Crypto World
The quantum threat is already here

Disclosure: The views and opinions expressed here belong solely to the author and do not represent the views and opinions of crypto.news’ editorial.
Quantum computing is often framed as a distant storm on the horizon, and not yet relevant to today’s cryptographic systems. In 2026, that framing is dangerously misguided. The Ethereum Foundation’s recent decision to launch a dedicated Post-Quantum (PQ) cryptography team, backed by $2 million in funding, is a watershed moment for the industry. The world’s most influential smart contract ecosystem is no longer treating quantum risk as theoretical; it is acting on the correct assumption that cryptographic disruption could arrive far sooner than expected.
Summary
- Quantum risk is no longer theoretical: The Ethereum Foundation’s post-quantum team signals that cryptographic disruption is being treated as an imminent infrastructure threat, not a distant possibility.
- Harvest-now, decrypt-later is the real danger: Millions of exposed public keys could be drained overnight once quantum capability crosses the threshold — no gradual warning, just systemic shock.
- Migration won’t be seamless: Upgrading trillion-dollar blockchains to post-quantum cryptography could require massive downtime, creating ripple effects across ETFs, custody, banking, and global markets.
The quantum threat is already a present market risk, not a future technical problem, and crypto’s failure to treat it as such will define the next systemic crisis. Some readers may find this view overly alarmist or argue that highlighting quantum risk could undermine confidence in digital assets. Others may object that this perspective challenges long-held assumptions about Bitcoin’s resilience and the pace of technological change. However, these contentions radically underestimate how close we are to a cryptographic collapse.
From theory to strategic priority
It’s important to note that quantum computing is no longer confined to academic research. Nation-states, defense agencies, and major technology companies are racing to build machines capable of solving problems classical computers can’t. The risk is not merely computational speed but the potential collapse of cryptographic trust itself.
This urgency is now reflected in some landmark policy developments. The European Commission and EU Member States recently released a coordinated roadmap to transition the bloc’s digital infrastructure to post-quantum cryptography. It stipulates that by 2026, all Member States must begin national PQC strategies; by 2030, critical infrastructure must adopt quantum-resistant encryption; and by 2035, the transition should be completed across all feasible systems.
The Ethereum Foundation’s decision to allocate funding and talent toward post-quantum research mirrors this new reality.
The dangerous comfort of long timelines
Despite these developments, some industry voices continue to downplay the risk. Bitcoin (BTC) pioneer Adam Back has argued that Bitcoin faces no meaningful quantum threat for 20 to 40 years. This position rests on the assumption that danger only begins when a quantum computer can break cryptographic keys in real time.
The threat does not start when quantum machines arrive at full strength; it starts when attackers can harvest public keys today and wait. Deloitte recently reported that roughly four million Bitcoin, around 25% of all usable supply, sit in addresses that expose public keys vulnerable to quantum attacks. Once a sufficiently advanced quantum computer exists, those wallets could be drained almost instantly using Shor’s algorithm.
The damage would not unfold gradually. It would be sudden, asymmetric, and irreversible.
Why upgrading is not a simple fix
Supporters of the long-horizon view argue that Bitcoin and other blockchains can simply adopt the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s post-quantum cryptography standards when the time comes. But cryptographic migration is a protocol-level transformation, not a routine patch.
Researchers estimate that upgrading Bitcoin to a quantum-resistant cryptosystem could require up to 75 days of downtime, or over 300 days if the network must operate at reduced capacity to limit attack vectors during migration. For a trillion-dollar asset class, such a disruption would ripple through exchanges, derivatives markets, ETFs, institutional custody systems, and payment rails. This is a risk the market is not currently pricing in.
Blockchains are not alone in this exposure, as the global banking and payments infrastructure relies on the same cryptographic standards now considered vulnerable. A quantum breach would compromise not just assets, but identity systems, digital signatures, interbank settlements, and automated clearing mechanisms.
In practical terms, this could mean frozen payment rails, invalidated digital contracts, and emergency shutdowns of financial networks. The shock would move beyond crypto into equity markets, foreign exchange, and sovereign debt, creating a systemic crisis rooted in broken trust.
When AI and quantum outpace governance
This risk is amplified by the ongoing proliferation of AI, which is accelerating discovery, automation, and exploitation. When paired with quantum computing, it creates a scenario in which machine-scale attacks outpace human governance and regulatory response. Laws move in years. Algorithms move in milliseconds, and the gap is widening continuously. Decentralized systems were designed to remove single points of failure, yet cryptographic fragility threatens to reintroduce them at the foundation layer.
If cryptographic assumptions change, valuations will follow, and capital will increasingly favor quantum-resilient infrastructure. Risk premiums on legacy chains will widen, and regulators will increasingly demand transparency around cryptographic readiness, and institutional investors will expect quantum-risk disclosures. The Ethereum Foundation’s decision is an early signal that the markets will not ignore for long.
Crypto World
Strategy buys 2,486 BTC as a rare pattern points to a Bitcoin price crash
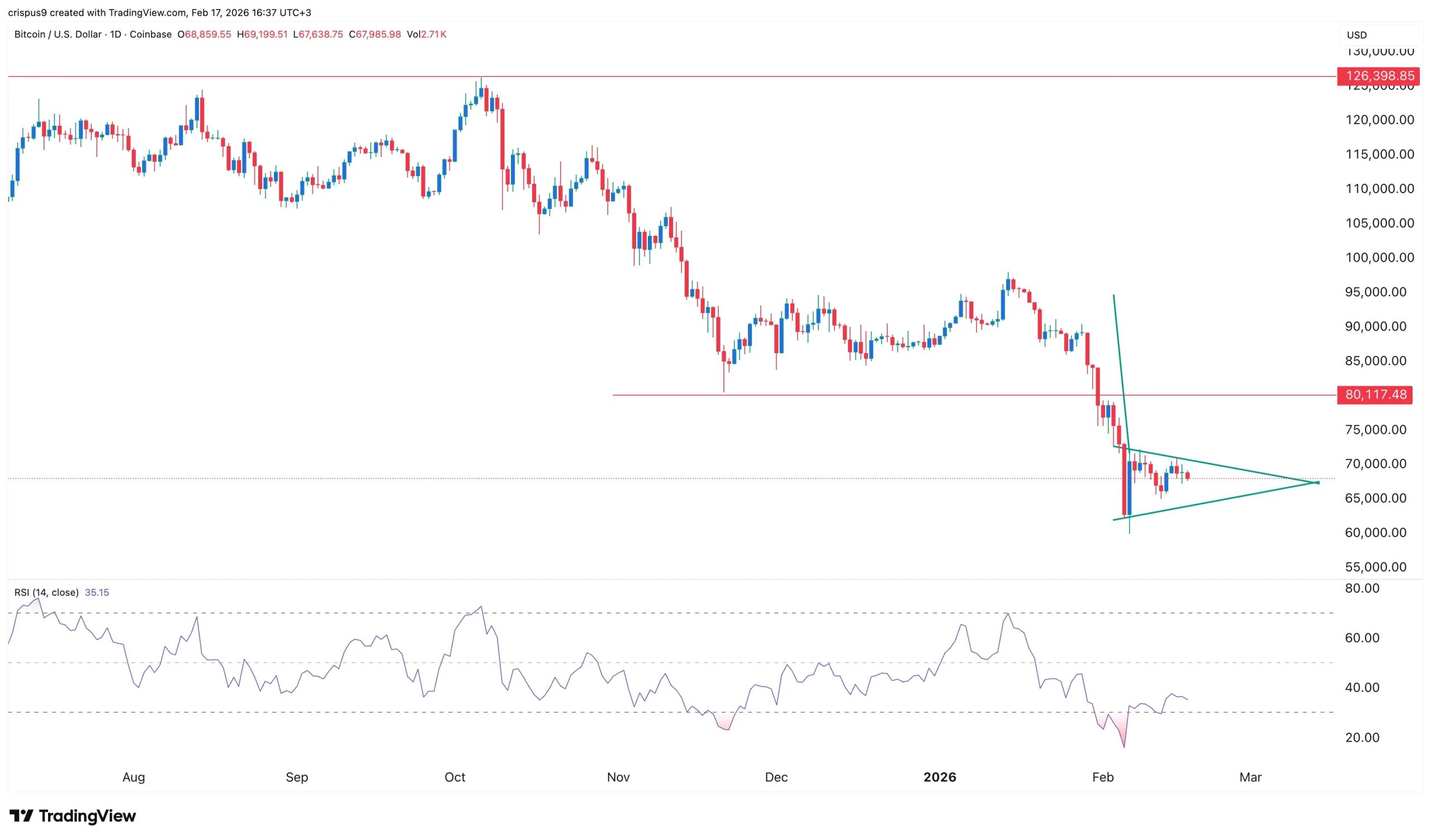
Michael Saylor’s Strategy continued its Bitcoin buying spree last week, even as crypto winter persisted, and the coin formed a rare chart pattern pointing to more near-term downside.
Summary
- Strategy, formerly known as MicroStrategy, acquired 2,486 Bitcoin last week.
- The company now holds over 717,000 coins worth nearly $50 billion.
- Technical analysis suggests that the Bitcoin price is forming a bearish pennant pattern, pointing to a crash.
In an X post, Saylor noted that the company bought 2,496 Bitcoin (BTC) last week for $168 million. This purchase brought its total holdings to 717,131 coins, now valued at nearly $50 billion.
Strategy executed the purchase by selling shares, a move that has continued to dilute its shareholders. Data show that the company still has over $7.8 billion in common shares to sell and an additional $20 billion in preferred STRK.
The company now has over 312 million of outstanding shares, much higher than what it had a few years ago. This dilution will continue, as Michael Saylor has pledged to buy Bitcoin forever. He also revealed that he plans to swap its debt for shares in the future.
Bitcoin price technical analysis points to a crash
The ongoing Strategy acquisition is happening amid concerns that Bitcoin may continue falling in the near term. In a statement last week, Standard Chartered warned that Bitcoin may drop to $50,000 before recovering. The bank reduced its target for the coin from $150,000 to $100,000.
Bitcoin is facing other headwinds, including the tumbling futures open interest, which has moved to $43 billion, down from last year’s high of $95 billion.
At the same time, there are rising odds of a prolonged conflict in the Middle East despite the ongoing talks between Iran and the United States. Donald Trump has sent another carrier to the region, while Iran is conducting drills at the Strait of Hormuz.
A conflict in the Middle East would have a major impact on Bitcoin, which has proven that it is not a safe haven asset.
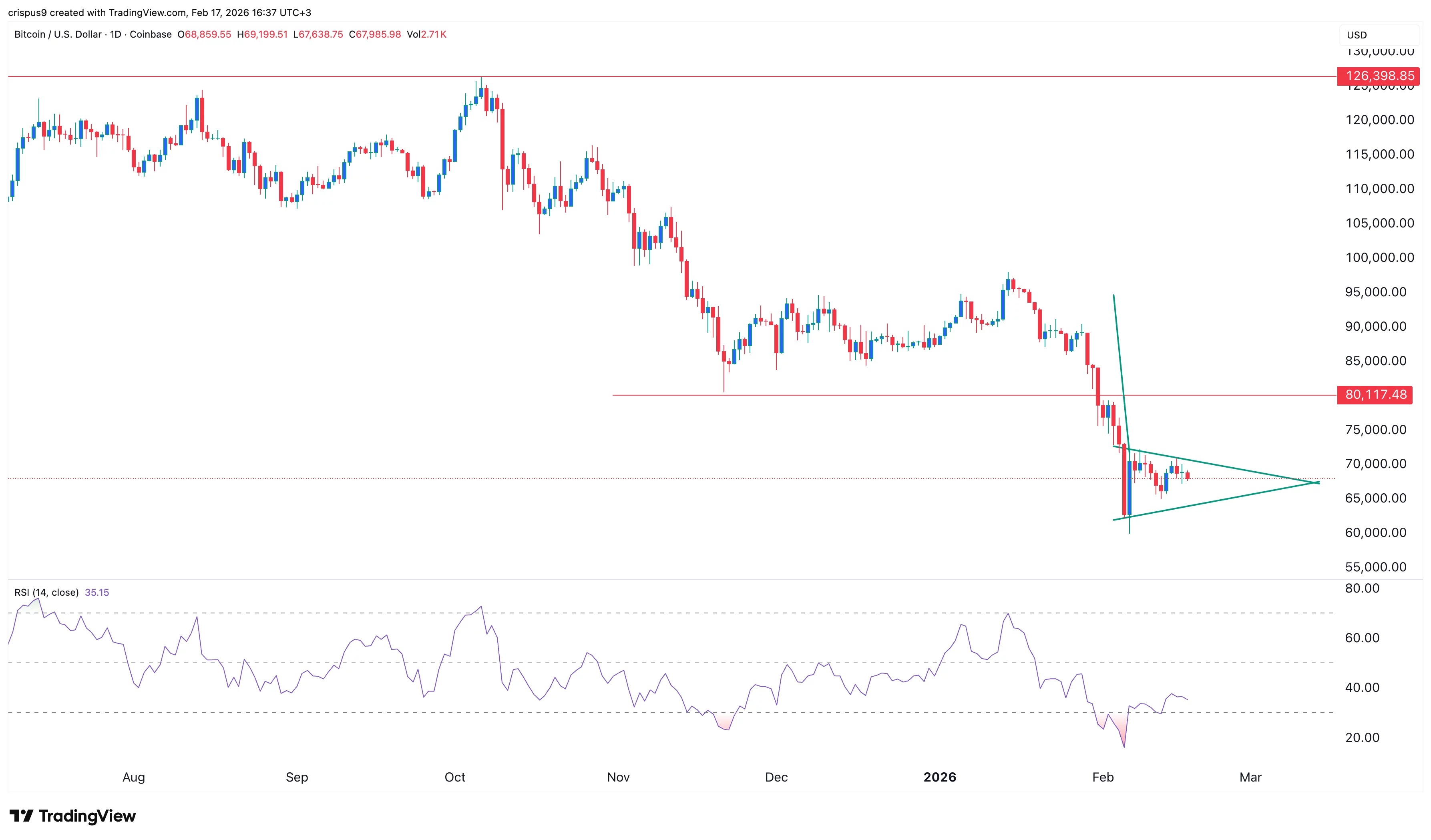
Technical analysis indicates that the Bitcoin price is slowly forming a bearish pennant pattern, consisting of a vertical line and a symmetrical triangle. The two lines of the triangle are nearing their confluence, meaning that the coin may soon drop to the year-to-date low of $60,000.
The bearish Bitcoin price outlook will become invalid if it moves above the key resistance level at $80,117, its lowest level in November last year.
Crypto World
Starknet Taps EY’s Nightfall for Institutional Privacy on Ethereum Rails

Starknet developer StarkWare has integrated EY’s Nightfall privacy protocol to let institutions run private payments and decentralized finance (DeFi) activity on public Ethereum-aligned rails, targeting banks and corporates that need confidentiality without giving up auditability.
In a Tuesday release shared with Cointelegraph, StarkWare positioned the move as a way for enterprises to use a shared, open layer-2 rather than closed, bank-only networks, while working with a Big Four firm that already audits many of the organizations it wants to onboard.
The integration brings Nightfall, an open-source zero-knowledge (ZK) privacy layer built by EY, that lets transactions be verified without revealing underlying data, onto Starknet to enable private B2B and cross-border payments, confidential treasury management and 24/7 tokenized asset transfers onchain.
StarkWare said that institutions will also be able to access Ethereum DeFi for activities such as lending, swaps and yield strategies, with transactions private by default but supporting selective disclosure, auditability and Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
Related: Arbitrum, Optimism and Base weigh in after Vitalik questions L2 scaling model
Starknet and Nightfall target institutional flows
StarkWare frames this as a “major breakthrough” in making public blockchains usable for institutional capital that has so far been deterred by full onchain transparency and the resulting compliance and competitive risks.
Eli Ben-Sasson, StarkWare co-founder and CEO and a founding scientist of privacy-focused cryptocurrency Zcash (ZEC), said in the release that blockchains could give every institution “the equivalent of a private superhighway for stablecoins and tokenized deposits,” positioning Nightfall on Starknet as a concrete step toward that vision.
Alex Gruell, StarkWare’s global head of business development, told Cointelegraph that Nightfall was “particularly useful for institutions requiring ready-to-go KYC verification as part of their onboarding to the blockchain,” and part of a broader privacy push on Starknet.

He said that while crypto native teams had “moved mountains” building ZK infrastructure, the EY-built system added a complementary layer of institutional credibility and “regulatory fluency.”
Related: Vitalik Buterin tempers vision for ETH L2s, pushes native rollups
Gruell also cast Starknet plus Nightfall as an interoperability layer between institutions, contrasting it with what he claimed are “siloed” institutional environments on rival networks, which he said “do not serve as an interoperability infrastructure,” and permissioned models such as Canton Network, which are “not yet integrated with the Web3 ecosystem.”
He stressed that Nightfall would remain permissionless and fully integrated into Starknet, with a staged rollout, where initial deployment focused on “private payments and transfers with compliance gating and secure sequencing in place,” while “verifier upgrades and expanded functionality follow as the system scales.”
Starknet’s growth and teething trouble
Starknet has steadily grown into one of the larger ZK rollups by total value locked (TVL), currently about $280 million, with usage primarily driven by DeFi protocols and native ecosystem apps.
At the same time, Starknet’s rapid scaling push has exposed reliability challenges. In 2025, the network suffered major outages tied to sequencer and infrastructure issues, prompting public post-mortems and commitments to harden reliability before courting more institutional flow.
Magazine: Back to Ethereum — How Synthetix, Ronin and Celo saw the light
Crypto World
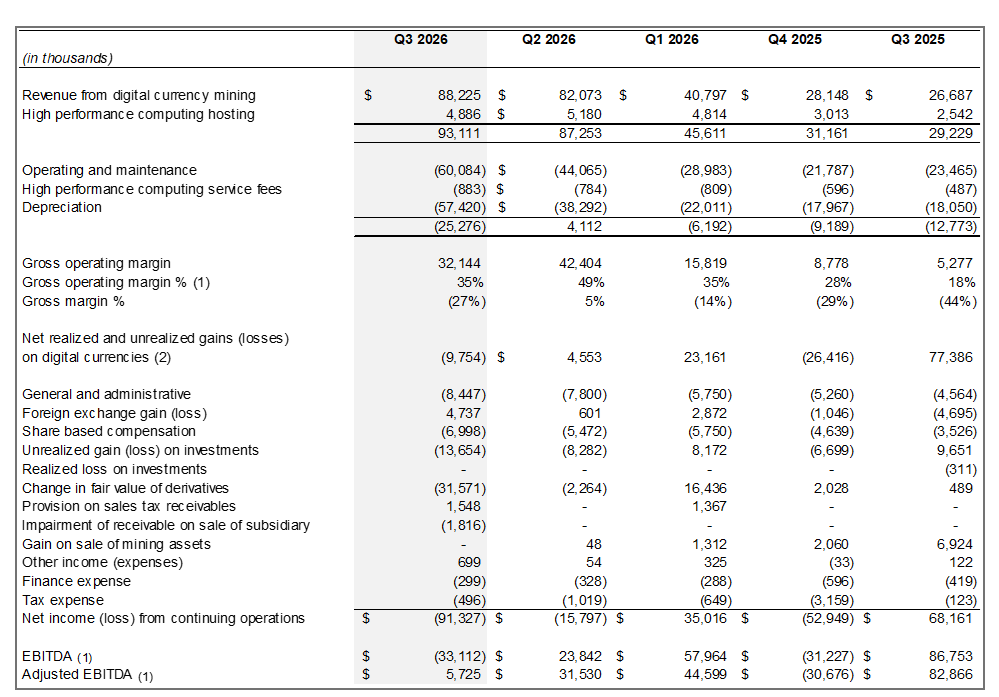
HIVE Delivers Record Q3 Revenue and Margin Growth
Editor’s note: In a sector defined by rapid changes in energy costs and compute demand, HIVE Digital Technologies reports a standout quarter that highlights the resilience of its dual-engine model — steady Bitcoin hashrate expansion alongside high-growth BUZZ AI HPC. The Q3 results, led by record revenue of $93.1 million and a gross margin of $32.1 million, reflect disciplined scaling across renewable-powered infrastructure and an accelerating AI compute strategy. The company’s Paraguay expansion and GPU cloud initiatives illustrate how HIVE is positioning for longer-term margin expansion, recurring revenue and geographic diversification.
Key points
- Record quarterly revenue of $93.1 million, up 219% YoY and 7% QoQ, with gross margin of $32.1 million (34.5%).
- Bitcoin hashrate capacity reached 25 EH/s, with BUZZ HPC growth accelerating.
- AI GPU expansion: 504 Nvidia GPUs under a $30 million contract, live deployments in Q1 2026, lifting HPC revenue and targeting $140 million ARR by Q4 2026 with 11,000 GPUs.
- Paraguay expansion and renewable-powered infrastructure underpin margin growth and geographic diversification.
Why this matters
This quarter demonstrates HIVE’s ability to scale a renewable-powered data center platform while expanding into AI compute markets. The dual-engine approach provides resilience against sector volatility, leveraging Bitcoin hashrate expansion as a cash generator and BUZZ HPC as a high-growth, recurring revenue stream. With Paraguay infrastructure, green energy and new AI deployments, HIVE is positioned for margin expansion and geographic diversification into Latin America.
What to watch next
- Deployments of 504 Nvidia GPUs live in Q1 2026 and expected ARR uplift to $140 million by Q4 2026 as GPU AI Cloud evolves.
- Paraguay expansion: energization of the additional 100 MW at Yguazú targeted for Q3 2026 and 63 hectares of land acquisition supporting growth.
- Anticipated overall energy footprint of 540 MW by year-end, with evaluation of incremental megawatts for future EH/s growth.
Disclosure: The content below is a press release provided by the company/PR representative. It is published for informational purposes.
HIVE Delivers Record Q3 Revenue of $93.1 Million with $32.1 Million Gross Operating Margin, Up Over 6x Year-Over-Year
This news release constitutes a “designated news release” for the purposes of the Company’s prospectus supplement dated November 25, 2025 to its short form base shelf prospectus dated October 31, 2025.
San Antonio, TX, February 17, 2026 — HIVE Digital Technologies Ltd. (TSX.V: HIVE) (Nasdaq: HIVE) (FSE: YO0) (BVC: HIVECO) (referred to as the “Company” or “HIVE”), a global leader in sustainable data center infrastructure, announced its results for the third quarter ended December 31, 2025 (all amounts in US dollars, unless otherwise indicated).
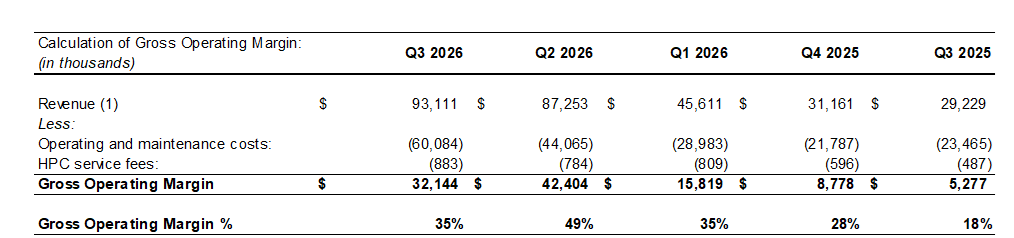
HIVE delivered record quarterly revenue of $93.1 million, representing 219% year-over-year growth and 7% quarter over quarter growth, and Adjusted EBITDA of $5.7 million. Gross operating margin expanded significantly to $32.1 million (34.5%), up more than sixfold compared to $5.3 million in the prior year period.
This quarter marks the strongest “dual-engine” growth in HIVE’s history, driven by the rapid scale-out of its Bitcoin hashrate fleet to an installed base of 25 Exahash per Second (EH/s) by period end December 31, 2025 and accelerating demand for BUZZ HPC platforms.
Q3 FY2026 Financial Highlights:
• Total Revenue: $93.1 million, a 219% increase from $29.2 million in Q3 FY2025 and a 7% increase over last quarter. Gross operating margin was $32.1 million or 34.5%, up from 18% in fiscal Q3 FY2025. See the calculation of direct costs and mining margin included below in this press release.
• Digital Currency Hashrate Revenue: $88.2 million, up 8% from Q2 FY2026, reflecting a 41% quarter-over-quarter increase in average hashrate to 22.9 EH/s, partially offset by approximately 10% lower Bitcoin prices and 15% higher network difficulty. This hashrate revenue was achieved at a direct cost of $57.8 million, of which approximately 90% is energy costs. See the calculation of direct costs included below in this press release.
• Bitcoin Output: Generated 885 Bitcoin, representing a 23% quarter over quarter increase, despite a 15% rise in network difficulty.
• HPC Revenue: BUZZ HPC revenue was $4.9 million during the quarter. This revenue was achieved against direct costs of $2.3 million.
• G&A: $8.4 million, up from $7.8 million in Q2 2026, primarily as a result of increased staff to support HIVE’s global expansion, including Paraguay, and the BUZZ HPC business. Notably, while gross operating margin increased more than 6x year-over-year, corporate G&A grew only 1.8x over the same period, demonstrating operating leverage and disciplined scaling.
• Net Loss: GAAP net loss of $91.3 million was primarily driven by $57.4 million in accelerated depreciation related to the Paraguay expansion and non-cash revaluation adjustments. The loss reflects HIVE’s decision to depreciate the next-generation ASIC fleet over a two-year cycle, rather than the typical four-year schedule, to reflect the faster pace of efficiency improvements and shorter economic lives of new ASICs—a conservative approach aligned with our strong growth in Paraguay and focus on operating income.
• Adjusted EBITDA: $5.7 million.
OPERATING PERFORMANCE: SCALE WITH DISCIPLINE
Infrastructure Expansion
• Completed Paraguay Buildout and Achieved 25 EH/s: Operating 440 megawatts (MW) of global, hydro-powered capacity with 25 EH/s installed and 22.9 EH/s average operational hashrate, while reaching 17.5 Joules per Terahash (J/TH) fleet efficiency; record completion of 300 MW of green-energy Tier-I infrastructure brought online in 6 months (from May 2025 to November 2025).
• Land & Power: The company signed an additional 100 MW PPA in Yguazú and bought 10 hectares of land, with energization targeted for Q4 2026. This maintains our growth in Paraguay by an additional 10 EH/s. Subsequent to the quarter end, the Company has purchased an additional 63 hectares of land.
Positioning for AI and HPC Growth
Future Capacity & Growth Outlook
• Accelerating AI Revenue: In February 2026, the Company signed a 2-year, $30 million contract for 504 Nvidia B200 GPUs. Expected deployments to be live in calendar Q1 2026 at Bell’s Tier-III facility; adds ~1$15 million of ARR and lifts HPC annualized revenue ~75% (from $20 million to $35 million). Targeting $140 million ARR by Q4 2026 for GPU AI Cloud with 11,000 GPUs, subject to market conditions and successful infrastructure deployment.
• BUZZ’s Growth Plan: Targeting $225 million ARR for total HPC revenue for BUZZ HPC and GPU AI Cloud by end of calendar 2026 or early 2027 as GPU cloud and colocation capacity expands.
• Strengthened Runway for Scalable Compute: By year-end, HIVE expects to operate a 540 MW energy footprint (440 MW currently operating, plus the additional 100 MW PPA contracted). Existing and incremental megawatts will be evaluated to preserve flexibility for highest-value deployments – toward expanding EH/s or supporting future AI and high-performance computing workloads.
Management Insights
Frank Holmes, HIVE’s Executive Chairman, stated, “This quarter marked an inflection point for HIVE. We delivered record revenue, scaled our renewable-powered Tier-I hashrate platform to 25 EH/s and accelerated our AI strategy. These milestones reflect disciplined execution across both engines of our business – Bitcoin hashrate services as the cash generator and BUZZ as our high-growth HPC platform, positioning HIVE for diversified, recurring revenue growth. Demand for AI compute continues to rise, and HIVE is leveraging its long track record in high-performance compute infrastructure and deep technical expertise in AI cloud services and data center operations to capture that opportunity. Notably, we are also positioning Paraguay to be a leader in HPC for Latin America. With abundant and stable green energy, and a government that is strongly-aligned with the United States, we believe Tier-III data centers are the future in Paraguay. Our future deployments in Paraguay will have the architecture and infrastructure footprint for Tier III future deployments as we build out our powered land. Our team has ordered the substation for the additional 100 MW at Yguazú, which we expect to come online in calendar Q3 2026. Moreover, the Company has a strategic alignment with Paraguay’s largest Tier III telecom datacenter operator, where we are sending a cluster of high-performance GPUs which will operate on the BUZZ AI Cloud out of Asuncion. Thus, by laying the foundation for long-term and rapid scale HPC Tier III Data Center deployment with our next 100 MW in Yguazú, and curating HIVE’s first Latin America GPU AI cloud proof-of-concept this quarter from Asuncion, our vision is to be a first mover in Latin America, powering the AI industrial revolution with renewable energy from Paraguay. HIVE will be a key economic driver for Paraguay, as we anticipate materially contributing to the GDP growth of the country through our data center construction expenditures and stable and long-term consumption of power from the Itaipu Dam, which will strengthen Paraguay’s domestic energy market and drive revenue for ANDE and the government. President Santiago Pena has demonstrated great leadership, along with Marcos Riquelme and Ruben Ramirez Lezcano, which gives us the confidence to advance our investments into Paraguay.”
Mr, Holmes continued, “Our wholly owned subsidiary, BUZZ AI has begun to demonstrate the scale of its earnings power. With this growth, our early-stage Paraguay platform becomes even more strategic, as we partner with a leading Tier III telecom data center operator in the country and deploy our first cluster of high-performance GPUs into that facility, demonstrating that our GPU chips have arrived and that Paraguay can be a cornerstone market for BUZZ in Latin America. Tier I data centers are a critical first step in building the power and infrastructure backbone required for future Tier III AI and HPC data centers, and we see them as the key runway for grid buildout and long-term capacity planning across our global platform. This is the strategy we are executing in Canada and Sweden today, and now in Paraguay as we develop large-scale, renewable powered Tier I capacity that can be systematically upgraded into Tier III AI and HPC data centers over time.”
Aydin Kilic, President & CEO, stated, “This quarter demonstrated HIVE’s execution in both our Tier-I hashrate platform and GPU AI Cloud. Our business has scaled substantially over the last year. Notably, our gross operating margin has increased over 6x YoY, from $5.3 million period end December 31, 2024 to $32.1 million this current period end December 31, 2025. At HIVE, we pursue accretive growth with a high-performance work culture, and this exponential growth in gross operating margin relative to corporate G&A reflects our expertise to scale with our Tier-I hashrate platform. Furthermore, this growth in corporate G&A includes added key personnel and talent to our BUZZ HPC and GPU AI Cloud business. In this fiscal quarter, we announced the purchase of 504 next-generation AI-optimized GPUs, and last week, ahead of their installation in March 2026 in the BUZZ Canada West facility, we announced the entire cluster was leased on a two-year fixed term contract valued at $30 million. As we expand BUZZ, we are leveraging our proven infrastructure operating model and deep technical expertise in AI to deliver GPU cloud and colocation capacity quickly and reliably for enterprise customers. With Tier-III+ capacity across Canada, Sweden and a growing pipeline of multi-year GPU cloud and colocation demand, we believe HIVE is positioned to build a durable, high-margin, recurring revenue platform through 2026 and beyond. This dual-engine strategy provides continued growth and sustained cashflow as we navigate the recent volatility in Bitcoin hashrate revenues.”
Darcy Daubaras, HIVE’s CFO, stated, “This quarter demonstrates strong revenue growth and operating margin expansion despite a more competitive hashrate environment. Accelerated depreciation impacted net income, but reflects conservative accounting and disciplined balance sheet management. We believe our cost structure and renewable power strategy position us to generate attractive operating margins as competition increases.”
Strategic Positioning
HIVE’s “dual-engine” strategy — Bitcoin infrastructure as cash generator and BUZZ AI Cloud as high-growth recurring revenue — provides diversification and capital allocation flexibility.
The Company remains focused on:
• Expanding gross operating margin
• Scaling recurring AI revenue
• Maintaining disciplined G&A growth
• Preserving balance sheet strength
With renewable-powered infrastructure across Canada, Sweden, and Paraguay, HIVE believes it is positioned to build a durable, margin-driven digital infrastructure platform through 2026 and beyond.
Conference Call Information
HIVE will hold its fiscal Q3 2026 earnings call on Tuesday, February 17 at 8:00 AM EST. To participate in this event, please log on or dial in approximately 5 minutes before the call.
Date: February 17, 2026
Time: 8:00 AM EST
Webcast: Registration link here
Dial-in: Provided after registration
Financial Statements and MD&A
The Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements and Management’s Discussion and Analysis (MD&A) thereon for the three months ended December 31, 2025 will be accessible on SEDAR+ at www.sedarplus.ca under HIVE’s profile and on the Company’s website at www.HIVEdigitaltechnologies.com.
¹ The Company has presented certain non-GAAP measures in this report. The Company uses EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA as a metric that is useful to management, the board and investors for assessing its operating performance on a cash basis before the impact of non-cash items and acquisition related activities. EBITDA is net income or loss from operations, as reported in profit and loss, before finance income and expense, tax and depreciation and amortization. Adjusted EBITDA is EBITDA adjusted for by removing other non-cash items, including share-based compensation, finance expense, depreciation and one-time transactions. The following table provides an illustration of the calculation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA for the last five quarters:
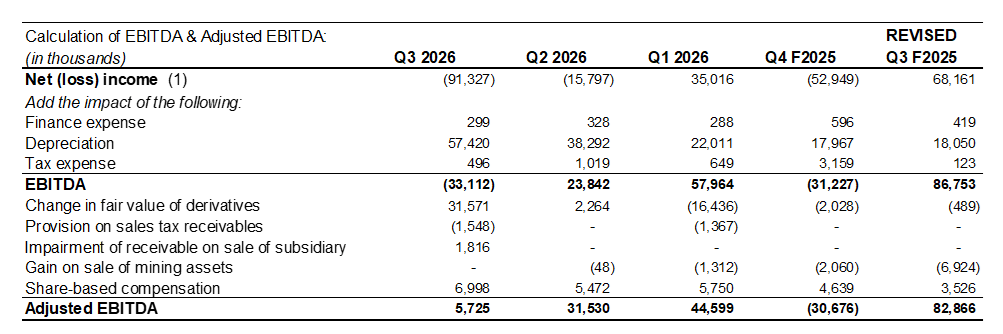
² Net realized and unrealized gains (losses) on digital currencies is calculated as the change in fair value (gain or loss) on the coin inventory, and the gain (loss) on the sale of digital currencies which is the net difference between the proceeds and the carrying value of the digital currency.
³ The following represents the Revenue and related costs that comprise the gross mining margin. We include connectivity, security, data center maintenance, and electrical equipment maintenance. Electrical costs may vary quarter over quarter.
*Average revenue per BTC is for hashrate services operations only and excludes HPC operations.
⁴ References to annualized revenue and run-rate revenue are considered future-oriented financial information. Readers should be cautioned that this information is used by the Company only for the purpose of evaluating the merit of this line of its business operations and may not be appropriate for other purposes.
Quarterly ATM Sales Report
For the three-month period ended December 31, 2025, the Company issued 4,925,948 common shares (the “November 2025 ATM Shares”) pursuant to the at-the-market offering commenced in November 2025 (the “November 2025 ATM Equity Program”) for gross proceeds of C$22.0 million ($15.8 million). The November 2025 ATM Shares were sold at prevailing market prices, for an average price per November 2025 ATM Share of C$4.47. Pursuant to the November 2025 ATM Equity program, a cash commission of $153 thousand on the aggregate gross proceeds raised was paid to the sales agents in connection with its services under the November 2025 ATM Equity Program.
About HIVE Digital Technologies Ltd.
Founded in 2017, HIVE Digital Technologies Ltd. is the first publicly listed company to mine digital assets powered by green energy. Today, HIVE builds and operates next-generation Tier-I and Tier-III data centers across Canada, Sweden, and Paraguay, serving both Bitcoin and high-performance computing clients. HIVE’s twin-turbo engine infrastructure-driven by hashrate services and GPU-accelerated AI computing-delivers scalable, environmentally responsible solutions for the digital economy.
For more information, visit hivedigitaltech.com, or connect with us on:
X: https://x.com/HIVEDigitalTech
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@HIVEDigitalTech
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/hivedigitaltechnologies/
LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/company/hiveblockchain
On Behalf of HIVE Digital Technologies Ltd.
“Frank Holmes”
Executive Chairman
For further information, please contact:
Nathan Fast, Director of Marketing and Branding
Frank Holmes, Executive Chairman
Aydin Kilic, President & CEO
Tel: (604) 664-1078
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release.
Forward-Looking Information
Except for the statements of historical fact, this news release contains “forward-looking information” within the meaning of the applicable Canadian and United States securities legislation and regulations that is based on expectations, estimates and projections as at the date of this news release. “Forward-looking information” in this news release includes but is not limited to: the acquisition of the new sites in Paraguay and Toronto and their potential, the timing of it becoming operational; business goals and objectives of the Company, including its target hashrate milestones and the costs to achieve the milestones; the results of operations for the three and nine months ended December 31, 2025; the expected costs of maintaining and growing its operations; financial information related to annualized run rate; the acquisition, deployment and optimization of the hashrate fleet and equipment; the continued viability of its existing Bitcoin hashrate services operations; the receipt of government consents; and other forward-looking information concerning the intentions, plans and future actions of the parties to the transactions described herein and the terms thereon.
Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in such forward-looking information include, but are not limited to: the inability to complete the construction of the Paraguay acquisition on an economic and timely basis and achieve the desired operational performance; the ongoing support and cooperation of local authorities and the Government of Paraguay; the volatility of the digital currency market; the Company’s ability to successfully mine digital currency; the Company may not be able to profitably liquidate its current digital currency inventory as required, or at all; a material decline in digital currency prices may have a significant negative impact on the Company’s operations; the regulatory environment for cryptocurrency in Canada, the United States and the countries where our hashrate facilities are located; economic dependence on regulated terms of service and electricity rates; the speculative and competitive nature of the technology sector; dependency on continued growth in blockchain and cryptocurrency usage; lawsuits and other legal proceedings and challenges; government regulations; the global economic climate; dilution; future capital needs and uncertainty of additional financing, including the Company’s ATM Program and the prices at which the Company may sell Common Shares in the ATM Program, as well as capital market conditions in general; risks relating to the strategy of maintaining and increasing Bitcoin holdings and the impact of depreciating Bitcoin prices on working capital; the competitive nature of the industry; currency exchange risks; the need for the Company to manage its planned growth and expansion; the need for continued technology change; the ability to maintain reliable and economical sources of power to run its cryptocurrency hashrate assets; the impact of energy curtailment or regulatory changes in the energy regimes in which the Company operates; protection of proprietary rights; the effect of government regulation and compliance on the Company and the industry; network security risks; the ability of the Company to maintain properly working systems; reliance on key personnel; global economic and financial market deterioration impeding access to capital or increasing the cost of capital; share dilution resulting from the ATM Program and from other equity issuances; the construction and operation of facilities may not occur as currently planned, or at all; expansion may not materialize as currently anticipated, or at all; the digital currency market; the ability to successfully mine digital currency; revenue may not increase as currently anticipated, or at all; it may not be possible to profitably liquidate the current digital currency inventory, or at all; a decline in digital currency prices may have a significant negative impact on operations; an increase in network difficulty may have a significant negative impact on operations; the volatility of digital currency prices; the anticipated growth and sustainability of electricity for the purposes of Tier-I hashrate services in the applicable jurisdictions; the inability to maintain reliable and economical sources of power for the Company to operate Tier-I hashrate assets; the risks of an increase in the Company’s electricity costs, cost of natural gas, changes in currency exchange rates, energy curtailment or regulatory changes in the energy regimes in which the Company operates and the adverse impact on the Company’s profitability; the ability to complete current and future financings, any regulations or laws that will prevent the Company from operating its business; historical prices of digital currencies and the ability to mine digital currencies that will be consistent with historical prices; an inability to predict and counteract the effects of pandemics on the business of the Company, including but not limited to the effects of pandemics on the price of digital currencies, capital market conditions, restriction on labour and international travel and supply chains; and, the adoption or expansion of any regulation or law that will prevent the Company from operating its business, or make it more costly to do so.
The forward-looking information in this news release reflects the Company’s current expectations, assumptions, and/or beliefs based on information currently available to the Company. In connection with the forward-looking information contained in this news release, the Company has made assumptions about its objectives, goals or future plans, the timing thereof and related matters. The Company has also assumed that no significant events occur outside of the Company’s normal course of business. Although the Company believes that the assumptions inherent in the forward-looking information are reasonable, forward-looking information is not a guarantee of future performance, and accordingly, undue reliance should not be put on such information due to its inherent uncertainty. The Company disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking information, whether because of new information, future events or otherwise, other than as required by law.
Crypto World
BTC Must Reclaim These Key Levels to End the Downtrend
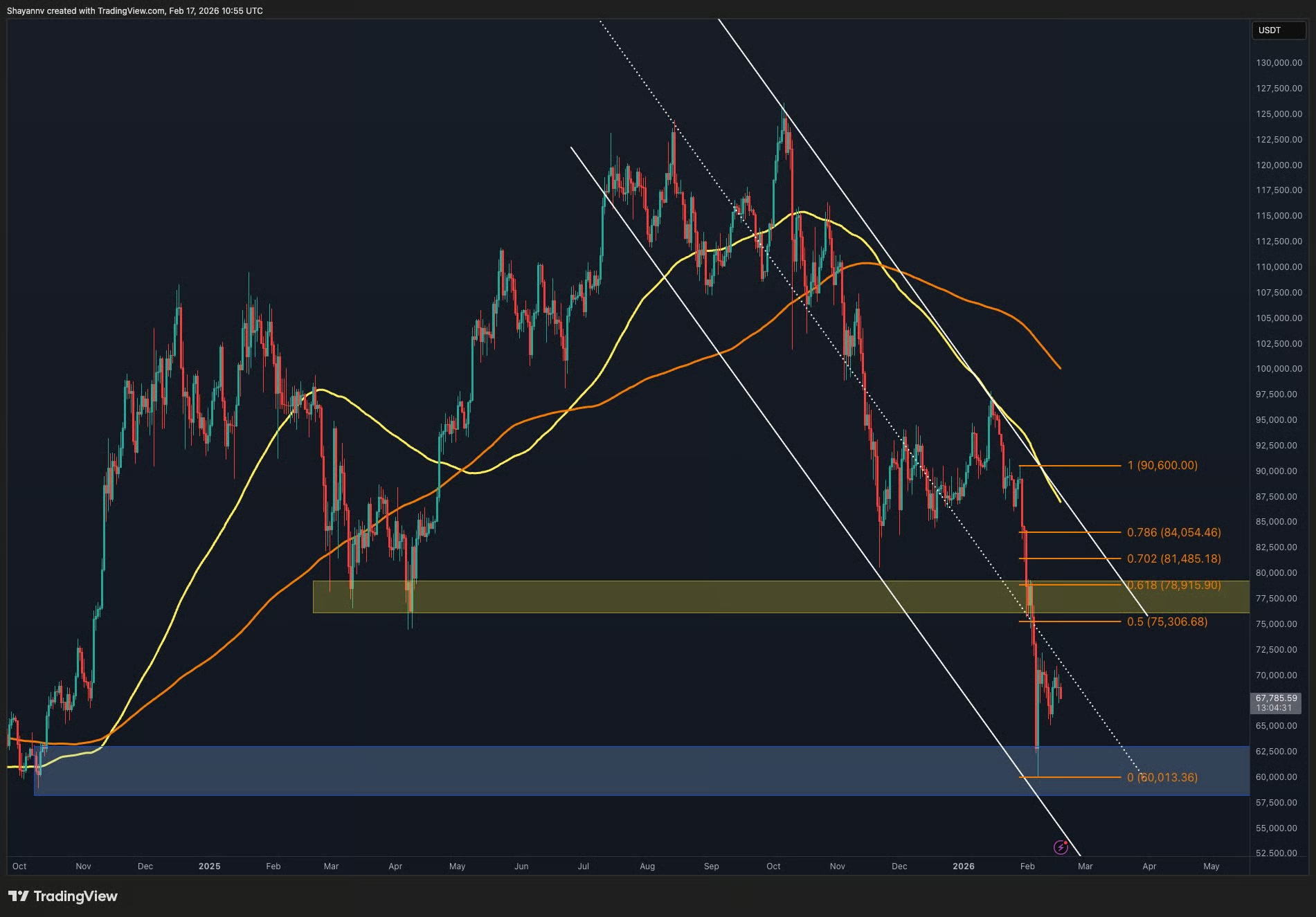
Bitcoin’s broader structure continues to reflect a dominant bearish trend, yet the recent price action shows a short-term recovery attempt from the major demand zone around $60K–$62K. At this stage, the market is positioned between a higher-timeframe bearish structure and a developing lower-timeframe corrective rebound.
Bitcoin Price Analysis: The Daily Chart
On the daily timeframe, the asset is still trading within a well-defined descending channel, with both the upper and lower boundaries clearly guiding the macro structure. After losing the $79K level and breaking decisively below the $75K range, Bitcoin accelerated toward the major blue demand zone around $60K, where a strong reaction occurred.
The recent bounce from this region has pushed the price back toward the mid-$60Ks to high-$60Ks area, but the overall structure remains corrective. The price is still trading below the channel’s midline and beneath the 100- and 200-day moving averages, both of which are sloping downward.
As long as Bitcoin remains below the broken $75.3K support and under the $78.9K–$81.4K Fibonacci cluster, the broader bias on the daily timeframe stays bearish. The current recovery appears to be a pullback within a dominant downtrend rather than the start of a confirmed reversal.
BTC/USDT 4-Hour Chart
Zooming into the 4-hour timeframe, the corrective nature of the rebound becomes more evident. After the sharp capitulation wick into the $60K region, the price formed a local base and initiated a rebound toward the $70K area. However, this recovery is unfolding beneath a descending trendline and below the prior breakdown structure.
The $73K–$76K supply zone, which previously acted as support, now stands as a strong resistance area. Until the asset reclaims this region and invalidates the sequence of lower highs, the short-term structure remains vulnerable to another leg down.
The recent consolidation around the high-$60Ks reflects a temporary equilibrium between buyers defending the higher low and sellers protecting overhead resistance. A decisive break above the descending trendline could open the door toward the mid-$70Ks, while failure to sustain momentum increases the probability of a renewed test of the $60K demand zone.
Onchain Analysis
On-chain data from the Long-Term Holder SOPR (LTH-SOPR) suggests that sustained downside pressure is beginning to affect even Bitcoin’s most resilient cohort, marking a subtle but important shift in market dynamics.
Although the annual average LTH-SOPR remains elevated at 1.87, the metric has recently dropped below the critical 1.0 threshold, reaching 0.88—a configuration not seen since the late stages of the 2023 bear market. Historically, such breakdowns tend to occur during more advanced corrective phases, when even strong hands begin reducing exposure under sustained pressure.
That said, broader timeframe data paints a more nuanced picture. The monthly average SOPR still stands at 1.09, implying that, on aggregate, long-term holders are still realizing profits. Full-scale capitulation has typically coincided with much deeper compressions, with prior bear market bottoms marked by monthly SOPR levels approaching 0.5.
In this context, the current move does not yet confirm structural capitulation. Rather, it signals early stress among long-term participants—an inflection point that could either stabilize if market conditions improve or evolve into deeper distribution should selling pressure intensify.
SECRET PARTNERSHIP BONUS for CryptoPotato readers: Use this link to register and unlock $1,500 in exclusive BingX Exchange rewards (limited time offer).
Disclaimer: Information found on CryptoPotato is those of writers quoted. It does not represent the opinions of CryptoPotato on whether to buy, sell, or hold any investments. You are advised to conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. Use provided information at your own risk. See Disclaimer for more information.
Crypto World
Cysic founder challenges Charles Hoskinson over Google Cloud role in Midnight


Cysic founder Leo Fan argued that blockchain projects relying heavily on hyperscalers like Google Cloud and Microsoft’s Azure risk undermining crypto’s decentralization ethos, at Consensus Hong Kong 2026.
Fan’s comments came after Cardano founder Charles Hoskinson outlined Midnight, Cardano’s privacy-focused project, and announced partnerships with companies including Google and Telegram. Midnight is scheduled to launch its mainnet at the end of March, according to Hoskinson.
Hoskinson defended working with hyperscalers, arguing that no single layer-1 blockchain can handle the computational demands required for global, privacy-preserving systems.
“When people spend a trillion dollars building data centers,” he said, referring to major cloud providers, “we should probably use what they spent the trillion dollars on instead of trying to build a completely different network.”
Midnight Foundation CEO Fahmi Syed said the network will debut with 10 federated nodes as part of what he described as a “responsible” path toward decentralization. Google Cloud is among early collaborators providing infrastructure support.
Justifying the single point of failure
Hoskinson said Midnight is designed to offload heavy computational workloads, particularly those tied to privacy and zero-knowledge cryptography, to cloud providers such as Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. He added that technologies like multi-party computation and confidential computing would allow providers to supply hardware capacity without accessing the underlying data.
During a stage demonstration, Hoskinson said Midnight processed thousands of transactions per second with Microsoft Azure powering the backend compute layer.
Fan, however, argued that relying on hyperscalers for core compute still introduces structural centralization risks.
“If your validators look decentralized but all run on the same data center in that’s still a single point of failure,” Fan told CoinDesk. “Blockchain is supposed to remove single points of failure. If the infrastructure is centralized, that’s a contradiction.”
Cysic, operates a decentralized compute network focused on zero-knowledge proof generation. He said one customer reduced proof-generation time from as much as 90 minutes on AWS to roughly 15 minutes using Cysic’s distributed hardware network.
“In some scenarios, we can deliver better performance,” Fan said. “We don’t need to defeat them immediately, but we can compete.”
How decentralization should be defined
Midnight is not outsourcing its blockchain to Google or Microsoft. The base network runs its own nodes, and Hoskinson emphasized that hyperscalers provide hardware capacity rather than governance or protocol control.
He described Midnight as a neutral coordination layer that could dynamically route workloads between cloud providers, arguing that encrypted computation and confidential computing environments ensure providers “just provide the hardware.”
Fan’s critique focuses on a different layer of the stack.
Even if data is encrypted and workloads can shift between providers, reliance on a small number of global infrastructure operators concentrates power at the compute layer, particularly as demand for GPUs and data center capacity intensifies, Fan said.
The disagreement is less about whether Midnight is centralized in a strict technical sense and more about how decentralization should be defined.
Hoskinson’s approach prioritizes cryptographic neutrality over hardware ownership. Fan said that decentralization must extend to the compute layer itself.
Rather than calling for a complete rejection of hyperscalers, Fan advocated a hybrid approach.
“Use big vendors in a limited way,” he said. “Combine them with decentralized networks to make the system more robust. Do not give up decentralization because that’s the nature of our community.”
As blockchain networks pursue enterprise adoption and global scale, the divide between building parallel infrastructure and integrating with Big Tech may define crypto’s next phase.
Crypto World
Steak ‘n Shake Reports Bitcoin Acceptance Has ‘Dramatically’ Lifted Sales in 9 Months
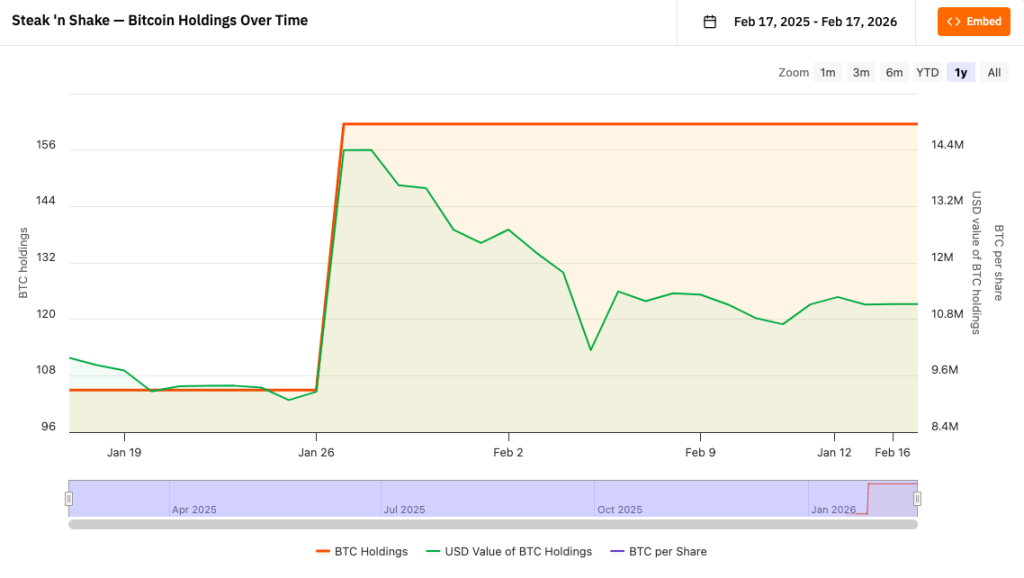
In a bullish bit of news for everyday crypto usage, Steak ‘n Shake reports that Bitcoin payments have “dramatically” lifted same-store sales over the last nine months.
The 90-year-old burger chain is now routing all crypto revenue directly into a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve, effectively blending retail operations with institutional asset accumulation.
This is no longer just a marketing stunt, it’s a balance sheet strategy.
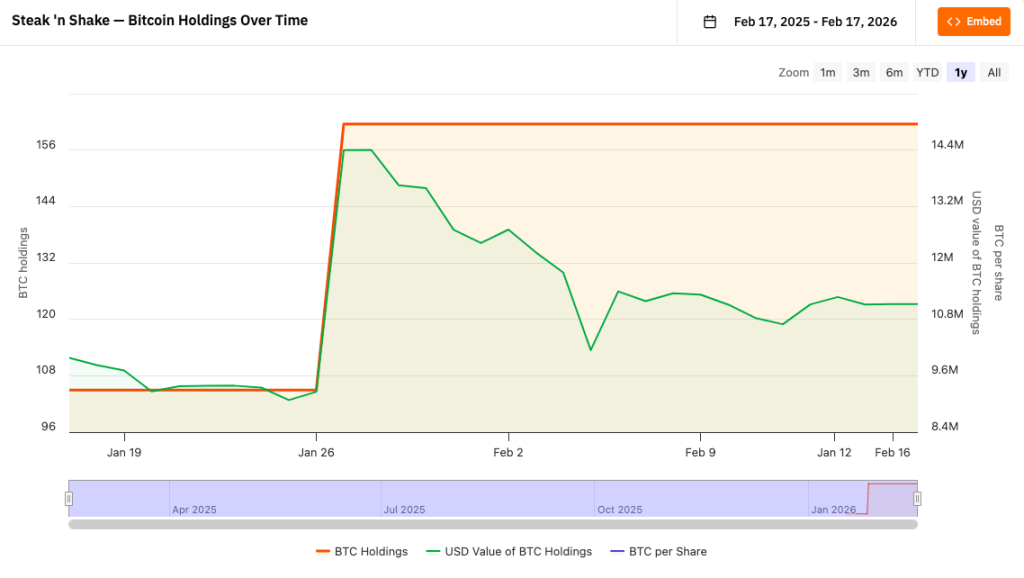
- Sales Growth: Reported 15% same-store sales jump by October 2025 and 18% growth in 2026, significantly outpacing industry averages.
- Treasury Strategy: The company now holds approximately 168.6 BTC (valued near $15 million) in its Strategic Bitcoin Reserve.
- Operational Efficiency: Lightning Network transactions have reduced payment processing fees by nearly 50% compared to traditional credit cards.
Is Data Finally Overtaking the Hype?
Steak ‘n Shake began this pivot nine months ago, and the data suggests it is paying off.
While Wall Street firms like BlackRock and Goldman Sachs are quietly doubling down on crypto, this chain chose to go loud.
Unlike competitors testing the waters with third-party processors that instantly convert to fiat, Steak ‘n Shake is holding the asset.
The company stated the move has driven a “sharp rise” in sales. It signals a shift from using crypto as a novelty to treating it as both digital gold and digital cash.
Corporate adoption is shifting from tech-native firms to traditional businesses seeking hard asset reserves.
Discover: The best meme coins on the market.
Inside the Treasury and Bonus Model
The financials show a dense commitment to the ecosystem. Steak ‘n Shake has accumulated approximately 168.6 Bitcoin, valued at around $15 million.
This reserve was built through a mix of customer receipts and direct treasury allocations, including a $10 million initial investment in May 2025 and subsequent buys in January 2026.
This mirrors how other firms plan to equitize convertible debt into Bitcoin to strengthen long-term solvency.
Beyond holding the asset, the operational mechanics are yielding immediate margins. By processing payments via the Lightning Network, the chain reports transaction fee savings of nearly 50% versus standard credit card rails.
The strategy extends to the workforce as well. Starting March 1, the company will issue bonuses to hourly employees at company-operated locations.
Workers will accrue $0.21 worth of Bitcoin for every hour worked, creating a vesting retention mechanism tied to the asset’s performance.
A New Standard for Retail?
Steak ‘n Shake’s metrics challenge the narrative that Bitcoin is too slow or volatile for commerce.
The burger chain’s immediate planned expansion into El Salvador, where Bitcoin is legal tender, signals global ambitions.
This integration reflects a broader institutional trend. As Trump-linked Truth Social files for Bitcoin staking ETFs and Elon Musk’s X launches smart cashtags for trading, the infrastructure between consumer apps and crypto rails is hardening.
Steak ‘n Shake just provided the proof of concept that it works for burgers, too.
Discover: The best new crypto to watch out for.
The post Steak ‘n Shake Reports Bitcoin Acceptance Has ‘Dramatically’ Lifted Sales in 9 Months appeared first on Cryptonews.
Crypto World
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) Drops 2.2%, Leading Index Lower
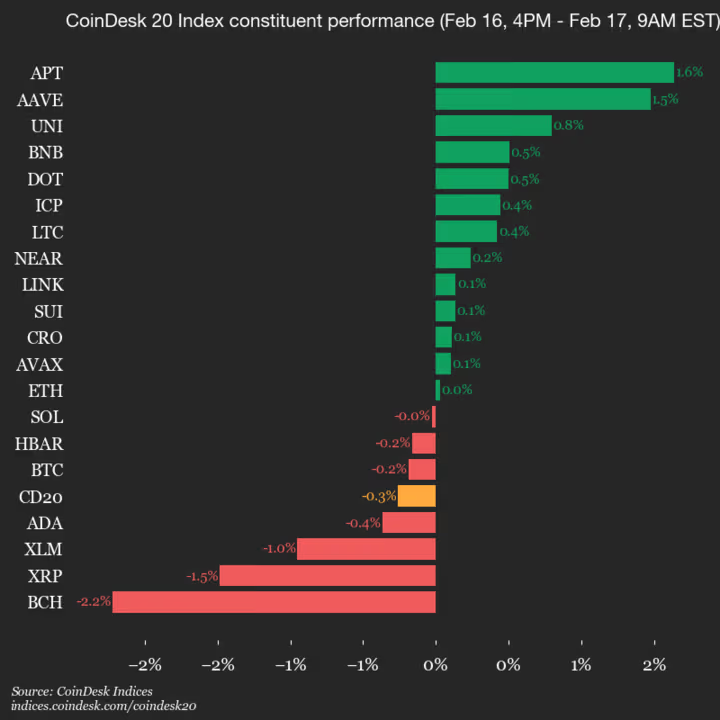
CoinDesk Indices presents its daily market update, highlighting the performance of leaders and laggards in the CoinDesk 20 Index.
The CoinDesk 20 is currently trading at 1979.83, down 0.3% (-5.15) since 4 p.m. ET on Monday.
Thirteen of the 20 assets are trading higher.

Leaders: APT (+1.6%) and AAVE (+1.5%).
Laggards: BCH (-2.2%) and XRP (-1.5%).
The CoinDesk 20 is a broad-based index traded on multiple platforms in several regions globally.
Crypto World
Tom Lee says crypto sentiment is as poor as 2018 and 2022 bottoms


BitMine Immersion Technologies (BMNR), the largest Ethereum treasury company, purchased 45,759 ether last week, extending its buying spree despite the sharp pullback in crypto prices.
The haul was the largest weekly purchase this year in token terms, bringing the firm’s total ETH holdings to 4,371,497 tokens, the company said in a Monday update. That’s equivalent to $8.7 billion at current prices, while the company is estimated to be sitting on almost $8 billion in paper losses.
The firm also raised its cash pile to $670 million, alongside its small bitcoin stash and equity stakes, including a $200 million position in Beast Industries. Total assets stand at $9.6 billion, while BitMine’s share of ETH’s total supply rose to 3.62%.
BitMine has now staked over 3 million ETH — about 69% of its holdings — that generate $176 million in annualized rewards, according to Chairman Tom Lee. The firm’s staking operations currently yield 2.89% annualized.
Lee said sentiment in crypto markets remains depressed, drawing comparisons to the lows of 2018 and 2022. But he argued the current environment differs in that there have been no major collapses of large players.
“Investor sentiment and enthusiasm are rock bottom, reminding us of the forlornness and dejection seen at the November 2022 lows and depths of 2018 crypto winter,” he said. “Rather, it seems like crypto has remained weak since the ‘price shock’ and massive deleveraging seen on October 10th.”
Lee also highlighted developments from last week’s Consensus Hong Kong conference, where he cited tokenization, artificial intelligence (AI) integrations and proof-of-humanity infrastructure as long-term growth drivers for Ethereum.
“The price of ETH is not reflective of the high utility of ETH and its role as the future of finance,” Lee said. “Hence, we continue to buy ETH even as crypto moves through this ‘mini-winter.’”
Read more: Tom Lee says stop timing the bottom and start buying the dip
Crypto World
Bitcoin Long Term Holders Quietly Accumulate Near $68,000
Bitcoin has struggled to regain upward momentum in recent sessions. The price has remained range-bound amid uncertain macro conditions. Volatility in equities and rate expectations has capped recovery attempts.
With short-term signals mixed, attention shifts to long-term holders, or LTHs. This cohort has historically shaped major Bitcoin reversals. Their behavior now offers critical insight into whether BTC is nearing a turning point.
Sponsored
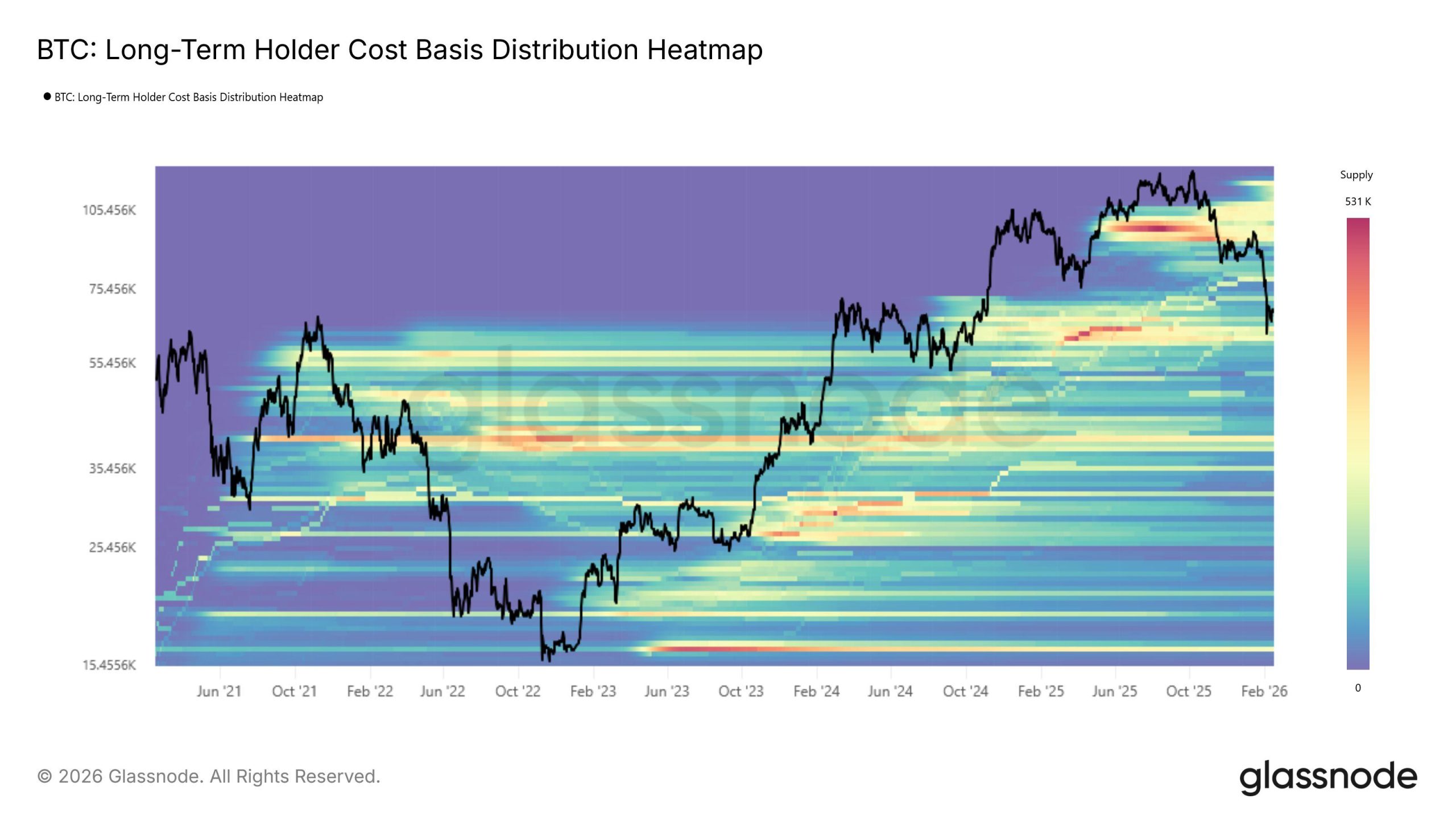
Bitcoin LTHs Have a Critical Support Established
The LTH CBD Heatmap highlights significant supply density above $65,000. This cluster is anchored in the 2024 first-half accumulation range. That zone has repeatedly absorbed recent selling pressure. Strong demand there suggests conviction among experienced Bitcoin holders.
This support band has acted as a buffer during pullbacks. Capital accumulated during prior consolidation phases remains largely dormant. As long as this structure holds, large-scale distribution appears unlikely.
Want more token insights like this? Sign up for Editor Harsh Notariya’s Daily Crypto Newsletter here.
A decisive breakdown below this range would change the narrative. It could open the path toward Bitcoin’s Realized Price, currently near $54,000. However, such a move seems less probable while LTH supply remains stable. The data suggests holders are not preparing for capitulation.
Sponsored
How Are LTHs Reacting?
The Long-Term Holder Net Unrealized Profit and Loss, or NUPL, has recently declined. This metric measures aggregate unrealized gains within long-term wallets. Falling NUPL indicates shrinking profitability among this BTC cohort.
Historically, extended NUPL declines have coincided with deeper price corrections. Similar patterns appeared in February 2020 and June 2022. In those periods, weakening profitability led to broader capitulation events.
Sponsored
This cycle appears different. Institutional flows and spot Bitcoin ETF support have strengthened structural demand. Persistent inflows from regulated products provide a stabilizing force. As a result, LTHs may be less inclined to exit positions despite margin compression.
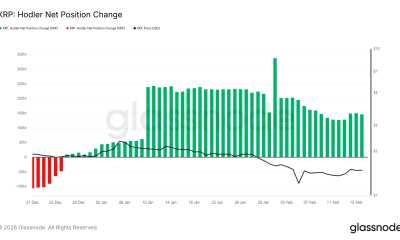
HODLer Net Position Change data shows Bitcoin LTHs are accumulating rather than distributing. Rising green bars on the metric suggest coins are moving into long-term storage. This is a positive sign as their accumulation tends to stick for a long while, unlike STHs, who are prone to selling at the first sign of profits.
Continued inflows into LTH wallets reinforce this trend. Accumulation during uncertainty can slow downside momentum, and if this pattern persists, it may help establish a foundation for a broader Bitcoin price recovery.

Sponsored
BTC Price Is Still Under Resistance
Bitcoin is trading at $68,282 at the time of writing. The primary near-term target remains reclaiming the $70,000 level. This psychological barrier has capped upside for roughly ten days.
The $68,342 support level is critical in the short term. Strong defense of this zone could enable BTC to challenge the $70,610 resistance. A confirmed breakout may extend gains toward $73,499 and potentially higher if momentum accelerates.
Downside risk remains present under adverse macro conditions. A break below $65,158 would weaken the current structure. Losing that support could expose Bitcoin to a deeper retracement. In such a scenario, price could gravitate toward the Realized Price near $58,000.
Crypto World
NEXO token surges as the crypto lending platform returns to US

- NEXO returns to the US with fully compliant crypto services.
- NEXO token rises to $0.8871, up 9.4% over the past week.
- Key support lies at $0.8655, with the immediate resistance near $0.9619–$1.07.
NEXO, the native token of the crypto lending and financial services platform Nexo, has seen a notable uptick in price following the company’s return to the United States nine months after announcing it would return.
The token currently trades at around $0.8871, marking a 5.7% surge in 24 hours and a 9.4% gain over the past week, reflecting renewed investor confidence and growing anticipation surrounding the platform’s US relaunch.
The platform originally exited the US market three years ago due to regulatory hurdles.
At the time, Nexo faced scrutiny over its crypto lending products, leading to a temporary halt of its services to American customers.
Now, the company has returned with a fully compliant approach after partnering with Bakkt, a regulated US infrastructure provider, to ensure its offerings meet local financial regulations.
Nexo’s relaunch in the United States
The US relaunch brings back key services that had previously been unavailable.
Users can once again access flexible and fixed-term crypto yield programs, allowing investors to earn interest on their digital assets.
Additionally, Nexo is offering a fully integrated crypto exchange for spot trading.
This gives US clients the ability to buy, sell, and trade supported cryptocurrencies directly on the platform.
Crypto-backed credit lines have also returned, and users can borrow against their digital holdings without having to sell them, providing liquidity while retaining exposure to the assets.
The platform has reintroduced its loyalty program, rewarding clients for participation and activity.
Fiat on and off-ramps are now available, enabling smooth transfers between bank accounts and the platform.
The partnership with a regulated US provider ensures that all these services operate within a compliant framework.
This regulatory alignment not only mitigates risk but also strengthens institutional confidence in NEXO’s operations.
NEXO price forecast
The combination of Nexo’s regulatory-compliant relaunch, a strong product suite, and favourable technical indicators makes the token one to watch in the coming weeks.
Looking ahead, the first major support is at $0.8655, which is crucial for maintaining upward momentum.
If this level holds, the token could test its first major resistance at $0.9619.
Breaking above $0.9619 may open the path to $1.02, with a further target at $1.07.
On the downside, analysts note that if the support at $0.8655 fails, NEXO could slide toward the next support level at $0.7923.
However, the token’s short-term performance will likely depend on the platform’s adoption in the US, liquidity on exchanges, and overall crypto market sentiment.
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoBig Tech enters cricket ecosystem as ICC partners Google ahead of T20 WC | T20 World Cup 2026
-

 Tech6 days ago
Tech6 days agoSpaceX’s mighty Starship rocket enters final testing for 12th flight
-

 Video23 hours ago
Video23 hours agoBitcoin: We’re Entering The Most Dangerous Phase
-

 Tech3 days ago
Tech3 days agoLuxman Enters Its Second Century with the D-100 SACD Player and L-100 Integrated Amplifier
-

 Video4 days ago
Video4 days agoThe Final Warning: XRP Is Entering The Chaos Zone
-

 Tech11 hours ago
Tech11 hours agoThe Music Industry Enters Its Less-Is-More Era
-

 Crypto World7 days ago
Crypto World7 days agoBlockchain.com wins UK registration nearly four years after abandoning FCA process
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
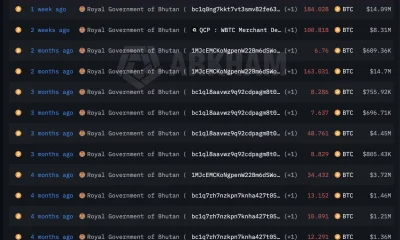
Crypto World4 days agoBhutan’s Bitcoin sales enter third straight week with $6.7M BTC offload
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoPippin (PIPPIN) Enters Crypto’s Top 100 Club After Soaring 30% in a Day: More Room for Growth?
-

 Video5 days ago
Video5 days agoPrepare: We Are Entering Phase 3 Of The Investing Cycle
-
 Crypto World5 hours ago
Crypto World5 hours agoCan XRP Price Successfully Register a 33% Breakout Past $2?
-

 Video6 hours ago
Video6 hours agoFinancial Statement Analysis | Complete Chapter Revision in 10 Minutes | Class 12 Board exam 2026
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoThe strange Cambridgeshire cemetery that forbade church rectors from entering
-

 Sports12 hours ago
Sports12 hours agoGB's semi-final hopes hang by thread after loss to Switzerland
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoBarbeques Galore Enters Voluntary Administration
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoCrypto Speculation Era Ending As Institutions Enter Market
-
 Crypto World5 days ago
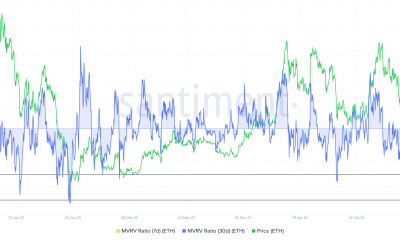
Crypto World5 days agoEthereum Price Struggles Below $2,000 Despite Entering Buy Zone
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoWhy was a dog-humping paedo treated like a saint?
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoMan dies after entering floodwater during police pursuit
-
 Crypto World4 days ago
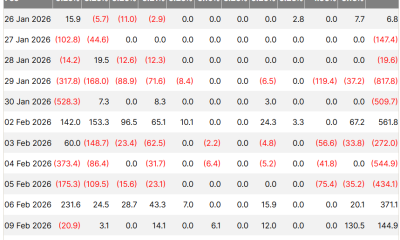
Crypto World4 days agoBlackRock Enters DeFi Via UniSwap, Bitcoin Stages Modest Recovery













