- NASA formally approves personal smartphones for government missions beginning with Crew-12
- Artemis II will carry consumer phones alongside traditional spaceflight imaging equipment
- Fast-tracked hardware approval marks a procedural shift inside NASA operations
NASA has confirmed its astronauts will now be allowed to carry personal smartphones on crewed missions, starting with Crew-12 and the delayed Artemis II flight.
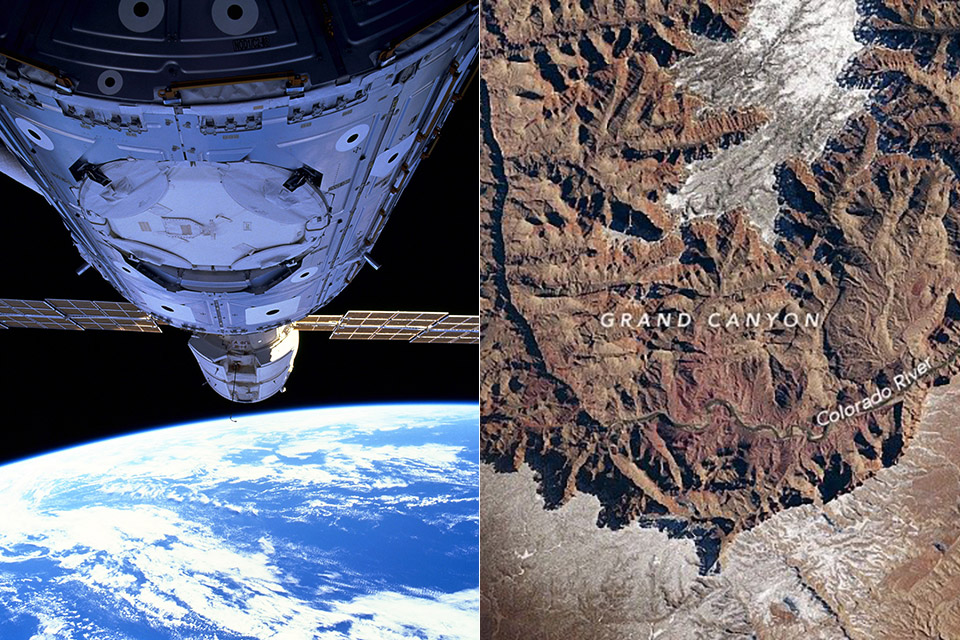
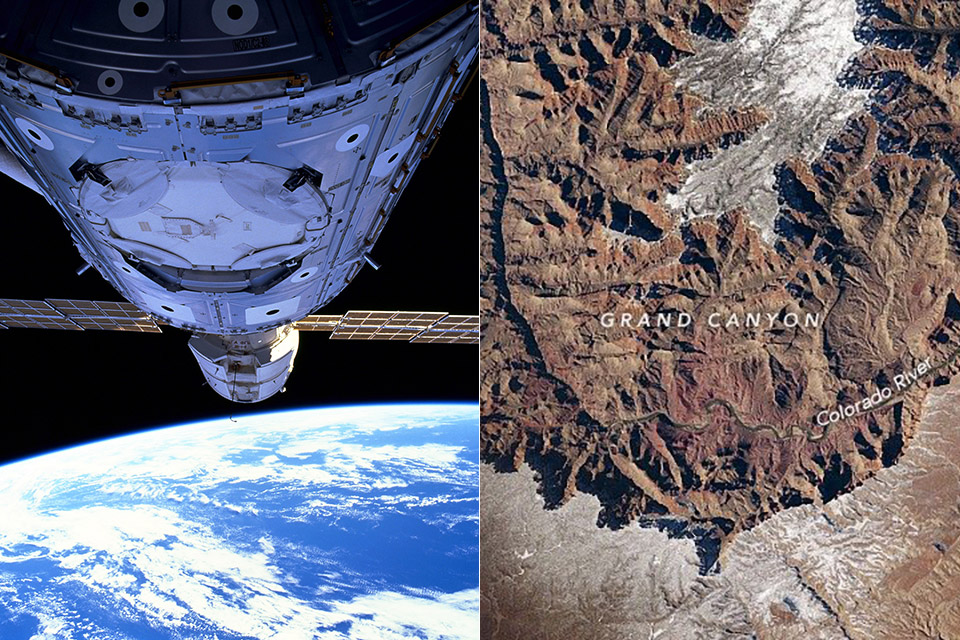
Crew-12 is scheduled to travel to the International Space Station in mid-February 2026, while Artemis II is now expected to launch in March.
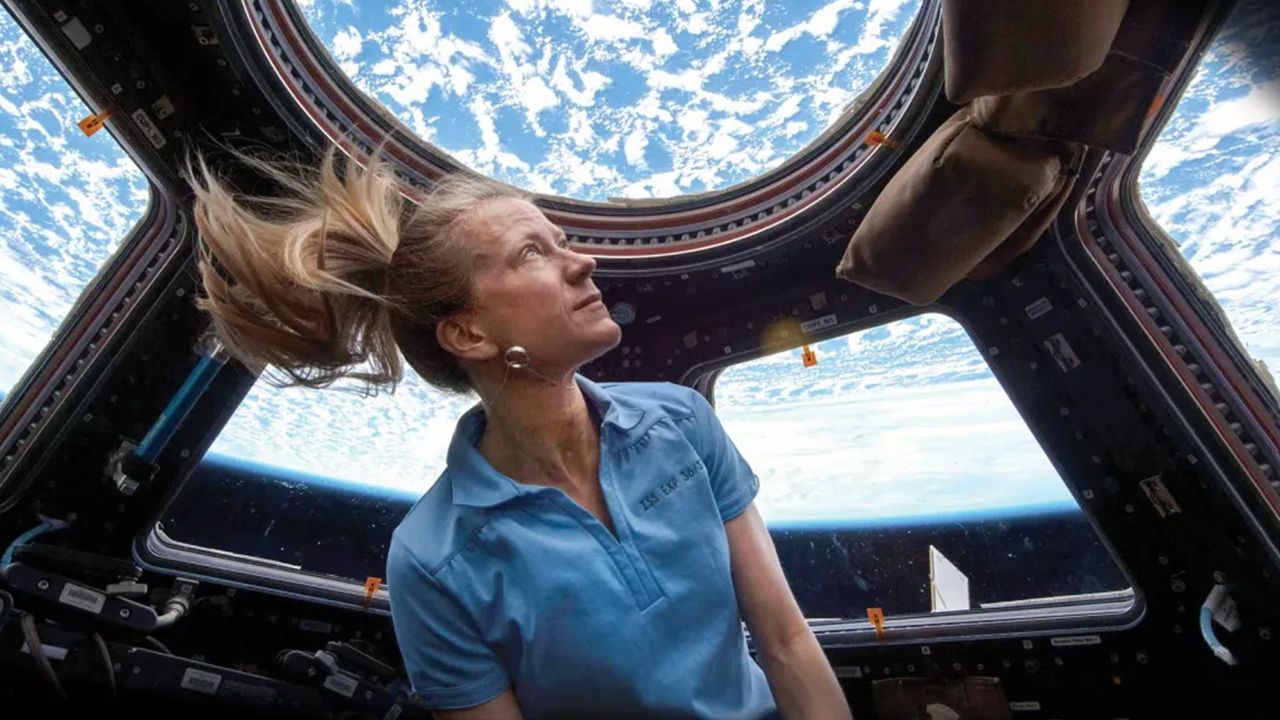
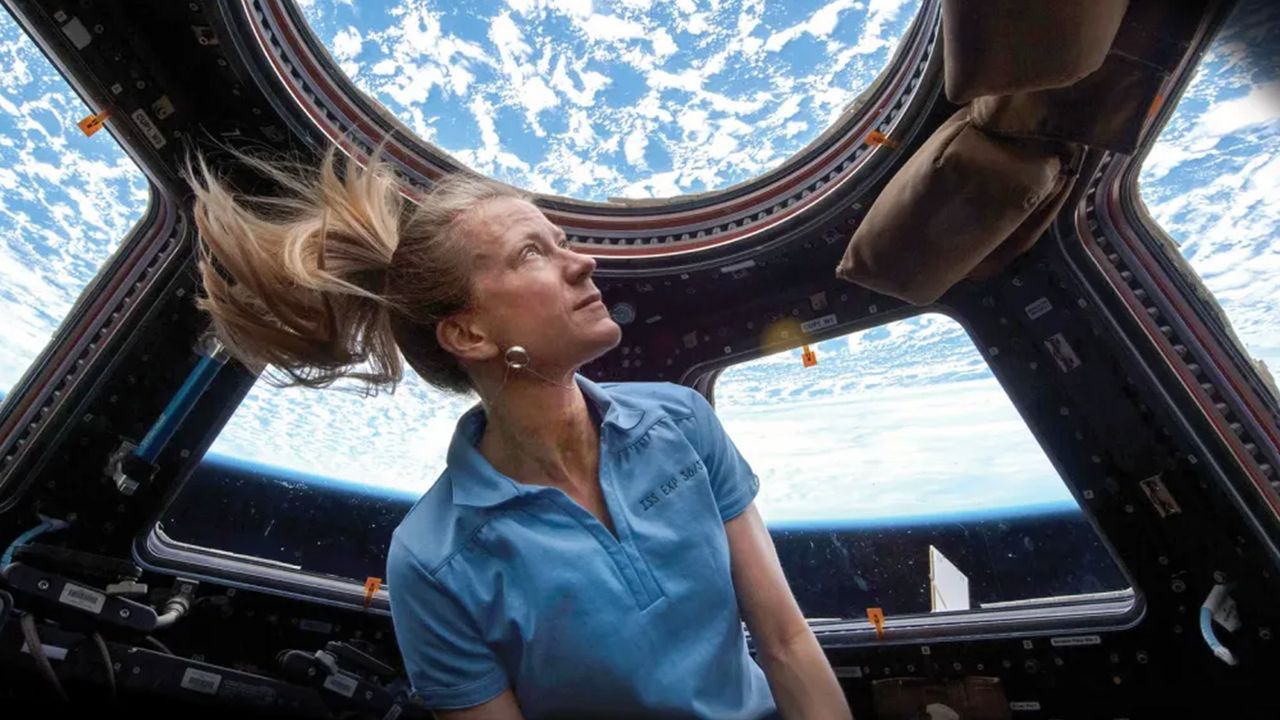
The policy change allows astronauts to use modern iPhone and Android devices during missions, marking a shift away from NASA’s long reliance on agency-supplied cameras.
Policy change expands crew access to personal hardware
NASA administrator Jared Isaacman said the decision was driven by a desire to give crews more flexible tools for documenting their experiences and sharing images and video with the public.
“We are giving our crews the tools to capture special moments for their families and share inspiring images and video with the world,” Isaacman wrote on X.
NASA leadership framed the move as more than cultural, and the agency had to fast-track the approval of modern consumer hardware for spaceflight.
They argue the same urgency will support future scientific research in orbit and on the lunar surface.
The swift adoption of capable hardware could matter more than strict adherence to legacy procedures.
“Just as important, we challenged long-standing processes and qualified modern hardware for spaceflight on an expedited timeline,” Isaacman added.
“That operational urgency will serve NASA well as we pursue the highest-value science and research in orbit and on the lunar surface.”
Until now, astronauts relied largely on Nikon DSLR cameras and GoPros, many of which were designed years ago – and while those devices remain capable, they lack the immediacy and versatility of modern smartphones.
Smartphones combine advanced sensors, image stabilization, ultra-wide lenses, and video features into a single device that astronauts already know how to use.
NASA believes that familiarity may allow crews to capture more spontaneous moments without interrupting scheduled mission tasks or relying on specialized equipment.
With smartphones available, future missions may generate far more informal imagery and video than previous expeditions.
The change raises the likelihood of more frequent updates from orbit and deep space, potentially making upcoming missions among the most thoroughly documented in NASA history.
However, the agency has not outlined specific limits on personal content creation, though mission safety rules still apply.
Smartphones have flown to space before, including on private SpaceX missions, so the concept is not entirely new, but what is different is NASA formally approving personal devices for flagship government missions.
While the agency describes this as “a small step in the right direction”, it reflects a willingness to reconsider conservative technology rules.
The long-term impact will depend on whether expedited qualification becomes standard practice or remains limited to low-risk hardware such as personal smartphones.
Follow TechRadar on Google News and add us as a preferred source to get our expert news, reviews, and opinion in your feeds. Make sure to click the Follow button!
And of course you can also follow TechRadar on TikTok for news, reviews, unboxings in video form, and get regular updates from us on WhatsApp too.