Crypto World
Solana price confirms bull trap as local structure shifts bearish
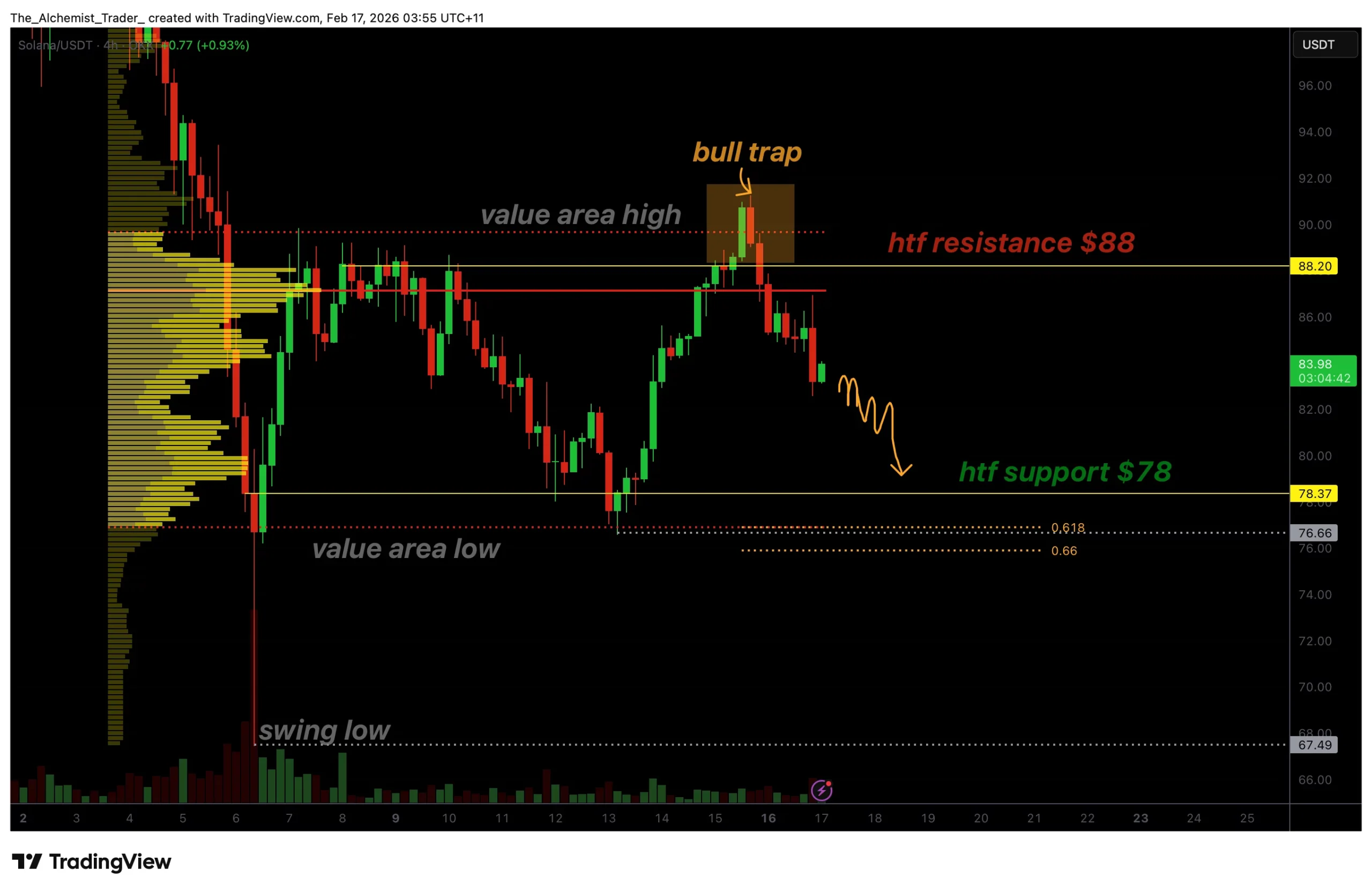
Solana’s price invalidated its recent breakout attempt after failing to hold above key resistance, confirming a bull trap and shifting the short-term market structure back to bearish.
Summary
- Failed breakout above $88 confirms bull trap, trapping late buyers
- Rejection at the point of control signals bearish control, favoring downside rotation
- $78 support is the key level to watch, with potential reaction or swing-failure setup
Solana (SOL) price has entered a critical corrective phase after recent price action failed to sustain acceptance above major resistance levels. What initially appeared to be a bullish continuation has now revealed itself as a classic bull trap, catching late buyers before the price reversed sharply lower.
This type of failed breakout often marks an important inflection point, especially when it occurs at high-timeframe resistance and value extremes.
As price rotates back into its prior trading range, technical signals suggest that downside continuation is now the higher-probability scenario in the immediate short term.
Market participants are closely watching how Solana behaves as it approaches key support levels, where either further breakdown or a reactive bounce may emerge.
Solana price key technical points
- Bull trap confirmed above $88 resistance, invalidating the bullish breakout
- Rejection at the point of control signals weakness, favoring range rotation lower
- $78 high-timeframe support comes into focus, with Fibonacci confluence below
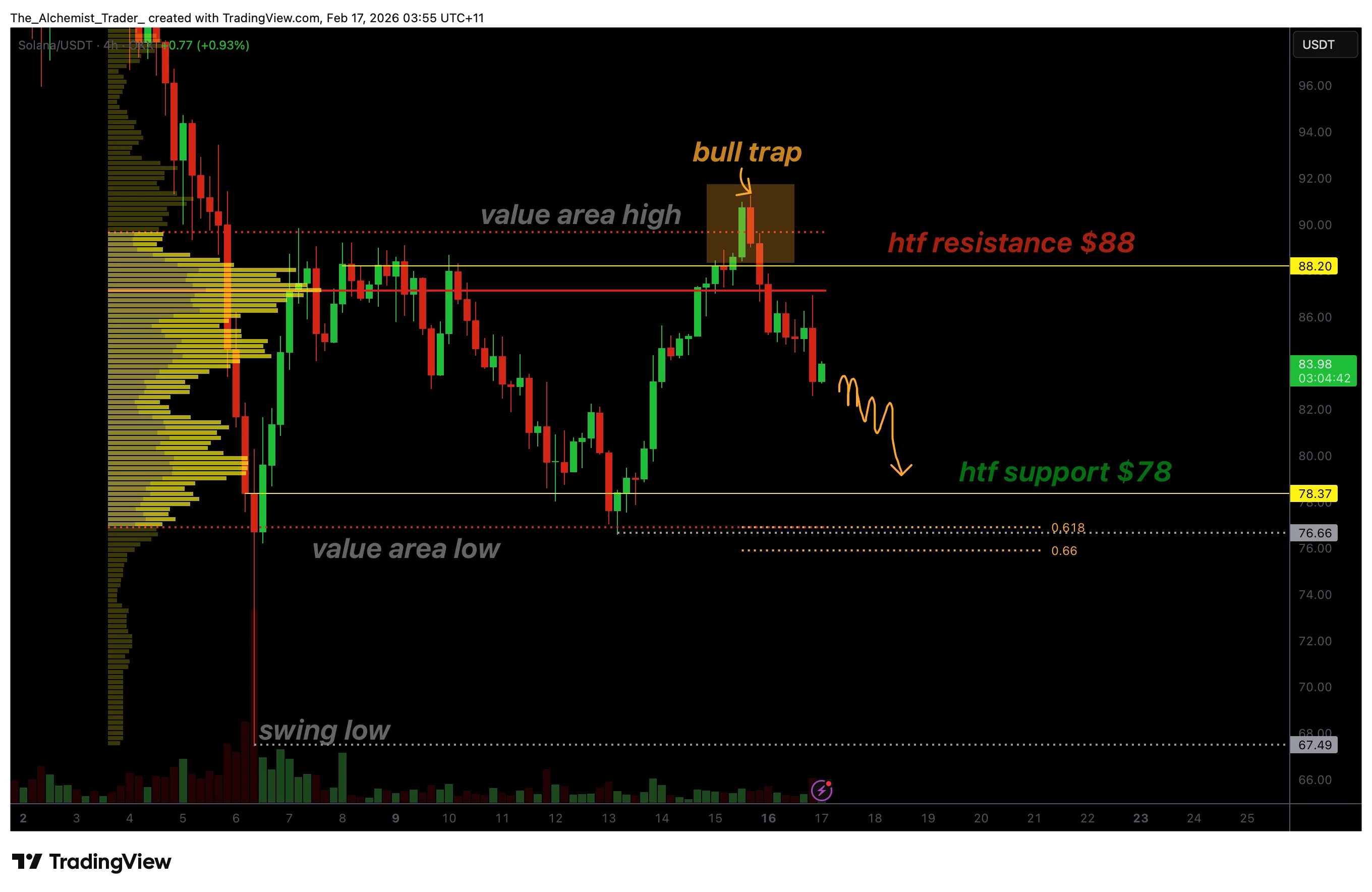
Solana’s recent rally pushed price above the value area high and into high-timeframe resistance near the $88 region. However, this move lacked sustained acceptance. Instead of consolidating above the resistance, the price quickly stalled and reversed, signaling that buyers were unable to maintain control at higher levels.
This behavior is characteristic of a bull trap, where price briefly trades above resistance to attract breakout buyers before reversing back into the prior range. Once acceptance above resistance fails, the resulting move lower is often sharp as trapped longs are forced to exit positions.
The inability to hold above the value area high was the first warning sign. This level typically defines the upper boundary of fair value within a range, and rejection here often leads to rotations back toward lower value.
Rejection at point of control confirms bearish shift
Following the failure above resistance, Solana rotated back into the trading range and attempted to stabilize near the point of control (POC). The POC represents the price level at which the highest trading volume has occurred and often serves as a balance point during consolidation phases.
However, Solana was unable to reclaim or hold above this level. The rejection at the POC confirms that sellers remain dominant and that the market has transitioned from balance into renewed imbalance. When a price is rejected at the POC after a failed breakout, it significantly increases the probability of a full-range rotation.
This rejection marks a clear shift in short-term market structure, turning the local bias bearish and opening the path toward lower support levels.
$78 support becomes the immediate downside target
With local structure now bearish, attention turns to the next major downside level. High-timeframe support near $78 stands out as the primary target. This region aligns with the value area low and represents the lower boundary of the broader trading range.
Importantly, the 0.618 Fibonacci retracement rests just below this level, adding further technical confluence. Fibonacci retracement zones often act as magnets for price during corrective phases, particularly after failed breakouts.
A move into this region would complete a full range rotation and likely coincide with increased volatility as liquidity is tested. Whether Solana stabilizes or continues to decline will depend heavily on the reaction at this support zone.
Swing failure pattern could signal reversal
While the immediate bias favors downside continuation, the $78 region is not just a bearish target — it is also a potential inflection zone. If price sweeps below this support, tests the 0.618 Fibonacci level, and then quickly reclaims the level, it could form a swing failure pattern (SFP).
Such behavior would indicate a liquidity grab rather than a true breakdown and could mark the beginning of a corrective bounce or even a larger reversal, depending on volume and follow-through. For this reason, price action around $78 should be monitored closely rather than treated as an automatic breakdown.
What to expect in the coming price action
From a technical, price action, and market structure perspective, Solana’s recent rejection confirms a bull trap and shifts short-term momentum firmly bearish. As long as the price remains below the value area high and the point of control, downside continuation toward the $78 support zone remains the higher-probability outcome.
Until bullish acceptance returns above key value levels, rallies should be treated with caution. The market is now in a corrective rotation phase, and how Solana reacts around $78 will likely define the next major move.
Crypto World
Paradigm reframes Bitcoin mining as a grid asset, not energy drain

A surge in AI data-center activity has rekindled a long-running energy debate, pitting grid operators and policymakers against critics who warn that massive computing operations threaten power reliability and push up electricity costs in parts of the United States. In this backdrop, a February 2026 research note from Paradigm reframes Bitcoin mining within electricity markets, arguing that it behaves as a flexible demand source rather than a static drain on energy resources. The note, which surveys grid conditions and market signals, estimates Bitcoin’s current share of global energy use at about 0.23% and its global carbon emissions at roughly 0.08%. It emphasizes that the network’s issuance schedule and periodic reward reductions inherently cap long-run energy growth, shaping how miners respond to price signals and competing generators. The analysis by Paradigm’s Justin Slaughter and Veronica Irwin, anchored by a public discussion of energy modeling assumptions, invites a more nuanced view of mining’s role in modern electricity systems, beyond broad environmental comparisons.
Key takeaways
- Paradigm argues that Bitcoin mining is best viewed as flexible grid demand, adjusting consumption in response to real-time electricity prices and grid stress rather than remaining a fixed, unresponsive load.
- The note quantifies mining’s slice of the energy pie—about 0.23% of global energy use and roughly 0.08% of global carbon emissions—while noting the long-run growth is economically constrained by the fixed issuance schedule and periodic halving of rewards.
- Critiques of mining energy use that rely on per-transaction measurements are highlighted as misleading, since energy consumption is tied to network security and miner competition, not transaction volume alone.
- With increasing AI data-center deployments, several miners are partially pivoting to AI workloads to capture higher margins, reshaping the industry’s profile and demand patterns for power.
- The policy implication is a shift from alarmist energy comparisons to evaluating mining within the broader electricity market—raising questions about how regulators should model and price flexible demand in grid planning.
Tickers mentioned: $BTC
Sentiment: Neutral
Market context: The conversation sits at the intersection of expanding AI infrastructure, grid reliability concerns, and a broader shift toward demand-side flexibility in electricity markets as crypto miners and traditional energy users alike react to price signals and regulatory frameworks.
Why it matters
The framing offered by Paradigm has the potential to recalibrate how policymakers and market participants think about crypto mining. If mining is treated as a responsive load that can scale up or down with grid conditions, it could be integrated more deliberately into demand-response programs and ancillary-services markets. This view challenges simplistic comparisons that measure energy use in isolation or rely on per-transaction efficiency metrics, which may obscure how miners contribute to grid resilience during periods of surplus or shortage.
The discussion also taps into a broader industry trend: the repurposing of crypto-era infrastructure to artificial intelligence workloads. As margins in traditional mining shift and data-center economics evolve, several players have begun to reallocate hardware and capacity toward AI processing. The shift has been noted across industry reporting and is reflected in the pathways taken by some miners to pursue higher-margin opportunities while continuing mining activities where economics permit. For example, coverage of the AI-data-center wave highlights how existing facilities and equipment can be adapted to meet surging demand for AI workloads, potentially altering regional power usage profiles and pricing dynamics.
At the core of Paradigm’s argument is the idea that energy modeling should reflect the realities of competitive electricity markets rather than rely on static benchmarks. By foregrounding grid conditions, price signals, and the possibility of demand response, the authors argue that Bitcoin mining’s energy footprint can be contextualized within the wider ecosystem of grid economics. This does not absolve miners of responsibility for energy use, but it suggests a framework in which policy decisions are informed by how mining interacts with supply and demand in real time, including its capacity to absorb excess generation or reduce demand during stress events.
The note also emphasizes that energy use and emissions are not the only metrics at play. Understanding where mining sits on the supply curve—where electricity is produced or curtailed—can illuminate why certain regions attract mining operations at particular times and how these operations might contribute to stabilizing grids during peak periods. In this sense, the narrative shifts from a binary “drain vs. benefit” debate to one about how energy users of all kinds can participate in a more dynamic, price-responsive market environment.
As AI infrastructure expands, the mining ecosystem’s response matters for both regional policy and investor sentiment. The industry’s evolving footprint—toward AI workloads in some cases—could influence where and how power is allocated, how utilities price peak versus off-peak energy, and how regulators design frameworks that accommodate flexible demand. While Paradigm’s conclusions are not universal prescriptions, they provide a structured lens for evaluating mining within electricity markets rather than through narrow environmental comparisons alone. The broader takeaway is a push for more sophisticated, market-responsive energy modeling that accounts for price signals, grid constraints, and the real-world behavior of miners under variable conditions.
What to watch next
- Publication and discussion of Paradigm’s February 2026 note and any ensuing responses from policymakers or industry groups.
- New analyses or grid studies examining the elasticity of mining demand in response to real-time pricing and transient grid conditions.
- Regulatory activity at state or federal levels addressing crypto-mining energy use, permitting, and integration with demand-response programs.
- Updates on the mining-to-AI workload transition, including pilot projects and capital reallocation by major miners such as those that have publicly discussed strategic shifts.
Sources & verification
- Paradigm, “Clarifying misconceptions about Bitcoin mining” (February 2026) – note the energy-use and emissions figures and the discussion of market signals. https://www.paradigm.xyz/2026/02/clarifying-misconceptions-about-bitcoin-mining
- Discussion of AI data centers and Bitcoin mining’s local resistance in the U.S. referencing grid- and energy-demand concerns. https://cointelegraph.com/news/ai-data-centers-local-resistance-bitcoin-mining
- Bitcoin mining outlook and profitability shifts in the context of AI-driven infrastructure changes. https://cointelegraph.com/news/bitcoin-mining-outlook-2026-ai-profitability-consolidation
- Bitcoin miner production data illustrating the scale of winter-storm disruption in the U.S. https://cointelegraph.com/news/bitcoin-miner-output-us-winter-storm-latest-data
Bitcoin mining as flexible grid demand in the AI era
Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) mining is increasingly described as a dynamic, price-driven participant in electricity markets rather than a fixed-energy burden. The February 2026 Paradigm note insists that miners act as flexible loads, changing consumption in response to grid stress or surplus supply. This reframing rests on the premise that energy use is not merely a function of transaction volume; it is tied to network security, miner competition, and how power markets price electricity in real time. In practical terms, mining operations tend to gravitate toward the lowest-cost energy sources, often leveraging off-peak generation or surplus capacity, which enables them to scale demand up or down as conditions warrant. The ability to modulate consumption makes mining responsive to price signals, a characteristic that can be valuable to grid operators seeking to balance supply and demand without relying solely on traditional capacity additions.
AI data centers have accelerated this discussion, as industry coverage highlights shifts in crypto-era infrastructure toward AI workloads in some cases. While Bitcoin mining remains a core use case for many facilities, the broader trend underscores how high-density computing can be repurposed to align with profitability drivers and grid economics. Several traditional mining operators, including Hut 8, HIVE Digital, MARA Holdings, TeraWulf, and IREN, have begun exploring partial transitions toward AI processing, highlighting how portfolio strategy can adapt to evolving margins and demand profiles. The implications for energy policy are meaningful: rather than treating all high-energy activities as equivalent, regulators may consider how to integrate flexible-demand resources into reliability and pricing frameworks while maintaining environmental safeguards.
Paradigm’s argument also emphasizes that energy models should reflect the realities of constrained energy systems. If mining adapts to price signals and grid conditions, its contribution to energy demand may be more volatile but potentially more compatible with markets seeking to absorb intermittent generation or reduce peak demand. The authors point to a broader energy-economics logic: when miners respond to scarcity or surplus, they participate in price formation and help balance the system—an argument that invites policymakers to evaluate mining within the rightsized context of electricity markets and grid resilience rather than through simplistic energy-versus-environment comparisons. The discussion aligns with recent coverage of AI infrastructure’s supercycle, suggesting that the real opportunity lies not in static energy tallies but in understanding how demand shapes and responds to evolving grid dynamics.
Crypto World
Court Slams BitBoy With Punitive Damages Over Viral Accusations Against Kevin O’Leary


Armstrong had previously published O’Leary’s private phone number and urged followers to harass him as a supposed murderer.
A United States federal judge has ordered crypto influencer Ben Armstrong, previously known as “BitBoy,” to pay $2.8 million after he failed to defend himself in a defamation lawsuit brought by investor and television personality Kevin O’Leary.
According to court documents, US District Judge Beth Bloom of the Southern District of Florida entered the default judgment on Thursday, while citing Armstrong’s lack of any response during the proceedings. The damages award includes roughly $78,000 for reputational harm, $750,000 for emotional distress, and $2 million in punitive damages.
Background of the Case
The case stems from a series of posts Armstrong published on X in late March 2025, in which he accused O’Leary and his wife of murder and alleged they paid millions of dollars to cover up their involvement in a fatal 2019 boating collision in Ontario.
Two people were killed when one boat struck another on a lake, but O’Leary was only a passenger and was never charged. His wife, Linda O’Leary, on the other hand, was later acquitted of careless operation of a vessel following a 13-day trial. Armstrong publicly disclosed O’Leary’s private phone number and urged followers to contact him as a “real-life murderer.” These posts prompted a temporary suspension from the platform.
In January 2026, Armstrong moved to overturn the default judgment. He said incarceration and mental health problems prevented his involvement, while sealed filings referenced a bipolar disorder diagnosis. The court rejected the request and noted that Armstrong had been properly served and waited nearly a year before taking action.
Legal Woes
The ruling further expands the list of legal troubles facing Armstrong, who has faced repeated arrests since 2023. He was taken into custody in March 2025 on a fugitive warrant tied to alleged threats sent to a Georgia judge and was arrested again in June 2025 on multiple counts of harassing phone calls.
Armstrong was removed from the BitBoy Crypto brand in August 2023 after its parent company cited substance abuse concerns, which ended his run as one of the most visible figures in crypto media.
His career was repeatedly overshadowed by controversy, including admissions of paid promotions for failed or fraudulent projects and a high-profile legal dispute with YouTuber Atozy that he ultimately abandoned after a backlash from the crypto community.
SECRET PARTNERSHIP BONUS for CryptoPotato readers: Use this link to register and unlock $1,500 in exclusive BingX Exchange rewards (limited time offer).
Crypto World
Tokenized Real-World Assets See 13.5% Growth Amid Crypto Market Slump

TLDR
- The total value of tokenized real-world assets increased by 13.5% over the past 30 days.
- Ethereum led the growth in tokenized assets, with a $1.7 billion rise in value.
- Tokenized US Treasuries and government debt remain the largest category in the market.
- Institutional participation is growing, with major players like BlackRock and JPMorgan entering the space.
- Tokenized money market funds are evolving, now serving as collateral in trading and lending markets.
Tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) have seen consistent growth, with the total value of onchain RWAs rising 13.5% over the past month. Despite the broader cryptocurrency market shedding $1 trillion in value, the tokenized asset sector continues to show resilience. The demand for tokenized RWAs, especially among institutional investors, reflects a growing interest in utilizing blockchain for traditional financial products.
Ethereum Leads Growth in Tokenized Assets
Ethereum recorded the highest growth in tokenized asset value, with an increase of $1.7 billion. Other blockchain networks, such as Arbitrum and Solana, followed closely, showing $880 million and $530 million in growth, respectively. The surge in value across these networks reflects the broader adoption of blockchain-based tokenized products.
The rise in Ethereum’s dominance highlights the growing role of the blockchain in asset tokenization. As the blockchain’s infrastructure strengthens, more institutions are entering the space, increasing demand for tokenized products. The growth in tokenized asset issuance has also contributed to the overall market rise.
Tokenized US Treasuries and government debt continue to dominate the tokenized asset space, accounting for over $10 billion in onchain products. These assets have seen continuous inflows, which further support their dominant position. As demand grows, more tokenized government securities are being issued on public blockchains.
The expansion of tokenized government debt demonstrates the increasing appeal of blockchain for settling traditional financial assets. Large institutions such as BlackRock, JPMorgan, and Goldman Sachs have shown active participation in this growing market. Their involvement indicates that tokenized government products are becoming a key focus of institutional investment.
Institutional Participation Drives Tokenized Asset Growth
The demand for tokenized assets points to deeper institutional participation in the space. Asset managers are increasingly issuing and settling tokenized versions of traditional financial products. Tokenized money market funds, which were once seen as yield vehicles, are now serving as collateral in trading and lending markets.
BlackRock’s move into decentralized finance with the launch of its tokenized US Treasury fund is one of the latest examples of institutional involvement. This shows a shift in how traditional financial institutions are engaging with blockchain technology.
Crypto World
Mike McGlone Forecasts Bitcoin Price Could Fall to $10,000 Amid Economic Concerns

TLDR
- Mike McGlone warns that Bitcoin could drop to $10,000 due to rising recession risks in the U.S.
- The long-standing “buy the dip” mentality may no longer support risk assets, including cryptocurrencies.
- McGlone highlights Bitcoin’s volatility and predicts a potential reversion to $56,000 before a possible $10,000 decline.
- Broader market instability, including low volatility in major stock indices, contributes to the ongoing crypto price decline.
- Jason Fernandes disagrees with McGlone’s forecast, suggesting a $40,000 to $50,000 price range instead of a collapse to $10,000.
Bloomberg Intelligence’s Mike McGlone has raised concerns about the future of Bitcoin. In a recent analysis, he suggested that the ongoing decline in cryptocurrency prices could signal broader financial stress. McGlone also warned that Bitcoin could revert to as low as $10,000, especially if a U.S. recession becomes more likely.
The analyst observed that the market’s traditional “buy the dip” mentality, which has supported risk assets since 2008, may be losing its strength. McGlone pointed out that the worsening situation in the cryptocurrency market is contributing to broader market volatility. He highlighted several macro indicators suggesting heightened risk conditions in global financial markets.
Bitcoin Price Faces Potential Decline to $10,000
McGlone’s analysis specifically mentions Bitcoin’s vulnerability in the current financial environment. He noted that Bitcoin, which recently fluctuated around $68,800, could continue to struggle. According to McGlone, the cryptocurrency’s decline reflects a broader market breakdown, suggesting that the “buy the dip” mindset may no longer be effective.
He further explained that Bitcoin could fall back toward $10,000 if stock markets continue to weaken. McGlone’s chart comparing Bitcoin to the S&P 500 highlighted how both assets were underperforming. He pointed out that Bitcoin’s volatile nature means it is unlikely to remain above current levels if equity markets experience further instability.
In his analysis, McGlone identified a potential reversion level of $56,000 for Bitcoin. This value corresponds to the 5,600 mark for the S&P 500, adjusted for Bitcoin’s volatility. Beyond this, McGlone predicts that the cryptocurrency could fall further, potentially reaching the $10,000 threshold.
Broader Market Volatility Contributes to Crypto Price Decline
McGlone attributes the ongoing volatility in the cryptocurrency market to broader financial instability. The U.S. stock market’s capitalization relative to GDP is at a century-high, signaling potential bubbles. He noted that the low volatility observed in major stock indices like the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100 could be masking underlying risks.
Furthermore, McGlone emphasized the “imploding” crypto bubble and the role of factors like “Trump euphoria” in amplifying market stress. While gold and silver are seeing a resurgence, McGlone believes their rise could eventually spill over into equities. He noted that rising market volatility might further challenge asset prices across the board, including cryptocurrencies.
Contrasting Views on Bitcoin’s Future
While McGlone’s thesis on Bitcoin’s potential fall to $10,000 has drawn attention, it has also faced criticism. Jason Fernandes, co-founder of AdLunam, disagreed with McGlone’s view. Fernandes argued that market excesses can resolve through mechanisms like time, rotation, or inflation erosion, rather than necessarily collapsing.
According to Fernandes, Bitcoin’s price could instead stabilize between $40,000 and $50,000 in response to a macro slowdown. He pointed out that a crash to $10,000 would require more severe conditions, including liquidity contraction and financial stress. Fernandes believes that a true recession, marked by global liquidity drainage, would be needed for such a dramatic decline.
However, McGlone’s analysis continues to gain attention, as it reflects rising concerns over both the cryptocurrency and broader market conditions. His forecast suggests that Bitcoin, along with other risk assets, remains highly susceptible to a changing macroeconomic environment.
Crypto World
Binance Founder CZ Urges Faster Evolution of Privacy Features in Crypto

TLDR
- Changpeng Zhao, founder of Binance, emphasizes that privacy is the most significant unresolved issue in the cryptocurrency industry.
- Zhao argues that Bitcoin and most cryptocurrencies lack adequate privacy features, leaving users vulnerable to tracking.
- CZ highlights that blockchain transactions are traceable, especially with KYC practices on centralized exchanges.
- The Binance founder calls for the development of better privacy infrastructure to enable secure crypto payments while complying with regulations.
- Binance’s history with privacy coins, such as the delisting of Monero, raises concerns about the exchange’s stance on privacy.
Changpeng Zhao, the founder of Binance, has stressed the importance of privacy in the cryptocurrency sector. He pointed out that most digital assets lack sufficient privacy protections, making users vulnerable in ways traditional currency does not. Speaking on the All-In Podcast, CZ emphasized the need for faster advancements in crypto privacy.
Privacy Concerns for Cryptocurrency Payments
CZ argued that privacy plays a fundamental role in society but is currently inadequate in most cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. “Bitcoin was designed to be pseudo-anonymous,” he explained. “But in reality, every transaction on the blockchain can be traced, especially with KYC on centralized exchanges.” This, he noted, exposes users to risks like unwanted tracking, especially in scenarios such as hotel bookings where third parties might gain access to personal information.
He further elaborated on how payment privacy is a significant hurdle as the cryptocurrency industry moves toward mainstream adoption. With major players like AI agents and institutional investors getting involved, the open ledger design of blockchains like Bitcoin remains a challenge. CZ believes that to achieve widespread use, privacy features must evolve to meet the needs of both businesses and consumers.
Binance and Privacy Coins
Despite CZ’s calls for better privacy features, Binance’s own history with privacy coins has been controversial. In February 2024, Binance delisted Monero (XMR), which at the time was the largest privacy coin. This decision came shortly after CZ stepped down as CEO of Binance, and it led to a 17% drop in Monero’s price. Binance has often cited factors such as trading volume and liquidity in delisting assets, claiming it takes action when a coin no longer meets its standards.
CZ’s comments also raised questions about Binance’s stance on privacy coins like Zcash (ZEC). Last year, Binance included Zcash in a community vote on potential delistings. Zcash’s founder, Zooko Wilcox, raised concerns directly with Binance, highlighting the importance of privacy features in cryptocurrency transactions.
The Need for Widespread Privacy Infrastructure
While privacy coins like Monero and Zcash exist, CZ and industry experts suggest that they are not a complete solution. Nic Puckrin, a digital asset analyst, believes the focus should be on developing broader privacy-preserving infrastructure. Puckrin stressed that the issue isn’t to make payments untraceable but to ensure privacy while staying compliant with regulations. He argued that businesses must adopt these privacy features to enable secure crypto payments.
In the face of these challenges, CZ acknowledged that privacy features are a crucial aspect for crypto’s future. Although law enforcement may seek transparency for security reasons, CZ is confident that privacy can be enhanced without undermining efforts to track bad actors.
Crypto World
Paradigm Challenges Bitcoin Mining Narrative Amid AI Data Center Boom
The rapid buildout of AI data centers has revived a long-running debate over energy consumption, with critics arguing that large computing operations, including Bitcoin mining, strain power grids and drive up electricity prices.
As Cointelegraph previously reported, the surge in AI data center construction has fueled local resistance in several US regions, with residents and lawmakers raising concerns about power demand and rising electricity costs. Bitcoin (BTC) mining has increasingly been linked to the broader debate over high-density computing infrastructure.
In a recent research note, crypto investment firm Paradigm pushed back on that narrative, arguing that Bitcoin mining is frequently misunderstood and often mischaracterized in public energy debates. Rather than treating mining as a static energy drain, Paradigm frames it as a participant in electricity markets, one that responds to price signals and grid conditions.
Paradigm’s Justin Slaughter and co-author Veronica Irwin also challenge several common assumptions used in energy modeling. For example, they note that some analyses measure Bitcoin’s energy use on a per-transaction basis, even though mining energy consumption is tied to network security and competition among miners, not transaction volume.
Other models assume energy production is effectively limitless or that miners will continue operating regardless of profitability, assumptions Paradigm argues are unrealistic in competitive power markets.
According to Paradigm, Bitcoin mining currently accounts for about 0.23% of global energy consumption and about 0.08% of global carbon emissions. Because the network’s issuance schedule is fixed and mining rewards decline about every four years, Paradigm argues that long-term energy growth is constrained by economic incentives.

Related: Bitcoin miner production data reveals scale of US winter storm disruption
Bitcoin mining as flexible grid demand
A central pillar of Paradigm’s argument is demand flexibility.
Bitcoin miners typically seek out the lowest-cost electricity, often sourced from surplus or off-peak generation.
Mining operations can scale consumption based on grid conditions, reducing usage during periods of stress and increasing it when supply exceeds demand. In that sense, Paradigm describes mining as a flexible load, similar to energy-intensive industries that respond to real-time pricing signals.
The debate has taken on new urgency as AI data center expansion accelerates. As Cointelegraph recently reported, some crypto-era infrastructure is now being repurposed to support artificial intelligence workloads, with companies shifting from Bitcoin mining to AI data processing to pursue higher margins. Several traditional Bitcoin miners, including Hut 8, HIVE Digital, MARA Holdings, TeraWulf and IREN, have begun making partial transitions.
By framing mining as responsive demand rather than constant consumption, Paradigm’s report shifts the debate from environmental alarmism to grid economics. The implication for policymakers is that Bitcoin mining should be evaluated within the broader electricity market rather than through simplified energy comparisons.
Related: The real ‘supercycle’ isn’t crypto, it’s AI infrastructure: Analyst
Crypto World
South Korea Uses AI to Detect Crypto Market Manipulation

South Korea is accelerating its crypto market supervision by shifting from manual investigations to AI-powered surveillance. The Financial Supervisory Service (FSS) is upgrading its Virtual Assets Intelligence System for Trading Analysis (VISTA) to automate the initial detection of suspicious activity, a move aimed at coping with the speed and scale of modern digital-asset trading. The upgrade, supported by funding through 2026, enables sliding-window analysis across overlapping time frames to flag abnormal patterns such as sudden volume spikes or atypical price movements. In tandem, regulators are planning to extend AI capabilities to identify networks of coordinated trading accounts and trace the sources of funds used in manipulation. Officials also explore proactive interventions, including potential temporary suspensions of transactions or payments, to curb illicit gains before they can be withdrawn.
Key takeaways
- The Financial Supervisory Service’s upgraded VISTA now performs the initial detection of suspicious trading using automated algorithms rather than relying solely on human investigators.
- A sliding-window grid search method segments trading data into overlapping time frames to identify abnormal patterns, such as unusual volume surges or abrupt price moves.
- Through 2026, the FSS plans to add AI tools capable of detecting networks of coordinated trading accounts and tracing the funding sources behind manipulation schemes.
- Regulators are weighing proactive interventions, including temporary suspensions of transactions or payments, to block illicit gains before withdrawal or laundering.
- The move signals a broader shift toward continuous, AI-assisted oversight in digital-asset markets to align crypto supervision with evolving market dynamics.
Market context: Link the story to broader crypto conditions (liquidity, risk sentiment, regulation, ETF flows, macro, or sector trends) WITHOUT inventing facts.
Why it matters
The shift to automated surveillance reflects regulators’ need to keep pace with the sheer volume and velocity of crypto trading. In markets where a single exchange can process thousands of trades in minutes, manual review struggles to keep up, creating gaps that manipulators may exploit. By automating the detection of irregular activity, authorities can flag suspect intervals with far greater speed and consistency, reducing the window during which illicit actors can operate unchecked. Yet, automation also raises questions about the balance between vigilance and overreach. As algorithms flag patterns that resemble manipulation, there is a risk of false positives that could disrupt legitimate trading activity if not carefully managed.
For market participants, the move toward AI-driven oversight could raise the bar for compliance. Exchanges and custodians will need to ensure data quality and interoperability so that automated systems can access comprehensive, timely information. Regulators’ increased reliance on machine learning models may also spur new governance practices around model validation, transparency, and accountability. The net effect could be a more resilient market environment where manipulative tactics are detected earlier, but with continued diligence to avoid unintended penalties on innocent actors.
Beyond crypto-specific implications, the initiative signals regulators’ intent to harmonize digital-asset oversight with traditional financial markets. Korea’s exploration of proactive intervention intersects with broader debates on supervisory tools, due-process safeguards, and the threshold for action in fast-moving markets. If Korea proves effective, other jurisdictions may adopt similar AI-enabled approaches, extending the reach of automated risk detection across asset classes and trading venues.
What to watch next
- Milestones in the AI upgrade rollout through 2026, including when specific detection modules for coordinated accounts and funding tracing become operation-ready.
- Details of the proposed proactive intervention mechanism, such as criteria, governance, and safeguards for temporary transaction suspensions.
- Results from internal tests demonstrating the accuracy and coverage of automated detection, including any externally verified validation.
- Regulatory guidance on cross-venue data sharing and the integration of AI surveillance with existing market surveillance frameworks.
- Any expansion of AI-based monitoring to other asset classes or to cross-border coordinated trading investigations.
Sources & verification
- Official statements or documentation from the Financial Supervisory Service detailing the VISTA upgrade and its automated detection capabilities.
- Technical briefings or regulator notes describing the sliding-window grid search approach used to scan trading data.
- Public announcements about funding or timelines for AI enhancements through 2026.
- Regulatory notices or policy discussions about a potential payment-suspension mechanism to curb illicit gains.
- Industry coverage on pump-and-dump groups and spoofing in crypto markets for context on monitoring challenges.
South Korea deploys AI-powered surveillance to tighten crypto market oversight
The Financial Supervisory Service’s upgrade to VISTA represents a deliberate shift from reactionary, case-by-case probes to proactive, continuous monitoring of digital-asset markets. The upgraded system can autonomously identify likely manipulation windows across the entire data set, a capability regulators say was not feasible with earlier, manually driven methods. In internal testing, the AI detected all known manipulation periods from completed investigations and also highlighted additional intervals that human analysts had previously missed. This progress is framed as a necessary response to the extraordinary pace and complexity of today’s crypto markets, where millions of transactions occur across dozens of tokens every hour.
Central to the upgrade is a sliding-window grid search, a methodological choice that allows the model to examine overlapping time segments of varying durations. Rather than requiring investigators to guess where misconduct might lie, the algorithm evaluates every potential sub-period for telltale signs—such as sudden price spikes followed by rapid reversals or unusual bursts in trading volume. By prioritizing high-risk windows, the system helps analysts focus on the most suspicious intervals, enabling faster, more targeted inquiries. One striking insight from industry observers is that in crypto markets, some manipulation can unfold in under five minutes, a time frame that challenges human monitoring but is well within the reach of automated systems.
The upgrade is more than a technical upgrade; it signals regulators’ intent to extend AI capabilities beyond detection to prevention and enforcement. Through 2026, the FSS plans to implement tools that map networks of trading accounts that operate in coordination—an important step in dismantling capital flows that underpin manipulation schemes. The regulator also aims to perform large-scale analyses of trading-related text across thousands of crypto assets, seeking to correlate promotional narratives with price movements and to understand how attention shocks translate into market risk. And by tracing the origin of funds used in manipulation, authorities hope to build stronger enforcement cases and curb the ability of bad actors to launder proceeds.
As with any AI-driven regime, the initiative faces practical and philosophical challenges. Regulators acknowledge that automated surveillance must be complemented by human oversight to address issues such as cross-venue manipulation and off-platform coordination, which may elude any single venue’s view. Regular evaluation is required to mitigate bias or drift in models and to avoid flagging legitimate activity. The plan explicitly states that AI tools are intended to support, not replace, investigators, reinforcing the role of experienced analysts in interpreting and acting on automated signals.
Beyond the Korean context, the effort echoes a broader transition in financial markets toward real-time surveillance that blends traditional risk controls with modern data science. The Korea Financial Services Commission has even discussed a broader governance framework for algorithmic trading that would apply across asset classes, coupling market surveillance with behavioral signals and automated risk scoring. The overarching objective is a more resilient system capable of identifying irregularities promptly, while maintaining due-process protections and avoiding overreach that could disrupt legitimate market activity.
As policymakers weigh the regulatory levers, observers will look for concrete demonstrations of how these AI tools perform in live markets. The integration of automated detection with proactive interventions—such as potential temporary suspensions of transactions tied to suspected manipulation—could reshape how traders approach liquidity, risk, and compliance. The evolving framework may also influence how other jurisdictions craft AI-enhanced surveillance, potentially accelerating a global shift toward more transparent and accountable crypto markets.
For readers seeking deeper context, related analyses on pump-and-dump groups and the use of spoofing in crypto trading are available here: pump-and-dump groups: are they legal? and how scammers use fake transaction simulation sites to steal crypto.
Crypto World
$321 Million in Crypto Tokens Unlock This Week: What to Watch
The crypto market will welcome tokens worth more than $321 million in the third week of February 2025. Major projects, including LayerZero (ZRO), YZY (YZY), and KAITO (KAITO), will release significant new token supplies.
These unlocks could introduce market volatility and influence short-term price movements. So, here’s a breakdown of what to watch.
Sponsored
1. LayerZero (ZRO)
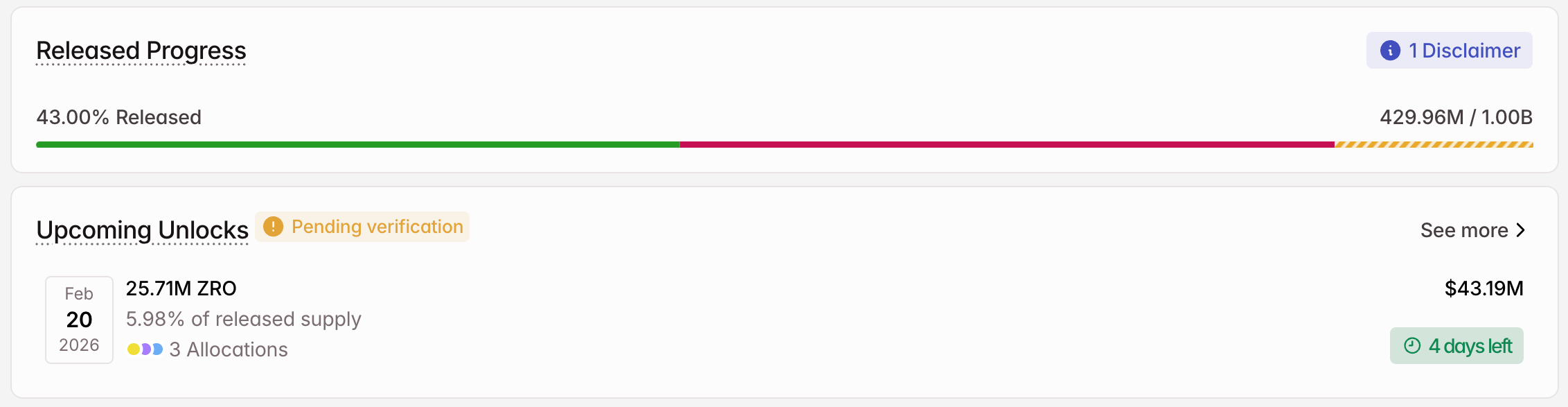
- Unlock Date: February 20
- Number of Tokens to be Unlocked: 25.71 million ZRO
- Released Supply: 429.96 million ZRO
- Total Supply: 1 billion ZRO
LayerZero is an interoperability protocol that connects different blockchains. Its primary goal is to facilitate seamless cross-chain communication. Thus, it enables decentralized applications (dApps) to interact across multiple blockchains without relying on traditional bridging models.
The team will unlock 25.71 million tokens on February 20, representing 5.98% of the released supply. Moreover, the supply is worth approximately $43.19 million.

LayerZero will award 13.42 million altcoins to strategic partners. Core contributors will get 10.63 million ZRO. Lastly, 1.67 million ZRO are for tokens repurchased by the team.
Sponsored
2. YZY (YZY)
- Unlock Date: February 17
- Number of Tokens to be Unlocked: 62.5 million YZY
- Released Supply: 362.5 million YZY
- Total supply: 1 billion YZY
YZY is a cryptocurrency token associated with the rapper Ye (formerly known as Kanye West). It is positioned as part of the broader “YZY MONEY” ecosystem, which includes the YZY token, a payment platform called Ye Pay, and a physical YZY Card.
On February 17, YZY will unlock 62.5 million tokens worth around $20.34 million. The tokens represent 17.24% of the released supply.
Sponsored
The team will allocate 50 million altcoins to Yeezy Investments LLC, Vesting 2. Moreover, it will direct 12.5 million tokens to Yeezy Investments LLC, Vesting 1.
3. Kaito (KAITO)
- Unlock Date: February 20
- Number of Tokens to be Unlocked: 32.6 million KAITO
- Released Supply: 306.49 million KAITO
- Total Supply: 1 billion KAITO
Kaito is an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Web3 information platform that aggregates and analyzes cryptocurrency market data from diverse sources like social media, governance forums, news, and more. The KAITO token serves as a medium of exchange, governance tool, and incentive mechanism within the platform.
Sponsored
On February 20, the team will unlock 32.6 million tokens, representing 10.64% of the current released supply. The supply is worth approximately $10.08 million.
The team will split the unlocked tokens five ways. The foundation will receive 1.19 million tokens. Core contributions will get 6.94 million tokens. Furthermore, early backers will receive 2.31 million KAITO.
Finally, the team will direct 7.16 million KAITO for ecosystem and network growth and 15 million tokens for long-term creator incentives.
In addition to these, other prominent unlocks that investors can look out for in the third week of February include ZKsync (ZK), Solv Protocol (SOLV), ApeCoin (APE), and more, contributing to the overall market-wide releases.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Holds Key Level, Altcoins Aim To Follow: Will Bears Relent?
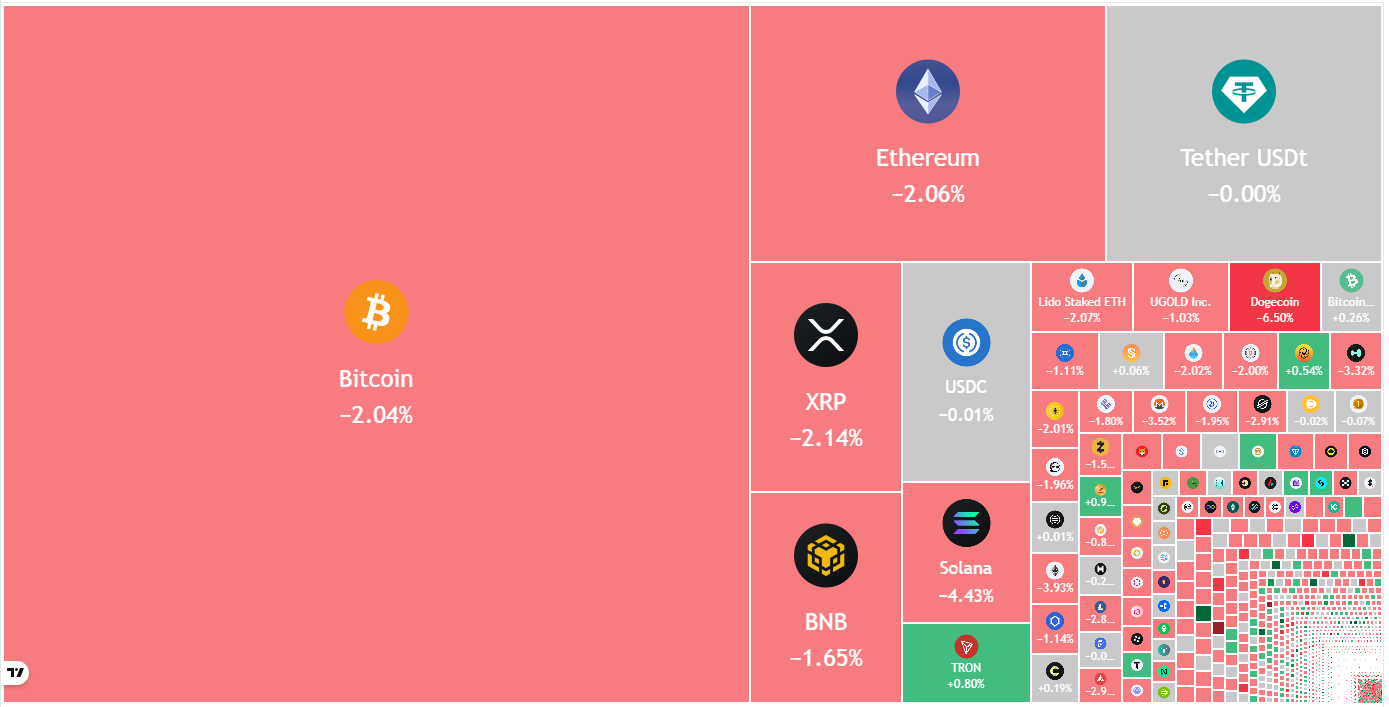
Key points:
-
Bitcoin remains under pressure as bears are selling on rallies near the $74,508 resistance
-
The bears are mounting a solid defense in several major altcoins at higher levels, indicating a negative sentiment.
Bitcoin (BTC) has started the new week on a cautious note as bulls attempt to maintain the price above $67,500. Investors are not rushing in to buy the dip, as seen from the $133.3 million in outflows from BTC exchange-traded products last week. The total outflows from crypto investment products have risen to $3.8 billion over the past four weeks, according to a CoinShares update on Monday.
If BTC ends the month below $79,500, it will record its first-ever consecutive negative monthly closing in January and February. With more than 22% loss, BTC is staring at its worst first-quarter performance since the 49.7% loss in 2018, per CoinGlass data.

Despite BTC’s weak performance and uncertain near-term direction, Strategy co-founder Michael Saylor indicated in a post on X that the company is buying more BTC. That will be Strategy’s 99th BTC transaction, showing their long-term bullish view remains intact.
Could BTC and the major altcoins defend the support levels and start a strong relief rally? Let’s analyze the charts of the top 10 cryptocurrencies to find out.
S&P 500 Index price prediction
The S&P 500 Index (SPX) is witnessing a tough battle between the bulls and the bears at the support line of the ascending channel pattern.

The moving averages are on the verge of a bearish crossover, and the relative strength index (RSI) is in the negative territory, indicating that the bears are making a comeback. The index may start a deeper correction to 6,720 and then to solid support at 6,550 if the price breaks below the 6,780 level.
Buyers will have to propel the price above the 7,002 level to retain control. If they manage to do that, the index may resume its uptrend and surge toward the 7,290 level.
US Dollar Index price prediction
The US Dollar Index (DXY) has been trading below the moving averages, but the bears have failed to challenge the 96.21 to 95.55 support zone.

The bulls will try to strengthen their position by pushing the price above the moving averages. If they can pull it off, the index may rally to 99.49 and then to the overhead resistance at 100.54.
Contrarily, if the price turns down sharply from the moving averages, it suggests that the bears continue to sell on rallies. The index may the next leg of the downtrend on a close below the 95.55 support.
Bitcoin price prediction
Sellers are attempting to halt BTC’s recovery near $71,000, indicating that the bears remain sellers on rallies.

The sellers will have to pull the price below the $65,000 level to remain in command. The BTC/USDT pair may then retest the critical $60,000 level. If the $60,000 support cracks, the next stop is likely to be $52,500.
Buyers will have to drive the Bitcoin price above the breakdown level of $74,508 to signal that the bearish momentum is weakening. The pair may then surge toward the 50-day SMA ($83,910), where the bears are expected to mount a strong defense.
Ether price prediction
Ether (ETH) once again turned down from the $2,111 level on Sunday, indicating that the bears are fiercely defending the level.

Sellers will attempt to pull the price below the immediate support at $1,897. If they do that, the ETH/USDT pair may drop to the $1,750 level. Buyers are expected to defend the $1,750 level with all their might, as a close below it may sink the pair to $1,537.
Instead, if the Ether price turns up and breaks above the 20-day EMA ($2,221), it signals that the selling pressure is reducing. The pair may then rally to the 50-day SMA ($2,744).
BNB price prediction
BNB’s (BNB) relief rally fizzled out at $642 on Sunday, indicating that the bears are selling on every minor rise.

The bears will attempt to increase their hold by pulling the BNB price below the $570 level. If they manage to do that, the BNB/USDT pair may extend its decline to psychological support at $500.
The bulls will have to drive the price above the 20-day EMA ($686) to suggest that the bears are losing their grip. The pair may then climb to $730 and subsequently to the 50-day SMA ($817).
XRP price prediction
XRP (XRP) turned up from the support line of the descending channel pattern on Friday and pierced the 20-day EMA ($1.53) on Sunday.

However, the bears successfully defended the breakdown level of $1.61 and pulled the XRP price back below the 20-day EMA. The bulls are unlikely to give up easily and will make another attempt to clear the $1.61 level.
If they succeed, the XRP/USDT pair may rise to the 50-day SMA ($1.81). Such a move suggests that the pair may remain inside the channel for some more time.
Sellers will have to tug the price below the support line to gain the upper hand. The pair may then retest the Feb. 6 low of $1.11.
Solana price prediction
Buyers are attempting to push Solana (SOL) back above the breakdown level of $95, but the bears have held their ground.

The Solana price may trade inside the $76 to $95 range for some time. Such a move increases the likelihood of an upside breakout. The SOL/USDT pair may then rally toward $117.
This positive view will be negated in the near term if the price turns down and breaks below the $76 support. The pair may then retest the Feb. 6 low of $67, where the buyers are expected to step in.
Related: $75K or bearish ‘regime shift?’ Five things to know in Bitcoin this week
Dogecoin price prediction
Dogecoin (DOGE) turned down from the breakdown level of $0.12 on Sunday, indicating that the bears are defending the level.

The 20-day EMA ($0.10) is flattening out, and the RSI is just below the midpoint, signaling a possible range-bound action in the near term. The DOGE/USDT pair may swing between $0.08 and $0.12 for a few days.
Buyers will gain the upper hand on a close above the $0.12 resistance. That opens the doors for a rally to $0.16. Alternatively, the advantage will tilt in favor of the bears on a close below $0.08. The Dogecoin price may then slump to $0.06.
Cardano price prediction
Cardano’s (ADA) relief rally reached the 20-day EMA ($0.29) on Saturday, which is expected to act as a stiff hurdle.

If the bulls do not give up much ground to the bears, the possibility of a break above the 20-day EMA increases. That suggests the ADA/USDT pair may remain inside the descending channel for some more time. A break and close above the downtrend line signals a potential short-term trend change.
Sellers will have to pull the Cardano price below the support line to extend the downward move toward the next support at $0.20.
Bitcoin Cash price prediction
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) surged above the 20-day EMA ($544) on Friday, indicating that the bears are losing their grip.

The recovery is facing resistance at the 50-day SMA ($578), but a positive sign is that the bulls have not allowed the Bitcoin Cash price to slip back below the 20-day EMA. That increases the likelihood of the continuation of the relief rally. If buyers pierce the 50-day SMA, the BCH/USDT pair may reach $600.
Sellers will have to swiftly yank the price below the 20-day EMA to apply pressure on the bulls. The pair may then skid to the $500 support.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision. While we strive to provide accurate and timely information, Cointelegraph does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any information in this article. This article may contain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Cointelegraph will not be liable for any loss or damage arising from your reliance on this information.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Weekly RSI Echoes Mid-2022 Bear Market as BTC Plays Liquidity

Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) briefly surged toward the $70,000 level on a U.S. bank holiday before retreating, underscoring how thin liquidity can amplify price moves in markets with limited participants. The session featured swift reversals as major venues saw shallow order books, allowing large players to push the price in sharp, short-lived bursts and then pull back just as quickly. Traders described a day of both dramatic squeezes and measured pauses, with liquidity gaps creating a backdrop where price action could swing without a clear directional trend. While the move rekindled talk of potential bottoming signals, observers cautioned that a single holiday-driven spike is not a proof point for a durable trend, particularly given the broader context of a market accustomed to volatile cross-currents.
Key takeaways
- Holiday-thinned liquidity on a U.S. trading day amplified both upside and downside moves, with BTC briefly touching $70,000 before a pullback.
- Price action occurred in a tight range, described by analysts as a pattern of “breakouts and shakeouts” that failed to establish a decisive breakout.
- CoinGlass tracked roughly $120 million in crypto liquidations across four hours, highlighting the reflexive nature of order-book dynamics during low-volume sessions.
- Weekly RSI readings dipped to 27.8, the lowest since June 2022, fueling discussions about potential cycle lows and macro bottoming patterns.
- Market commentary emphasized ongoing liquidity-driven reversals, with notable divergence in activity on different exchanges and persistent bullish-bias signals outside of a handful of venues.
- A sequence of social posts from traders highlighted mixed sentiment, with some noting net buying pressure overall while exceptions persisted on certain platforms such as OKX.
Tickers mentioned: $BTC
Price impact: Neutral. The episode demonstrated how thin liquidity can drive rapid intraday reversals without signaling a sustained directional shift.
Trading idea (Not Financial Advice): Hold. Given the absence of a clear breakout and the sensitivity to depth on holiday sessions, traders may prefer to wait for a more decisive move backed by stronger liquidity and higher-volume participation.
Market context: The latest price activity reflects a broader pattern in crypto markets where liquidity constraints during holidays or low-volume sessions can magnify swings. It also sits amid ongoing debates about macro risk sentiment, ETF-related flows, and the persistence of risk-on versus risk-off dynamics that shape digital-asset price formation.
Why it matters
The episode matters because it exercises a fundamental risk for traders: price discovery in environments where liquidity is not consistently deep. Thin order books can magnify both hopeful breakouts and fear-driven reversals, making risk management and position sizing more critical than in normal trading conditions. For market participants, the contrast between a swift move to the multi-year high vicinity and a rapid retracement underscores how much of Bitcoin’s price action still depends on the availability of buyers and sellers at key price levels rather than on a sustained flow of capital. The event also provides a practical test bed for risk controls, as exchanges and liquidity providers calibrate their resilience to sudden, liquidity-driven shocks.
From a technical perspective, weekly RSI readings toward oversold territory suggest potential patience is warranted before drawing conclusions about a longer-term bottom. Yet the narrative is not binary: the same chart readings were cited in past cycles as precursors to stalled consolidations or gradual basing patterns rather than immediate recoveries. Analysts emphasized that while the current RSI dip resembles patterns seen in previous bear markets, it does not guarantee a repeat of those outcomes. The broader takeaway is a need to monitor how price, momentum, and volume evolve together in the weeks ahead, particularly as markets digest macro inputs and any incremental developments in crypto regulation or product approvals that could influence risk appetite.
On-chain and on-exchange observations further enrich the story. Market participants noted blocks of liquidity getting reconfigured as bids and offers were removed and re-placed at new levels, reinforcing the sense that order-book dynamics played a leading role in the day’s action. The interplay between short-term liquidations, bid-ask wall reformation, and whale activity suggested a tug-of-war between buyers aiming for a breakout and sellers defending certain price zones. In this context, a minority of observers highlighted a pattern that echoes the bear-market conditions of 2022, while others warned that a single holiday-driven session is not the best proxy for broader market health or a definitive trend reversal.
Social signals added texture to the narrative. One prominent trader noted that net buying pressure remained robust across most venues, with OKX standing out as an exception where the balance shifted toward selling pressure. The dialogue around the differing dynamics across exchanges highlighted how venue-specific liquidity can shape price trajectories in real time, contributing to a landscape where market participants must weigh cross-exchange liquidity, funding conditions, and cross-venue order flow as part of a single, evolving story.
Beyond Bitcoin itself, observers highlighted ongoing patterns in price response to liquidity shocks across the crypto market. The day’s action fed into a broader conversation about how investors seasonally recalibrate risk, particularly during holiday windows when traditional liquidity pools are thinner and risk sentiment can swing on a coin flip. While the event did not trigger any explicit new catalysts, its implications for short-term trading strategies—particularly those relying on liquidity-driven breakouts—remain a focal point for traders who seek to understand how much of BTC’s price movement is driven by depth versus fundamental shifts in demand.
What’s different about $BTC from yesterday is that net buying is maintained except for OKX. pic.twitter.com/x3Y1OegrsI
— CW (@CW8900) February 16, 2026
What to watch next
- Follow BTC price action in the next several sessions to determine if a sustained move beyond the current range emerges on higher liquidity.
- Monitor the weekly RSI to see whether momentum stabilizes above oversold territory or slides deeper, which could influence near-term bias.
- Track liquidation flows and changes in order-book depth across major venues to assess whether the market is rebalancing its risk tolerance.
- Observe cross-exchange buy/sell pressure differences, particularly after the holiday period, to gauge whether a broader consolidation or a fresh breakout is forming.
- Keep an eye on macro catalysts and regulatory developments that could shift appetite for risk assets in the coming weeks.
Sources & verification
- TradingView BTCUSD price action within the holiday session showing moves toward and away from $70,000 (BTCUSD chart).
- CoinGlass liquidity and liquidation data indicating roughly $120 million in liquidations over four hours.
- Material Indicators’ analysis of BTC/USDT liquidity and whale activity on major exchanges.
- Social posts from Daan Crypto Trades and Keith Alan discussing RSI patterns and bear-market similarities.
- Public social post from CW highlighting net buying dynamics and exchange-specific commentary.
Rewritten Article Body: Liquidity squeezes and RSI signals shape BTC price action on a holiday
Bitcoin, trading as Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC), confronted a unique set of conditions on a U.S. bank holiday: liquidity was thin, and that scarcity amplified even modest market forces into notable intraday moves. The price briefly tested the $70,000 mark before retreating, a pattern consistent with the kind of rapid, liquidity-driven reversals that have become familiar in low-volume sessions. Rather than a clean breakout, the action unfolded in a narrow corridor, with bids and asks repeatedly clearing and reforming at new levels as traders recalibrated risk exposure in the absence of the usual institutional floor.
Market observers described a day of “breakouts and shakeouts”—moments when prices appeared ready to run but were quickly checked by the lack of robust order-book depth. The dynamic is a reminder that, on days when major markets are closed, a handful of large participants can move prices meaningfully without the broader market’s participation. The net effect was a series of swift moves that left many participants unsure of the prevailing directional bias, reinforcing a common refrain: liquidity is the prime mover in such environments, more so than fresh macro catalysts or new fundamental data.
Data from CoinGlass illustrated the scale of activity during the session: approximately $120 million in liquidations occurred across a four-hour window. This is a hallmark of a market where thin liquidity can produce outsized volatility, as participants face sudden sifts in supply and demand balance. In practical terms, those who believed the momentum favored a sustained tilt toward the upside found themselves facing rapid opposition as new walls formed above and below the current price to absorb incoming bids or offers. The absence of deep liquidity magnifies the impact of individual large trades, making every order a potential flash point for the next move.
On the technical front, a closer look at momentum indicators painted a nuanced picture. Weekly RSI readings dipped toward oversold territory, with the metric landing at 27.8 on one trading day—its lowest reading since June 2022. Some analysts pointed to this as a potential bottoming signal, drawing parallels to prior bear-market cycles where oversold conditions laid the groundwork for a period of consolidation and eventual macro recovery. Others cautioned that history does not guarantee a repeat outcome and that the present pattern could diverge from 2022 depending on subsequent liquidity and macro dynamics. The discussion underscored how traders weigh technical signals in conjunction with the underlying liquidity environment, rather than relying on any single indicator in isolation.
Beyond the numbers, the day’s narrative included qualitative observations about exchange-specific activity. Traders noted that buying pressure remained more robust than on the previous session, with the exception of OKX, where selling pressure appeared to dominate. This divergence highlighted how different venues can diverge in real time, driven by liquidity distributions, funding conditions, and the behavior of large players who shuttle capital across platforms. A prominent market participant summarized the sentiment on social media, noting that net buying was generally positive across most venues, but the OKX discrepancy reminded the market that liquidity fragmentation persists and can influence short-term outcomes in unpredictable ways.
In a broader context, the episode fed into ongoing discussions about how crypto markets navigate cycles of risk appetite and liquidity stress. While the price action did not deliver a definitive directional signal, it reinforced a familiar pattern: during periods of limited depth, price discovery is a two-way process propelled by cautious, incremental moves rather than a single decisive breakout. The presence of “breakouts and shakeouts” as a recurring motif highlights how traders are adapting to a market structure where depth can evaporate quickly, forcing participants to reprice their expectations with each new order that clears the book.
Looking forward, the market will likely want to see a more explicit signal of conviction—whether it be a sustained move above a key level with robust volume or a decisive breakdown that confirms a shift in risk sentiment. For now, the data suggests that the landscape remains dominated by short-term liquidity dynamics rather than a clear, long-term directional thesis. The ongoing debate about potential bottoming signals versus continued consolidation is a reminder that, in crypto markets, the path of least resistance is often determined by how much liquidity remains available to absorb the next wave of orders.
//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-
 Crypto World7 days ago
Crypto World7 days agoU.S. BTC ETFs register back-to-back inflows for first time in a month
-

 Video5 hours ago
Video5 hours agoBitcoin: We’re Entering The Most Dangerous Phase
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoLuxman Enters Its Second Century with the D-100 SACD Player and L-100 Integrated Amplifier
-

 Video3 days ago
Video3 days agoThe Final Warning: XRP Is Entering The Chaos Zone
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-
 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoBhutan’s Bitcoin sales enter third straight week with $6.7M BTC offload
-

 Video5 days ago
Video5 days agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-
 Crypto World7 days ago
Crypto World7 days agoEthereum Enters Capitulation Zone as MVRV Turns Negative: Bottom Near?
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoThe strange Cambridgeshire cemetery that forbade church rectors from entering
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoBarbeques Galore Enters Voluntary Administration
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoCrypto Speculation Era Ending As Institutions Enter Market
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoEthereum Price Struggles Below $2,000 Despite Entering Buy Zone
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWhy was a dog-humping paedo treated like a saint?
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoMan dies after entering floodwater during police pursuit
-
 Crypto World3 days ago
Crypto World3 days agoBlackRock Enters DeFi Via UniSwap, Bitcoin Stages Modest Recovery
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoUK construction company enters administration, records show
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoWinter Olympics 2026: Australian snowboarder Cam Bolton breaks neck in Winter Olympics training crash












