Business
Why the US is buying icebreakers from Finland
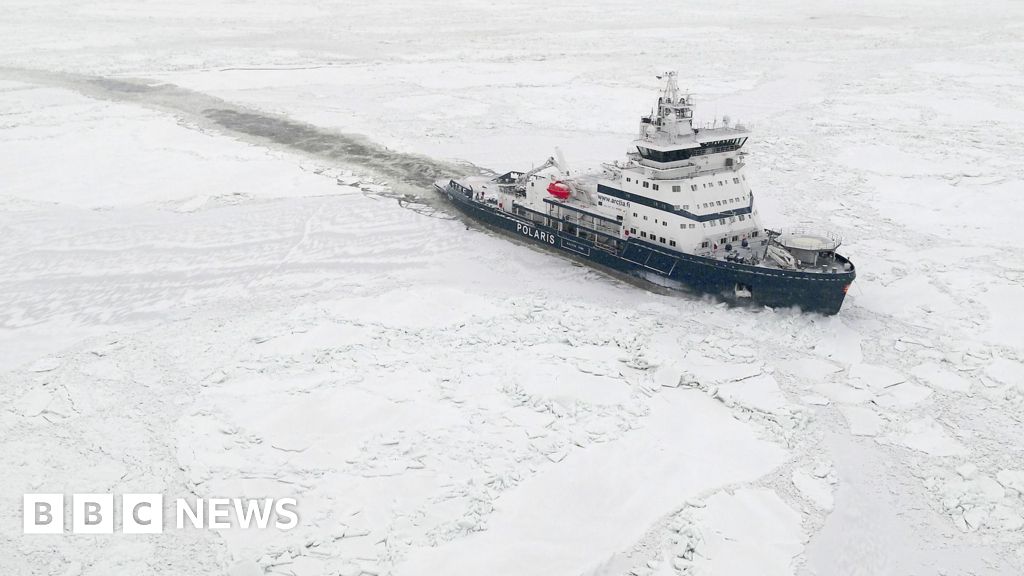

This US concern comes as climate change continues to make the Arctic Ocean more navigable for cargo ships, at least if icebreakers lead the way by cutting a path. This opens up commercial trade routes from Asia to Europe, either above Russia, or north of Alaska and Canada’s mainland, and down past Greenland.
Business
Is Claude Still Down? Anthropic’s Claude AI Chatbot Hit by Widespread Outage Amid Surge in Demand
Anthropic’s popular Claude AI chatbot experienced a global outage on March 2, 2026, leaving thousands of users unable to access the service for several hours as the company attributed the disruption to unprecedented demand following recent explosive growth in usage.
The incident, which began early Monday morning U.S. time, affected consumer-facing platforms including claude.ai, the Claude mobile apps, Claude Code (the AI-powered coding assistant) and Claude Opus 4.6, the company’s latest flagship large language model. Business integrations via the Claude API remained operational throughout, allowing enterprises to continue using the technology without interruption.
Anthropic first acknowledged the problem on its official status page at 11:49 UTC (6:49 a.m. ET), posting that it was “currently investigating” elevated errors across multiple services. Subsequent updates detailed issues tied to login and logout pathways on claude.ai, with some API methods failing and users encountering HTTP 500 internal server errors, 529 service unavailable codes, timeouts and messages such as “Claude will return soon” or “That’s not working right now. You can try again later.”
Service-monitoring platform Downdetector recorded a sharp spike in reports, peaking at nearly 2,000 user complaints around 6:40 a.m. ET. Complaints originated from regions worldwide, including the United States, Europe, India and Africa, indicating a broad rather than localized failure.
In statements provided to media outlets including Mashable, Bloomberg and The Hill, Anthropic emphasized that the outage stemmed from “unprecedented demand” observed over the preceding week. The company had seen Claude climb to the top of app store rankings in multiple categories shortly before the incident, reflecting rapid adoption amid growing interest in its safety-focused AI capabilities.
“We’re grateful to our users while the team works to match the incredible demand we’ve seen for Claude in recent days,” Anthropic said in a direct statement shared with reporters around 11 a.m. ET. The company confirmed resolution shortly thereafter, declaring all consumer-facing services “back up and running” by late morning Pacific time after deploying fixes and monitoring recovery.
The disruption lasted approximately two to three hours for most users, though intermittent issues persisted in some cases as systems stabilized. Anthropic’s status page transitioned from “Investigating” to “Identified” and “Fix Implemented” phases before marking the primary incident resolved, with follow-up monitoring for related components.
Industry observers noted the outage highlights the challenges facing fast-growing AI providers. Claude’s rise has positioned it as a strong competitor to models from OpenAI and Google, particularly among users valuing its constitutional AI approach that prioritizes helpfulness without excessive caution or bias. Recent benchmarks showed Claude Opus 4.6 outperforming rivals in certain reasoning and coding tasks, fueling the surge that strained infrastructure.
“This is the classic ‘success tax’ in AI services,” said one analyst familiar with cloud scaling for large language models. “When a model suddenly tops charts and sees viral adoption, even robust systems can buckle under traffic spikes that exceed provisioning forecasts.”
Unlike previous outages at rival platforms, Anthropic’s consumer services bore the brunt while the enterprise API stayed online — a deliberate architectural choice that shielded paying business customers from impact. Developers integrating Claude into workflows reported no downtime on that front, underscoring the company’s focus on reliability for high-stakes applications.
User reactions on social media and forums like Reddit ranged from frustration to understanding, with many expressing sympathy for the team handling the influx. Some speculated the timing coincided with backlash against competitors, including OpenAI’s reported partnerships, prompting a temporary shift of users to Claude.
Anthropic has not disclosed specific technical root causes beyond authentication and API method failures, nor provided details on capacity expansions underway. The company has invested heavily in infrastructure since its founding, partnering with major cloud providers and securing billions in funding to scale compute resources.
As of March 4, 2026, Anthropic’s status page showed no active major incidents related to the March 2 event, though a separate unresolved issue with usage reporting lingered under monitoring following a fix deployment. Downdetector indicated normal activity levels, with no elevated reports in the preceding 24 hours.
The episode serves as a reminder of the fragility in the booming generative AI sector, where demand can outpace even the most prepared operators. For Anthropic, the outage arrived at a pivotal moment of market momentum, testing its ability to convert viral interest into sustained reliability.
Users affected by the brief downtime were advised to refresh sessions or check status.claude.com for real-time updates in future incidents. Anthropic pledged continued improvements to handle growing traffic, signaling confidence that such disruptions would remain rare as scaling efforts advance.
With Claude now restored and demand showing no signs of abating, the company appears poised to capitalize on its position while addressing the infrastructure lessons from this high-visibility hiccup.
Business
Is King Khalid International Airport Open? Airport Remains Open Amid Regional Airspace Disruptions

RIYADH, Saudi Arabia — King Khalid International Airport (RUH), Saudi Arabia’s busiest aviation gateway and a key hub for Saudia and other carriers, continues to operate normally as of March 4, 2026, despite widespread flight suspensions, delays and cancellations triggered by escalating Middle East tensions following U.S. and Israeli military actions against Iran.

Airport authorities and flight-tracking services confirm that the facility has not closed and maintains active arrivals and departures, though passenger volumes and route availability have been significantly curtailed by airspace restrictions across neighboring countries and beyond. Official sources, including the airport’s website kkia.sa, direct travelers to verify individual flight status via WhatsApp at 920020090 rather than assuming routine operations.
Riyadh Airports Company, which manages King Khalid International Airport, has not issued any closure notices. Recent updates emphasize ongoing coordination with airlines to handle affected services while prioritizing safety. Flightradar24 data shows live activity at RUH, with weather conditions stable at around 12-14°C, light winds and low-to-moderate delay indices for arrivals (1.2-1.4) and departures (1.1-1.6) as of mid-morning local time. FlightAware reports a 9% year-over-year dip in activity but no full shutdown, with 92 cancellations noted in the prior 24 hours — a figure reflecting regional ripple effects rather than an airport-specific halt.
The disruptions stem from broader geopolitical fallout. Multiple airlines, including Saudia, have extended suspensions to select destinations through March 4 at 23:59 GMT. Routes to Amman, Kuwait, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha, Bahrain, Moscow and Peshawar remain grounded, with carriers citing airspace closures in Qatar, parts of the UAE, Iraq and other areas as the primary cause. Saudia’s advisory urges passengers to check directly for updates, as some services may resume on a case-by-case basis pending clearance.
International carriers have followed suit. KLM suspended flights to Riyadh until March 9, while Air France, Cathay Pacific and others canceled or postponed services to RUH and other Saudi points through early March. Akasa Air halted operations to Riyadh and nearby Gulf cities for March 3, offering refunds or rebookings. Reports indicate thousands of flights canceled region-wide, with hubs like Dubai and Doha facing near-total ground stops, pushing rerouting demand toward open Saudi airspace.
Despite these challenges, King Khalid International Airport has positioned itself as a relative stable point. Industry commentary highlights Saudi Arabia’s decision to keep its skies accessible, allowing limited transit and outbound traffic when neighboring facilities remain shuttered. Private aviation sources note surging demand for charters from Riyadh to Europe, with costs reaching six figures for high-end evacuations.
The airport recently completed a major operational overhaul that bolsters its resilience. From February 16-25, 2026, Riyadh Airports executed the largest terminal reallocation in KKIA’s history, shifting airline assignments to improve connectivity and efficiency. Under the new layout:
– Terminals 1 and 2 handle international flights by national carriers like Saudia and the emerging Riyadh Air.
– Terminals 3 and 4 focus on domestic operations.
– Terminal 5 serves foreign international carriers.
The transition, processed amid over 1 million passengers and 7,650 flights, raised combined capacity for Terminals 3 and 4 from 16 million to 25 million annually. Overall airport throughput is projected to climb from 42 million passengers in 2025 to 56 million by end-2026 — a 33% increase aligning with Saudi Vision 2030 goals to elevate Riyadh as a global transit hub.
Passengers report mixed experiences. While core infrastructure functions, check-in areas and baggage systems face strain from rerouted traffic and canceled flights. The airport advises against heading to terminals without confirmed bookings, as access may be restricted to verified travelers to manage crowds and security.
Official messaging remains cautious. The kkia.sa site repeatedly directs users to flight status checks and provides maps, terminal info and destination lists without indicating any suspension. No active major alerts appear on the announcements page beyond standard advisories.
Travelers planning to use King Khalid International Airport should:
– Confirm status directly with airlines or via the dedicated WhatsApp line (920020090).
– Monitor real-time platforms like Flightradar24, FlightAware or Trip.com for live arrivals/departures.
– Prepare for potential delays, rebookings or alternative routing, especially on regional Gulf, Levant or select European/Asian routes.
– Review government travel advisories, as evolving airspace rules could impact even open corridors.
As the region navigates the crisis, King Khalid International Airport’s continued operations underscore Saudi Arabia’s strategic role in maintaining connectivity amid chaos. While far from normal — with reduced frequencies and widespread cancellations — the facility stands open, processing available traffic and supporting recovery efforts as conditions permit.
Analysts expect gradual normalization if de-escalation occurs, but warn that prolonged restrictions elsewhere could sustain pressure on Riyadh’s infrastructure. For now, RUH remains a functional lifeline in a disrupted Middle East aviation landscape.
Business
Early skills vital for quality education, panel says

Barriers to students achieving desired learning outcomes start to appear in classrooms in the early years.
Business
5 Questions with Nicholas Mukhtar on Strategy, Governance, and What Executives Get Wrong
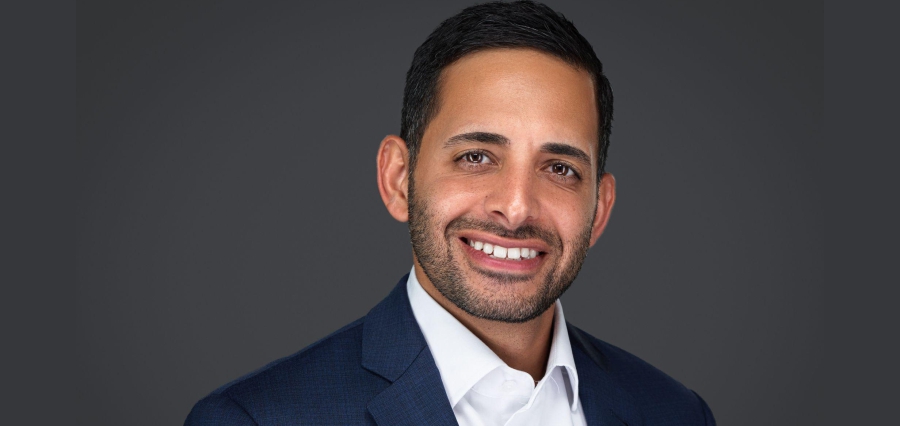

Few consultants arrive at business consulting through public health. Nicholas Mukhtar did. After founding Healthy Detroit in 2013, growing it to a $15 million annual budget, and earning recognition from the American Public Health Association as the National Public Health Organization of the Year in 2017, he shifted focus — first to advising government offices and congressional leaders through Healthy Communities, LLC, then to building Tera Strategies, his Fort Lauderdale-based management consulting firm, where he now advises CEOs, family offices, medical directors, and wealth management practices nationwide.
That career arc, from community health organizer to senior business consultant, has given Nicholas Mukhtar a cross-sector lens that surfaces patterns other advisors tend to miss. He sat down to answer five questions on the state of business leadership, what governance structures actually require, and where most executives lose their way before they realize it.
Q1: You transitioned from leading a major nonprofit to advising private-sector executives. What does one world teach you about the other?
Mukhtar says the mechanics of both worlds are more similar than most people expect. Running Healthy Detroit showed him that whether the organization is a city park health initiative or a family-owned company, the core problems are almost always structural, and the transition from scrappy startup to functioning institution is a universal challenge. “I look at companies in two different buckets,” he said. “One are these large established companies that do function much like these big city governments or these bureaucratic machines that sometimes can’t get out of their own way. And then this other bucket, it’s the startup machine.”
He draws a direct line between what he observed building a public-private partnership model in Detroit — where government bureaucracy consistently blocked innovation — and what he encounters inside large corporations today. His consulting approach reflects that framework: different organizations require fundamentally different interventions, and treating them the same is one of the more expensive mistakes a leader can make. The observation carries weight against current data. A 2025 NACD survey of directors found that a majority of board members flagged improvements to planning oversight and risk management as top priorities, signaling that even at the governance level, organizations are grappling with the gap between stated direction and execution capability.
Q2: You work extensively with family offices on governance and succession. What is the single biggest mistake you see them make?
Mukhtar’s answer is consistent across nearly every family office engagement he takes on: not getting children involved early enough. The consequences, when they surface, tend to be severe. “You don’t know what life has in store,” he said. “You’ll see situations where someone will pass on or there’ll be an accident or something, and these kids truly have no idea what their parents have built, how they built it, how things are set up, what to do.”
The scale of the problem is considerable. According to a 2025 report from RBC Wealth Management and Campden Wealth, nearly half of all family offices expect a generational transition within the next decade, yet only 69% now have a formal succession plan in place, up from just 53% the previous year. Research published by Simple, a family office advisory firm, found that without a defined decision-making framework, families become dangerously dependent on one or two individuals, and when those individuals are suddenly unavailable, the organization has no structure to fall back on. The clients Mukhtar describes getting it right start their children with small investment accounts as early as age ten or eleven. “Just teaching them the value of having time in the market, saving money, creating buckets,” he said. “Put 30% here, put 30% here, put 30% here.” The families that struggle, in his experience, are the ones so consumed by building that they lose sight of who they are building for.
Q3: When a new client comes to you, what is the root problem you find most often — and what question do you wish they had asked themselves before picking up the phone?
Mukhtar says the answer is almost always the same, regardless of industry, company size, or ownership structure. “I kid you not,” he said, “that seems to be 90% of the problems across the board. It’s just people need to talk.” He does not frame this as a matter of individual personality or interpersonal skill. He ties communication failure to a structural condition — the chronic overstimulation of modern professional life, where executives are pulled across so many competing demands that the act of sitting down and asking a direct question has become genuinely difficult to prioritize.
The organizational cost of that failure is well-documented. Research from the 2025 Top Workplaces survey found that the most consequential gap organizations face is failing to keep employees informed during periods of change. When that gap persists, the trust holding performance cultures together begins to erode. Mukhtar sees it play out at the individual level too: people on the verge of leaving a job without ever articulating what they actually need from their employer. “Did you as the employee sit down with the business owner and explain to them why you want something different and what you’re actually looking for?” he said. “It can be really that simple.” His prescription is not elaborate. “People just get pulled in so many different directions,” he said, “and a lot of it is you just need to simplify things and have a conversation about why isn’t this working.”
Q4: Most executives say they believe in clear strategy. Why do so few actually execute it?
Mukhtar traces the gap between belief and execution to a single recurring failure: treating every organization as though the same solution applies. He pushes back on universal prescriptions, and his reasoning is grounded in observation rather than theory. “If I talk to 10 CEOs, they all have a very different style, a different way of looking at things,” he said. “There’s not one size fits all solution to any problem. And I think that you have to really approach it as such.”
That view carries weight against current data. A 2024-2025 McKinsey survey of more than 400 senior executives worldwide found that only 21% reported their organization’s strategy passed four or more of the firm’s rigorous Ten Tests of evaluation, a 40% drop from results captured a decade and a half earlier. A separate analysis found that 68% of middle managers in a McKinsey study admitted they actively edit out negative information before passing it up the chain, meaning executives are often finalizing plans based on a picture that no longer reflects conditions on the ground. For mature organizations functioning like large bureaucratic institutions, Mukhtar argues the answer often involves outside thinking: someone without institutional attachments who can ask the questions insiders have stopped asking. For younger companies still finding their structure, the work is different. “There’s a lot of growing pains in a lot of these companies that are startups trying to transition to full functioning companies,” he said. “Every entity, every person’s unique and you have to treat it as such.”
Q5: What do you want to be working on over the next several years, and where do you think the biggest opportunities in your field are?
Mukhtar is direct about his ambitions, and they run closer to outcomes than to growth metrics. He describes wanting work where results are visible and concrete, rather than projects measured on timelines too long to produce real accountability. “I like taking on projects where I can really see outcomes,” he said. “I’m an outcomes-driven person. I don’t like working on things that you’re not going to see the outcomes for a hundred years.”
That orientation points him toward healthcare reform as a priority, specifically Medicaid, where he spent several years earlier in his career and believes substantial, measurable change remains possible. “There’s a lot of opportunity to use Medicaid to really help people and get them to a place where they’re healthy and contributing members of society,” he said. “I don’t think that’s how our Medicaid system’s being used today.” More broadly, Nicholas Mukhtar says he wants to grow Tera Strategies to the point where he can be genuinely selective about his engagements, choosing clients and projects based on fit and impact rather than volume. He is not descriing scale for its own sake. He is describing the ability to pursue the kind of work that produces the outcomes he watched unfold in Detroit — a park where children were playing basketball on a court that had been an abandoned lot, a block that looked different because someone chose to intervene. “To see those outcomes and to see kids actually using something that you had a role in building,” he said, “that’s my passion. That’s what I love doing. That’s what drives me.”
Learn More: Nicholas Mukhtar shares new analysis on decision-making in complex organizations
Business
At Close of Business podcast March 4 2026

Ella Loneragan talks to Nadia Budihardjo about why WA home care providers are working hard to adjust to market changes.
Business
Aussie shares dive as investors brace for energy shock
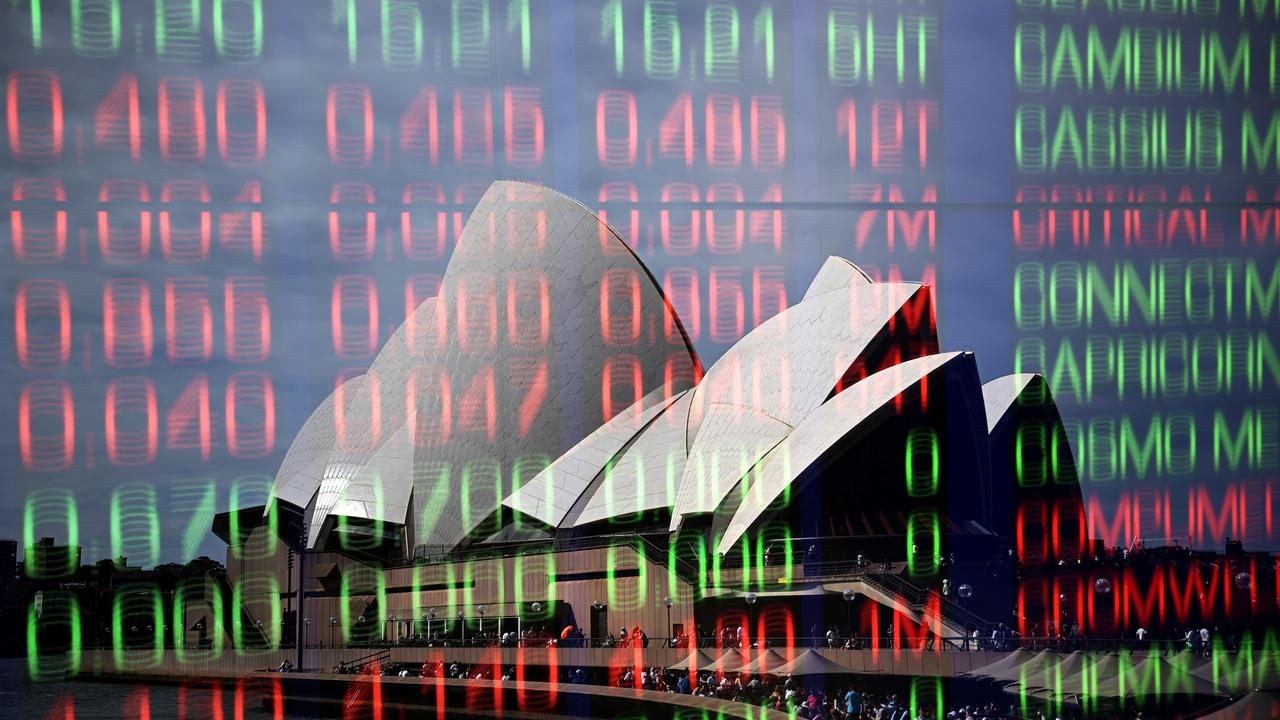

Australia’s share market has logged its second-worst session of 2026, on concerns a sustained oil price shock will intensify inflation and spark steeper interest rates.
Business
Diesel Prices Outgain Gasoline, Risking Higher Transportation Costs for Goods
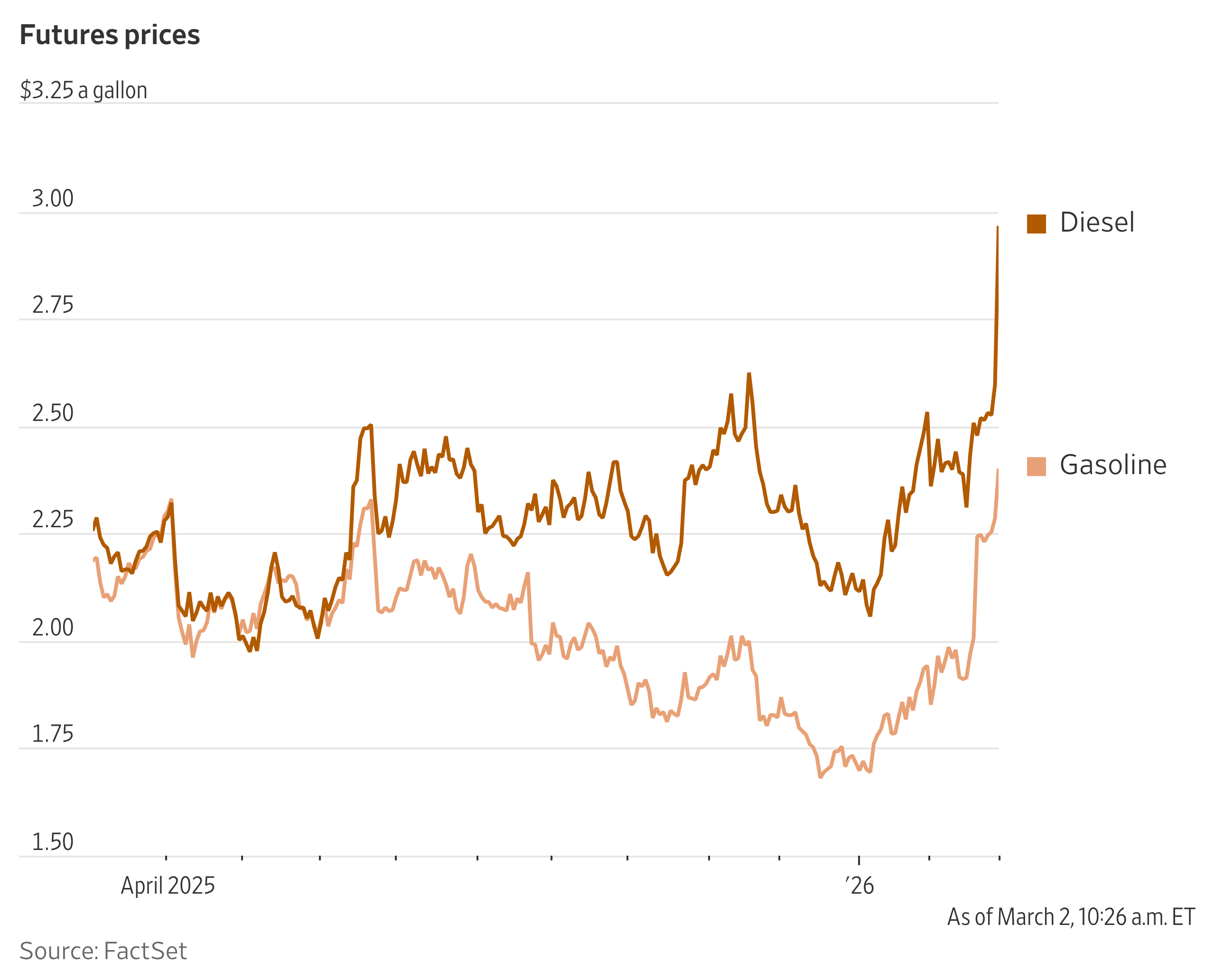
American consumers are focused on prices at the pump following U.S. and Israeli strikes against Iran, and it’s looking like truckers might be in for the biggest shock.
Diesel futures rose 12% in New York, ending Monday at $2.9004 a gallon in the biggest daily gain since early 2022 when Russia invaded Ukraine. Gasoline futures, meanwhile, added 3.7% to settle at $2.3706 a gallon, the highest price since August 2024.
Relatively low fuel prices have been a bright spot in the Trump administration’s efforts to rein in the cost of living ahead of November’s midterm elections. While more expensive gasoline will surely frustrate U.S. drivers, higher diesel prices have the potential to raise shipping costs and those of goods broadly.
Business
Coffey to depart as Claremont FC CEO

Claremont Football Club has announced that longstanding chief executive Darcy Coffey will depart Tigerland at the end of the month.
Business
Usana Health Sciences CIO Benedict Peter sells $88,258 in stock

Usana Health Sciences CIO Benedict Peter sells $88,258 in stock
Business
TLT Is Having Its Worst Day In 2026
So far, this bond fund hasn’t suffered a bigger blow this year.
Popularly known as TLT, the iShares 20+ Year Treasury Bond ETF, a long-duration bond fund, is down 1.4% today.
This would be its worst single day percentage decline in 2026. The last time it fell by more than today was on Dec. 1, 2025, when it fell 1.6%, according to Dow Jones Market Data.
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoITV enters Gaza with IDF amid ongoing genocide
-

 Politics24 hours ago
Politics24 hours agoAlan Cumming Brands Baftas Ceremony A ‘Triggering S**tshow’
-

 Fashion5 days ago
Fashion5 days agoWeekend Open Thread: Iris Top
-

 Tech3 days ago
Tech3 days agoUnihertz’s Titan 2 Elite Arrives Just as Physical Keyboards Refuse to Fade Away
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoCuba says its forces have killed four on US-registered speedboat | World News
-
Sports4 days ago
The Vikings Need a Duck
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoDubai flights cancelled as Brit told airspace closed ’10 minutes after boarding’
-

 NewsBeat6 days ago
NewsBeat6 days agoManchester Central Mosque issues statement as it imposes new measures ‘with immediate effect’ after armed men enter
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days ago‘Significant’ damage to boarded-up Horden house after fire
-

 NewsBeat4 days ago
NewsBeat4 days agoThe empty pub on busy Cambridge road that has been boarded up for years
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoAbusive parents will now be treated like sex offenders and placed on a ‘child cruelty register’ | News UK
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDiscord Pushes Implementation of Global Age Checks to Second Half of 2026
-

 Entertainment2 days ago
Entertainment2 days agoBaby Gear Guide: Strollers, Car Seats
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoOnly 4% of women globally reside in countries that offer almost complete legal equality
-

 Tech5 days ago
Tech5 days agoNASA Reveals Identity of Astronaut Who Suffered Medical Incident Aboard ISS
-
Politics3 days ago
FIFA hypocrisy after Israel murder over 400 Palestinian footballers
-

 NewsBeat3 days ago
NewsBeat3 days agoEmirates confirms when flights will resume amid Dubai airport chaos
-

 Crypto World5 days ago
Crypto World5 days agoFrom Crypto Treasury to RWA: ETHZilla Retreats and Relaunches as Forum Markets on Nasdaq
-

 NewsBeat2 days ago
NewsBeat2 days agoIs it acceptable to comment on the appearance of strangers in public? Readers discuss
-

 Tech3 days ago
Tech3 days agoViral ad shows aged Musk, Altman, and Bezos using jobless humans to power AI









