Crypto World
LayerZero Unveils Zero L1 Blockchain With DTCC, ICE, and Citadel Partnerships

TLDR:
- Zero launches with 165 blockchain connections through LayerZero’s existing messaging infrastructure.
- DTCC, ICE, and Citadel partnerships bring $3.7 quadrillion in annual securities clearing to the platform.
- Real-time ZK proof system enables transaction finalization in seconds versus traditional batching delays.
- Three specialized zones handle general computing, private payments, and trading with 2M TPS capacity each.
LayerZero has announced Zero, a new Layer 1 blockchain designed to address institutional barriers in digital asset adoption.
The network features three specialized zones for general computing, private payments, and trading infrastructure. Zero leverages LayerZero’s existing interoperability protocol to connect with 165 blockchains at launch.
Major financial institutions including DTCC, ICE, and Citadel have announced partnerships with the platform.
Technical Architecture Addresses Scalability Constraints
Traditional blockchain networks face performance limitations because every validator processes identical transactions.
According to analysis from Delphi Digital, “blockchains are slow because every node does the same work.” This redundant design ensures security but restricts throughput across the network. Zero implements a different model that separates transaction execution from verification processes.
The platform employs a smaller group of block producers to execute transactions and generate zero-knowledge proofs.
Validators then verify these proofs rather than re-executing every transaction. Delphi Digital notes that validators download “less than 0.5% of actual block data,” which lets the network scale without forcing all participants to operate expensive hardware infrastructure.
LayerZero rebuilt the technology stack across multiple layers to eliminate bottlenecks. The system includes QMDB for storage operations, FAFO for parallel execution, SVID for networking functions, and Jolt Pro for proof generation.
FAFO manages parallel compute scheduling. LayerZero claims their system “achieves over 1 million transactions per second” through this architecture.
Proof generation represents the most challenging technical component. Current zero-knowledge systems batch thousands of transactions to offset computational costs, creating delays in finalization.
LayerZero addresses this through real-time proving technology. The company states its Jolt Pro system “can generate proofs fast enough for transactions to finalize in seconds.”
This approach could eliminate latency issues that currently limit zero-knowledge chains in high-frequency applications.
Institutional Partnerships Signal Market Strategy
Zero operates as a standalone L1 that integrates with LayerZero’s messaging protocol. The network maintains EVM compatibility, allowing developers to deploy existing Solidity contracts without modifications.
Each of Zero’s three zones shares a common settlement layer while executing independently. LayerZero claims “each zone can handle 2M TPS with horizontal scaling as more zones are added.”
Tether’s USDt0 stablecoin already runs on this infrastructure. Delphi Digital reports the token has moved “over $70 billion in crosschain transfers since launch.”
This existing adoption demonstrates the network’s operational capacity before the broader Zero platform launches.
The project secured partnerships with established financial institutions on the same announcement day. DTCC clears $3.7 quadrillion in securities annually and operates core settlement infrastructure for U.S. markets.
ICE owns the New York Stock Exchange and manages trading platforms across multiple asset classes. Citadel ranks among the largest market makers globally, handling substantial daily trading volume.
Delphi Digital observes that “institutions want blockchain rails but won’t use what exists.” Fragmentation across multiple chains and transparent transaction records prevent many institutions from adopting existing platforms.
The payments zone incorporates privacy features designed to meet confidentiality requirements for institutional money movement. This positions Zero as infrastructure for regulated entities rather than retail cryptocurrency users.
Crypto World
Ethereum apps can’t just pay their way to real adoption, Vitalik warns


Vitalik Buterin says crypto apps must move beyond “pay users or fail,” using incentives only to offset early risks while focusing on real utility and committed communities.
Summary
- Vitalik Buterin rejects “pay users or fail” as a growth model, arguing that sustainable incentives mirror normal businesses where revenue from some users funds value for others.
- He says early rewards can fairly compensate liquidity providers and early adopters for smart contract, hack, and project failure risks, but should fade as protocols mature and audits reduce risk.
- Buterin warns that airdrops and social media payout schemes inflate metrics with low-quality activity, while real adoption comes from useful apps and committed community contributors.
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has weighed in on ongoing debates within the cryptocurrency industry regarding user acquisition strategies, cautioning against reliance on unsustainable financial incentives.
Buterin goes on recent cryptocurrency rant
In a recent online discussion on X, Buterin responded to claims that cryptocurrency applications cannot achieve meaningful adoption without airdrops or token rewards. The debate centered on whether financial payouts remain essential for building network effects in the sector.
Buterin acknowledged that incentives reflect current market conditions but warned against adopting a “pay users or fail” growth strategy, according to his posts on the social media platform.
The Ethereum co-founder drew distinctions between sustainable and unsustainable reward structures. Sustainable models involve paying certain users from revenue collected from others, creating an economic loop that mirrors traditional business models where income funds growth, he stated.
Buterin said paying users during early project stages can be justified in specific circumstances. Liquidity providers face risks including potential hacks or project failure, as new protocols carry technical and security vulnerabilities, he noted. Rewards in these cases serve as compensation for assuming elevated risk levels.
Once projects complete audits and establish trust within the sector, risk levels decline and high rewards become unnecessary, according to Buterin’s analysis.
The approach differs from paying users solely to generate activity or traffic, he stated. Paying all users during early growth phases can create long-term sustainability issues, as teams may incorrectly assume future profits will cover initial spending. Activity often drops once rewards end because many users joined exclusively for payouts, Buterin noted.
Aggressive reward campaigns risk undermining cryptocurrency communities, according to the post. Projects that compensate users for posting promotional content frequently produce unintended outcomes, with creators focusing on earning rewards rather than producing quality content. Activity typically declines when payments cease, as users lack incentives to continue platform engagement.
Buterin distinguished between decentralized finance applications and social platforms. In DeFi, capital functions uniformly regardless of provider, he stated. On social platforms, quality and active users carry more significance than user base size.
Committed community members often build tools, write documentation and answer forum questions without expecting rewards, according to Buterin. These contributions tend to strengthen projects over time, he stated.
Effective incentives should offset temporary weaknesses in early-stage products and decline as those weaknesses diminish, Buterin argued. Campaigns that pay users to inflate metrics can create appearances of adoption while failing to build sustainable communities.
“The bulk of the effort should be on making an actually-useful app. This was historically ignored, because it’s not necessary for narrative engineering to create a speculative bubble. But now it is necessary,” Buterin wrote.
The Ethereum co-founder argued that the cryptocurrency sector is gradually transitioning toward models driven by real utility rather than reward-led growth. Strong incentive structures compensate for early disadvantages and naturally phase out as projects mature, according to his statements.
Crypto World
Nasdaq Drops 2% as AI Jitters Spread
The Nasdaq Composite led a broad market selloff on Thursday, as artificial intelligence fears reemerged on Wall Street.
The tech-heavy index sank 2%. The S&P 500 dropped 1.6%. The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 663 points, or 1.3%.
The Roundhill Magnificent Seven ETF closed down nearly 11% from its closing high of $69.06 on Oct. 29, according to Dow Jones Market Data. A decline of 10% or more from a recent high means an index is in correction territory.
Crypto World
DOJ warns of Valentine’s Day romance scams


As Valentine’s Day approaches, the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of Ohio is warning the public about a surge in romance scams that target people through online relationships and often lead to financial loss, including requests for cryptocurrency payments.
Summary
- The U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of Ohio issued a Valentine’s Day warning about a surge in romance scams, many involving cryptocurrency payments.
- Scammers build fake online relationships over weeks or months before requesting money for “emergencies,” travel, or bogus crypto investments.
- Officials urge the public never to send gift cards, wire transfers, or cryptocurrency to someone they have not met in person, citing rising financial losses nationwide.
Criminals behind these schemes exploit victims’ trust and emotions by posing as romantic partners on dating sites, social media and messaging apps.
After building what appears to be a genuine relationship over weeks or months, scammers eventually ask victims for money, often under the guise of emergencies, travel costs or investment opportunities.
How crypto romance scams typically work
“Romance scammers are not looking for love — they are looking for money,” said U.S. Attorney David M. Toepfer. “They prey on trust and emotion … never send money to someone you have not met in person.”
According to the federal warning, fraudsters typically follow a pattern:
- They create fake profiles using stolen photos.
- Claim to work overseas in the military, oil rigs or business.
- Quickly profess deep feelings or commitment.
- Shift conversations off public platforms to private messaging.
Red flags include early declarations of love, excuses for not meeting in person, repeated “emergencies,” and unusual payment requests, especially gift cards, cryptocurrency or wire transfers.
Such scams have grown more sophisticated in recent years. In some cases, victims are directed to bogus investment platforms that promise unrealistically high returns before the scammers disappear with funds.
National reports have found that romance and confidence scams accounted for significant losses, often involving cryptocurrency transactions.
Crypto World
Are Quantum-Proof Bitcoin Wallets Insurance or a Fear Tax?
Cryptocurrency wallet makers and security companies are pushing out post-quantum products even though large-scale quantum computers capable of breaking Bitcoin do not exist yet.
The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) finalized its first post-quantum cryptography standards in 2024 and called for migrations before 2030.
As standards bodies plan for a gradual cryptographic transition, parts of the wallet market are already monetizing that future.
“I do feel that it is a bit of a fear tax. We know that quantum computers are far away — still five to 15 years away,” Alexei Zamyatin, co-founder of Build on Bitcoin (BOB), told Cointelegraph.
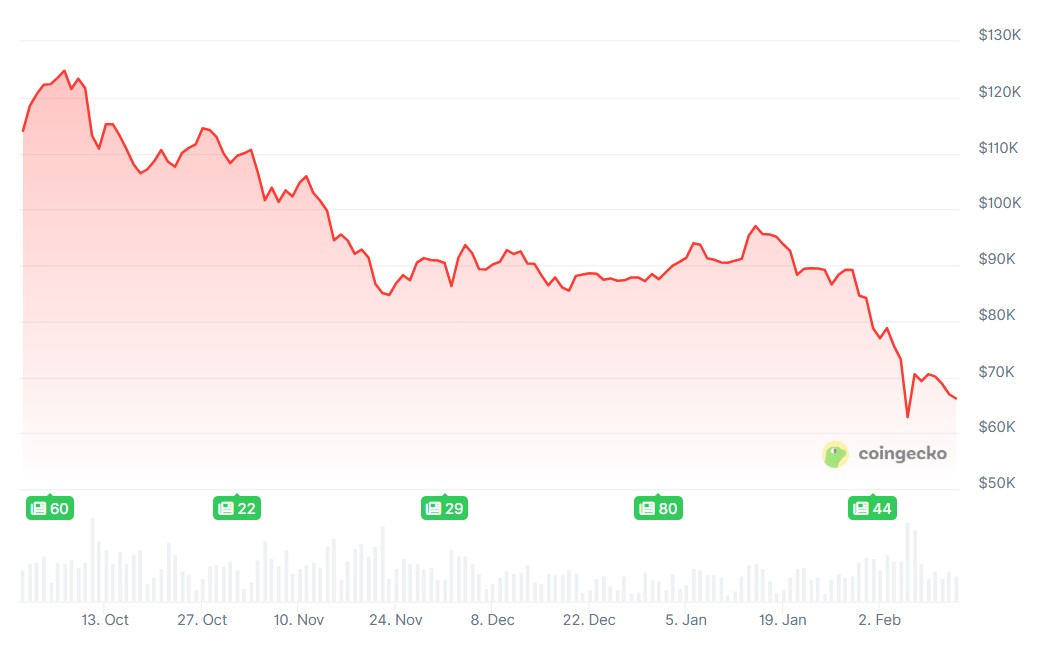
Bitcoin is trading roughly 50% below its October 2025 all-time high. Among the handful of theories attempting to explain crypto’s recent decline is a growing concern that quantum computing risks may be deterring institutional capital from Bitcoin.

The quantum risk is not zero, and it is not sudden
The quantum vulnerability often discussed is Bitcoin’s Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm, which authorizes transactions. In theory, a powerful quantum computer could derive a private key from an exposed public key and claim the coins sitting in an address.
Today’s quantum hardware isn’t capable of breaking the elliptic curve signatures. But that doesn’t mean threat actors are waiting around for a technical breakthrough.
“Many users expect a single ‘Q-Day’ in the future when cryptography suddenly fails. In reality, risk accumulates gradually as cryptographic assumptions weaken and exposure increases,” Kapil Dhiman, CEO and co-founder of Quranium, told Cointelegraph.
“Harvest now, decrypt-later strategies are already active, meaning data and signatures exposed today are being collected against future capability,” he said.
Related: What if quantum computers already broke Bitcoin?
In Bitcoin’s case, the concern is for older exposed public keys. Once a public key appears onchain, it remains permanently visible. Modern address formats obscure public keys until coins are spent.
CoinShares Bitcoin researcher Christopher Bendiksen said that just 10,230 Bitcoin (BTC) sit in addresses with publicly exposed public keys that would be vulnerable to a sufficiently powerful quantum attack.

The quantum fear business
While the Bitcoin community debates how far away quantum computing is, crypto wallet makers are operating on their own clock.
Trezor’s Safe 7 is marketed as a “quantum-ready” hardware wallet. Separately, qLabs recently introduced the Quantum-Sig wallet, which it claims embeds post-quantum signatures directly into its signing process.

BOB’s Zamyatin argued that wallet-level defenses would not solve Bitcoin’s quantum risk. Bitcoin transactions are authorized using a signature scheme embedded in the protocol itself. If that cryptography were ever broken, the fix would require a protocol-level change.
“I personally wouldn’t invest a lot of money into a quantum wallet right now because I don’t even know what protection it gives me for Bitcoin. It can’t really give me any protection, in my opinion, because Bitcoin doesn’t have a quantum-resistant signature scheme yet.”
Ada Jonušė, executive director at qLabs, agreed that full quantum resilience requires protocol-level defense. However, brushing off modern infrastructure as a fear tax overlooks the transitional nature of security upgrades.
“Quantum risk is not binary. Even before a protocol-level migration occurs, there is a real ‘harvest now, decrypt later’ threat,” she told Cointelegraph, claiming that qLabs’ approach reduces exposed key surface.
“Quantum readiness is about proactive infrastructure planning, not fear monetization,” Jonušė said.
Related: Bitcoin’s quantum countdown has already begun, Naoris CEO says
Trezor also admitted that blockchains themselves need to change their cryptography and protocol. But Tomáš Sušánka, the company’s chief technology officer, told Cointelegraph that wallets can implement protections right away instead of waiting for protracted blockchain upgrades.
“Once the blockchains upgrade, wallets must also support the same algorithms to remain compatible,” Sušánka said. He added that Trezor Safe 7 uses a post-quantum algorithm to protect against future quantum computers forging digital signatures and signing malicious firmware updates.
Market incentives and Bitcoin’s governance hurdle
Unlike iPhones, which are released almost every year, hardware wallets and other security products typically have multi-year product lifecycles. Introducing post-quantum features in a new product gives a reason for customers to buy a new device, even if the threat is distant.
“Yes, parts of the crypto industry do have incentives to amplify quantum risk, but that incentive is increasingly driven by regulatory and institutional alignment, not short-term sales alone,” said Dhiman, whose Quranium powers the Qsafe wallet.
“For most users, quantum-secure wallets today function as long-term insurance. The responsible approach is to acknowledge the transition ahead, avoid urgency driven by fear and choose systems designed to evolve without forcing abrupt replacements.”
Several blockchains are advancing with post-quantum strategies, but Bitcoin has been relatively hesitant. Some of the network’s most influential voices have brushed off the threat as a problem for the future.
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum has a widely recognized figurehead. Co-founder Vitalik Buterin has advocated for post-quantum preparations, and the network has been steering in that direction.
For Bitcoin, the issue is social consensus, coordination and the willingness to act, according to Zamyatin.
“It’s not like [Bitcoin has] one person that everyone will follow. It will require a broad social consensus, which is very hard to achieve,” he said.
Wallet makers agree that full quantum protection has to come from the protocol. But even if the risk is years away, they can act as insurance to help investors sleep better at night, though some argue they amount to a fear tax.
Magazine: Is China hoarding gold so yuan becomes global reserve instead of USD?
Cointelegraph Features and Cointelegraph Magazine publish long-form journalism, analysis and narrative reporting produced by Cointelegraph’s in-house editorial team and selected external contributors with subject-matter expertise. All articles are edited and reviewed by Cointelegraph editors in line with our editorial standards. Contributions from external writers are commissioned for their experience, research or perspective and do not reflect the views of Cointelegraph as a company unless explicitly stated. Content published in Features and Magazine does not constitute financial, legal or investment advice. Readers should conduct their own research and consult qualified professionals where appropriate. Cointelegraph maintains full editorial independence. The selection, commissioning and publication of Features and Magazine content are not influenced by advertisers, partners or commercial relationships.
Crypto World
Bhutan’s Bitcoin sales enter third straight week with $6.7M BTC offload
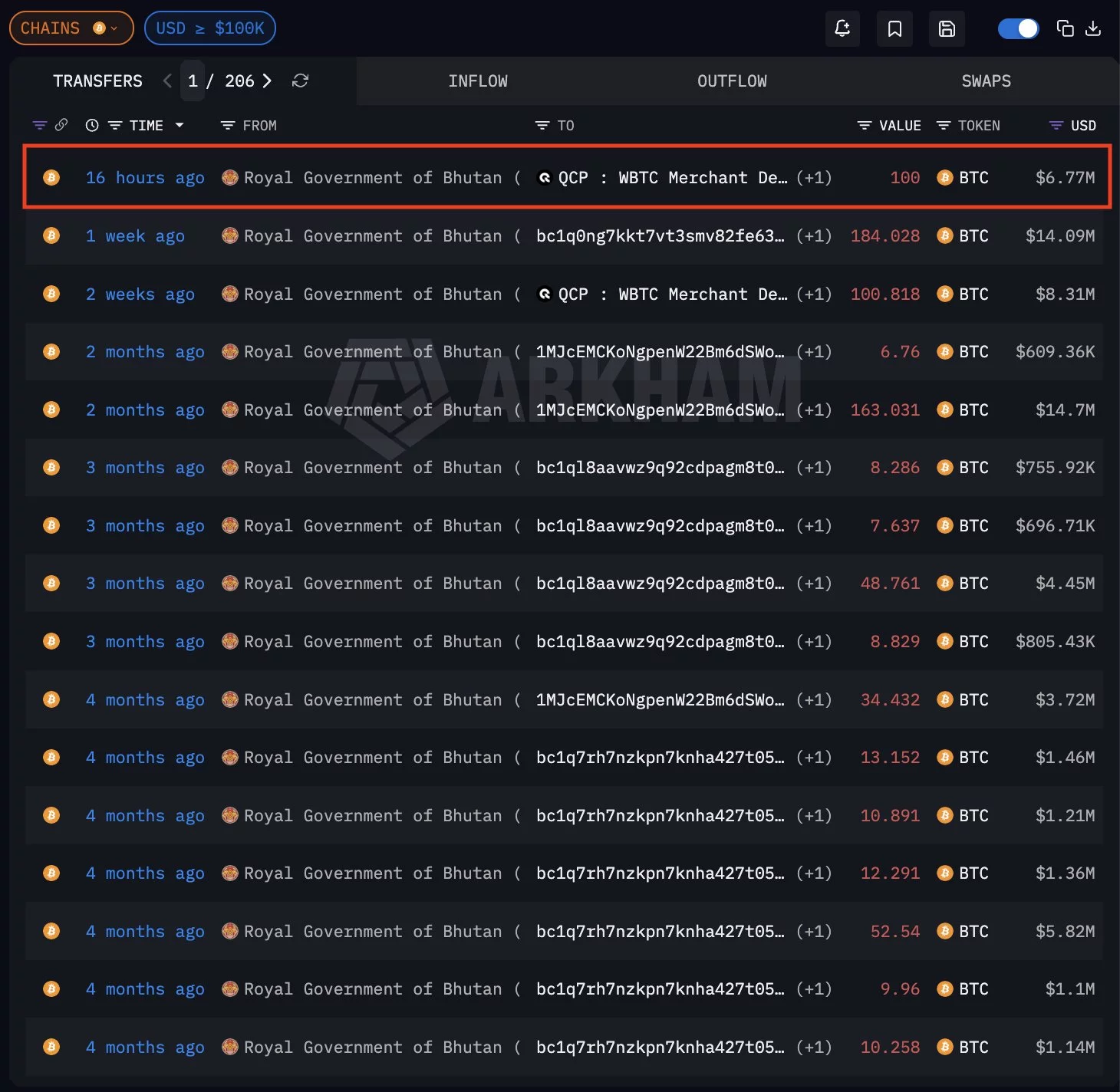
Bhutan has sold another 100 Bitcoin worth approximately $6.7 million, according to blockchain analytics platform Arkham Intelligence, which flagged the transaction in a recent post.
Summary
- Bhutan sold another 100 BTC worth about $6.7 million, marking its third consecutive week of Bitcoin transfers, according to Arkham Intelligence.
- On-chain data shows structured, repeated deposits to a QCP-linked WBTC merchant address, suggesting gradual treasury management rather than a single large liquidation.
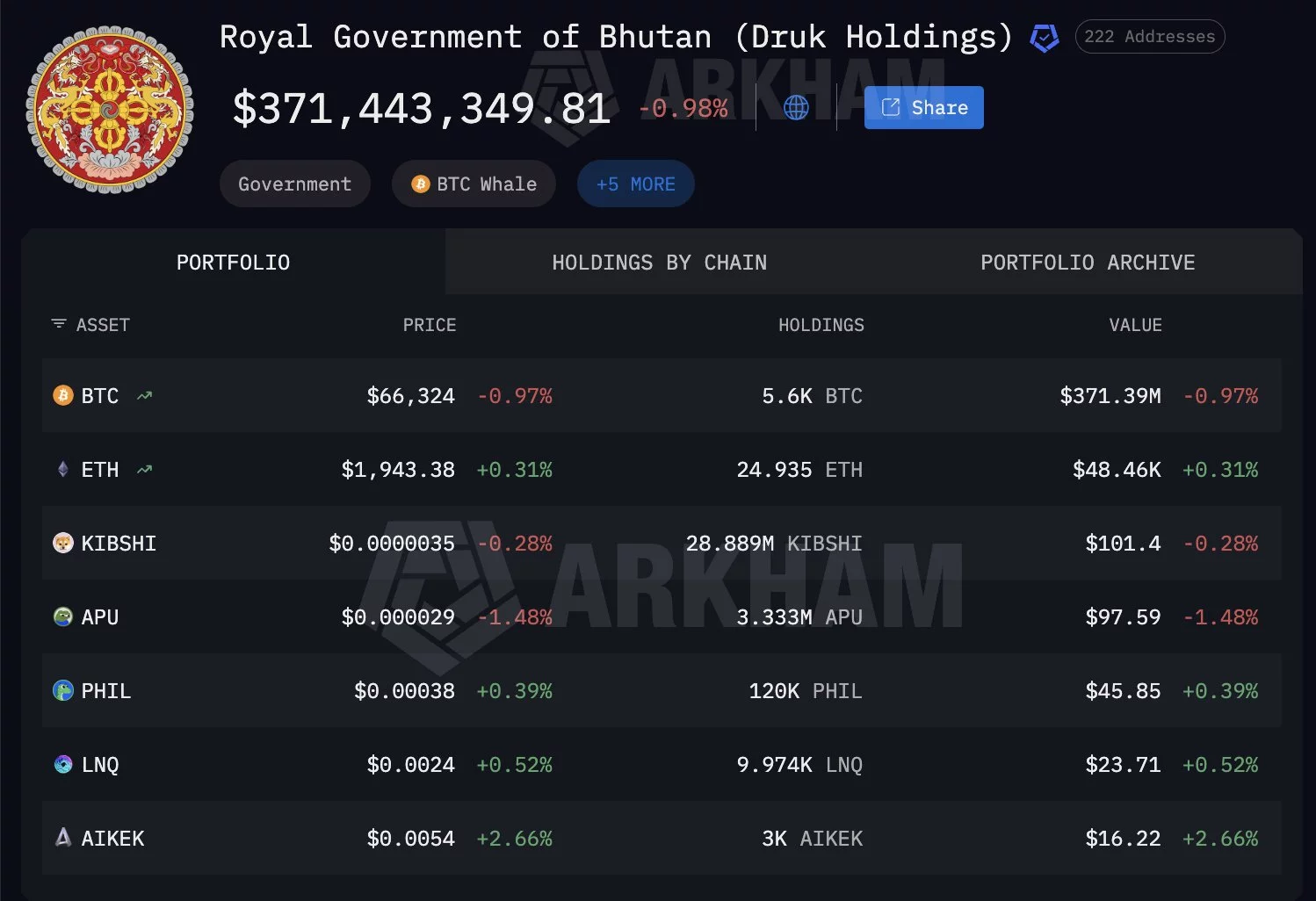
- Despite ongoing sales, Bhutan still holds roughly 5,600 BTC valued at around $372 million, keeping it among the largest sovereign Bitcoin holders.
On-chain data shared by Arkham shows the transfer occurred roughly 16 hours prior to the alert, with 100 Bitcoin (BTC) moved from wallets labeled as belonging to the Royal Government of Bhutan to an external address identified as a QCP-linked WBTC merchant deposit.
The transaction is part of what Arkham describes as three consecutive weeks of Bitcoin selling activity.
Bhutan’s weekly Bitcoin selling activity continues
The data indicates Bhutan has been gradually offloading Bitcoin in recent weeks.
Transaction history visible in Arkham’s dashboard shows multiple BTC transfers over recent weeks, including movements of 184 BTC and 100 BTC batches. The consistent pattern of deposits suggests structured selling rather than a single large liquidation.
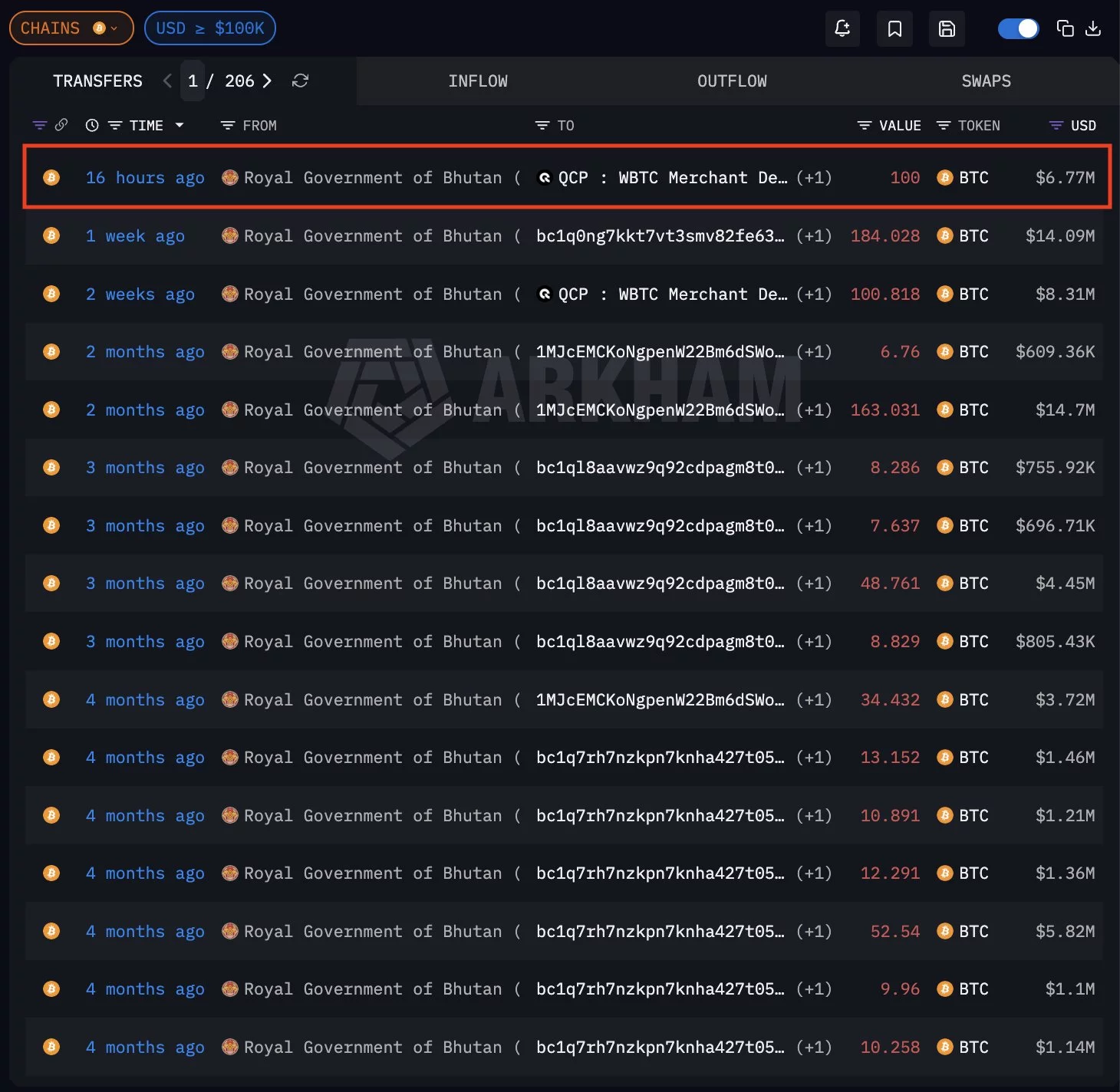
Moreover, Arkham previously reported that the country sold at least $100 million worth of BTC in September 2025, and the latest transaction suggests that the selling strategy is ongoing.
Bitcoin mining slows down after halving
Bhutan’s Bitcoin reserves are largely tied to its state-backed mining operations. The country had announced plans to scale its mining capacity to up to 600 megawatts in partnership with Bitdeer Technologies.
However, Arkham noted that on-chain mining inflows appear to have slowed following Bitcoin’s April 2024 halving event, which reduced block rewards and increased pressure on mining profitability.
The slowdown may be contributing to Bhutan’s gradual treasury sales.
Despite recent sales, Arkham data shows Bhutan still holds approximately 5,600 BTC, valued at around $372 million, across identified wallets. The holdings position Bhutan among the more significant sovereign Bitcoin holders globally.
While the transfers do not necessarily confirm immediate market selling, repeated exchange-linked deposits often signal liquidity preparation. Market participants will likely monitor whether Bhutan’s weekly BTC movements continue in the coming weeks.
Crypto World
Regional banks must partner with crypto startups now

Disclosure: The views and opinions expressed here belong solely to the author and do not represent the views and opinions of crypto.news’ editorial.
The GENIUS Act has turbocharged the United States stablecoin market, and the U.S.’s biggest banks are already cashing in. Regional banks must partner with crypto startups now if they are to bridge the digital gap, provide customers with access to the market, and share in booming stablecoin revenues. If not, they risk being locked out of the market entirely by their larger counterparts.
Summary
- Stablecoins are now a revenue line, not a side bet: $33T in annual volume and multibillion-dollar bank revenues show the opportunity is already being captured.
- Regional banks can’t outspend — but they can outpartner: Collaborating with regulated crypto startups lets them skip costly R&D and compete with Big Four infrastructure.
- The real risk is hesitation: As regulation matures and giants lock in early market share, inaction could permanently shut regional banks out of stablecoin payment flows.
In such a gloomy, bearish market environment, stablecoins have emerged as the unlikely winners. Courtesy of the dial-moving GENIUS Act, the market has been given its long-overdue seal of regulatory approval, seeing a mass uptick in consumer sentiment and institutional embrace as a result. Demand is high, mood is high, and the market is at its peak. And with a huge upside ready for the taking, regional banks cannot afford to miss out on their time in the spotlight.
Stablecoin transaction volumes rose to a record $33tn in 2025, and JPMorgan’s payments division generated over $4bn in revenue in Q2 alone last year after launching its own token. Amid current reports of earnings surges across Wall Street, one thing is clear to me: those who take the risk and invest in their ability to facilitate stablecoin transactions will win customers and revenues.
Of course, there is an obvious difference in scale between the Big Four and regional banks — but regional institutions do not need to dominate the market to benefit from it. Even in states that you’d expect to be brick-and-mortar strongholds, like Wyoming, consumer demand is booming.
Crucially, regional banks also have a strong presence in these communities. By tapping into stablecoins, they can attract new customers, including higher earners who are more likely to adopt cryptocurrency-based payment methods. Attracting and retaining customers are two of the biggest problems executives at these banks tell me they face, which is exactly why stablecoins must become a strategic priority if they are going to expand their customer base.
The problem is that many regional banks are already behind the curve on industry digitalization. It’s no secret that these capital-tight institutions don’t have the billion-dollar budgets of Bank of America and JPMorgan to invest in new technology, specialized stablecoin-friendly infrastructure, and in-house experimentation. That then leaves the question: how can these banks offer customers access to the stablecoin market, quickly, cost-effectively, and before the Big Four captures the bulk of consumer demand?
My answer is to partner with agile, frontline crypto startups. There are hundreds of cryptocurrency payment startups operating across the U.S. that can help regional banks bridge the digital gap. Equally, by leveraging startups’ tech-forward infrastructure, regional banks can skip costly in-house experimentation to meet consumer demand more efficiently.
On a larger scale, this way of thinking has already proven successful. JPMorgan, Standard Chartered, and others have partnerships with a variety of small- to large-cap crypto businesses, including Coinbase, Circle, and the startup Digital Asset. Non-traditional institutions, too, like Stripe, followed this route last year — acquiring the stablecoin orchestration platform Bridge to expand their offerings. It’s already tried and tested, which is why regional banks must also follow suit if they want a share of the spoils.
Of course, I’m not blind to the risks. The stablecoin market has a checkered past that carries significant reputational challenges, and regional banks are right to be cautious. Investors lost $40bn when TerraUSD crashed in 2022, and I have no doubt that weighs on executives’ minds.
But that was four years ago. Crypto — and indeed, stablecoins — are no longer the Wild West of financial services. In fact, with the GENIUS Act clarifying regulatory frameworks and strengthening anti-money laundering protections, stablecoins have become rapidly more mainstream in the global payments landscape for institutions and consumers alike.
Rather, concerns about the risks stablecoins pose are precisely why these partnerships are so critical. Regional banks, by working with regulated startups that already have technical frameworks, will be able to mitigate risk and avoid the costly mistakes that could come with building untested systems in-house.
The bigger danger facing regional banks is inaction. The four biggest U.S. banks currently command over half the industry’s total profits — and their dominance will only grow as they sweep up payments revenues. As regulation matures and larger banks lock in early market share, regional banks face a narrowing window of opportunity to capitalize on consumer demand.
Given that these larger institutions are unlikely to want to dilute their potential share of stablecoin revenues across thousands of competitors, the race to meet consumer demand is well and truly underway. If regional banks wait, they will gift industry titans yet another competitive edge, one that they just cannot afford to lose.
Crypto World
Crypto Stocks Rally: Coinbase (COIN) Soars 18%, Strategy (MSTR) Gains 10%

TLDR
- Coinbase (COIN) surged by 18% despite reporting a $666.7 million loss in Q4 2025 due to lower trading revenue.
- The increase in Coinbase’s stock came from strong long-term revenue growth, particularly in subscription and stablecoin services.
- Strategy (MSTR) rose 10% as Bitcoin prices rebounded and the company disclosed a purchase of over 1,100 BTC.
- Despite a multi-billion dollar quarterly loss, Strategy remains committed to holding Bitcoin through market downturns.
- Other crypto-linked stocks, including Circle (CRCL) and Galaxy Digital (GLXY), also saw positive gains in line with the sector’s upward momentum.
U.S. markets saw a rotation into risk assets today, with crypto-linked stocks such as Coinbase and Strategy among the biggest gainers. Despite mixed performances from broader indexes like the Dow and S&P 500, digital-asset exposure helped certain high-beta stocks outperform. Coinbase (COIN) surged more than 18%, while Strategy (MSTR) rose around 10%, benefitting from the rebound in Bitcoin prices.
Coinbase (COIN) Gains 18% Amid Mixed Earnings Results
Coinbase (COIN) was one of the standout performers in today’s market. The stock rose by over 18%, as traders took advantage of a dip in crypto exposure. The increase came even as the company posted a challenging earnings report for Q4 2025, with a loss of $666.7 million. This was its first quarterly loss in several quarters, driven by lower trading revenue as crypto trading volumes dropped.
Despite the loss, Coinbase managed to show strength in other areas. Long-term revenue streams, particularly subscription and services, helped cushion the negative sentiment. Stablecoin revenue, a major contributor, performed well. These factors allowed the company to maintain positive momentum, despite a tough earnings backdrop.
The stock has been under pressure in early 2026, having fallen roughly 34% year-to-date. Bitcoin prices have dropped about 30% in the past month, leading to lower trading volumes and squeezing one of Coinbase’s main revenue drivers. Analysts have expressed caution, with Monness Crespi & Hardt downgrading the stock from “buy” to “neutral” and setting a $120 price target.
Strategy (MSTR) Posts 10% Jump, Remains Committed to Bitcoin
Strategy (MSTR) also saw strong gains, rising about 10% as Bitcoin prices rebounded. Shares of the company have fluctuated heavily in line with Bitcoin’s price movements. Strategy’s commitment to adding to its Bitcoin treasury was also a key driver for the uptick. The firm disclosed the purchase of over 1,100 BTC, spending roughly $90 million at an average price near the high-$70,000 range.
Despite market turbulence, Strategy’s focus on holding Bitcoin through downturns has remained unchanged. The company posted a multi-billion dollar quarterly loss, mostly due to declines in the value of its Bitcoin holdings. Executive Chairman Michael Saylor reiterated the company’s strategy, stating that it would not sell Bitcoin during price downturns.
While the company’s Bitcoin-heavy balance sheet poses risks, Strategy has maintained a long-term holding posture. Saylor continues to defend this approach, emphasizing that the company is positioned to withstand extended volatility in Bitcoin’s price. These statements helped bolster investor confidence, despite the challenges faced in recent months.
Crypto World
Analyst Maps Out 2 Paths for Ripple’s Price


Where will XRP find a bottom and how high it would go in a subsequent bull market?
The popular cross-border token plunged hard recently, going from a January 6 peak of $2.40 to just over $1.10 during last Friday’s market-wide massacre. After crashing by over 50% within a relatively short period, it bounced off but remains sluggish below $1.40, still showing a 25% decline on a year-to-date scale.
The consensus in the cryptocurrency community is that the bear market has already begun, given the fact that not only XRP but BTC and many other larger-cap alts have plunged by 50% or more from their heights in 2025. As such, analysts have started to speculate where each asset’s bottom might be and how much pain investors would have to endure before they see a trend reversal.
$0.60 to $11?
ERGAG CRYPTO, who is among the most well-known and bullish members of the XRP army, mapped out two potential scenarios for Ripple’s cross-border token. In the first chart, the bottom is presented at $0.60, which would essentially erase all gains charted after Trump’s presidential election victory in late 2024 and push the asset back to its starting point at the time.
This chart comes with a deeper drawdown, continuous fear and disbelief, and weak hands getting flushed. On the upside, XRP could go on a sublime run once the market reverses and the bulls take over, with the analyst predicting a surge to a $11 top.
#XRP – Chart 1 or Chart 2?
💡This isn’t opinion. It’s math, structure, and market behavior.
💡Markets don’t reward comfort. They reward conviction under pressure.
💡Choose your pain or pain will choose you.
📉 Chart 1:
▫️Bottom: $0.60
▫️Top: $11
▫️ Deeper drawdown
▫️ Fear… pic.twitter.com/7KxtTwcd2A— EGRAG CRYPTO (@egragcrypto) February 13, 2026
More Modest Prediction
The alternative in ERGAG CRYPTO’s mapping was a second chart showing lower volatility ahead in both directions. The bottom would be around $0.90, while the top could be $8.5.
This scenario would provide investors with more comfort and less pain, but its upside potential would also be lower, the analyst added.
You may also like:
At the time of writing, both bottoms seem more likely to be reached, while the tops appear quite far-fetched. After all, XRP would have to skyrocket by 3x (or more) from its 2025 all-time high of $3.65 before it can challenge the double-digit price levels. In contrast, going to $0.90 or even $0.60 in the current market environment seems rather reasonable.
Nevertheless, market trends can change extremely quickly, and XRP has proven in the past that it’s capable of remarkable runs. After the US elections, it went from $0.60 to $3.40 in just a few months, which is a 466% surge.
SECRET PARTNERSHIP BONUS for CryptoPotato readers: Use this link to register and unlock $1,500 in exclusive BingX Exchange rewards (limited time offer).
Crypto World
What It Means for Ether Price

Ether traded back above the $2,000 level on Friday, extending gains after the US consumer price index print came in cooler than expected. The relief rally adds to a nascent recovery narrative that could open the door to a test of higher targets if momentum sustains. Market participants are parsing a mix of on-chain signals, leverage data, and institutional demand as they gauge whether this move can translate into a durable bottom or simply a short-lived bounce. With weekly closes in focus, traders are watching for follow-through in the days ahead, while crypto derivatives data continues to feed the debate over whether risk appetite is finally pivoting in Ethereum’s favor.
Key takeaways
- Ether futures’ open interest across major exchanges has fallen by about 80 million ETH in the past 30 days, signaling a broad reduction in leveraged exposure rather than new long bets.
- Binance, the largest venue by volume, led the decline with roughly 40 million ETH pulled from futures positions (about half of the total drop), underscoring a widespread de-risking trend across top platforms.
- Across Gate, Bybit and OKX, combined declines pushed the total among the four major platforms toward a cumulative drop of roughly 75 million ETH, suggesting the trend is not isolated to a single exchange.
- Funding rates on Binance slipped into deep negative territory (around -0.006), the lowest seen in about three years, implying extreme bearish positioning that could set the stage for a short squeeze if buyers re-emerge.
- Technically, Ether has carved out a bullish setup, breaking from a falling wedge and hovering near $2,050; a measured move could target around $2,150, with potential tests of the 100-period SMA near $2,260 and a path toward $2,500 if demand accelerates.
- On-chain activity and rising institutional demand have persisted as tailwinds, with cost-basis accumulation identified around the $1,880–$1,900 zone helping form a potential price base for further upside.
Tickers mentioned: $ETH
Sentiment: Bullish
Price impact: Positive. The cooler CPI print contributed to a rebound from the $2,000 area and increased odds of an extended bounce toward higher targets.
Trading idea (Not Financial Advice): Hold. The setup points to potential upside on continued demand signals, but traders should remain mindful of macro surprises and the possibility of renewed volatility if liquidity conditions shift.
Market context: The latest inflation data appears to have nudged investors back toward risk assets, helping to ease some of the near-term macro headwinds that had weighed on crypto markets. Although liquidity remains uneven across venues, the combination of weaker-than-expected inflation readings and supportive on-chain dynamics has contributed to a more constructive backdrop for Ethereum in the near term.
Why it matters
From a market perspective, Ethereum’s price action this week matters not only for holders but for the broader crypto ecosystem. The confluence of falling open interest and negative funding rates suggests many participants were trimming risk rather than chasing new bets, which can reduce the likelihood of rapid, force-driven liquidations in a downside scenario. In such environments, a cleaner backdrop often arises where a new rally can take hold more easily if buyers step in decisively, creating a more stable price base. The sustained improvement in network activity and inflows from institutional actors adds another layer of fundamental support that could help underpin a more durable recovery beyond short-term speculative moves.
On the on-chain front, the observed accumulation at sub-$2,000 levels signals a cadre of investors is building a longer-term stance, a factor that matters because the health of Ether’s network—usage, validator activity, and transaction throughput—has historically fed into price resilience. This dynamic aligns with discussions in the space about Ether’s role not just as a trading instrument but as a network with ongoing growth potential, particularly if demand from institutions and developers continues to accrete.
For market participants, the critical question is whether the $2,000 threshold can function as a genuine floor in the current cycle. If price can hold that level and push higher, momentum could attract fresh buyers and sequentially lift Ether toward the $2,150–$2,260 range in the near term, with a longer arc toward the $2,500 zone if fundamental and technical signals align. Conversely, a break below that level could accelerate downside risk, especially if systemic liquidity tightens or macro headlines shift sentiment once again. In either case, the latest data suggest that the market is closer to a base-building phase than a continuation of the prior downtrend.
What to watch next
- Monitor whether ETH holds the $2,000 support on continued trading sessions and whether buyers emerge at the next test of resistance around $2,150.
- Track open interest and funding rates across major exchanges for signs of capitulation ending or renewed leverage entering the market.
- Watch for a potential challenge to the 100-period simple moving average near $2,260 and any subsequent move toward $2,500 if momentum remains constructive.
- Observe on-chain signals, including ongoing accumulation patterns and institutional flow indicators, for signs of sustained demand beyond short-term price action.
Sources & verification
- CryptoQuant Quicktake: Ethereum open interest across major exchanges declines by over 80 million ETH in 30 days.
- CryptoQuant analysis on funding rates hitting -0.006, the lowest level since December 2022, signaling extreme bearish positioning.
- Glassnode heatmap data showing a cost-basis distribution with substantial support between $1,880 and $1,900 and roughly 1.3 million ETH accumulated there.
- On-chain signals and institutional inflows discussed in related coverage, including notes on network activity tailwinds for Ether.
Ether price action and outlook
Ether broke out of a descending wedge on the four-hour chart and traded around $2,050 at the time of observation. The measured move from the breakout points toward $2,150 highlights a near-term upside trajectory, with the potential to test higher resistance if the rally gains traction. The same chart framework points to possible retests of the 100-period simple moving average near $2,260, followed by a pathway toward the $2,500 horizon should momentum accelerate beyond the immediate levels.
On the downside, a firm hold above the psychological $2,000 level remains a critical anchor, reinforced by the 50-period moving average that has acted as interim support in recent sessions. The cost-basis distribution heatmap from Glassnode emphasizes a populated zone beneath the current price, where long-term holders have previously shown willingness to accumulate, which could provide a stabilizing force if price action turns choppy in the near term.
Historically, periods of negative funding rates at strong price floors have preceded short squeezes that sparked sharper moves to the upside. If the current dynamic persists—declining open interest, controlled leverage, and improving macro sentiment—ETH could establish a more durable base rather than form a brief rally followed by renewed volatility. As market attention shifts toward macro cues and ETF developments, investors will be watching how ETH behaves around key support levels and whether on-chain demand sustains the current trajectory.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Gains 4% As Soft US CPI Boosts March Rate-Cut Odds
Bitcoin (BTC) gained at Friday’s Wall Street open as a fresh US inflation surprise boosted the mood.
Key points:
-
Bitcoin price action heads toward key resistance after US CPI inflation data cools beyond expectations.
-
Crypto becomes a standout on the day as macro assets see a cool reaction to slowing inflation.
-
Traders stay wary on overall BTC price strength.
Bitcoin spikes on soft January CPI data
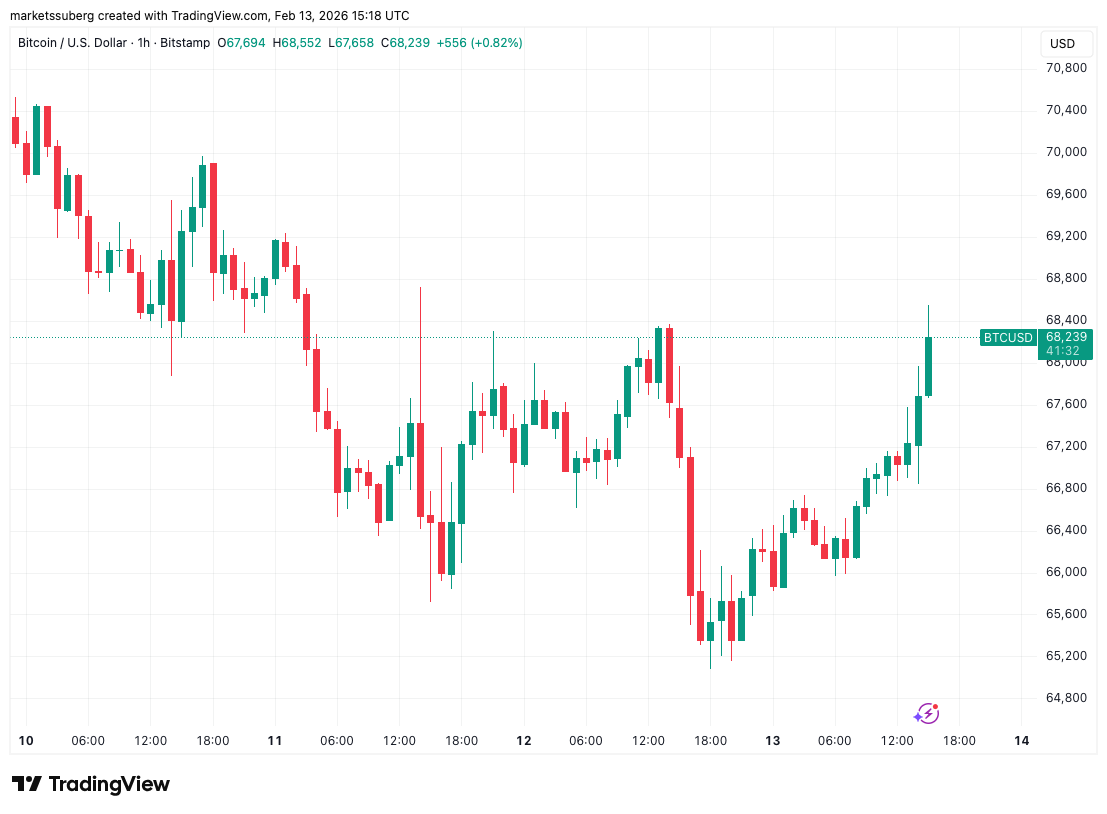
Data from TradingView showed up to 4% daily BTC price gains at the time of writing, with BTC/USD reaching $69,190 on Bitstamp.

The renewed upside came after the January print of the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) fell short of expectations.
As confirmed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), core CPI matched estimates of 2.5%, while the broader reading was 2.4% — 0.1% lower than anticipated.

Reacting, trading resource The Kobeissi Letter noted that CPI inflation was now at multiyear lows.
“Core CPI inflation is now at its lowest level since March 2021,” it wrote in a post on X.
“Odds of further interest rate cuts are back on the rise.”

Kobeissi referred to the prospects of the Federal Reserve cutting interest rates at its next meeting in March. As Cointelegraph reported, market expectations of such an outcome were previously at rock bottom, not helped by strong labor-market performance.
After the CPI release, odds of a minimal 0.25% cut remained at less than 10%, per data from CME Group’s FedWatch Tool.
Continuing, Andre Dragosch, European head of research at crypto asset manager Bitwise, argued that when viewed through the lens of Truflation, an alternative inflation meter, the CPI drop was “not really a surprise.”
📌RE: CPI Release
Not really a surprise there if you have been following the @truflation CPI number which has plummeted sub-1% already…
IYKYK pic.twitter.com/GPEUqaSNZI
— André Dragosch, PhD⚡ (@Andre_Dragosch) February 13, 2026
Elsewhere on macro, gold attempted to reclaim the $5,000 per ounce mark, while the US dollar index (DXY) sought a recovery after an initial CPI drop to 96.8.
US stocks, on the other hand, failed to copy Bitcoin’s enthusiasm, trading modestly down on the day at the time of writing.
Analyst eyes current range for BTC price higher low
Considering the outlook for BTC price action, market participants had little reason to alter their cautious positions.
Related: Binance teases Bitcoin bullish ‘shift’ as crypto sentiment hits record low
“$BTC Still consolidating in this falling wedge,” trader Daan Crypto Trades wrote in his latest X update.
“Attempted a break out yesterday but got slammed back down at the $68K level. That’s the area to watch if this wants to see another leg up at some point.”

Earlier, Cointelegraph reported on the significance of the $68,000-$69,000 zone, which plays host to both the old 2021 all-time high and Bitcoin’s 200-week exponential moving average (EMA).
“Whether you like it or not: Bitcoin remains to be in an area where I think that we’ll see a higher low come in,” crypto trader, analyst and entrepreneur Michaël van de Poppe predicted in his own forecast.
“It’s fragile, for sure, but it doesn’t mean that we’re not going to be seeing some momentum coming in from the markets.”

This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision. While we strive to provide accurate and timely information, Cointelegraph does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any information in this article. This article may contain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Cointelegraph will not be liable for any loss or damage arising from your reliance on this information.
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy Israel is blocking foreign journalists from entering
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoJD Vance booed as Team USA enters Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
 Business5 days ago
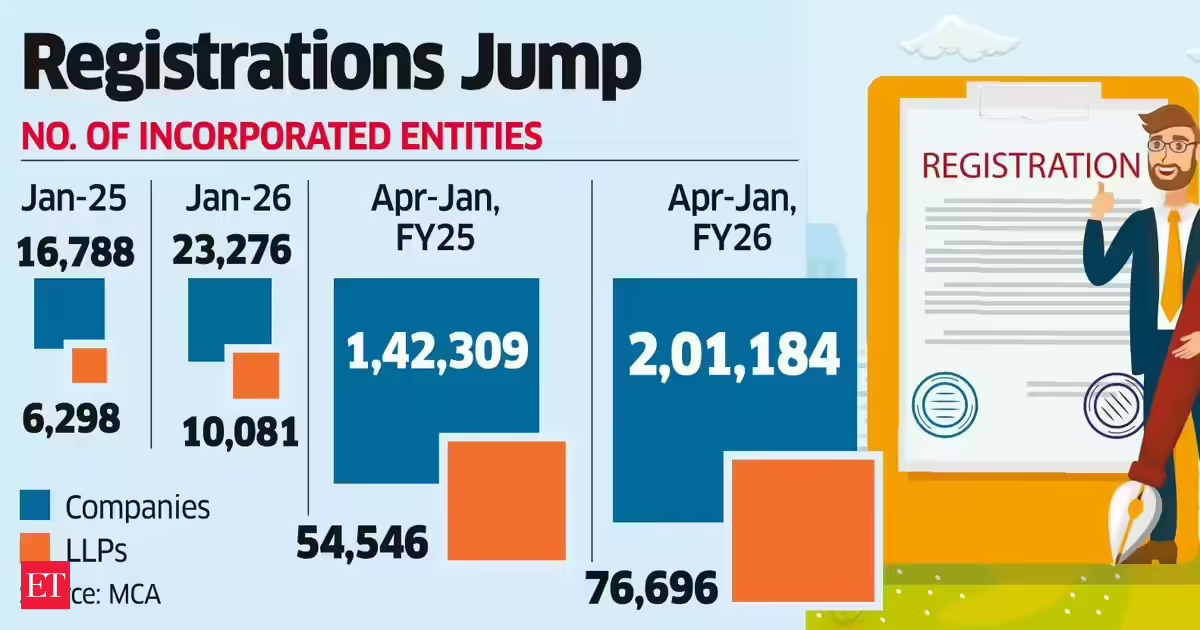
Business5 days agoLLP registrations cross 10,000 mark for first time in Jan
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoMia Brookes misses out on Winter Olympics medal in snowboard big air
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoCostco introduces fresh batch of new bakery and frozen foods: report
-

 Tech3 days ago
Tech3 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-

 NewsBeat5 days ago
NewsBeat5 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Team GB’s Mia Brookes through to snowboard big air final, and curling pair beat Italy
-

 Video16 hours ago
Video16 hours agoThe Final Warning: XRP Is Entering The Chaos Zone
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoBenjamin Karl strips clothes celebrating snowboard gold medal at Olympics
-
Sports7 days ago
Former Viking Enters Hall of Fame
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoThe Health Dangers Of Browning Your Food
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoJulius Baer CEO calls for Swiss public register of rogue bankers to protect reputation
-
 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-

 Video2 days ago
Video2 days agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month
-

 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-

 NewsBeat5 days ago
NewsBeat5 days agoResidents say city high street with ‘boarded up’ shops ‘could be better’
-
Sports4 days ago
Kirk Cousins Officially Enters the Vikings’ Offseason Puzzle
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoEthereum Enters Capitulation Zone as MVRV Turns Negative: Bottom Near?







