Tech
10 Red Flags to Watch For When Vetting a New Client

From my own experience, and from working with hundreds of entrepreneurs in the Business Booster accelerator, I’ve learned that not all clients are equally beneficial for a company’s growth. Some become partners and drivers of success, while others consume resources, drain energy, and ultimately hinder development. Learning to spot these clients early on is an invaluable skill. Our business architects and salespeople have shared their insights to help compile this list of warning signs that indicate a potentially problematic client.
1. Financial Instability and Limited Resources
This is perhaps the most obvious and alarming sign. If a client constantly delays payments to their employees or suppliers, if their business is critically dependent on loans, or if there’s no clear budget for a development project—this is a direct path to you not getting paid. This also includes a clear lack of qualified staff on the client’s side who would need to work with your product or implement changes. You might offer a brilliant solution, but there will be no one on the client’s end to implement it.
2. Over-reliance on a Few Large Clients
If more than 50-70% of a client’s revenue comes from one or two customers, their business is in a zone of turbulence. The loss of such a client, which is common in our unstable times, can lead to the collapse of their entire business and, along with it, your joint project. This is a risk that is not always worth taking.
3. Unprofessional Behavior and Violation of Ethical Norms
This includes any disrespect for business agreements: constantly rescheduling meetings without notice, ignoring messages, or being unwilling to apologize for their mistakes. As psychologists note, respect for others’ time and keeping agreements are basic signs of reliability. If a business partner (and a client is your partner in a project) demonstrates the opposite, you should be very wary.
4. Unrealistic Expectations Regarding Timelines and Results
The client expects a “magic pill” or immediate results that are objectively impossible within the stated timeframe or with the current resources of their company. In psychology, this is sometimes called a form of “magical thinking”—a belief in instant transformations without accounting for the real effort and time required. This is guaranteed to lead to disappointment and conflict.
5. Lack of Personal Involvement and Shifting Responsibility
This is one of the most frustrating flags for me. If a client wants you to “do everything turnkey,” isn’t willing to spend their own time participating in the process, making key decisions, or providing necessary information, it’s a huge sign that they’re not ready for real work. A project’s success is always a joint effort. As the saying goes, success has many fathers, but failure always has one culprit—the one who didn’t take responsibility.
6. Unwillingness to Provide Complete and Accurate Information
If, during the diagnostic phase or throughout the work, the client avoids answering questions, provides incomplete or contradictory data, or distorts facts, it undermines the foundation of trust. Without a complete picture, you can’t properly assess the situation and offer effective solutions. This is either a sign of distrust towards you or an attempt to conceal the real state of affairs, which is even worse.
7. Devaluing Your Experience and Arrogance
When you hear comments like “I know better” or “Your prices are too high for this nonsense” right from the start, be prepared for problems. A client who devalues your expertise is not ready to learn or accept your recommendations. How can you help someone who doesn’t want to be helped?
8. Negative Experience with Previous Contractors and Blame-Shifting
It’s a classic when a client complains about all their past contractors: these were incompetent, the second group cheated them, the third let them down. Meanwhile, they see no role they played in those failures. If “they” were to blame for all past problems, then in your future problems, it will likely be you who is to blame. This is a clear example of external attribution of blame, where a person is unable or unwilling to take responsibility for their actions and decisions. This is in stark contrast to successful leaders like Elon Musk or Jack Ma, who publicly admit their mistakes and learn from them.
9. Lack of Clear Goals and Vague Expectations
A client wants “successful success” or asks you to “surprise them,” but can’t specifically articulate what they want to achieve. At Business Booster, we always help clients set a clear goal at the start because without it, it’s impossible to build the right path. But if even after our efforts the client continues to live in the clouds, it’s a sure sign that the work will be chaotic and the criteria for evaluating results will be vague.
10. Unwillingness to Pay an Advance or Unreasonable Financial Expectations
This point complements the first, focusing not so much on the overall financial situation but on the willingness to pay for your specific work. If a client constantly negotiates down to absurd amounts, demands results without an advance payment, or offers a barter instead of money for serious services, it can indicate either their disrespect for your work or simple inability to pay, which they are trying to hide.
These 10 points are not an absolute verdict, but each one is a serious reason for a deep check and, possibly, for refusing the collaboration. Ignoring these “red flags” in the hope of “reforming” the client means setting yourself and your team up for stress, wasted time, and most likely, financial losses.
Remember: knowing how to say “no” to the wrong client is a strategic decision that frees up your resources for those who truly value your work and are ready to move toward success with you.
Tech
Meet two teens that prove that barbering is not an “old man’s trade”
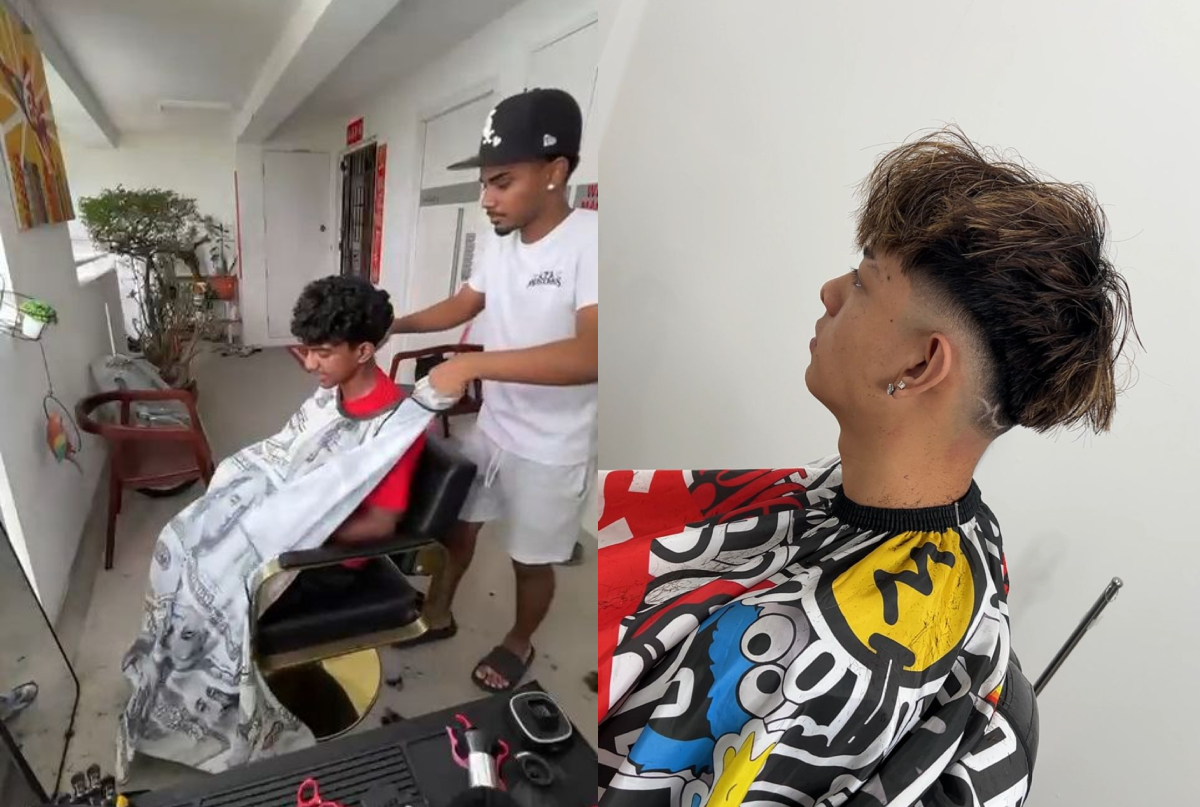

Not your usual uncle job: These teens are barbers on the side
Everyone has a go-to person for their hair, and for a growing clientele, the go-to person for their next fade is not a veteran, but 19-year-old Sujaish Kumar or 14-year-old Keanu Akbar.
While it’s easy to dismiss their work as a hobby, these two students have built successful brands from the ground up, earning recognition online and off—endeavours that gave them purpose after completing their studies.
Vulcan Post speaks to Sujaish and Keanu to find out how they paved their own way for themselves and other younger barbers in the old school trade.
Both of them picked up barbering by watching online videos
Getting a decent haircut was often a nightmare for Sujaish. He shared that ‘good barbers’ often charged S$30—out of budget for him and his friends in secondary school—leaving them to patronise shops that provided S$10-S$12 haircuts.
Unfortunately, keeping to that budget mean that the haircuts often came out uneven and messy. Frustrated, Sujaish decided to take matters into his own hands, challenging himself to provide better haircuts. The next day, he started watching tutorials on YouTube and TikTok.
“I had about S$50 saved up, so I just spent that on a pair of clippers. Then I basically had to beg my friends to let me cut their hair.” But even with having the right tools, the execution turned out to be harder than he thought.
“The first few haircuts were really really bad, uneven, and kind of demotivating,” Sujaish sheepishly shared, but that didn’t stop him from continuing to hone his craft, providing free haircuts for family, friends and their acquaintances at his HDB corridor.
Through word-of-mouth, Sujaish eventually gained a sizable following. Five months after he started, his cuts were good enough for him to charge S$5, which soon rose to S$8 per head. He also began promoting his services on TikTok, and one viral reel further grew his clientele base.
Even though he had to move his chair to his home upon receiving orders from the Housing Development Board (HDB), he continued making a name for himself online as a young barber, inspiring others, like Keanu, to do the same.
At the tender age of 12, Keanu was encouraged by his older brother to pick up barbering as a hobby, and he got him a set of tools to help him get started. As it turns out, Keanu’s older brother is friends with Sujaish himself, and that inspired his own suggestion.
Keanu shared a similar learning trajectory: picking up his skills from online tutorials and offering free haircuts for his family and friends to sharpen them. He started charging just S$3 per haircut after a year of practice and performed his services on a staircase at his HDB in Clementi. Word soon spread of his services, which helped him land an interview with local publication AsiaOne, which put his name out to the masses.
But beyond those opportunities, how did they actually sustain beyond the hype—one as long as their veteran seniors?
Scaling up a word-of-mouth service
While the traditional, word-of-mouth method got them started, both Sujaish and Keanu quickly diversified their reach, leaning heavily into social media, particularly TikTok, to scale up.
Going viral is not an easy feat, but Sujaish achieved just that with a video titled ‘How much I make as a 17-year-old barber in Singapore,’ where he earned S$195 in a single day. This financial transparency not only drew netizens but also attracted Singaporean news outlets Mothership and CNA.
Similarly, Keanu’s interview with Asiaone put him on the radar for more clients. The 14-year-old shared that since the interview, his Telegram subscribers doubled from around 150 to 350, and his TikTok following tripled from approximately 400-500 to 1,200.
However, viral success came with unforeseen challenges. Sujaish’s video caught the attention of the HDB, who informed him he could no longer operate in the corridor due to potential disturbance to neighbours, prompting him to move operations back inside his home.
Despite the change in settings, Sujaish continued to build his brand and reinvest his earnings for better tools and setups. He has also since raised his starting price to S$30 per haircut and started receiving requests from customers for house calls, where he could get paid a higher price of S$50.
This additional revenue stream gave Sujaish enough funds to open his own studio at Potong Pasir, which was around 100 sqft, or equivalent to a master bedroom in an HDB flat. While moving to a studio resulted in him forking out more than S$1,000 for flooring, rental and upgrades, he believes it was a gamble worth taking.
“Even from when I started, my goal was always to have my own private area where I could do my haircuts, and cutting hair at home was disturbing my family.”
Keanu has also moved his workstation to his home, not because he was told to, but out of a personal desire to provide a more comfortable experience for his clients. “Usually when it rains, I have to cancel my appointments because [my workspace] will get very wet and then people won’t like it.”
Beyond the fade
Aside from being able to earn from their side hustle, the trade has also instilled skillsets and qualities that can be used beyond barbering.
A self-proclaimed introvert, Keanu shared that picking up barbering helped him to gain confidence in engaging with strangers. “When I’m with my friends, I talk a lot. But other than that, I was really quiet in Primary school.”
Time management was also another skill he gained. He shared that he dedicates two and a half hours on selected weekdays and six hours on weekends, with the remainder of the time spent on his studies and leisure with family and friends.
“Maybe I’m not living like the full 14-year-old, but I don’t mind it.”
For Sujaish, barbering has allowed him to learn the foundations of building a business, from marketing himself to learning the operations. These allowed him to have an ambition to work towards opening a full-fledged barbershop and even starting a haircare brand.
Overall, both of them showed a new age of barbers that bring modern trends and tactics to a trade once seen as an “old man’s job” into a career still relevant in the modern world.
- Learn about our protagonists here:
- Read more stories we’ve written on Singaporean businesses here.
Featured Image Credit: Sujaish Kumar/ Keanu Akbar
Tech
Games Done Quick’s Back to Black 2026 event kicks off tomorrow
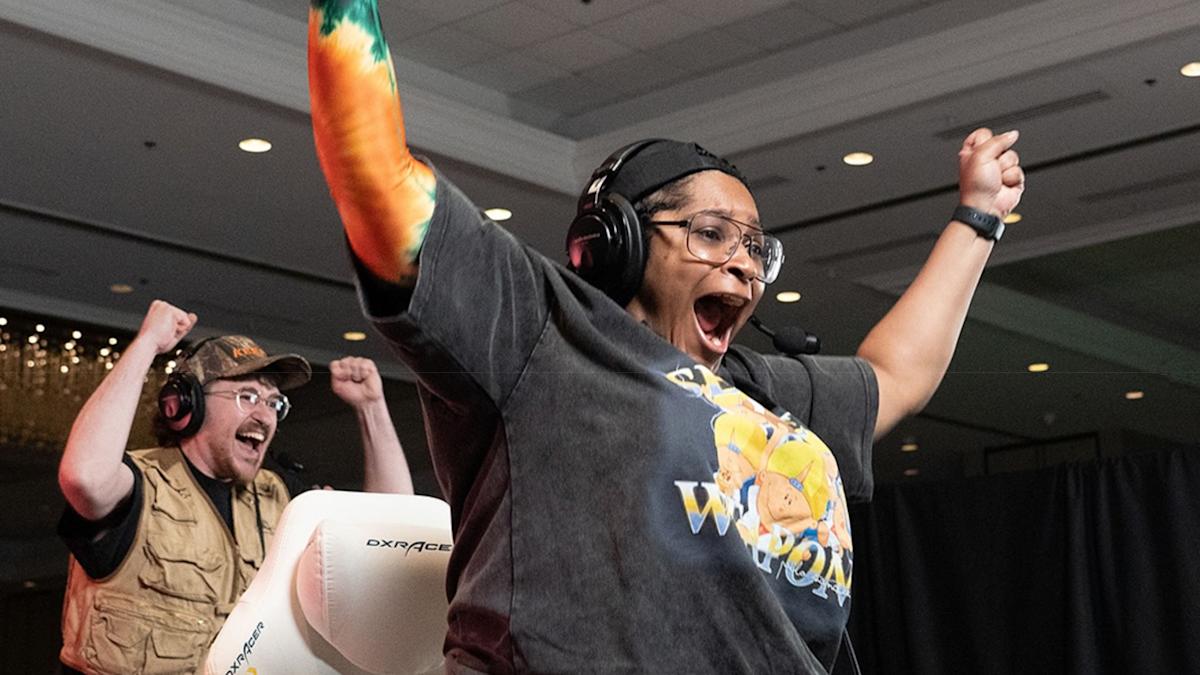
Hot on the heels of AGDQ in January, Games Done Quick is hosting its second speedrunning event of the year, Back to Black 2026, starting tomorrow, February 5. The four-day event is organized by Black in a Flash and is raising money for Race Forward, a nonprofit that works across communities to address systemic racism.
Back to Black is timed to the start of Black History Month and highlights the deep bench of talent in the Black speedrunning community. A few runs, like ones for Hades II, Donkey Kong Country and Silent Hill 4, were teased when Back to Black 2026 was announced last year. The full schedule has plenty of other runs worth checking out, though, like a co-op run through Plants vs Zombies: Replanted on February 5 or an Any% run of The Barbie Diaries: High School Mystery on February 6.
Back to Black 2026 will be live on Games Done Quick’s Twitch and YouTube channels from Thursday, February 5 through Sunday February 8.
Tech
Tinder looks to AI to help fight ‘swipe fatigue’ and dating app burnout

Tinder is turning to a new AI-powered feature, Chemistry, to help it reduce so-called “swipe fatigue,” a growing problem among online dating users who are feeling burned out and are in search of better outcomes.
Introduced last quarter, the Match-owned dating app said that Chemistry leverages AI to get to know users through questions and, with permission, accesses their Camera Roll on their phone to learn more about their interests and personality.
On Match’s Q4 2026 earnings call, one analyst from Morgan Stanley asked for an update on the product’s success so far.
Match CEO Spencer Rascoff noted that Chemistry was still only being tested in Australia for the time being, but said that the feature offered users an “AI way to interact with Tinder.” He explained that users could choose to answer questions to then “get just a single drop or two, rather than swiping through many, many profiles.”
In addition to Chemistry’s Q&A and Camera Roll features, the company plans to use the AI feature in other ways going forward, the CEO also hinted.
Most importantly, Rascoff said the feature is designed to combat swipe fatigue — a complaint from users who say they have to swipe through too many profiles to find a potential match.
The company’s turn toward AI comes as Tinder and other dating apps have been experiencing paying subscriber declines, user burnout, and declines in new sign-ups.
Techcrunch event
Boston, MA
|
June 23, 2026
In the fourth quarter, new registrations on Tinder were still down 5% year-over-year, and its monthly active users were down 9%. These numbers show some slight improvements over prior quarters, which Match attributes to AI-driven recommendations that change the order of profiles shown to women, and other product experiments.
Match said that this year, it aims to address common Gen Z pain points, including better relevance, authenticity and trust. To do so, the company said it is redesigning discovery to make it less repetitive and is using other features, like Face Check — a facial recognition verification system — to cut down on bad actors. On Tinder, the latter led to a more than 50% reduction in interactions with bad actors, Match noted.
Tinder’s decision to start moving away from the swipe toward more targeted, AI-powered recommendations could have a significant impact on the dating app. Today, the swipe method, which was popularized by Tinder, encourages users to think that they’re choosing a match from an endless number of profiles. But in reality, the app presents the illusion of choice, since matches have to be two-way to connect, and even then, a spark is not guaranteed.
The company delivered an earnings beat in the fourth quarter, with revenue of $878 million and EPS of 83 cents per share above Wall Street estimates. But weak guidance saw the stock decline on Tuesday, before rising again in premarket trading on Wednesday.
Beyond AI, Match will also increase its product marketing to help boost Tinder engagement. The company is committing to $50 million in Tinder marketing spend, which will include creator campaigns on TikTok and Instagram, where users will make claims that “Tinder is cool again,” Rascoff noted.
Tech
How Researchers Are Putting Students at the Center of Edtech Design

When researchers ask students to test educational technology products, a consistent pattern emerges: Tools that impress adults in demos often fall flat with the students who actually use them. Recent studies show that even well-designed products can frustrate students or create unnecessary mental strain when technical complexity gets in the way of learning. The disconnect means even promising tools aren’t reaching their full potential in real classrooms.
This gap between adult expectations and student experience is exactly what ISTE+ASCD, the Joan Ganz Cooney Center at Sesame Workshop and the youth research organization In Tandem aim to close through their collaborative work on student usability in edtech.
EdSurge spoke with three leaders from this collaborative effort: Vanessa Zuidema, co-founder and director of customer success at In Tandem; Dr. Medha Tare, senior director of research at the Joan Ganz Cooney Center; and Dr. Brandon Olszewski, senior director of research and innovation at ISTE+ASCD.
“To help clarify what matters most when it comes to student usability, we knew we needed to work with these partners to reach students, check our findings against others in the space and develop guidance for edtech providers,” Olszewski explains. “Sesame has extensive experience designing for young people and balancing high-quality learning with engagement. In Tandem connects young people with companies and organizations that need their voices at the table. ISTE+ASCD sits at the intersection of educational technology, learning design, and curriculum and instruction.”
Ahead of releasing a formal student usability framework later this year, the three organizations shared early findings about what students actually want from educational technology — and what it means for schools and developers.
EdSurge: Why focus specifically on student usability, and what does that mean in practice?
Tare: The field is very good at evaluating edtech from an adult perspective: alignment, evidence, safety, interoperability. But none of those frameworks capture what it’s like to be a kid trying to use a tool in real time.
In our research with students and product developers, we often saw cognitive load issues: students struggle with instructions, navigation or unclear affordances. We saw motivation issues: kids shut down when a feature feels intimidating or frustrating. Many existing evaluations don’t examine how struggling, multilingual or reluctant readers experience the same product quite differently.
Zuidema: While districts, school leaders and teachers all play critical roles, ultimately the student experience determines whether learning actually happens. Yet too often, product development processes overlook the people most affected: students themselves.
How does centering student voice change the way edtech products are designed?
Tare: You can count on young people to surface things adults would never catch. Kids are the experts in fun, not adults! In one case, an AI writing companion talked too much, repeated questions and “felt like a bot” to kids. Students redesigned the personality system to be less chatty, more responsive and more playful, and engagement shot up the next day.
In another case, developers initially assumed a read-aloud feature would help with assessment, but kids were often too anxious or unsure to speak. Student discomfort fundamentally shifted how developers approached assessment supports.
Zuidema: When you center student voice, you learn things about an edtech tool that adults simply can’t see. Testing early ideas with students helps product teams figure out if things like onboarding or screen design actually work before a tool is used in real classrooms. This keeps teams from building features based on adult guesses and saves them from costly rebuilds.
One example is customization. Adults often assume students want lots of choices in how everything looks. But many students say they prefer simple, steady designs and want more control over their learning path instead.
Olszewski: I’m generalizing here, but what we heard is that they don’t care about chatbots, and they don’t want to do anything for school on their phones except check due dates. I think these insights offer edtech providers some solid guidance on how to spend their energy when developing products.
What do students want from edtech?
Olszewski: Students want a clean user interface that feels intuitive, as if it were actually tested by real students. They don’t care about a lot of add-ons, advanced customization, badges and points. Instead, they want clear learning progressions that show them what’s next. They want to see language and scenarios that reflect who they are.
Zuidema: Students want tools that are simple to use, don’t waste time and feel made for how they actually learn. They want tools that let them move at their own pace and get feedback that actually makes sense.
Tare: Students want feedback that feels human and helpful: timely, specific, supportive and aligned to where they are in the process. For example, kids told one writing tool not to give grammar feedback while they were still generating ideas because it felt disruptive and demotivating. They want characters and tools that react to them in joyful, surprising ways. And they want tools that respect their intelligence: kids reject infantilizing features and lean into tools that challenge them while also supporting them.
What does it take to do rigorous, ethical student-centered usability research?
Zuidema: Conducting rigorous research with students starts with creating spaces where young people feel safe enough to be honest. When that trust is in place, they move beyond polite answers and offer the kind of deeper feedback that improves programs and products.
Organizations partner most effectively when they start with a clear sense of what they hope to learn and how they plan to use those insights. When students feel safe and respected, they offer the kind of honest, deeper insight that strengthens the work.
Tare: We recommend genuine youth partnership, not tokenism: Kids need time to build relationships, trained facilitators and multiple sessions to share deeper feedback. And there needs to be a willingness to change course: Product teams need to be ready to iterate, and sometimes to do so fundamentally. Kids are experts! We need to listen.
Olszewski: Young people under 18 rightfully are afforded special protections through Institutional Review Boards. Coordinating with the right organizations that have streamlined that work helps responsible research partners get right to the work of actually collecting data. That’s so helpful when the people we want to learn from don’t yet have a driver’s license!
How should school leaders evaluate edtech through the lens of student usability?
Olszewski: We know that alignment to standards and evidence supporting better student learning outcomes are top of mind — and those priorities can sometimes overshadow other important factors. We believe that products designed for usability, both for teachers and students, are more likely to improve teaching and learning. Our forthcoming student usability framework will provide concrete criteria for evaluating these factors. If your sandbox account of a product offers a jumbled user experience without a clear learning progression, that’s a signal it might not work well in practice.
Tare: Student usability should be given strong consideration. We advise school leaders to ask questions such as: Can students independently navigate the tool? Do multilingual learners and struggling readers experience friction? Does the tool maintain motivation, or diminish it? How does feedback feel to a child: supportive or punitive? This approach helps leaders choose tools that work for the students they actually serve.
Learn more: ISTE+ASCD’s student usability framework will be released later this year. In the meantime, educators and edtech decision-makers can explore ISTE’s Teacher Ready Evaluation Tool and related resources at iste.org/edtech-product-selection.
Tech
Snowflake and OpenAI forge $200M enterprise AI partnership


Snowflake and OpenAI have struck a multi-year, $200 million partnership to bring OpenAI’s advanced models, including GPT-5.2, directly into Snowflake’s enterprise data platform. The collaboration is designed to let Snowflake’s large customer base, more than 12,000 organisations, build AI agents and semantic analytics tools that operate on their own data without moving it outside Snowflake’s governed environment. Under the agreement, OpenAI models will be natively embedded in Snowflake Cortex AI and Snowflake Intelligence, making it possible to run queries, derive insights, and deploy AI-powered workflows using natural language interfaces and context-aware agents. Customers can analyse structured and unstructured data, automate…
This story continues at The Next Web
Tech
As Software Stocks Slump, Investors Debate AI’s Existential Threat

Investors were assessing on Wednesday whether a selloff in global software stocks this week had gone too far, as they weighed if businesses could survive an existential threat posed by AI. The answer: It’s unclear and will lead to volatility. From a report: After a broad selloff on Tuesday that saw the S&P 500 software and services index fall nearly 4%, the sector slipped another 1% on Wednesday. While software stocks have been under pressure in recent months as AI has gone from being a tailwind for many of these companies to investors worrying about the disruption it will cause to some sectors, the latest selloff was triggered by a new legal tool from Anthropic’s Claude large language model (LLM).
The tool – a plug-in for Claude’s agent for tasks across legal, sales, marketing and data analysis – underscored the push by LLMs into the so-called “application layer,” where these firms are increasingly muscling into lucrative enterprise businesses for revenue they need to fund massive investments. If successful, investors worry, it could wreak havoc across a range of industries, from finance to law and coding.
Tech
Vercel rebuilt v0 to tackle the 90% problem: Connecting AI-generated code to existing production infrastructure, not prototypes


Before Claude Code wrote its first line of code, Vercel was already in the vibe coding space with its v0 service.
The basic idea behind the original v0, which launched in 2024, was essentially to be version 0. That is, the earliest version of an application, helping developers solve the blank canvas problem. Developers could prompt their way to a user interface (UI) scaffolding that looked good, but the code was disposable. Getting those prototypes into production required rewrites.
More than 4 million people have used v0 to build millions of prototypes, but the platform was missing elements required to get into production. The challenge is a familiar one with vibe coding tools, as there is a gap in what tools provide and what enterprise builders require. Claude Code, for instance, generates backend logic and scripts effectively, but does not deploy production UIs within existing company design systems while enforcing security policies
This creates what Vercel CPO Tom Occhino calls “the world’s largest shadow IT problem.” AI-enabled software creation is already happening inside every enterprise. Credentials are copied into prompts. Company data flows to unmanaged tools. Apps deploy outside approved infrastructure. There’s no audit trail.
Vercel rebuilt v0 to address this production deployment gap. The new version, generally available today, imports existing GitHub repositories and automatically pulls environment variables and configurations. It generates code in a sandbox-based runtime that maps directly to real Vercel deployments and enforces security controls and proper git workflows while allowing non-engineers to ship production code.
“What’s really nice about v0 is that you still have the code visible and reviewable and governed,” Occhino told VentureBeat in an exclusive interview. “Teams end up collaborating on the product, not on PRDs and stuff.”
This shift matters because most enterprise software work happens on existing applications, not new prototypes. Teams need tools that integrate with their current codebases and infrastructure.
How v0’s sandbox runtime connects AI-generated code to existing repositories
The original v0 generated UI scaffolding from prompts and let users iterate through conversations. But the code lived in v0’s isolated environment, which meant moving it to production required copying files, rewriting imports and manually wiring everything together.
The rebuilt v0 fundamentally changes this by directly importing existing GitHub repositories. A sandbox-based runtime automatically pulls environment variables, deployments and configurations from Vercel, so every prompt generates production-ready code that already understands the company’s infrastructure. The code lives in the repository, not a separate prototyping tool.
Previously, v0 was a separate prototyping environment. Now, it’s connected to the actual codebase with full VS Code built into the interface, which means developers can edit code directly without switching tools.
A new git panel handles proper workflows. Anyone on a team can create branches from within v0, open pull requests against main and deploy on merge. Pull requests are first-class citizens and previews map directly to real Vercel deployments, not isolated demos.
This matters because product managers and marketers can now ship production code through proper git workflows without needing local development environments or handing code snippets to engineers for integration. The new version also adds direct integrations with Snowflake and AWS databases, so teams can wire apps to production data sources with proper access controls built in, rather than requiring manual work.
Vercel’s React and Next.js experience explains v0’s deployment infrastructure
Prior to joining Vercel in 2023, Occhino spent a dozen years as an engineer at Meta (formerly Facebook) and helped lead that company’s development of the widely-used React JavaScript framework.
Vercel’s claim to fame is that its company founder, Guillermo Rauch, is the creator of Next.js, a full-stack framework built on top of React. In the vibe coding era, Next.js has become an increasingly popular framework. The company recently published a list of React best practices specifically designed to help AI agents and LLMs work.
The Vercel platform encapsulates best practices and learnings from Next.js and React. That decade of building frameworks and infrastructure together means v0 outputs production-ready code that deploys on the same infrastructure Vercel uses for millions of deployments annually. The platform includes agentic workflow support, MCP integration, web application firewall, SSO and deployment protections. Teams can open any project in a cloud dev environment and push changes in a single click to a Vercel preview or production deployment.
With no shortage of competitive offerings in the vibe coding space, including Replit, Lovable and Cursor among others, it’s the core foundational infrastructure that Occhino sees as standing out.
“The biggest differentiator for us is the Vercel infrastructure,” Occhino said. “It’s been building managed infrastructure, framework-defined infrastructure, now self-driving infrastructure for the past 10 years.”
Why vibe coding security requires infrastructure control, not just policy
The shadow IT problem isn’t that employees are using AI tools. It’s that most vibe coding tools operate entirely outside enterprise infrastructure. Credentials are copied into prompts because there’s no secure way to connect generated code to enterprise databases. Apps deploy to public URLs because the tools don’t integrate with company deployment pipelines. Data leaks happen because visibility controls don’t exist.
The technical challenge is that securing AI-generated code requires controlling where it runs and what it can access. Policy documents don’t help if the tooling itself can’t enforce those policies.
This is where infrastructure matters. When vibe coding tools operate on separate platforms, enterprises face a choice: Block the tools entirely or accept the security risks. When the vibe coding tool runs on the same infrastructure as production deployments, security controls can be enforced automatically.
v0 runs on Vercel’s infrastructure, which means enterprises can set deployment protections, visibility controls and access policies that apply to AI-generated code the same way they apply to hand-written code. Direct integrations with Snowflake and AWS databases let teams connect to production data with proper access controls rather than copying credentials into prompts.
“IT teams are comfortable with what their teams are building because they have control over who has access,” Occhino said. “They have control over what those applications have access to from Snowflake or data systems.”
Generative UI vs. generative software
In addition to the new version of v0, Vercel has recently introduced a generative UI technology called json-render.
v0 is what Vercel calls generative software. This differs from the company’s json-render framework for a true generative UI. Vercel software engineer Chris Tate explained that v0 builds full-stack apps and agents, not just UIs or frontends. In contrast, json-render is a framework that enables AI to generate UI components directly at runtime by outputting JSON instead of code.
“The AI doesn’t write software,” Tate told VentureBeat. “It plugs directly into the rendering layer to create spontaneous, personalized interfaces on demand.”
The distinction matters for enterprise use cases. Teams use v0 when they need to build complete applications, custom components or production software.
They use JSON-render for dynamic, personalized UI elements within applications, dashboards that adapt to individual users, contextual widgets and interfaces that respond to changing data without code changes.
Both leverage the AI SDK infrastructure that Vercel has built for streaming and structured outputs.
Three lessons enterprises learned from vibe coding adoption
As enterprises adopted vibe coding tools over the past two years, several patterns emerged about AI-generated code in production environments.
Lesson 1: Prototyping without production deployment creates false progress. Enterprises saw teams generate impressive demos in v0’s early versions, then hit a wall moving those demos to production. The problem wasn’t the quality of generated code. It was that prototypes lived in isolated environments disconnected from production infrastructure.
“While demos are easy to generate, I think most of the iteration that’s happening on these code bases is happening on real production apps,” Occhino said. “90% of what we need to do is make changes to an existing code base.”
Lesson 2: The software development lifecycle has already changed, whether enterprises planned for it or not. Domain experts are building software directly instead of writing product requirement documents (PRDs) for engineers to interpret. Product managers and marketers ship features without waiting for engineering sprints.
This shift means enterprises need tools that maintain code visibility and governance while enabling non-engineers to ship. The alternative is creating bottlenecks by forcing all AI-generated code through traditional development workflows.
Lesson 3: Blocking vibe coding tools doesn’t stop vibe coding. It just pushes the activity outside IT’s visibility. Enterprises that try to restrict AI-powered development find employees using tools anyway, creating the shadow IT problem at scale.
The practical implication is that enterprises should focus less on whether to allow vibe coding and more on ensuring it happens within infrastructure that can enforce existing security and deployment policies.
Tech
Theory Professional Previews SR-221.3 Extreme-Output Full-Range Loudspeaker at ISE 2026, Headlining New SR Series for Pro Sound Reinforcement

Theory Professional, the professional division of Theory Audio Design, is making a serious first impression at ISE 2026 with its all-new SR Series — a family of premium passive and powered loudspeakers engineered for sound reinforcement with performance and fidelity that rivals much larger systems. At the heart of the lineup is the SR-221.3, a truly unique full-range loudspeaker that pushes the envelope of output, bandwidth, and coverage.
The SR-221.3 pairs dual 21-inch, 3,600 W low-frequency drivers with four 10-inch high-output carbon fiber midrange drivers and a 5-inch wide-band ring radiator compression driver. The result: an astonishing 27 Hz – 20 kHz (-3 dB) frequency response, up to ~140 dB SPL, and an ultra-wide 170° × 60° coverage pattern. One to two SR-221.3s can easily fill medium venues with high-fidelity, high-impact sound.
Theory Professional has designed the SR Series to deliver lively dynamics, refined acoustic accuracy, and sheer output capability, all in surprisingly compact cabinets that won’t dominate aesthetic spaces; whether installed or used portably. The series includes eight models; passive, active, portable, and install variants — all built-to-order and available in black or white. Optional upgrades include custom paint matching and weatherizing on passive units.
Thoughtful details throughout the SR Series — from ergonomic handles and multiple fly points to industry-standard mount points, pole cups, and a suite of accessories like the Theory SplitYoke multipurpose mounting brackets, caster kits, and a dolly board — make these systems as flexible as they are powerful. Q2 2026 delivery is planned for powered, passive, portable, and install versions.

SR Series Loudspeakers and Subwoofers: Eight High-Output Models Now Available from Theory Professional
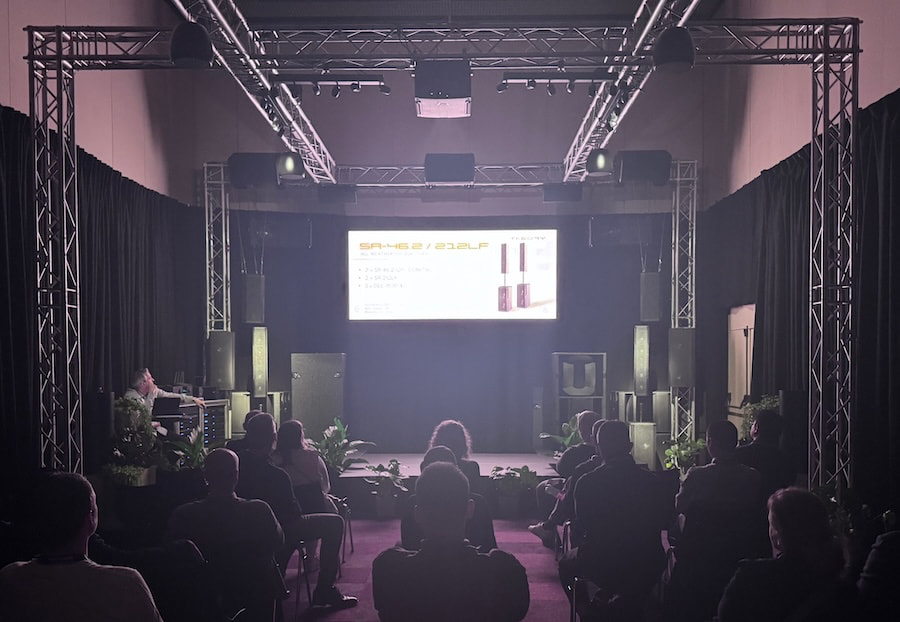
At ISE 2026, Theory Professional is demonstrating the new SR Series in Hall 8.0, Audio Demo Room D4, giving attendees a chance to hear exactly how far the company is pushing premium sound reinforcement. Demonstrations can be scheduled in advance, or you can stop by D4 to experience the system in action. More details are available at theoryprofessional.com.
Below is a clear breakdown of the eight SR Series loudspeakers and subwoofers available to order now, covering configuration, intended use, and key options.
SR Series Loudspeakers
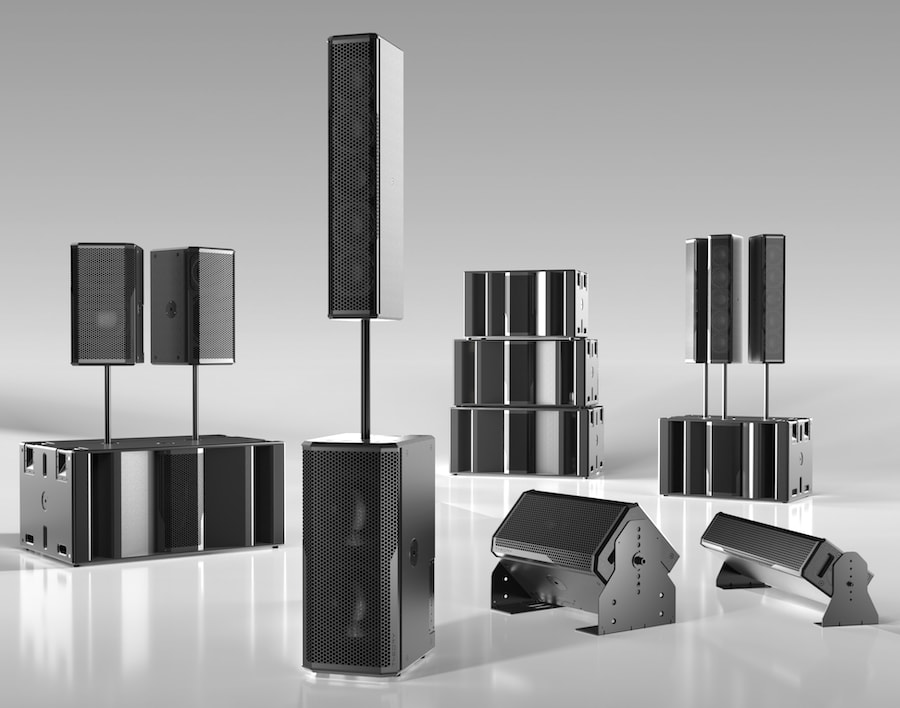

SR-46.2
- Quad 6-inch, 2-way multi-use loudspeaker
- Ultra-slender, tall-but-narrow enclosure with 120° conical coverage
- Available in passive and powered versions
- Included features:
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points and industry-standard mount points
- Optional:
- Theory SplitYoke Multipurpose Mounting Bracket Kit for horizontal or vertical surface mounting
SR-28.2
- Dual 8-inch, 2-way multi-use loudspeaker
- 80° × 60° elliptical horn
- Available in passive and powered versions
- Included features:
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points and industry-standard mount points
- Optional:
- Theory SplitYoke Multipurpose Mounting Bracket Kit for horizontal or vertical surface mounting
SR-112.2
- Single 12-inch, 2-way multi-use loudspeaker
- 80° × 60° elliptical horn
- Available in passive and powered versions
- Included features:
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points and industry-standard mount points
- Optional:
- Theory SplitYoke Multipurpose Mounting Bracket Kit for horizontal or vertical surface mounting
SR-212.2
- Full-range, multi-use loudspeaker with integrated subwoofer
- Dual 12-inch LF drivers and dual 8-inch mid drivers in a 3-way design
- Exceptionally compact enclosure at just 10 inches deep
- Available in passive and powered versions
- Included features:
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points
- Optional:
- Theory SplitYoke Multipurpose Mounting Bracket Kit
- Theory Caster Kit for portable applications
SR Series Subwoofers
SR-212LF
- Compact, high-output bass-reflex subwoofer
- Dual 12-inch, 1,400 W woofers
- Sonically matched to SR-46.2, SR-28.2, and SR-112.2
- Included features:
- Removable feet
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points
- Optional:
- Theory SplitYoke Multipurpose Mounting Bracket Kit
- Theory Caster Kit
SR-215LF
- Maximum-output, manifold bass-reflex subwoofer
- Dual 15-inch, 3,600 W woofers
- Sonically matched to SR-46.2, SR-28.2, and SR-112.2
- Included features:
- Removable feet
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points
- Optional:
- Theory Quick-Release or Standard Caster Kits
- Dolly Board for transport
SR-218LF
- Maximum-output, manifold bass-reflex subwoofer
- Dual 18-inch, 3,600 W woofers
- Sonically matched to SR-46.2, SR-28.2, and SR-112.2
- Included features:
- Removable feet
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points
- Optional:
- Theory Quick-Release or Standard Caster Kits
- Dolly Board for transport
SR-221LF
- Extreme-output, manifold bass-reflex subwoofer
- Dual 21-inch, 3,600 W woofers
- Sonically matched to SR-46.2, SR-28.2, and SR-112.2
- Included features:
- Removable feet
- Integral pole cups
- Ergonomic handles
- Fly points
- Optional:
- Theory Quick-Release or Standard Caster Kits
- Dolly Board for transport
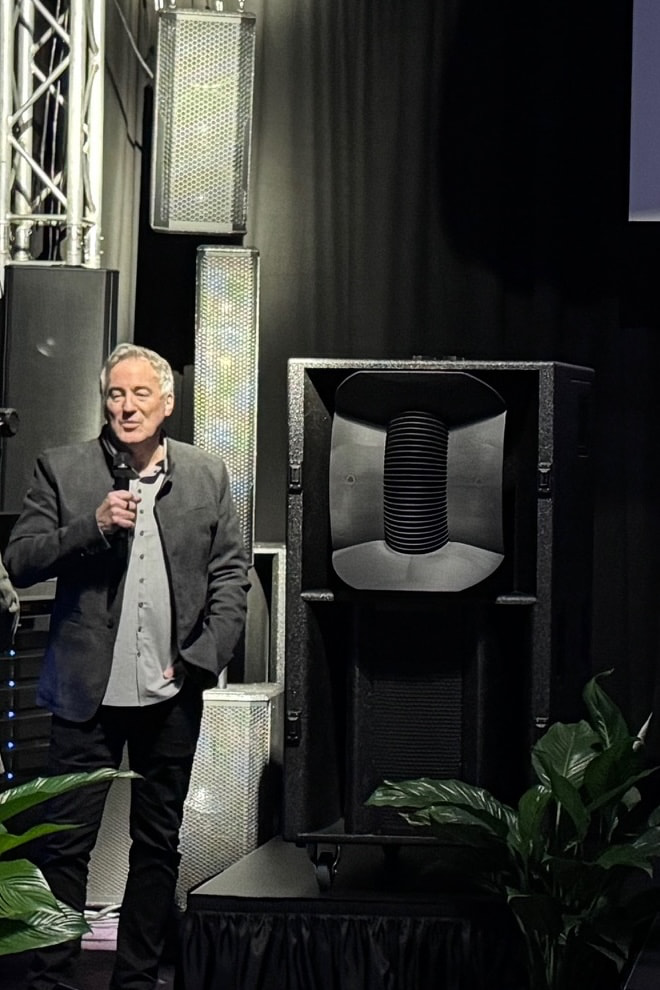

The Bottom Line
The SR-221.3 is still very much a proof of concept, and pricing has not been finalized. What is clear is that it will sit above Theory Professional’s existing SR models once it moves toward production. This is a true full-range loudspeaker loaded with expensive hardware — dual 21-inch, 3,600-watt low-frequency drivers, four 10-inch carbon-fiber midrange drivers, and a 5-inch wide-band ring-radiator compression driver — and there’s no scenario where that bill of materials leads to an “affordable” outcome.
With 27 Hz–20 kHz bandwidth (-3 dB), approximately 140 dB SPL, and 170° × 60° coverage, the SR-221.3 is designed to deliver high-output, high-fidelity sound at scale, with just one or two cabinets capable of filling medium-sized venues. Based on the pricing of Theory Professional’s current pro models, expect the SR-221.3 to land firmly in premium territory when it eventually reaches market — because nothing about this design suggests it’s meant to play in the shallow end.
For more information: theoryprofessional.com
Related Reading:
Tech
NASA's Artemis II will test laser communications system in lunar orbit
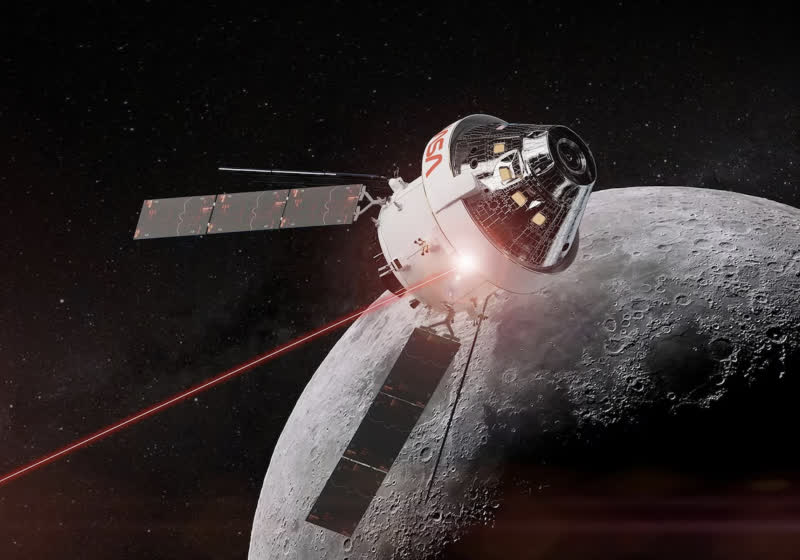
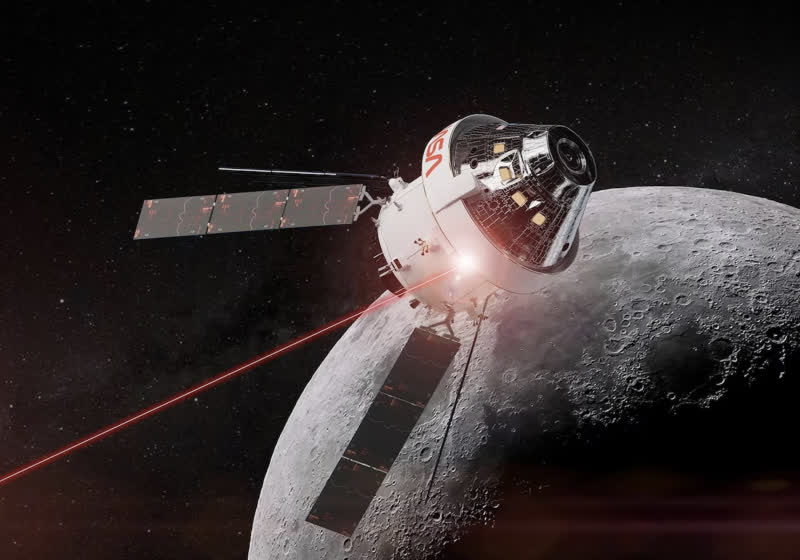


The mission will mark NASA’s first crewed test of laser communications in lunar orbit. O2O will use infrared light instead of radio frequencies to transmit voice, mission data, and high-resolution video back to Earth. While the technology has been tested on seven prior uncrewed missions, Artemis II is the first to…
Read Entire Article
Source link
Tech
CATL’s Next-Gen 5C Batteries Can Be Fully Recharged in 12-Minutes and Has Lifespan That Stretches Beyond a Million Miles
CATL’s innovative 5C battery claims to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry for drivers. CATL, or Contemporary Amperex Technology Limited, the world’s largest battery manufacturer, claims that a full charge takes only 12 minutes and has a lifespan of over a million miles.
The engineers at CATL worked on this battery to see if it could withstand a 5C charge (basically, an 80-kilowatt-hour pack could be charged at 400 kilowatts in roughly 12 minutes) without quickly wearing out. Yes, according to some estimations, a top-up would take about the same amount of time as filling up with gas, but this battery would withstand wear and tear better.
Sale
S ZEVZO ET03 Car Jump Starter 4000A Jump Starter Battery Pack for Up to 8.0L Gas and 7.0L Diesel Engines,…
- POWERFUL CAR BATTERY JUMP STARTER: The ET03 car battery jump starter can easily jump-start all 12V common vehicles with up to 8.0L gas and 7.0L diesel…
- STARTS 0V DEAD BATTERIES EASILY: This car battery jump starter has integrated the force start function in the jumper clamps, which delivers powerful…
- BACKUP PORTABLE POWER BANK: This jump starter battery pack can also work as a 74Wh large battery capacity portable power bank to charge your…
Under normal conditions, at 68°F (20°C), it retained at least 80% of its original capacity after 3,000 full charge-discharge cycles. When you add the figures up, that’s more than 1.8 million kilometers, or almost one and a half million miles. Or, in the blistering heat of 140°F (60°C) during the summer in Dubai, it managed 80% after 1,400 cycles, or almost 840,000 kilometers and a half million miles. CATL believes this is six times better than the current industry average for batteries put through a similar test.

So how did they manage to accomplish all of this? For starters, the cathode has a unique covering that keeps the battery from breaking down and losing metal ions during rapid charging and discharging. Second, the electrolyte contains an additive that detects and seals tiny breaches, preventing harmful lithium from leaking out and shortening battery life. Last but not least, there is a particular temperature-responsive coating on the separator that slows down the ions when things get heated locally, all of which contributes to a lower risk of things getting out of control.

Heat becomes considerably more of a concern when charging quickly. So they created a clever system that monitors the pack as a whole and precisely distributes coolant to the hotspots, keeping temperatures consistent across all cells and effectively adding years to the lifespan.

All of this implies that the battery no longer wears out as quickly when charging at high speeds. CATL believes it’s ideal for heavy users, large trucks, taxis, and ride-hailing vehicles. They will be the ones who gain from faster turnaround times and lower replacement prices. Passenger cars will follow once production begins, but there is no news on when the 5C variant will be available. Previous versions, such as the 4C technology released in 2023, were only stepping stones, and this is the next natural step.
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoSmart energy pays enters the US market, targeting scalable financial infrastructure
-
Crypto World6 days ago
Software stocks enter bear market on AI disruption fear with ServiceNow plunging 10%
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWhy is the NHS registering babies as ‘theybies’?
-
 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoAdam Back says Liquid BTC is collateralized after dashboard problem
-

 Video2 days ago
Video2 days agoWhen Money Enters #motivation #mindset #selfimprovement
-

 Tech12 hours ago
Tech12 hours agoWikipedia volunteers spent years cataloging AI tells. Now there’s a plugin to avoid them.
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoDonald Trump Criticises Keir Starmer Over China Discussions
-

 Fashion5 days ago
Fashion5 days agoWeekend Open Thread – Corporette.com
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoSky News Presenter Criticises Lord Mandelson As Greedy And Duplicitous
-

 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoU.S. government enters partial shutdown, here’s how it impacts bitcoin and ether
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoSinner battles Australian Open heat to enter last 16, injured Osaka pulls out
-
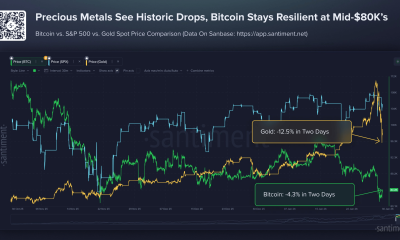
 Crypto World4 days ago
Crypto World4 days agoBitcoin Drops Below $80K, But New Buyers are Entering the Market
-
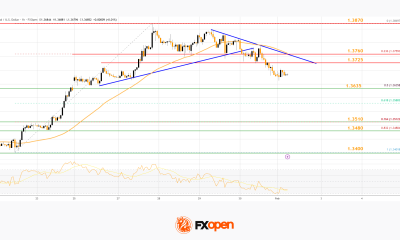
 Crypto World2 days ago
Crypto World2 days agoMarket Analysis: GBP/USD Retreats From Highs As EUR/GBP Enters Holding Pattern
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoKuCoin CEO on MiCA, Europe entering new era of compliance
-
Business5 days ago
Entergy declares quarterly dividend of $0.64 per share
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoShannon Birchard enters Canadian curling history with sixth Scotties title
-

 NewsBeat1 day ago
NewsBeat1 day agoUS-brokered Russia-Ukraine talks are resuming this week
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoGAME to close all standalone stores in the UK after it enters administration
-

 Crypto World21 hours ago
Crypto World21 hours agoRussia’s Largest Bitcoin Miner BitRiver Enters Bankruptcy Proceedings: Report
-

 Crypto World6 days ago
Crypto World6 days agoWhy AI Agents Will Replace DeFi Dashboards







