Chartered cuts 2026 BTC target from $150K → $100K and warns of a possible $50K flush first.
ETH ETFs… pic.twitter.com/H9W8lmAvRq
— Dear Bitcoiner ⚡️ (@DearBitcoiner) February 13, 2026
Notably, BTC tested support at $60k this month, and the elevated implied volatility, coupled with ETF exits, signals aggressive downside protection.
If outflows continue amid other highlighted downside triggers, the $50k level could be the next target.
Crypto World
AVAX Eyes $147 Target as Elliott Wave Pattern Signals Multi-Year Recovery Phase

TLDR:
- AVAX completed Wave 1 between $8-$5, now entering Wave 2 recovery phase within descending channel
- CryptoPatel targets $33, $58, $97, and $147 representing potential 2,489% expansion from bottom
- Critical support at $5.50 must hold on weekly close to maintain bullish Elliott Wave structure
- Analysis suggests multi-year setup through 2026-2027 suited for spot accumulation and patience
AVAX traders are monitoring a technical analysis that suggests the token could target $147 in the coming years. Crypto analyst CryptoPatel has identified an Elliott Wave formation on the weekly chart, indicating a possible recovery phase after a 95% correction from the 2021 all-time high.
The analysis places AVAX at a critical inflection point, with the asset trading within a multi-year descending channel.
Price action currently hovers near $8.86, presenting what the analyst describes as a macro support accumulation zone.
Technical Structure Shows Wave Completion
The technical framework outlined by CryptoPatel centers on Elliott Wave theory applied to AVAX’s weekly timeframe. According to the analysis shared on X, Wave 1 completed between $8 and $5, marking a macro bottom for the current cycle.
The token now enters what the analyst labels as Wave 2, representing an early recovery phase from the previous correction.
The descending channel formation has contained price action since the 2021 peak. This pattern shows a bearish breakdown followed by a retest of the lower trendline, creating what technical analysts call a deviation setup.
Market structure at these levels suggests accumulation by institutional participants, though this remains speculative based on price behavior rather than confirmed data.
Support zones have formed between $8 and $7, coinciding with weekly demand areas. The liquidity sweep into these zones mirrors fractal patterns from previous market cycles.
Additionally, the compression phase resembles historical accumulation periods that preceded major rallies in past bull markets.
Price Targets Extend Beyond $100 Mark
CryptoPatel’s forecast includes four distinct targets as the Elliott Wave structure potentially unfolds through 2026 and 2027. The progression starts at $33, followed by $58, then $97, before reaching a final target of $147.
These levels correspond to the mid-channel resistance and eventual upper boundary of the descending formation. From the identified bottom to the highest target, the expansion measures approximately 2,489%.
The bullish scenario requires sustained weekly strength with expansion toward mid-channel resistance zones. Price must demonstrate momentum capable of breaking through overhead supply levels that accumulated during the extended correction. However, the analysis also establishes clear invalidation parameters to manage risk exposure.
The critical support level sits at $5.50, representing the Wave 1 low. A weekly close beneath this threshold would negate the Elliott Wave count and suggest further downside potential. This makes the $5.50 level essential for bulls to defend on higher timeframes.
The analyst characterizes this setup as appropriate for spot accumulation and long-term positioning rather than short-term trading.
The asymmetric risk-reward profile stems from proximity to identified support versus the distance to upside targets.
Patience remains necessary as weekly timeframe patterns develop over extended periods, typically spanning months or years rather than days or weeks.
Crypto World
Coinbase Reports $667M Q4 Loss as Crypto Market Downturn Hits Revenues

Coinbase earnings just broke its streak, and not in a good way. After eight straight winning quarters, it posted a brutal $667 million net loss in Q4 2025. That is a punch to the face.
As crypto prices slid from their yearly highs, the exchange completely missed Wall Street revenue expectations.
Revenue came in at $1.78 billion. Sounds big, but it was below the $1.85 billion analysts expected. Transaction revenue was the real damage. Down 37% to $982.7 million.
That tells you everything about trader activity right now.
Key Takeaways
- Coinbase reported a $667 million net loss, its first profit miss since Q3 2023.
- Revenue fell 21.5% YoY to $1.78 billion, missing analyst expectations.
- Transaction fees plummeted 37% as retail traders exited the market.
- Shares (COIN) dipped 7.9% intraday but rebounded nearly 3% after hours.
Is the Bull Market Officially Over? How Coinbase Can Survive It
That $667 million loss is not just a bad quarter. It screams deeper cycle weakness. A big chunk of it came from unrealized losses on Coinbase own crypto holdings after prices collapsed from the October 2025 highs.
When Bitcoin falls from nearly $126,000 to the mid $60k range, nobody walks away clean. Not even the exchanges.
This kind of volatility feels similar to the uncertainty during the FTX fallout days. Brian Armstrong is still calling this downturn psychological.
Retail traders are barely active. Transaction revenue, which is the core engine of the business, dried up as volume vanished.
Casual money is staying on the sidelines. And that is the last thing Coinbase needed.
Discover: The best crypto to diversify your portfolio
COIN Stock Resilience or Dead Cat Bounce?
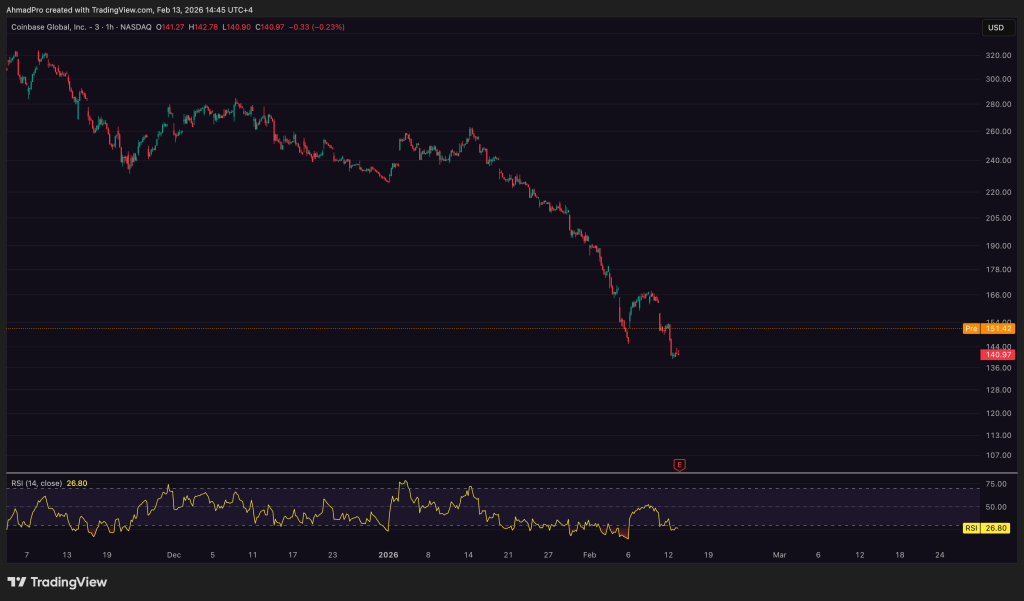
Even after that ugly earnings report, COIN stock actually climbed 2.9% in after-hours, sitting near $145. Sounds crazy, right?
But the stock had already dropped 7.9% during the regular session. Traders probably priced in the disaster before the numbers even hit.
Still, the outlook is not exactly comforting. Subscription and services revenue was the only real bright spot, up 13% to $727.4 million.
That helped soften the blow. But management is already guiding lower for Q1 2026, expecting that figure to fall into the $550 to $630 million range. That is not small.
If even the so-called stable revenue starts shrinking, the safety cushion gets thin fast. And if that happens, a retest of the $139 zone, near the 52-week lows, would not be surprising at all.
Discover: What is the next crypto to explode?
The post Coinbase Reports $667M Q4 Loss as Crypto Market Downturn Hits Revenues appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
Bitcoin ETFs Post $410M Outflows As Early-Week Momentum Fades
US spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) saw heightened selling on Thursday, with outflows accelerating the same day Standard Chartered lowered its 2026 Bitcoin forecast.
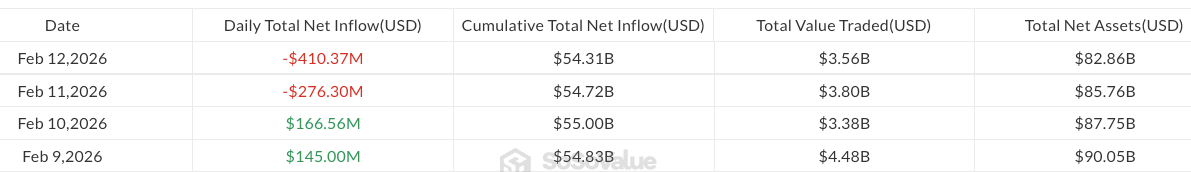
Spot Bitcoin (BTC) ETFs recorded $410.4 million in outflows, extending weekly losses to $375.1 million, according to SoSoValue data.
Unless Friday brings substantial inflows, the funds are on track for a fourth consecutive week of losses, with assets under management (AUM) nearing $80 billion, down from a peak of almost $170 billion in October 2025.

The selling coincided with Standard Chartered lowering its 2026 Bitcoin target from $150,000 to $100,000, warning that prices could fall to $50,000 before recovering.
“We expect further price capitulation over the next few months,” the bank said in a Thursday report shared with Cointelegraph, forecasting Bitcoin to drop to $50,000 and Ether (ETH) to $1,400.
“Once those lows are reached, we expect a price recovery for the remainder of the year,” Standard Chartered added, projecting year-end prices for BTC and ETH at $100,000 and $4,000, respectively.
Solana ETFs the only winners amid heavy crypto ETF outflows
Negative sentiment persisted across all 11 Bitcoin ETF products, with BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF (IBIT) and the Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund suffering the largest outflows of $157.6 million and $104.1 million, respectively, according to Farside.
Ether ETFs faced similar pressure, with $113.1 million in daily outflows dragging weekly outflows to $171.4 million, marking a potential fourth consecutive week of losses.
XRP (XRP) ETFs saw their first outflows of $6.4 million since Feb. 3, while Solana (SOL) ETFs bucked the trend, recording a minor $2.7 million in inflows.
Extreme bear phase not yet here as analysts expect $55,000 bottom
Standard Chartered’s latest Bitcoin forecast follows previous analyst forecasts that Bitcoin could dip below $60,000 before testing a recovery.
Crypto analytics platform CryptoQuant reiterated that realized price support remains at around $55,000 and has not yet been tested.
“Bitcoin’s ultimate bear market bottom is around $55,000 today,” CryptoQuant said in a weekly update shared with Cointelegraph.

“Market cycle indicators remain in the bear phase, not extreme bear phase,” CryptoQuant noted, adding: “Our Bull-Bear Market Cycle Indicator has not entered the Extreme Bear regime that historically marks the start of bottoming processes, which typically persist for several months.”
Related: Bernstein calls Bitcoin sell-off ‘weakest bear case’ on record, keeps $150K 2026 target
Bitcoin hovered around $66,000 on Thursday, briefly dipping to $65,250, according to CoinGecko data.
Despite ongoing selling pressure, long-term holder (LTH) behavior does not indicate capitulation, with holders currently selling around breakeven. “Historical bear market bottoms formed when LTHs endured 30–40% losses, indicating further downside may be required for a full reset,” CryptoQuant added.
Magazine: Bitcoin difficulty plunges, Buterin sells off Ethereum: Hodler’s Digest, Feb. 1 – 7
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy Israel is blocking foreign journalists from entering
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoJD Vance booed as Team USA enters Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
 Business5 days ago
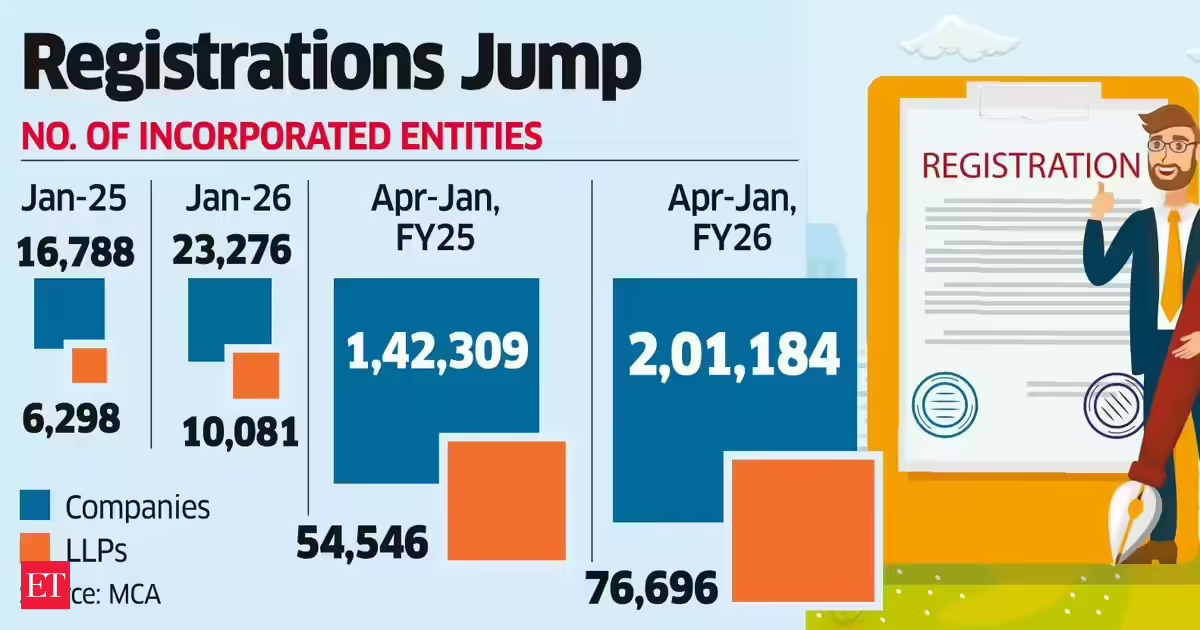
Business5 days agoLLP registrations cross 10,000 mark for first time in Jan
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-
 Tech7 days ago
Tech7 days agoFirst multi-coronavirus vaccine enters human testing, built on UW Medicine technology
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoCostco introduces fresh batch of new bakery and frozen foods: report
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-

 NewsBeat5 days ago
NewsBeat5 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Team GB’s Mia Brookes through to snowboard big air final, and curling pair beat Italy
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoBenjamin Karl strips clothes celebrating snowboard gold medal at Olympics
-
Sports6 days ago
Former Viking Enters Hall of Fame
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoThe Health Dangers Of Browning Your Food
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoJulius Baer CEO calls for Swiss public register of rogue bankers to protect reputation
-

 NewsBeat7 days ago
NewsBeat7 days agoSavannah Guthrie’s mother’s blood was found on porch of home, police confirm as search enters sixth day: Live
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
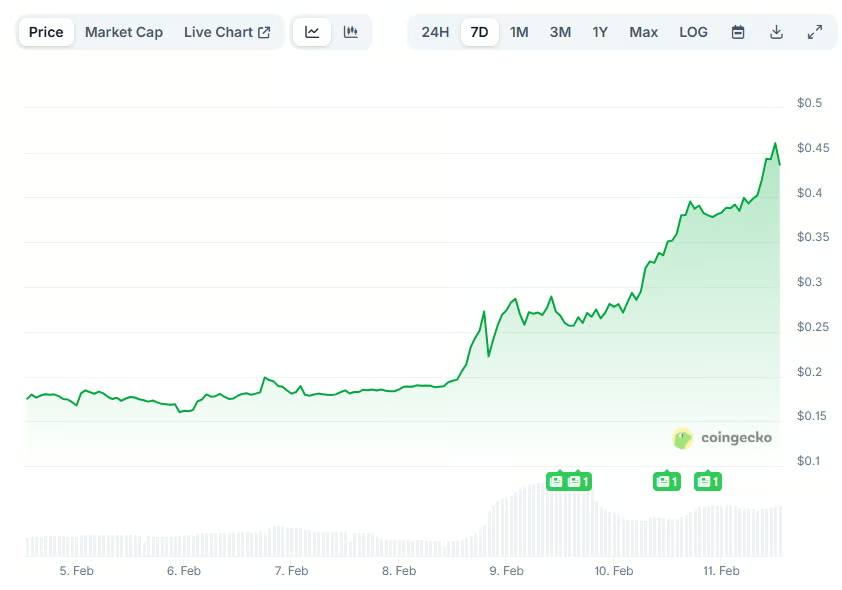
Crypto World2 days agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-

 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoResidents say city high street with ‘boarded up’ shops ‘could be better’
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month
-

 Video1 day ago
Video1 day agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-
Sports4 days ago
Kirk Cousins Officially Enters the Vikings’ Offseason Puzzle







 (@coinbase)
(@coinbase) 






